Kidneys
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
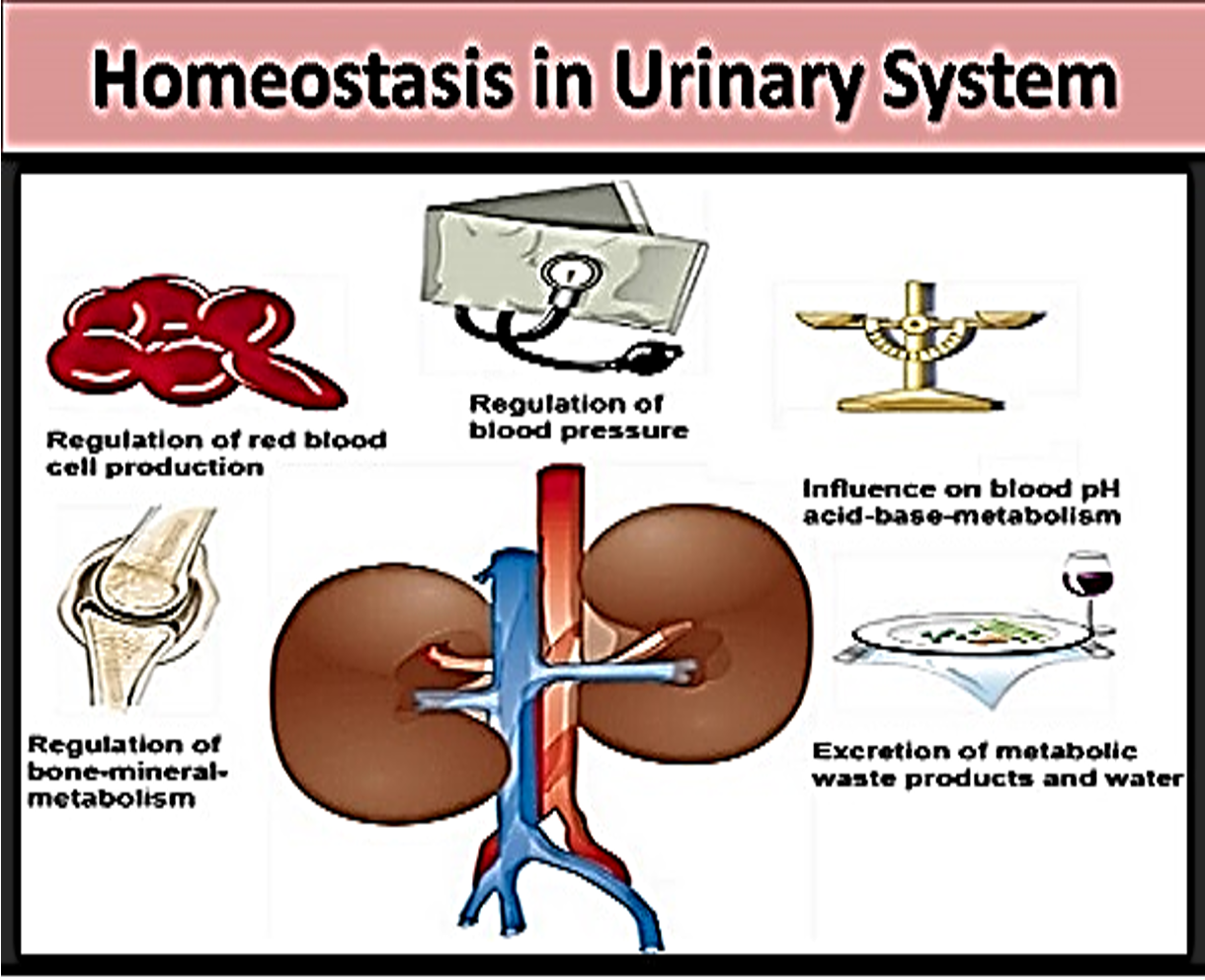
Homeostasis - Kidneys
Regulate bone-mineral metabolism
Secrete vitamin d for bone health
Regulate RBC production
Regulates BP
Fluids and sodium
Influence blood pH
H+ ions
Excrete metabolic waste and water
Kidney Function Labs
BUN, Creatinine, GFR, Specific Gravity (USG)
BUN
Blood test that measures amount of urea nitrogen in blood
Kidneys filter and remove urea from blood
10-20 mg/dL
Creatinine
Creatinine Levels
Filtered by kidneys and excreted in urine
0.5-1.2 mg/dL
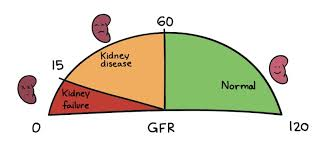
GFR
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Measures how well kidneys are filtering waste products from blood
>60
Specific Gravity (USG)
Concentration of particles in urine
Reflects kidney’s ability to dilute urine, higher = dehydration, diarrhea, sweating
1.002-1.030
Objective Data
Output, Frequency, Appearance
Output
At least 30 ml/hour
Oliguria = < 400 ml/24 hours
Polyuria = excessive quantity with uncontrolled diabetes
Frequency
Expected internal no more than 2 hours
On average 5-6 times/day
Nocturia = > 2 times/night
Appearance
Color: Cloudy, pink, orange, amber
Odor: Fishy = UTI, ammonia = dehydration, fruity = diabetes
Urine Color
Blue, Dark gray, Tea, Pink, Red, Orange, Amber, Yellow, Pale Yellow, Cloudy
Blue
Medication side effect (amitriptyline), foods (asparagus), dye after prostate surgery
Dark gray
Urine contains melanin, melanuria
Tea
Liver disease especially with pale stools, jaundice, myoglobinuria, some meds, food dyes, blood in urine
Pink
With menses, some foods (beets), laxatives, kidney stones, UTI
Red
Blood, cancer, prostate surgery, nephritis, cystitis
Orange
Medication side affect (warfarin), food + dyes, laxatives, dehydration, jaundice
Amber
Gold or concentrated with dehydration, some laxatives, food or supplements with B-complex vitamins
Yellow
Natural yellow = urochrome excretion (pigment from blood), bright neon = vitamins
Pale Yellow
Clear, watery with excess liquids acute viral hepatitis, cirrhosis
Cloudy
UTI, kidney stones
Common Problems
Urge incontinence, stress incontinence, nocturia, hematuria, dysuria
Urge Incontinence
Involuntary loss from overactive detrusor muscle in bladder
Stress Incontinence
Involuntary urine loss with physical strain, sneezing, or coughing
Nocturia
UTs, HF, diuretic medication
Hematuria
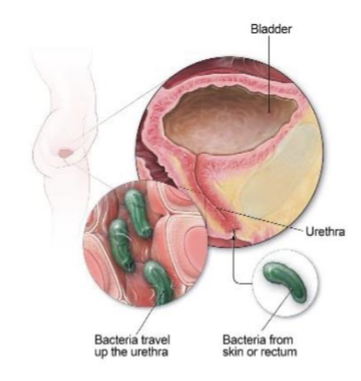
UTI, kidney infection, prostate, bladder, or kidney cancer
Dysuria
UTI, acute cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis
Aging Considerations Female
UTI, loss of elasticity and muscle tone, occurs at least 1x per year in 30% females over 85
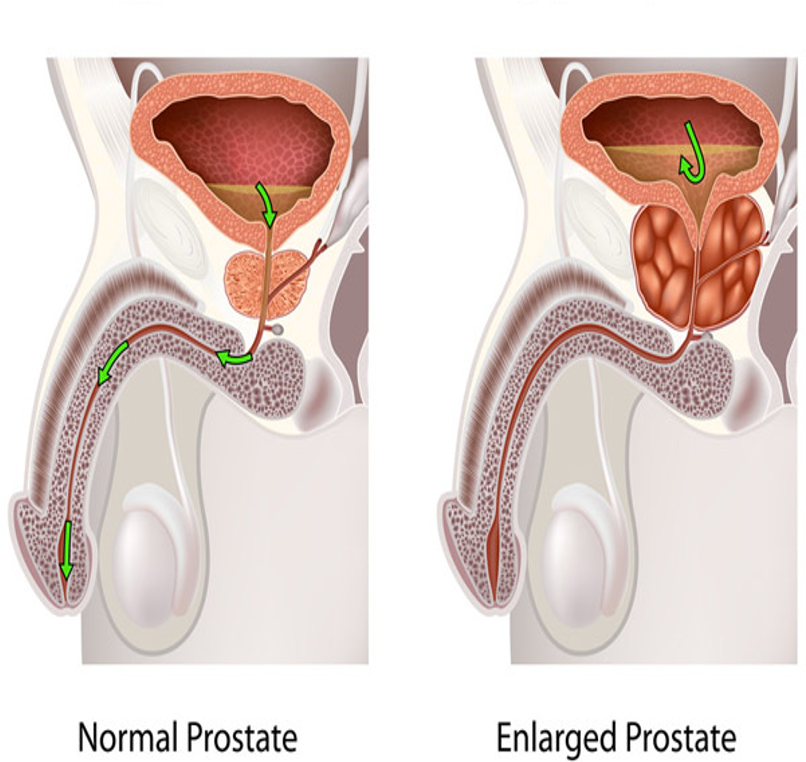
Aging Considerations Male
Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) occurs in 80% of men over 60