College Biology - Cellular Respiration Unit
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Why do we need oxygen? (COLLEGE LEVEL)
To make ATP
Energy from food “reloads” ATP
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the making of ATP
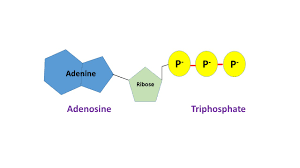
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) - what it looks like
Fully charged battery
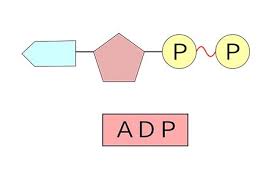
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) - what it looks like
Partially charged battery
Redox Reactions - two types
Oxidation AND Reduction
Oxidation
Loses electrons
Reduction
Gains electrons
Redox Reactions - how they work
In cells, when one substance is oxidized another is reduced
Transfer of electrons from one molecule to another molecule
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) - two types
NAD+AND NADH
NAD+
Empty bucket
NADH
Full bucket
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) - traits
Electron Carrier
Referred to as a “bucket”
Can carry 2 electrons
Redox Reaction
Glycolysis - bullet list
First to evolve
Least efficient
“Sugar splitting”
Happens in cytoplasm
Glycolysis - diagram + “must knows”
MUST KNOW:
Glucose
Fructose-1,6-Diphosphate
PGAL
Pyruvix Acid
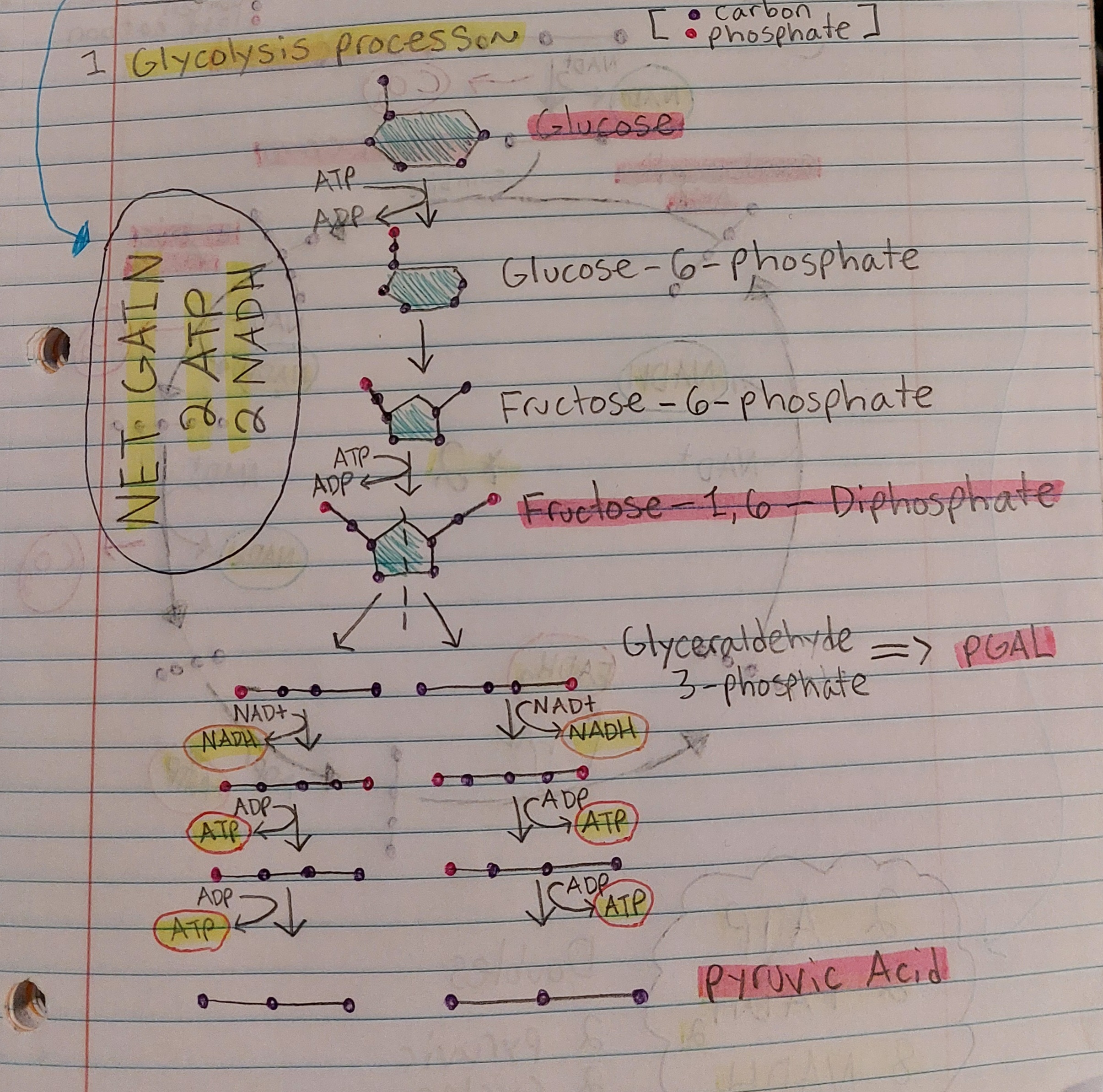
Glycolysis - net gain
2 ATP
2 NADH
Fermentation
If no oxygen is available
Anaerobic respiration
Alcoholic (yeast and bacteria)
Lactic Acid (muscles and bacteria)
Krebs Cycle - bullet list
AKA “Citric Acid Cycle”
Happens in Matrix of Mitochondria
2 turns per glucose (2 pyruvic acid)
Krebs Cycle - diagram + “must knows”
MUST KNOW:
Pyruvic Acid
Acetyl Co-a
Citric Acid
Oxaloacetic Acid
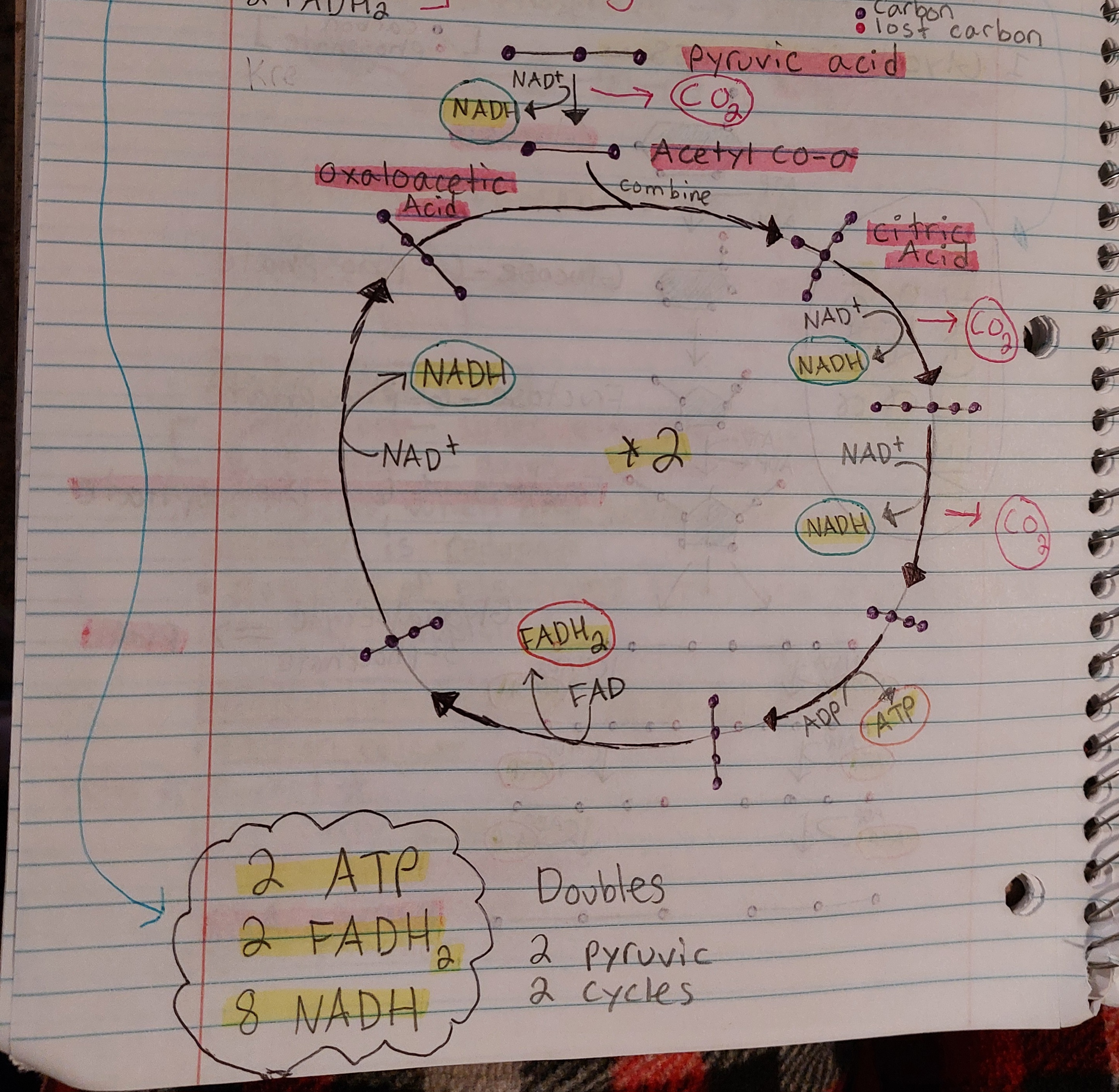
Krebs Cycle - net gain
Note: goes around twice, so double the diagram
2 ATP
8 NADH
2 FADH2
ETC: Electron Transport Chain - bullet list
MAIN EVENT
Happens in Cristae of Mitochondria
Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are used to make ATP
ATP Synthase
ETC: Electron Transport Chain - diagram
Note 1: Electrons go down
Note 2: Pay attention to small details
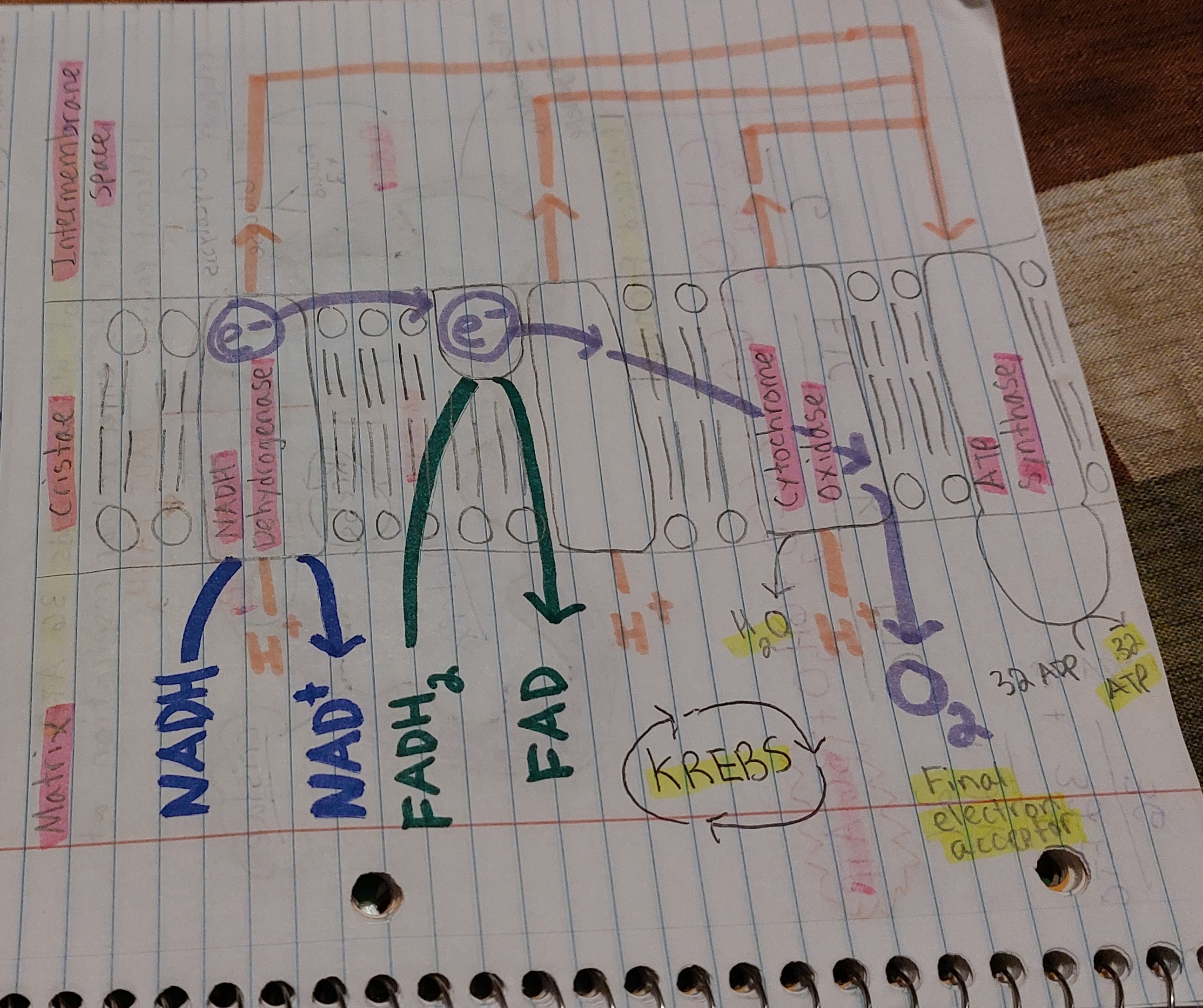
ETC: Electron Transport Chain - net gain
32 ATP
Net Gain / Gain Summary - ETC
(Note: -2 ATP for Active Transport)
10 NADH — 30 ATP
2 FADH2 — 4 ATP
How much ATP does 1 molecule of glucose yield in total?
36!
How much ATP is gained from all 3 steps?
2 ATP from Glycolysis
2 ATP from Krebs Cycle
32 ATP from Electron Transfer Chain
Cellular Respiration Formula
C6H12O6 + 6O2 — 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
Cellular Respiration Formula (parts)
Glycolysis
ETC
Krebs Cycle
ETC
(ALL)
Photosynthesis
Absorbs part of the visual spectrum
Green plants reflect green light
Pigments absorb light
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
Xanthophyl
Carotene
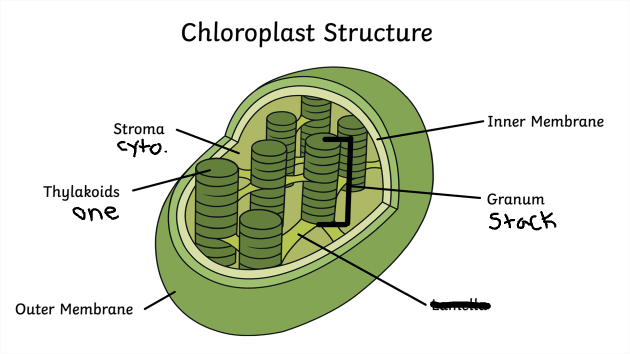
Chloroplast Review Traits and Diagram
Thylakoid
Stroma
Grana
Inner Membrane
Outer Membrane
Photosystems Traits
Pigments in the thylakoid membrane
Absorbs sun’s energy
Photosystems Steps (simplified)
Chlorophyll is oxidized … passes its electrons to the primary electron acceptor
Electrons are passed to electron acceptor instead of falling back to the original energy level
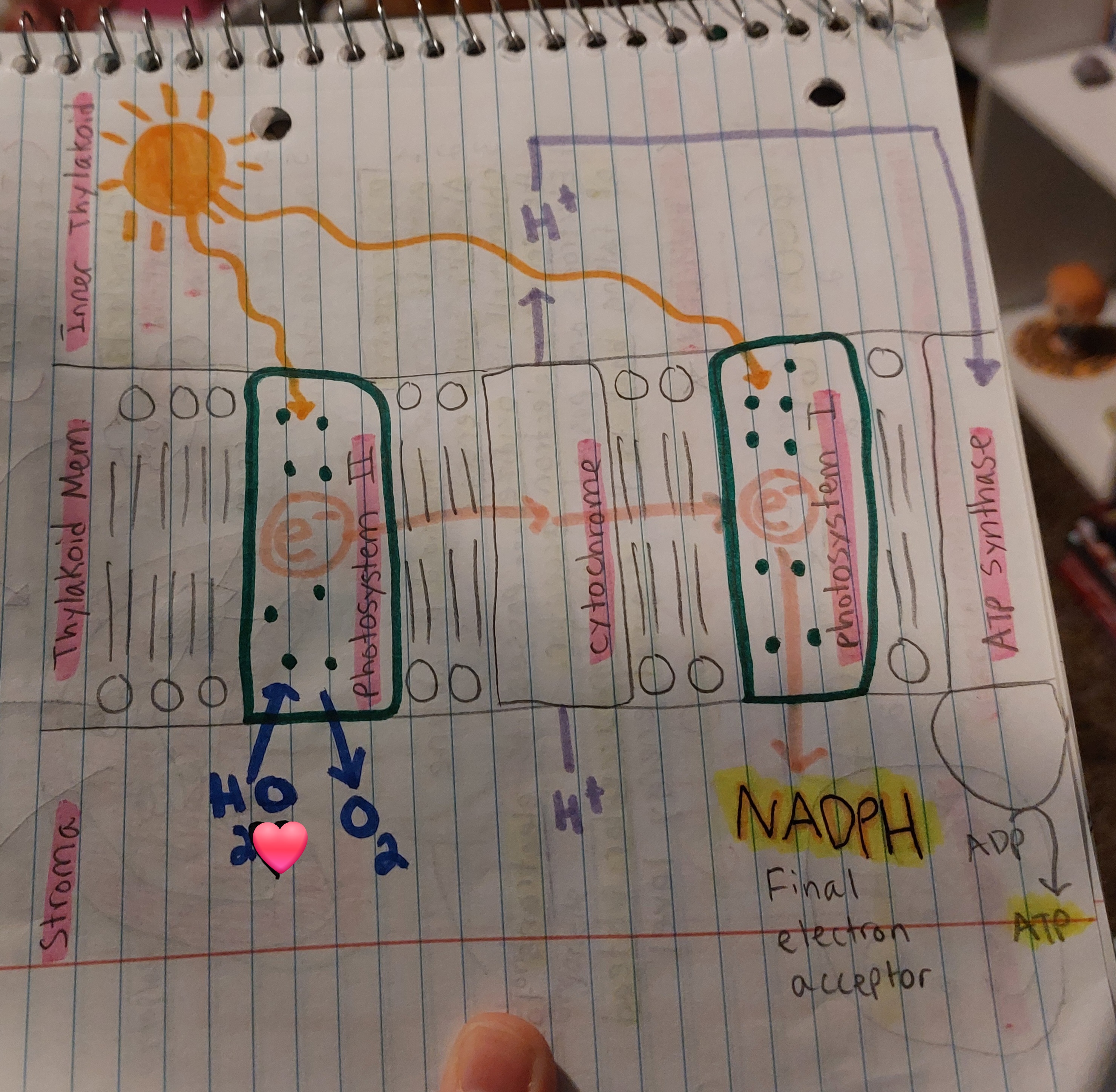
Light Dependent Reaction (LDR) - bullet list
Light energy is transferred to chemical energy
Happens in the thylakoid membrane
Electrons move through E.T.C.
Electrons are replaced by splitting water
Light Dependent Reaction (LDR) - net gain
Oxygen
NADPH
ATP
Empty Bucket - Plants
NADP+
Full Bucket - Plants
NADPH
Light Dependent Reaction (LDR) Diagram
Similar to E.T.C in Cellular Respiration
Compare: Stoma/Stomata and Stroma
They are both involved in the production of photosynthesis
Contrast: Stoma/Stomata and Stroma
However, stroma is the fluid in the chloroplast that LIR (Calvin Cycle) takes place in and stoma/stomata is the little mouth of the leaf that takes in carbon dioxide.
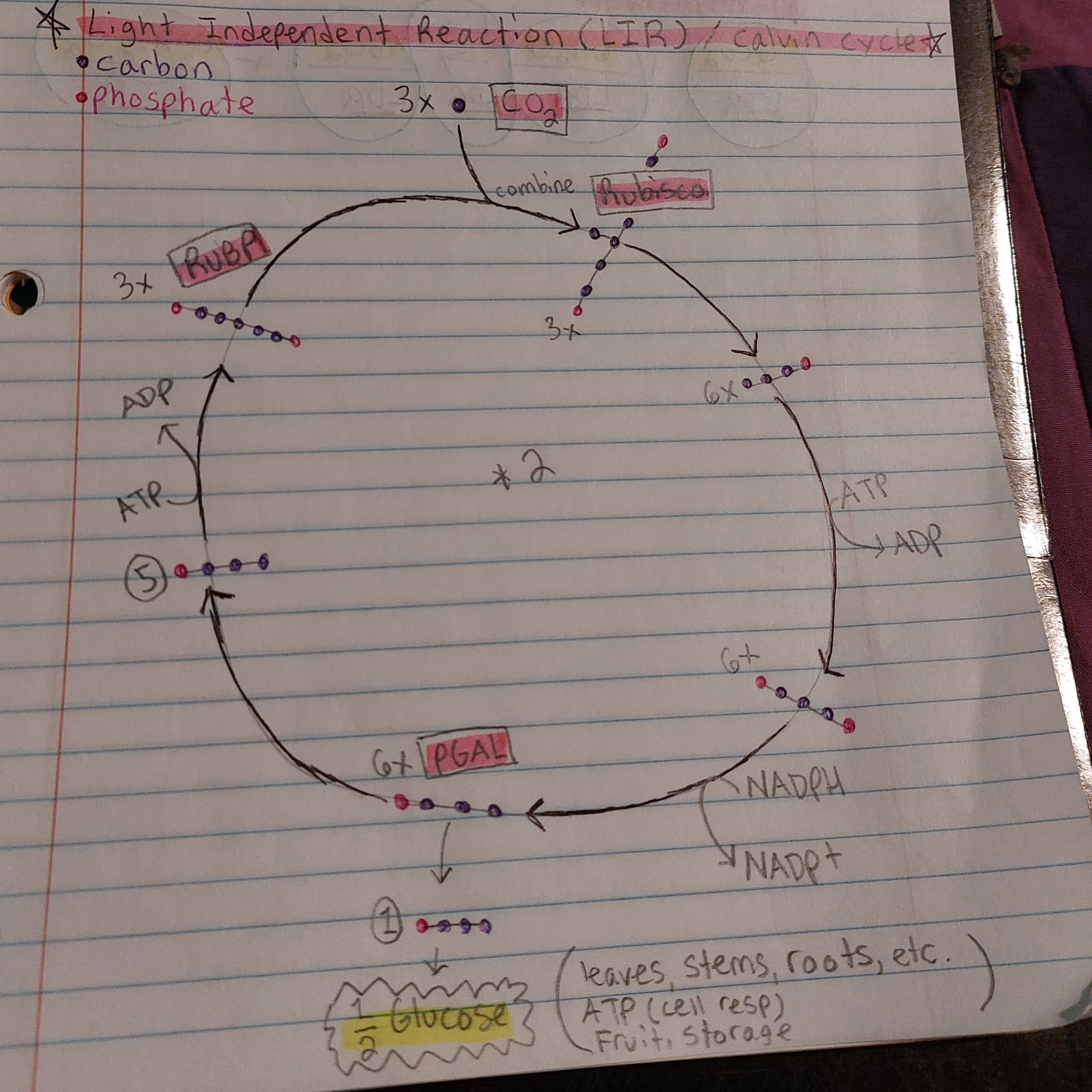
Calvin Cycle / LIR - bullet points
Melvin Calvin
C3
Fueled by ATP and NADPH
Happens in stroma
Uses CO2 to make glucose…
Calvin Cycle / LIR - diagram and must knows
CO2
Rubisco
PGAL
RUBP
Photorespiration
“Glitch” in the system
Rubisco binds with oxygen instead of carbon dioxide
Happens when it is hot
Less carbohydrate
Less plant growth
C4 Plants
Do not use Rubisco the same way as C3
CO2 is fixed into a 4 carbon molecule
CO2 is shuttled to the Calvin Cycle
C4 Advantage
Avoids photorespiration
C4 Disadvantage
Uses more ATP
CAM Plants
Warm and Dry climates
Close stomata during the day
CAM Plants - Night
C4 - carbon storage during the night
CAM Plants - Day
Calvin Cycle during the day - when ATP is available
Photsynthesis Formula
6CO2+ 6H2O — 6O2+ C6H12O6
(FLIP OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION)
— = light
C6H12O6 = glucose
Photoynthesis Formula (parts)
LIR
LDR
LDR
LDR
LIR
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Similarities
Both are biological processes that break down glucose to produce cellular energy
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Differences
However aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor to break down a large amount of energy, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and produces less energy.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Anaerobic metabolic process where sugars are converted into ATP and byproduct lactic acid
Alcoholic Fermentation
Microorganisms, primarily yeast, convert sugar (like glucose) into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as byproducts, especially in the absence of oxygen