Cell Biology Exam 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Cell Biology
Cells are the fundamental units of life.
Study of cells and their structure, function, and behavior.
Cell Theory
All organisms consist of one or more cells.
Cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Is Viruses living and why?
No, because it can’t perform the same functions as living things like metabolism or generating its own energy.
Requires a host cell to live and reproduce.
Are all cells the same in appearance and function?
No, cells can vary in appearance and function.
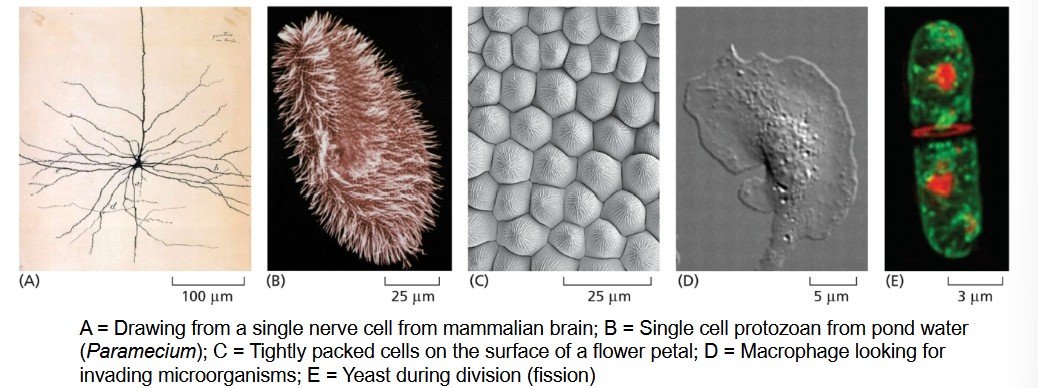
Are all cells enclosed by a membrane, and if so, what is its function?
Yes, every cell is enclosed by a membrane that regulates passage of materials between the cell and the environment.
Do living cells have a similar basic chemistry?
Yes, all living cells have:
Nucleotides, which are the building blocks for DNA and RNA
Amino acids, which are used for building proteins
DNA, which carries genetic information
The same processes of replication, transcription, and translation
Does all present-day cells come from the same ancestral cell?
Yes, all present-day cells have apparently evolved from the same ancestral cell.
If all cells came from the same ancestral cell, how is there evolution?
Genetic changes and selection are the basis of evolution.
What does genes provide?
Provides instruction for cell form, function, and complex behavior.
In one organism, do all the cells have the same or different genomes?
Within the same organism, all the cells usually have the same genome.
note: genome is the complete set of an organism’s DNA, including coded and non-coded areas.
Does differentiated cells express the same or different genes?
Differentiated cells does express different genes.
note: genes is a specific set of DNA that codes for a trait.
What is magnification?
Enlargement of physical appearances of something
What is resolution?
The ability to distinguish two separate points
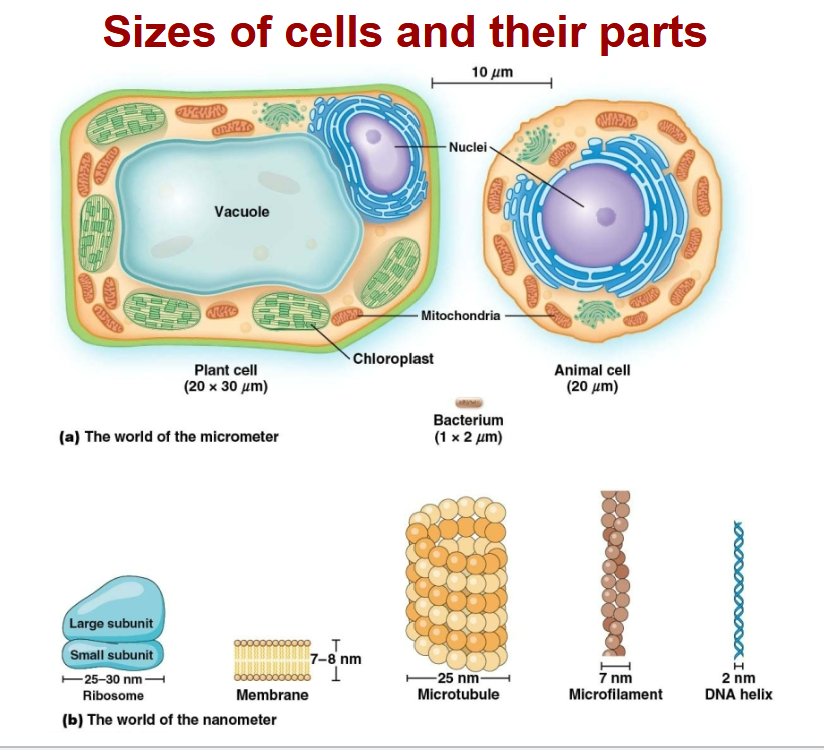
What length unit should be used to measure the size of a cell?
micrometers (μm)
Size of cells and their parts
Which one of the following statements about the cell is NOT true?
A: The cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms.
B: The different tissues and organs in multicellular organisms arise from differences in their genomes.
C: Every cell is enclosed by a cell membrane.
D: Living cells all have a similar basic chemistry.
E: All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Answer: B
It’s due to the differential expression of genes.
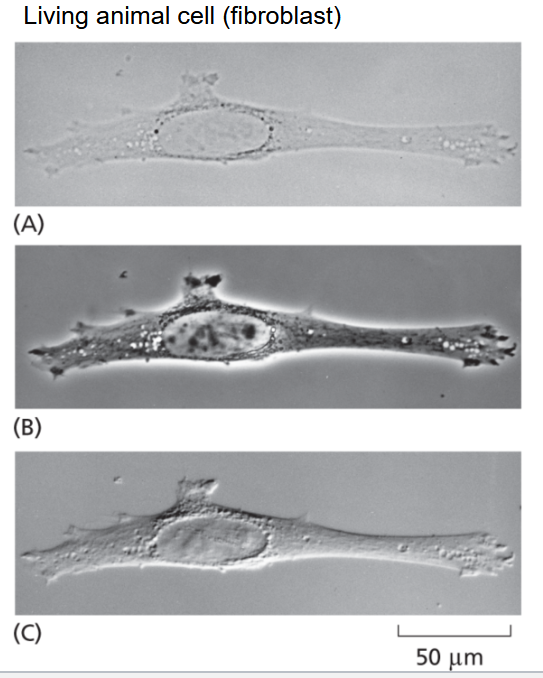
Light Microscope
Resolution: 0.2 μm
Allow examination of cells and some of their content
What is the requirement of samples for light microscopes?
Samples can be dead or alive
Samples must be relatively transparent and thin (can be sectioned if too thick)
Samples must contain contrast from either staining (dead) or use of different optics (alive)
What are the optics for Light Microscopy?
(A) Bright-field optics: has low contrast and usually needs staining.
(B) Phase-contrast optics: used for observing living cells and has halo effects.
(C) Interference-contrast optics: has 3D-like image, no halo effects, and enhanced edge contrast. Also relatively expensive.
Fluorescence microscopy
Resolution: 0.2 μm
Cellular structures are labeled with fluorescent molecules (dyes, antibodies)
The fluorescent molecules are excited, then emit light of a different wavelength
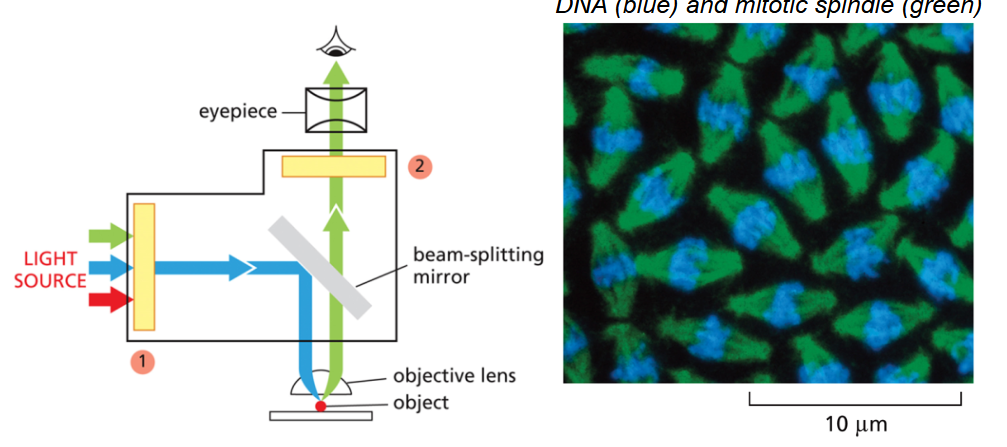
Confocal Microscopy
Specialized type of fluorescence microscopy
Resolution: 0.2 μm
Clear optical section is created by focusing laser beam on individual points.
Generates 3D image using a series of optical sections.
Ideal for live and thicker samples.
Super-resolution microscopy
Resolution: 10-20 nm (note: smaller than μm)
Allows insights into intracellular processes at a molecular level
Created by manipulating light in sophisticated ways or using computer methods to extract more information from the data
Electron Microscopy
a beam of electrons is transmitted through the specimen
was a major breakthrough for cell biology
limit of resolution is around 100 times better than light microscopes
magnification is much higher than light microscopes (up to 100,000 times)
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Resolution: 1 nm (smaller than μm)
Electrons and magnets are used to create and focus the image
Dead samples are sectioned and stained with electron dense materials to create contrast.
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Resolution: 2-30 nm
Uses dead samples that is heavy metal-coated
Scans with an electron beam
The pattern of electron scatter creates a 3D-like image
Which type of microscopy has the highest resolution?
Transmission electron microscopy
Which type of microscopy would you most likely chose if you want to analyze ultrastructural detail of chloroplasts?
A. Brightfield
B. Confocal fluorescence
C. Scanning EM
D. Transmission EM
D. Transmission EM
What is the family tree of life based on?
Based on genome sequence comparisons
What does the length of the branches represent on the family tree of life?
The lengths pf the branches are proportional to the differences among genomes.
Which of the following group is more recent and less diverse compared to the other two groups?
A. Eukaryotes
B. Bacteria
C. Archaea
A. Eukaryotes
Is Eukaryotes more closely related to Bacteria or Archaea?
Archaea
What are prokaryotes?
Single-celled organisms
Arose 3.5-3.8 billion years ago
Lack nuclei and other membrane bound organelles
Has 2 types: Bacteria and Archaea
Prokaryotes: pro (before) karyon (kernel, or nucleus)
What are Eukaryotes?
Contains nuclei and other membrane bound organelles
Found in single or multicellular organisms
Evolved 1.5 billion years ago
Eukaryote: eu (true) karyon (kernel, or nucleus)
What are the differences between Animal and Plant cell?
Plant cells has:
Cell wall
Plastids
Plasmodesmata
Vacuoles (large)
Animal cells has:
Centrioles
What are Organelles?
Specialized structures within a cell that performs specific functions
True organelles are surrounded by at least one membrane.
What is a nucleus?
Contains most of the cell’s genetic info (DNA)
the site of replication and storage of chromosomes
surrounded by two concentric membranes (nuclear envelope)
How can molecules pass in and out of the nucleus?
Nuclear pores within the nucleus envelope allow molecules to pass in and out of the