Pharmacology of antibiotics
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
antimicrobial chemotherapy
the use of drugs to selectively kill bacteria (and viruses/ fungi) without affecting the host
targets of antimicrobial chemotherapy
- bacterial cell wall
- bacterial ribosomes
- bacterial folate metabolism
- bacterial DNA gyrases
antibiotics
produced by an organism to attack other organisms e.g. penicillin
antibacterials
inhibit bacterial growth or kill bacteria and other microorganisms
penicillin examples
- amoxicillin
- benzylpenicillin
- flucloxacillin
- phenoxymethylpenicillin
- beta-lactam antibiotics
beta lactam antibiotics
β-Lactam antibiotics have a β-lactam ring in their molecular structure
- They include penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems
- They are bactericidal antibiotics that bind covalently to and inhibit penicillin binding proteins (PBPs)
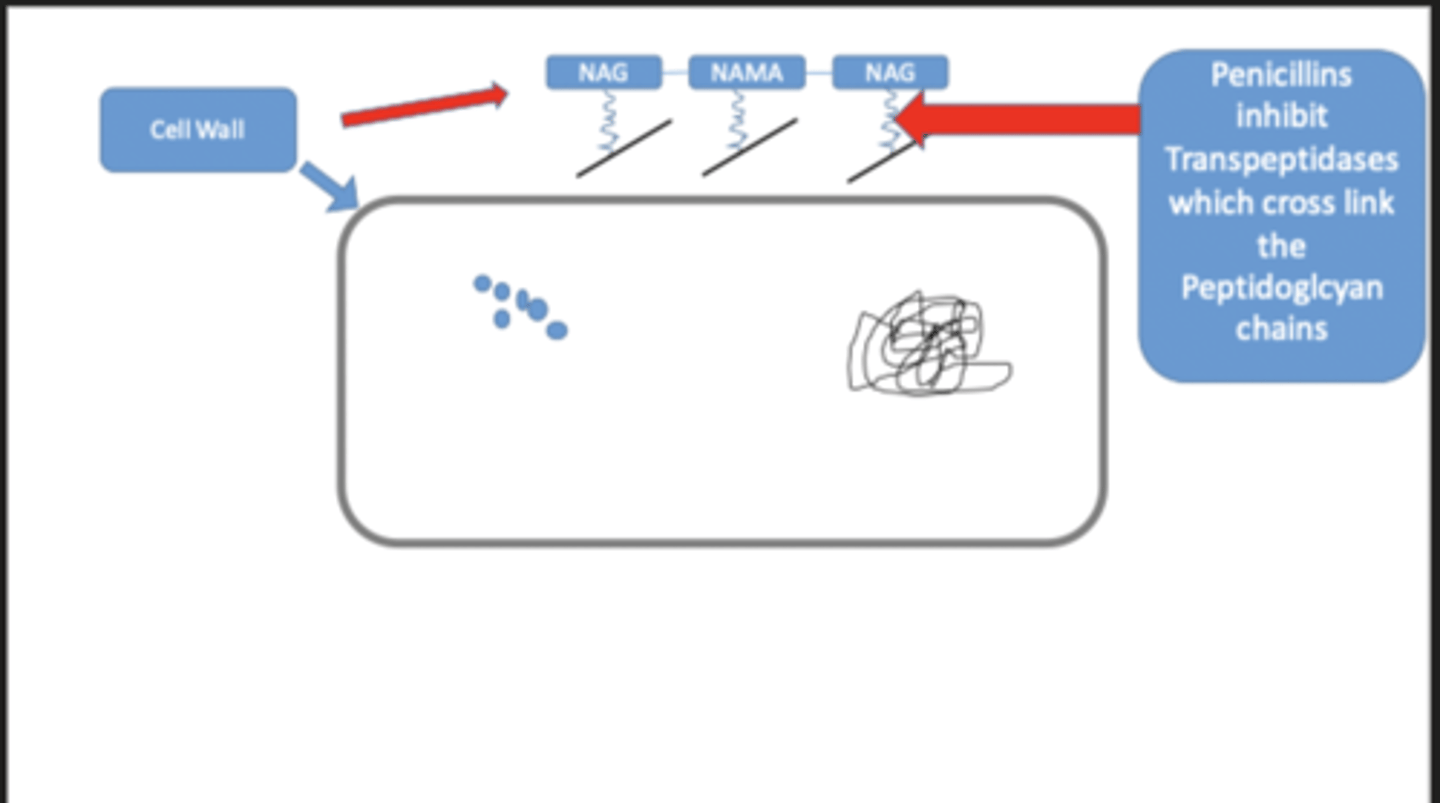
mode of action of penicillins
- target bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding irreversibly to a transpeptidase which cross-links peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall
- only effective against dividing organisms - division requires cells wall synthesis, leading to lysis
- bactericidal, causing lysis of the bacteria
considerations when prescribing antibiotics
- allergies
- pregnancy/breastfeeding
- specificity of antibiotic to pathogen
- susceptibility of pathogen to antibiotic
- side effects - no harm to patient
- pharmacokinetics - oral route/ IV - depends on bioavailability
- drug interactions
beta-lactamases - mech of action
Inhibit cell wall synthesis by binding to transpeptidase
what is added to some antibiotics to inhibit beta-lactamases?
clavulanic acid
penicillin allergy
rash, hives, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis
- immunogenic and therefore allergic reactions are possible on repeat exposure
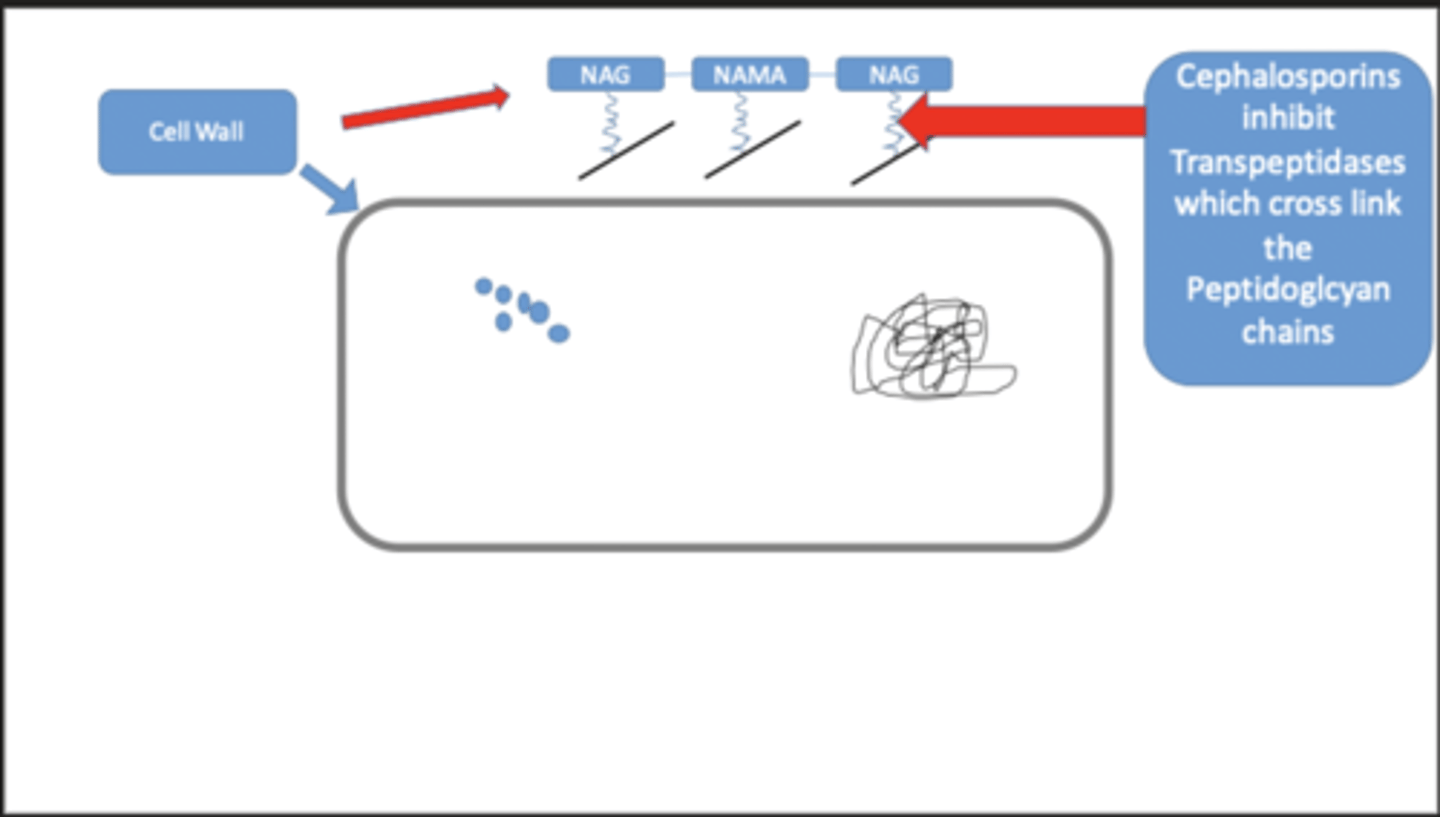
Cephalosporins
- Structurally and functionally similar to penicillins
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics that can be used by most patients that are allergic to penicillin
- e.g. cefaclor, cefalexin, cefotaxime, cefuroxime
- also beta-lactam antibiotics
what proportion of people with a penicillin allergy will also be allergic to cephalosporins?
0.5-6.5%
glycopeptides
- e.g. teicoplanin and vancomycin
- these also inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by inhibiting the growth of the peptidoglycan chain
- often used to manage severe infections due to 'superbugs' such as methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- largely bactericidal
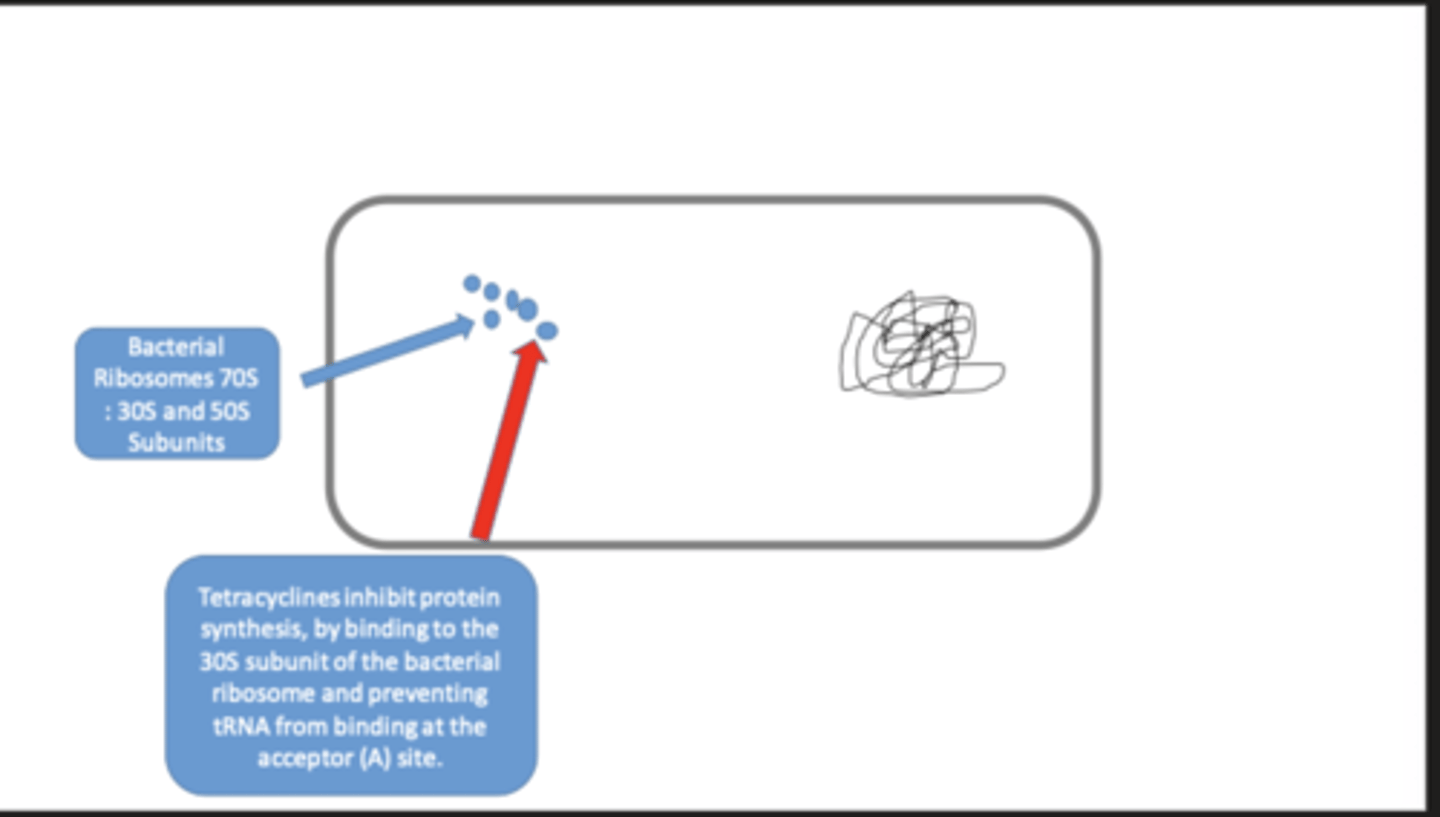
tetracyclines
- e.g. doxycycline and tetracycline
- inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome and preventing tRNA from binding at the acceptor (A) site
- actively accumulate in bacterial cells
- the are bacteriostatic
- their use has decreased due to resistance
Bacteriostatic
inhibits growth of bacteria
macrolides examples
Erythromycin and clarithromycin
structure
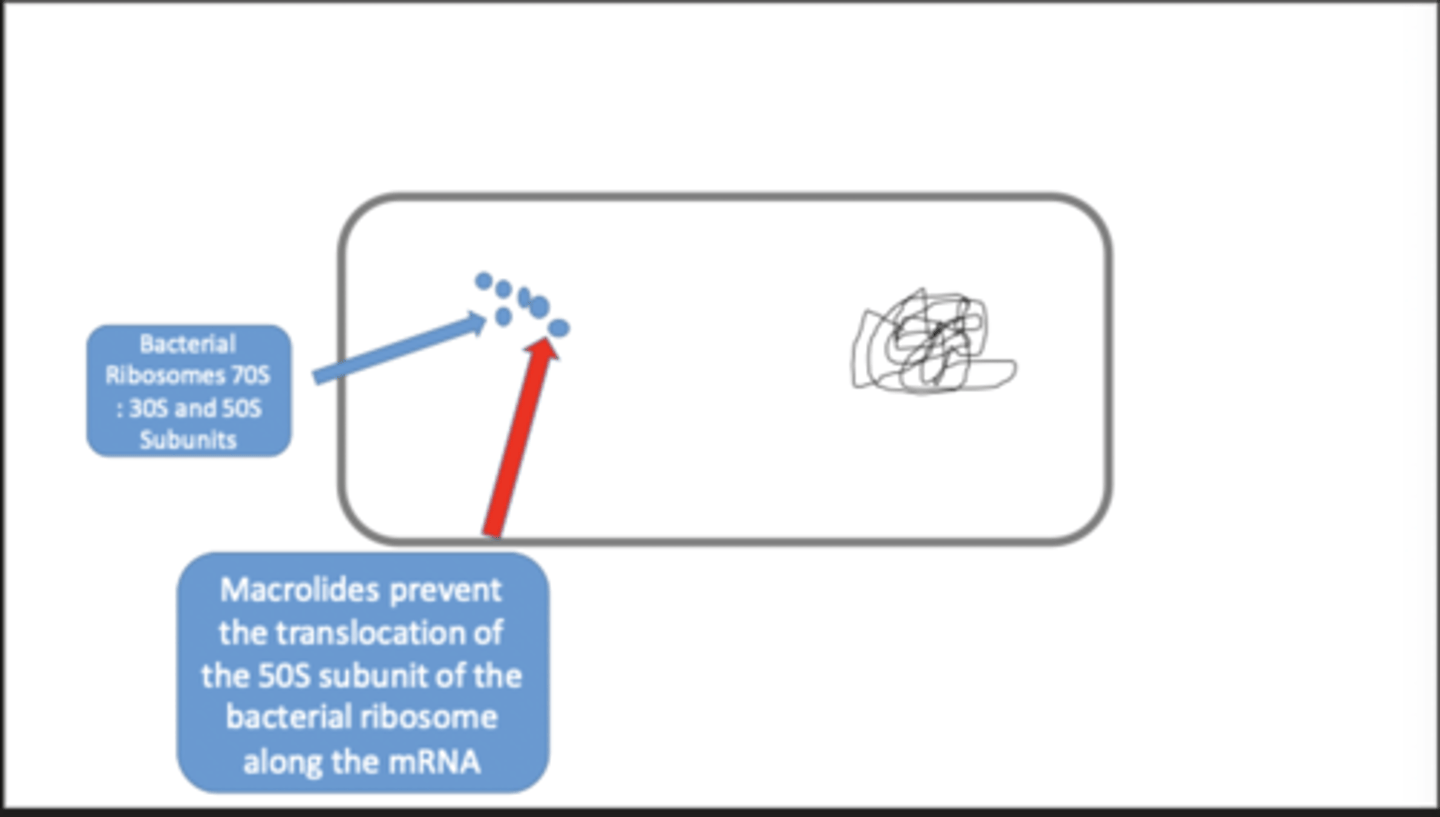
macrolides
- prevent the translocation of the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome along the mRNA
- prevent protein synthesis
- bacteriostatic action
- often used as an alternative to penicillin in patients with a pen allergy
- cytochrome P450 inhibitors and associated with a rage of drug interactions (increase concentrations of interacting drugs)
cytochrome P450 inhibitor
- the most common mechanism leading to drug-drug interactions
- CYP450 inhibition can be categorised as reversible or irreversible such as mechanism-based inhibition
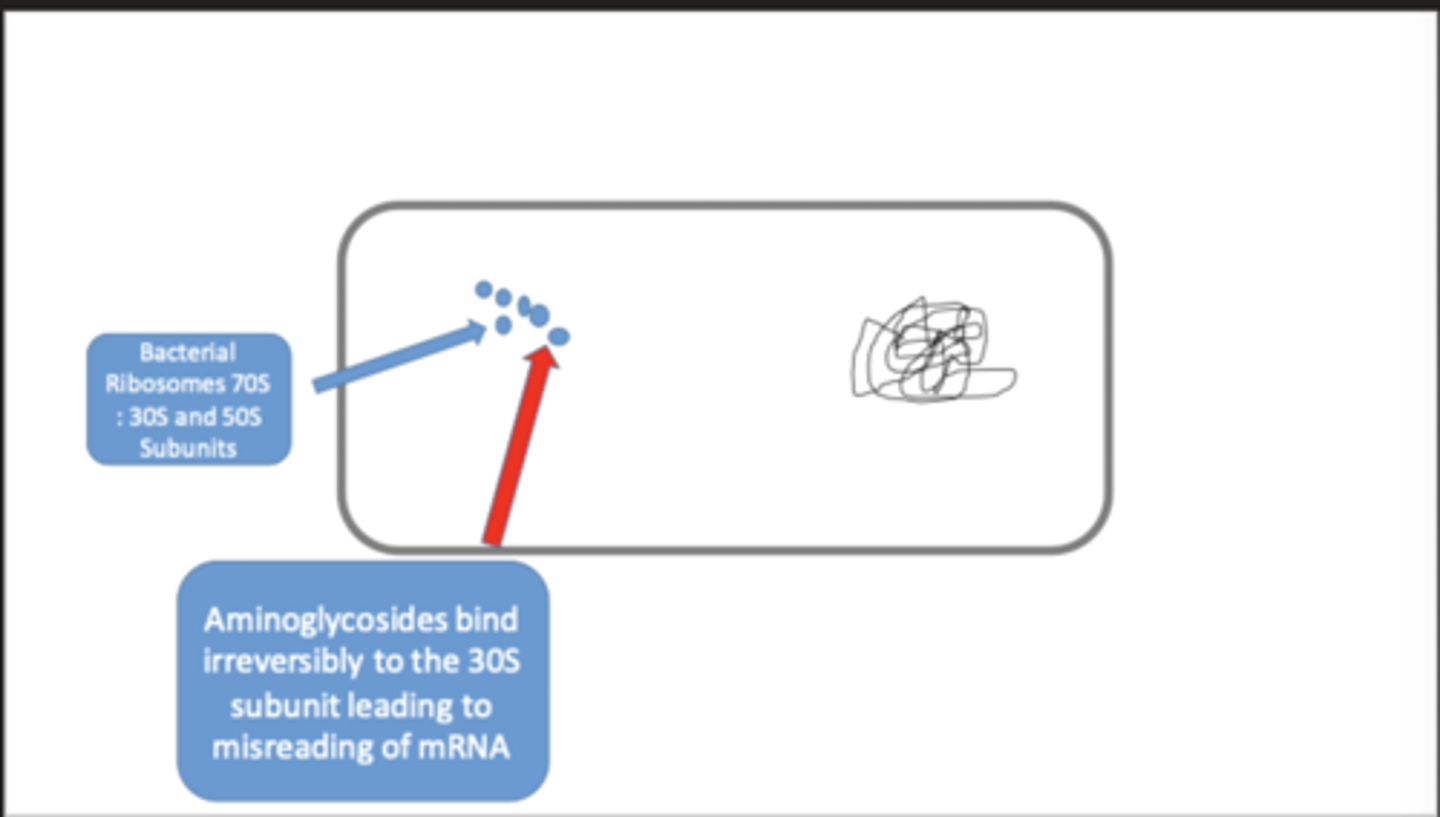
aminoglycosides examples
gentamicin, neomycin and tobramycin
mode of action of aminogylcosides
- bind irreversibly to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes, leading to the misreading of mRNA and interfere with protein synthesis
Synergy
combined force
gram negative
- Describing the group of bacteria that have a cell wall that is structurally more complex and contains less peptidoglycan than the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria
- Gram-negative bacteria are often more toxic than gram-positive bacteria
Why is aminoglycosides used
- complicated by toxicity - ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity
- clinically, their regimens are complex, so that there is a desired peak concentration to facilitate bacterial killing, but a low, sub-therapeutic trough conc. is used to reduce the chances of toxicity
- small therapeutic window
ototoxicity
Toxicity to the ears, often drug induced and manifesting as varying degrees of hearing loss that is likely to be permanent
Nephrotoxicity
damage to the kidneys by a toxic substance
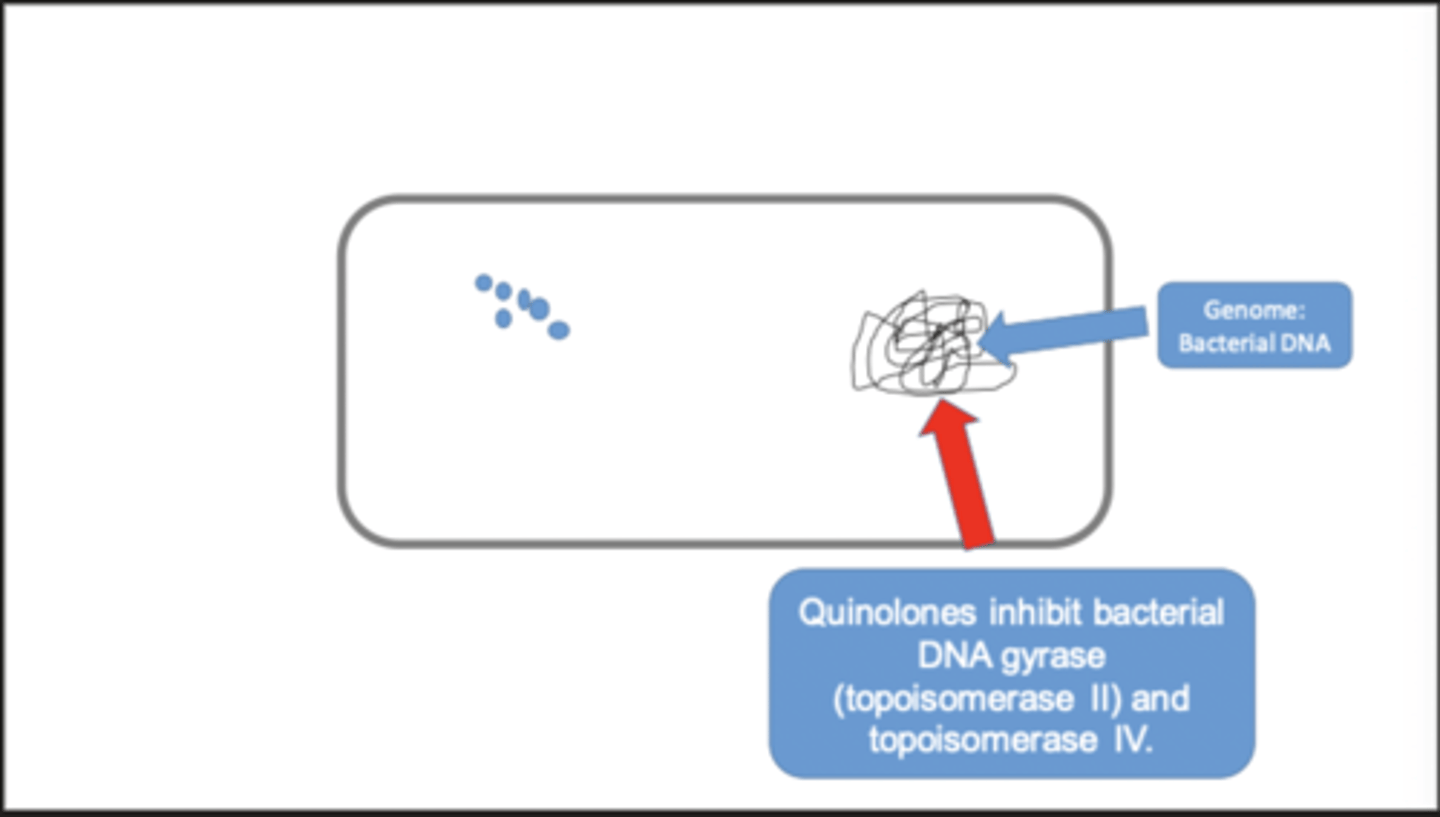
quinolones
- e.g. ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin
- these are inhibitors of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV
- gram -ve bacteria: DNA gyros is inhibited and effects the DNA repair and replication
- gram +ve bacteria: topoisomerase IV is the target and quinolones interfere with the separation of DNA strands on replication
trimethoprim
- structurally related to folate
- folate antagonist and inhibiting the bacterial dihydrofolate reductase, which converts folate to tetrahydrofolate
- trimethoprim is less potent against the human form of the enzyme
sulphonamides
- analogues of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and inhibit the growth of bacteria by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthesis, involved in the synthesis of folate from PABA (p-aminobenzoic acid)
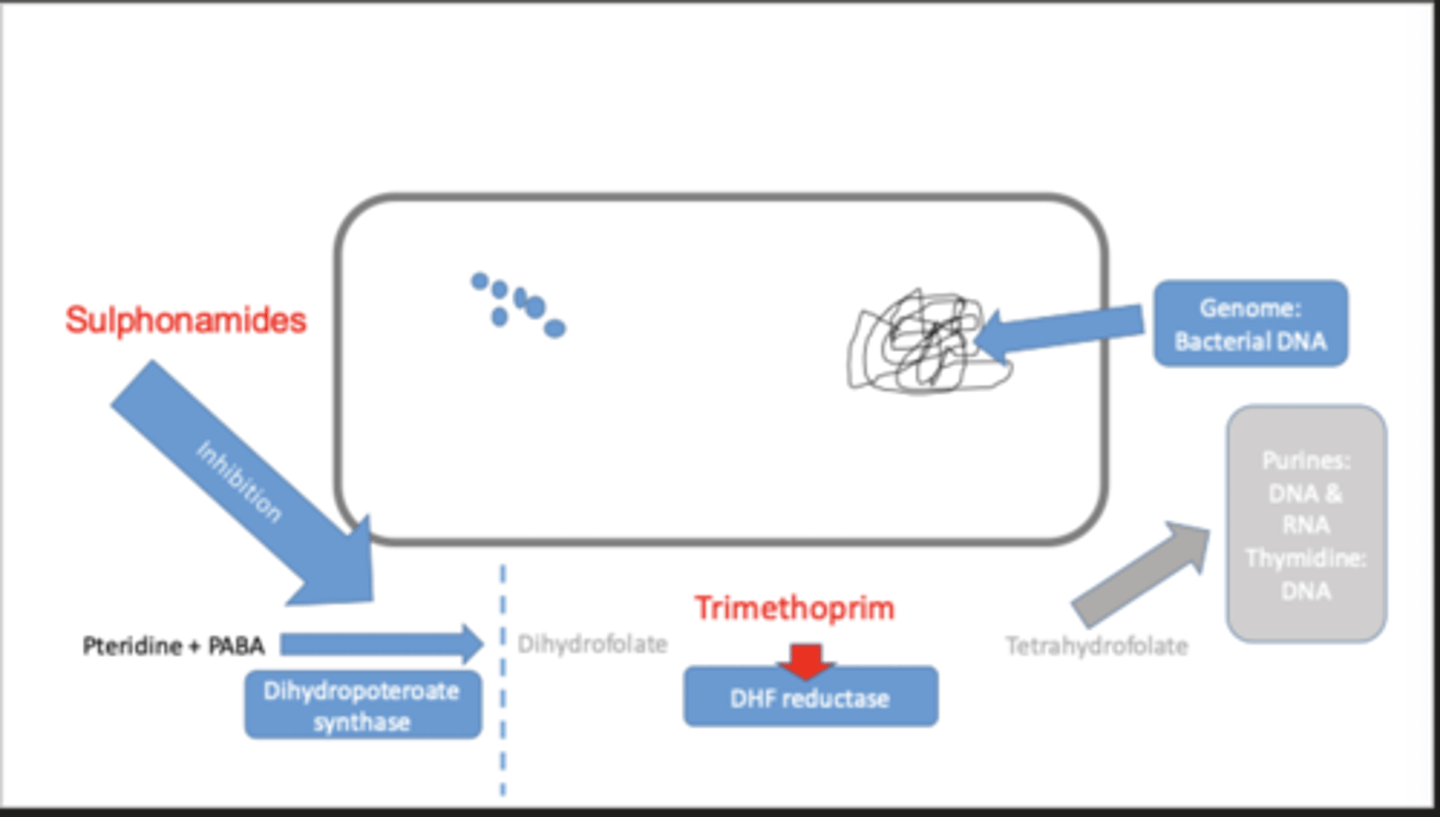
Sulphonamids and trimethoprim starve bacteria of what ???
Purines and thymidine
Metronidazole
- pro-drug which is activated by anaerobic bacteria to cytotoxic products which damages the helical structure of DNA, protein and the cell membrane
- used against anaerobic bacteria and protozoa
- used for anaerobic infections
relationship between beta-lactamases and penicillian
- some penicillins are inactivated by beta-lactamases secreted by resistant bacteria
- some penicillins are resistant to beta-lactamases
Which class of antibiotics are bactericidal (Suicidal) ?
Beta - lactams
Cephalosporins
Glycopeptides
Aminoglycosides
Quinolones
Metronidazole
BIG CATS GROWL AT QUICK MICE
What class of antibotics are bacteriostatic
Tetracyclines , macrolides, Sulphonamides
THE MIGHTY SHIELD