MCAT Organic Chemistry
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Fischer Projections
Vertical lines in
Horizontal lines out
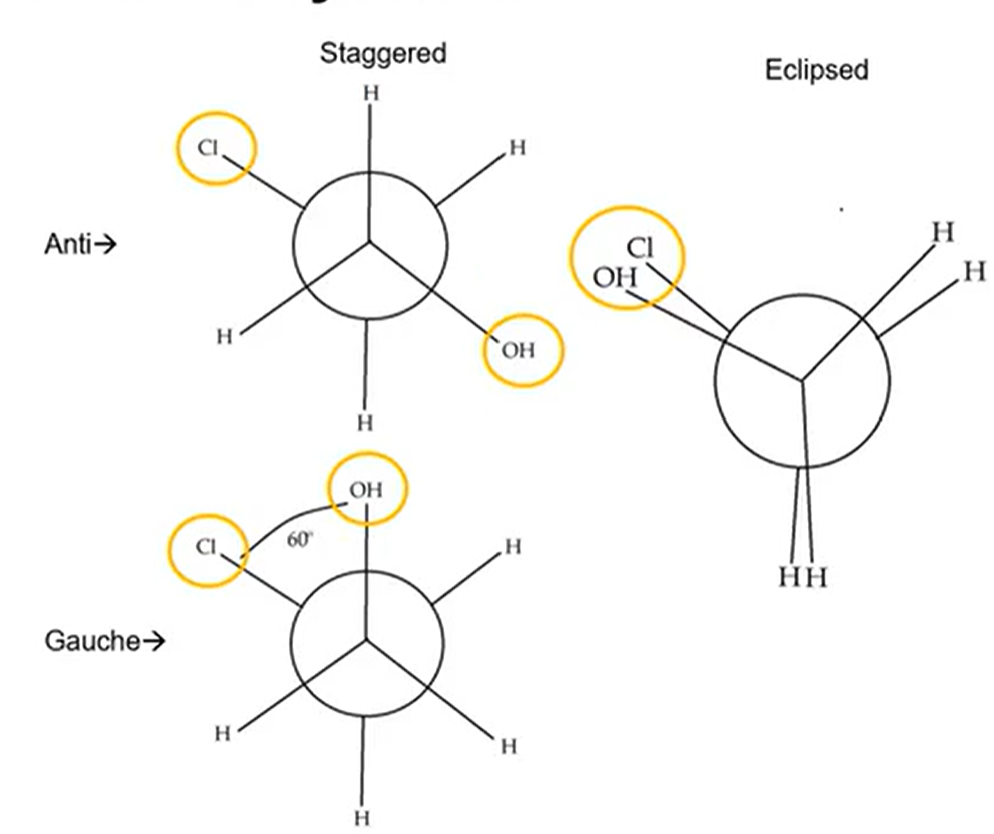
Newman Projection Stability Order
Anti > Gauche > Eclipsed
Chirality
The “handedness” of a molecule
Stereoisomers
Two forms of a molecule that differ by their stereochemistry
+/- or d/l system
ONLY at chiral centers
+/- or d/l system
How the molecules bends plane-polarized light
Clockwise: d- or +, dextro
Counterclockwise: l- or -, levo-
Chiral Center
4 different substituents
Requires asymmetry
NO chiral center if:
Double bond
Triple bond
2 or more of the same substituents
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
Higher atomic number = higher priority
If there is a tie, the tie winner is the one with the highest number substituent
If there is still a tie, move to the next atom down the chain, then 4, 5 etc. until tie is broken
Double bonds count as two bonds to a atom of the same atomic number; double bond to an atom will win a tie vs a single bond to the same atom. Triple bonds count as 3 and win over double bonds similarly
The heavier isotope wins the ties if we have two of the same element
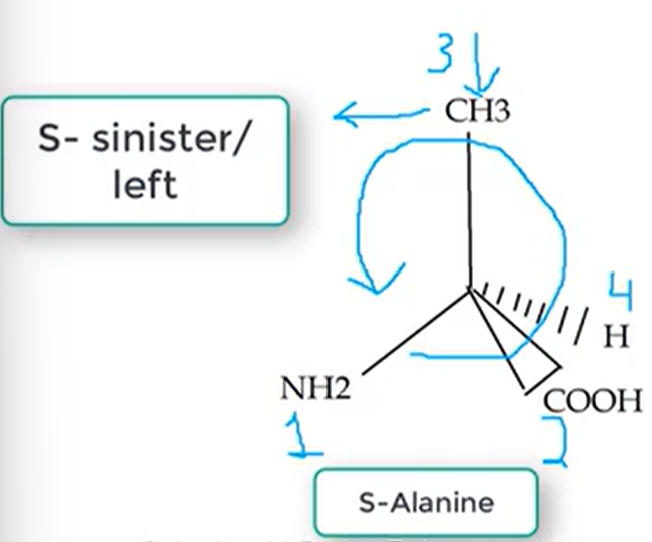
S Configuration
Sinister / LEFT
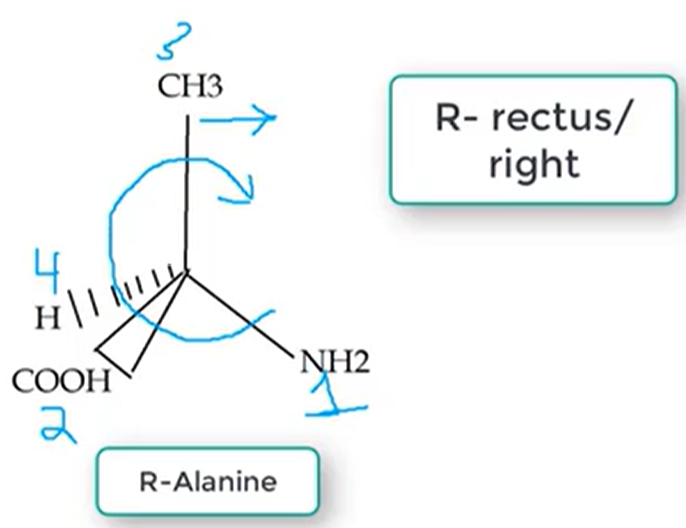
R Configuration
Rectus / RIGHT
When lowest priority atom is point out at you:
Determine the direction of the arrow (S or R), then flip it to the other one
If it was R, then answer would be S and vice versa
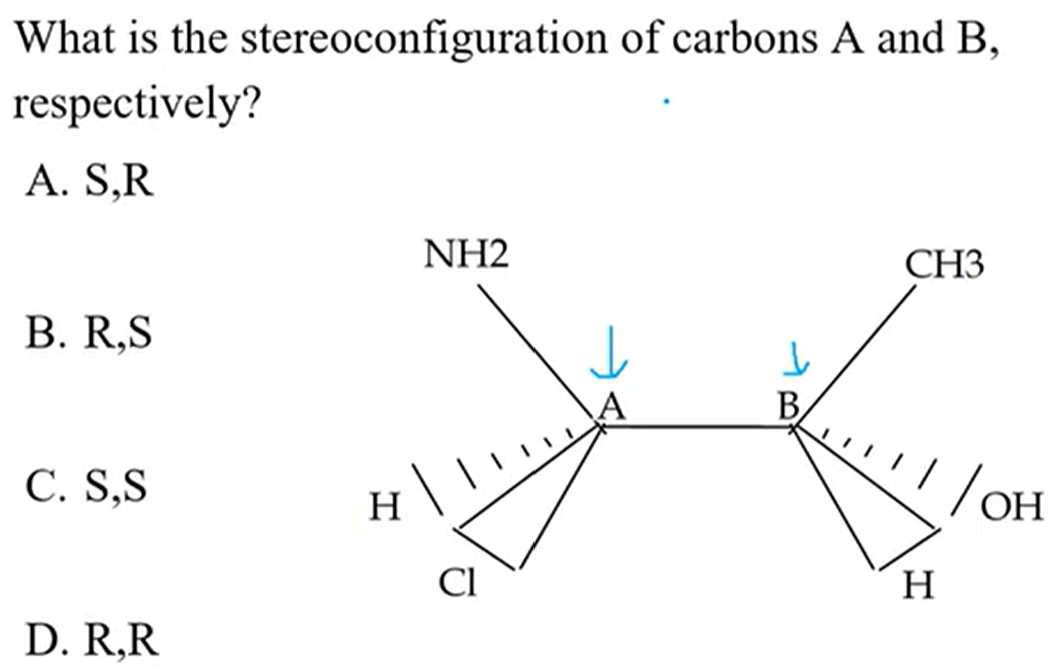
B. R, S