APES formulas/vocab
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Lincoln-Peterson Index
N=M*S/R
Population growth rate
(births-deaths)/total population size
(x100 for percentage)
1 calorie
4.184J
1 BTU
1.05 kJ
1 therm
100,000 BTU
Power
Energy/Time
1 watt
1 J/s
Rule of 70
70/Growth Rate
doubling time of a population
Efficiency
Energy Output/Energy Input x 100
percentage of energy that is converted from one form to another.
Gross Primary Productivity
rate of photosynthesis by plants
Net Primary Productivity
GPP - Respiration
Energy stored as biomass, available to consumers
half life
ln 2 (0.7)/decay constant
Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Combustion
Hydrocarbons (CxHy) + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Ocean Acidification
CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-
Photochemical Smog Formation
NOx + VOCs + heat + sunlight → smog
Nitrogen oxide is produced early in the day.
Ozone concentrations peak in the afternoon and are higher in the summer b/c produced by reactions between oxygen and sunlight.
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
O3 + Cl → O2 + ClO
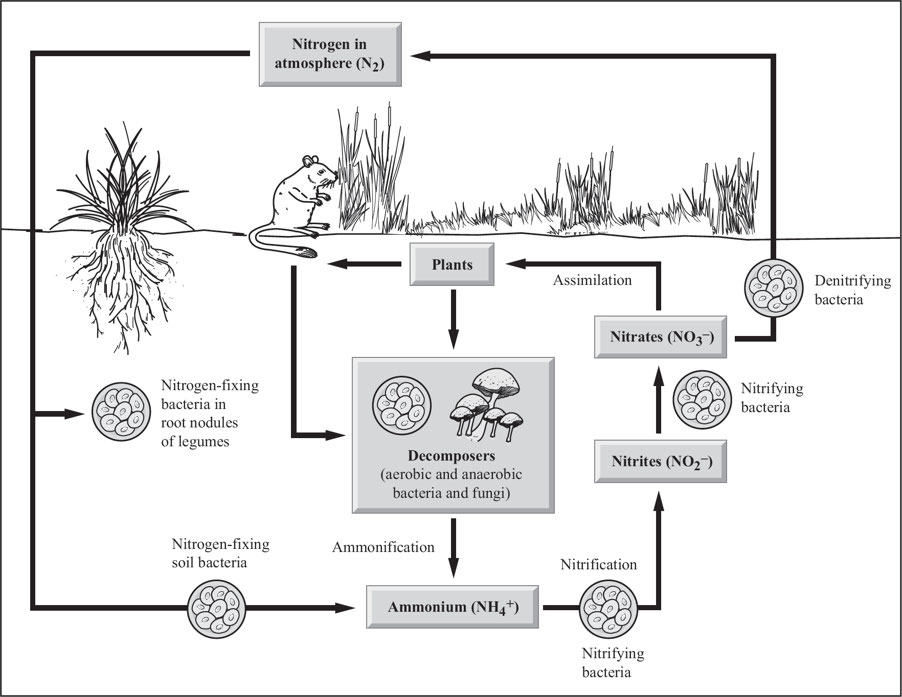
Nitrogen fixation
Atmospheric nitrogen → ammonia (NH3) or nitrate ions (NO3-), biologically usable forms of nitrogen.
Nitrification
Ammonia (NH3) → nitrite (NO2-) and nitrate (NO3-), most useful forms to plants
Assimilation
Plants absorb ammonia (NH3), ammonium ions (NH3+), nitrate ions (NO3-) through their roots.
Ammonification
Decomposing bacteria convert dead organisms/wastes (nitrates, uric acid, proteins, and nucleic acids) → NH3 and NH4+ (biologically useful forms)
Denitrification
Anaerobic bacteria convert NH3 → nitrites (NO2-), nitrates (NO3-), nitrogen gas (N2), nitrous oxide (N2O) to continue the cycle
Nitrogen cycle
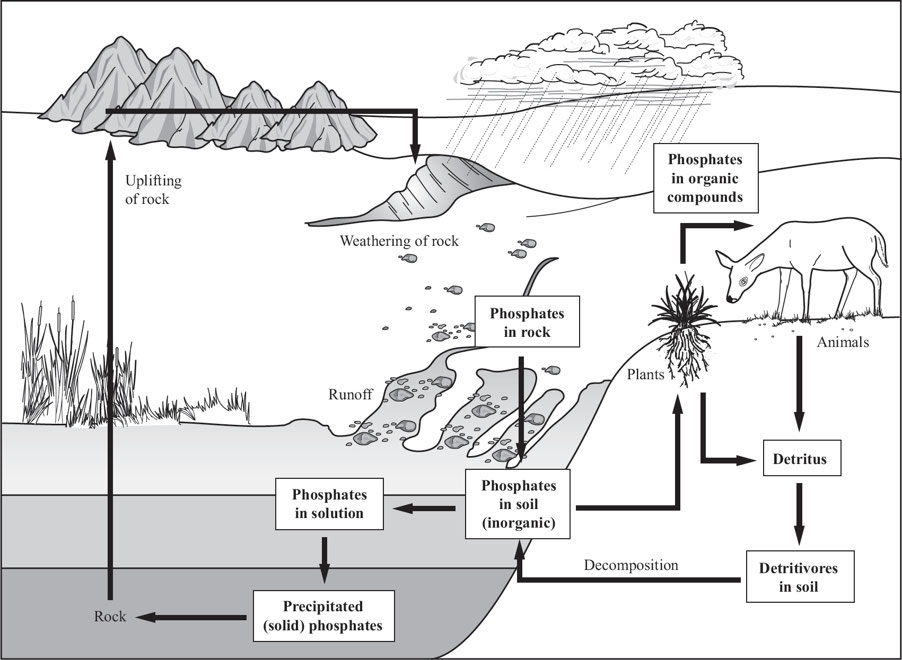
Phosphorus cycle
Furrow irrigation
cutting furrows between crop rows and filling them w/water
inexpensive, but ~1/3 of the
water is lost to evaporation and runoff.
Flood irrigation
flooding an agricultural field w/water
~ 20% of the water is lost to evaporation and runoff
can lead to waterlogging of the soil
Spray irrigation
pumping ground water into spray nozzles across an agricultural field.
more efficient than flood/furrow irrigation, only 1/4 or less of the water lost to evaporation or runoff
more expensive, requires energy to run
Drip irrigation
use perforated hoses to release small amounts of water to plant roots.
most efficient, only about 5% of water lost to evaporation and runoff.
expensive → not often used.
CAFOS
Concentrated animal feeding operation
used as a way to quickly get livestock ready for slaughter
crowded, animals are fed grains or feed not as suitable as grass
generate a large amount of organic waste → can contaminate ground/surface water
less expensive than other methods
Surface mining
removal of large portions of soil and rock (overburden) in order to
access the ore underneath.
Ex: strip mining removes the vegetation from an area → more susceptible to erosion
Mining impacts
wastes/slag: soil and rocks that are moved to gain access to the ore, tailings that remain when the minerals have been removed from the ore
As coal reserves get smaller, need to subsurface mining, which is very expensive.
3 types of coal
lignite, bituminous, anthracite
Crude oil
recovered from tar sands (combination of clay, sand, water, bitumen)
Cogeneration
when a fuel source is used to generate both useful heat and electricity.
Nuclear power
generated through fission: atoms of Uranium-235 stored in fuel rods are split into smaller parts after being struck by a neutron
Hydrogen fuel cell
use hydrogen as fuel, combining the hydrogen and oxygen in the air to form water and release energy (electricity) in the process. Water is the product (emission) of a fuel cell.
Clean Air Act
EPA regulated the use of lead, particularly in fuels, which dramatically decreased the amount of lead in the atmosphere
Volatile Organic Compounds
evaporate or sublimate at room temperature.
ex: formaldehyde, gasoline
thermal inversion
normal temperature gradient in the atmosphere is altered as the air temp at the Earth’s surface is cooler than the air at higher altitudes.
traps pollution close to the ground, esp smog + particulates.
indoor air pollutants
asphyxiant: Carbon monoxide
particulates: asbestos, dust, and smoke
natural source: radon, mold, and dust
human-made: insulation, VOCs, formaldehyde, lead
combustion: carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulates, and tobacco smoke.
Radon-222
naturally occurring radioactive gas produced by the decay of uranium found in some rocks and soils
can infiltrate homes as it moves up through the soil and enters homes via the basement or cracks in the walls or foundation.
also dissolved in groundwater that enters homes through a well.
can lead to radon-induced lung cancer
vapor recovery nozzle
device on a gasoline pump that prevents fumes from escaping into the atmosphere when fueling a motor vehicle.
catalytic converter
device for internal combustion engines that converts pollutants (CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons) in exhaust into less harmful molecules (CO2, N2, O2, and H2O).
Wet and dry scrubbers
devices that remove particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
do not easily break down in the environment because they are synthetic, carbon-based molecules (such as DDT and PCBs)
soluble in fat → accumulate in organisms’ fatty tissues
Primary treatment
physical removal of large objects
often via screens and grates, followed by the settling of solid waste in the bottom of a tank.
Secondary treatment
bacteria break down organic matter into CO2 and inorganic sludge which settles in the bottom of a tank.
The tank is aerated to increase the rate at which the bacteria break down the organic matter.
Tertiary treatment
use of ecological or chemical processes to remove any pollutants left in the water after primary and secondary treatment.
lethal dose 50% (LD50)
dose of a chemical that is lethal to 50% of the population of a particular species.
CFC substitutes
do not deplete the ozone layer, ex. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
HIPPCO
habitat destruction, invasive species, population growth, pollution, climate change, and over exploitation
main factors leading to a decrease in biodiversity.