AP HUG Unit 4.6-4.10
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Census
Official population Count but also includes data on age, race, and sex. Done every 10 years. Used to determine federal and state funding for planning and providing services and building/maintaining infrastructure.

Reapportionment
Process in which U.S. House of representative seats are re-allocated to different states, based off of population change.
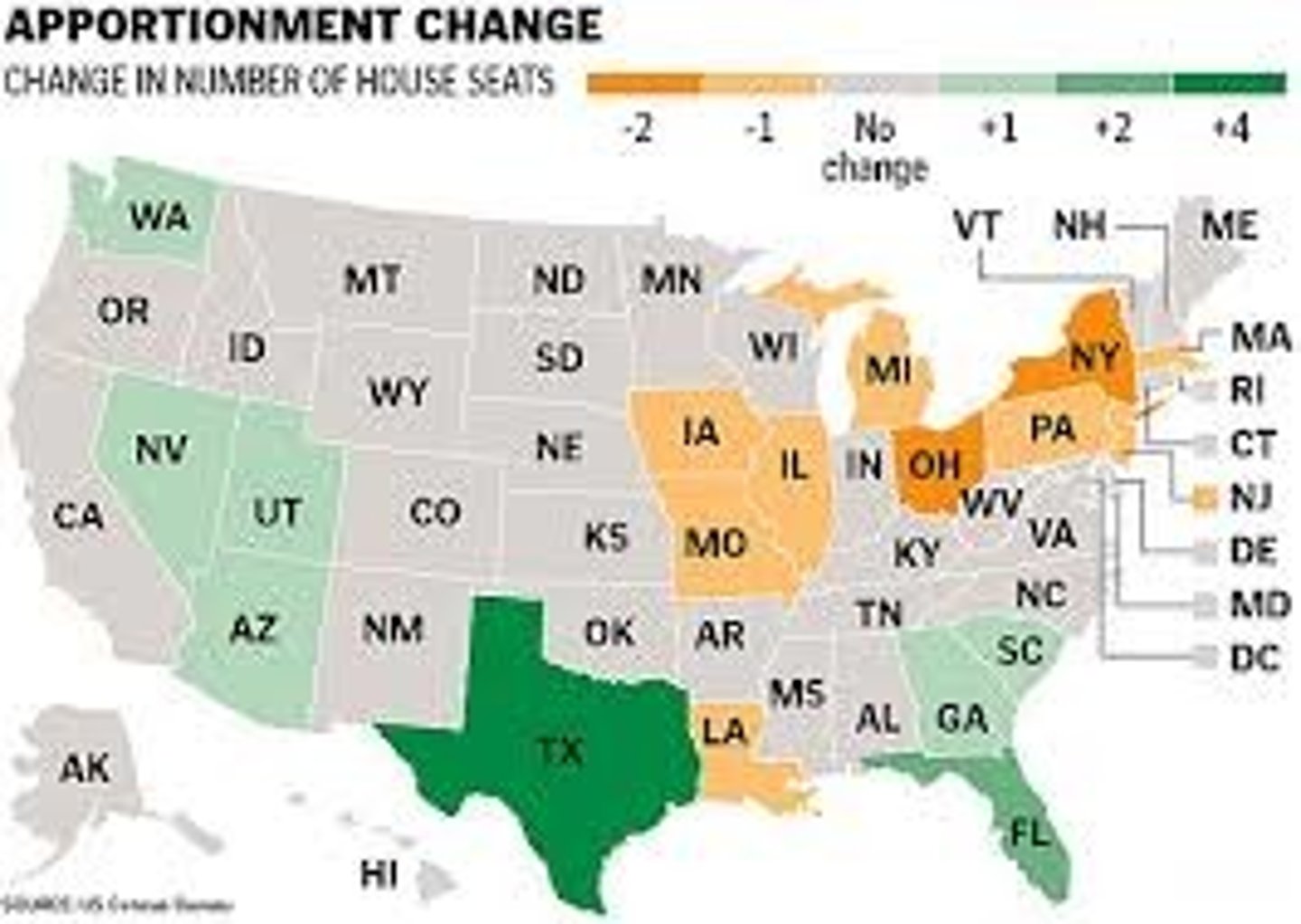
House of Representative
435 members

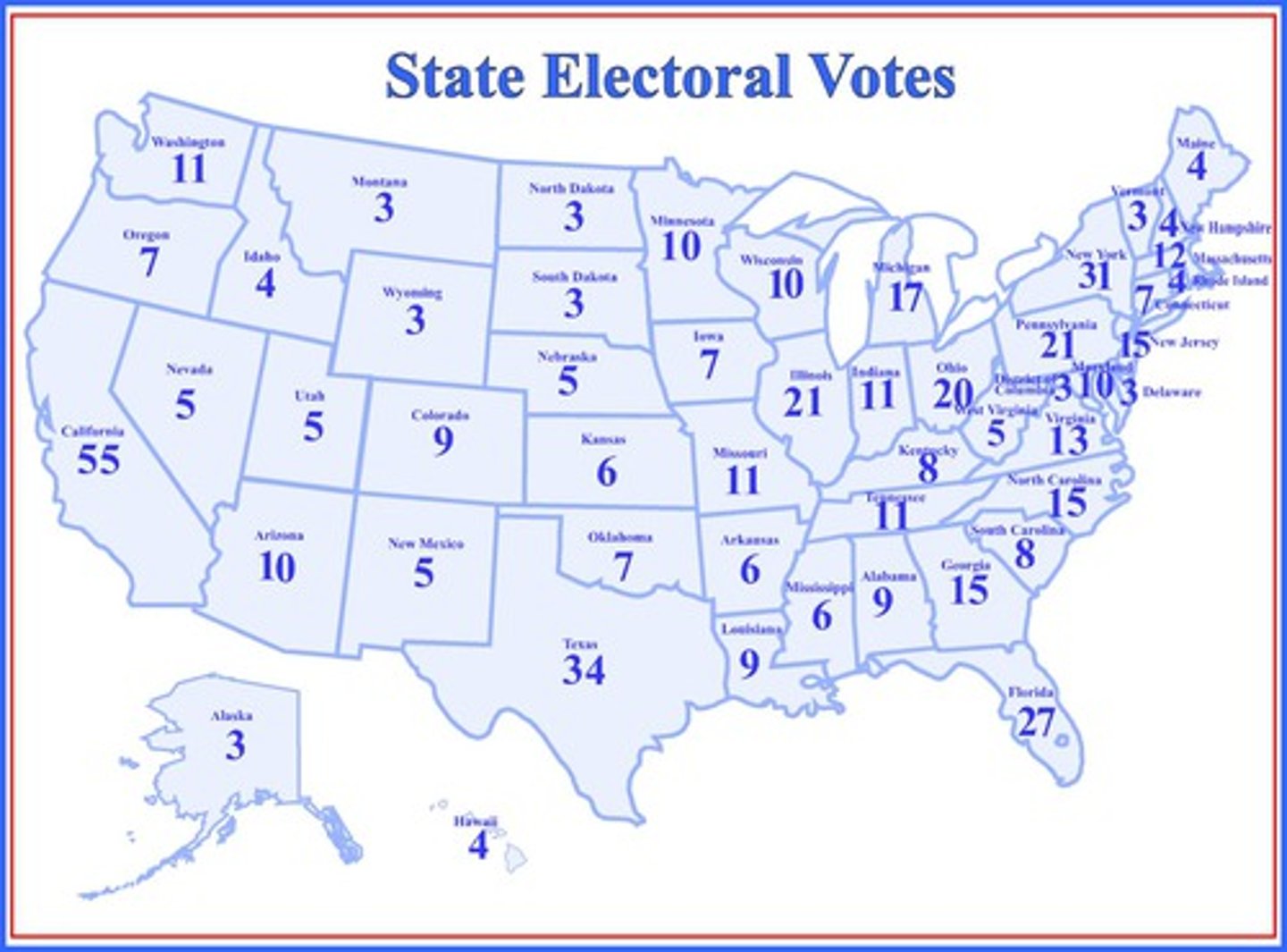
Electoral College
Organization that utilizes the popular vote to then vote for President.
Electorate
All the people in a country or area who are entitles to vote in an election

Voting District
A geographic term used by state and local governments to organize elections.
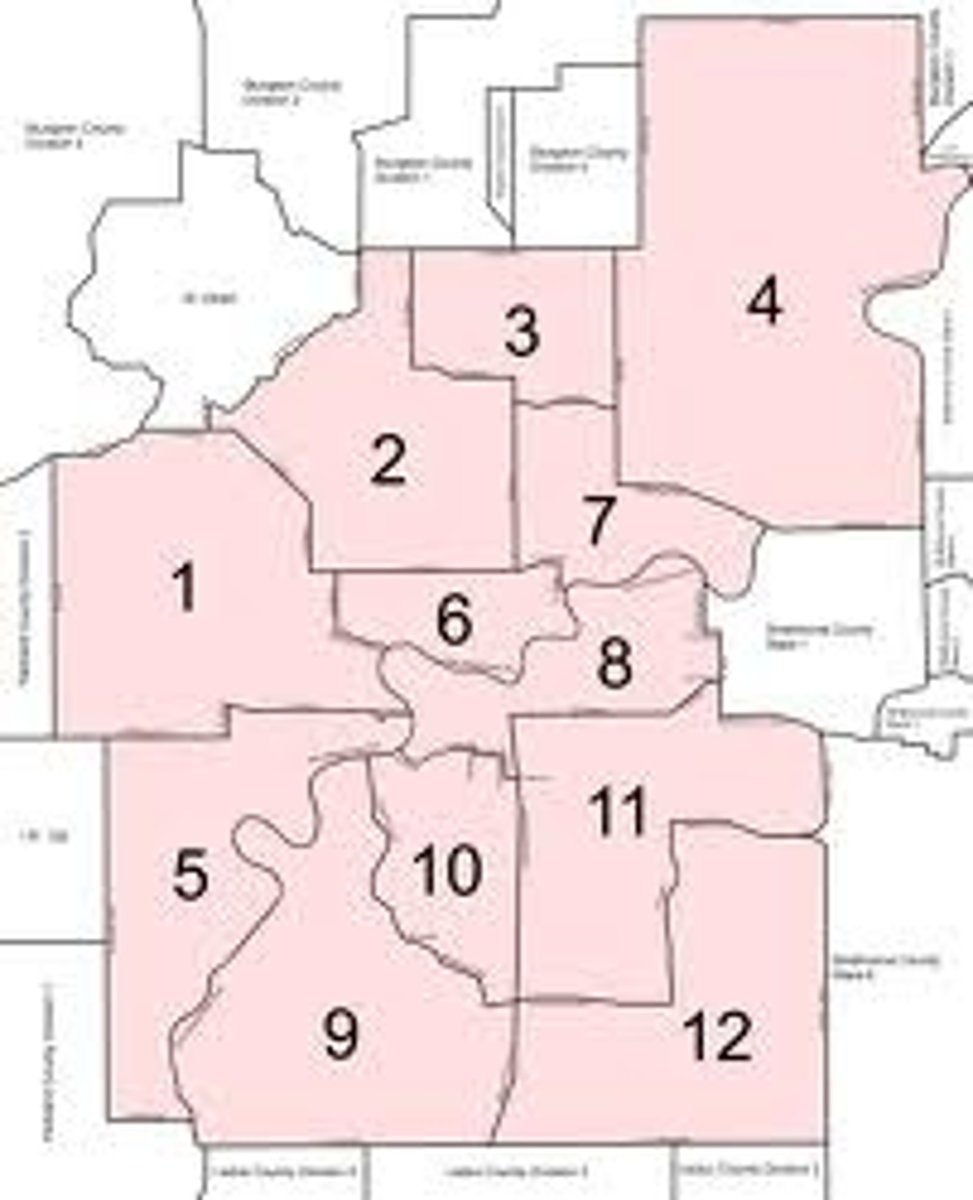
Redistricting
State's internal political boundaries that determine voting districts for the US hose of Representatives and the state legislature. Redrawn to accurately reflect the new census data.
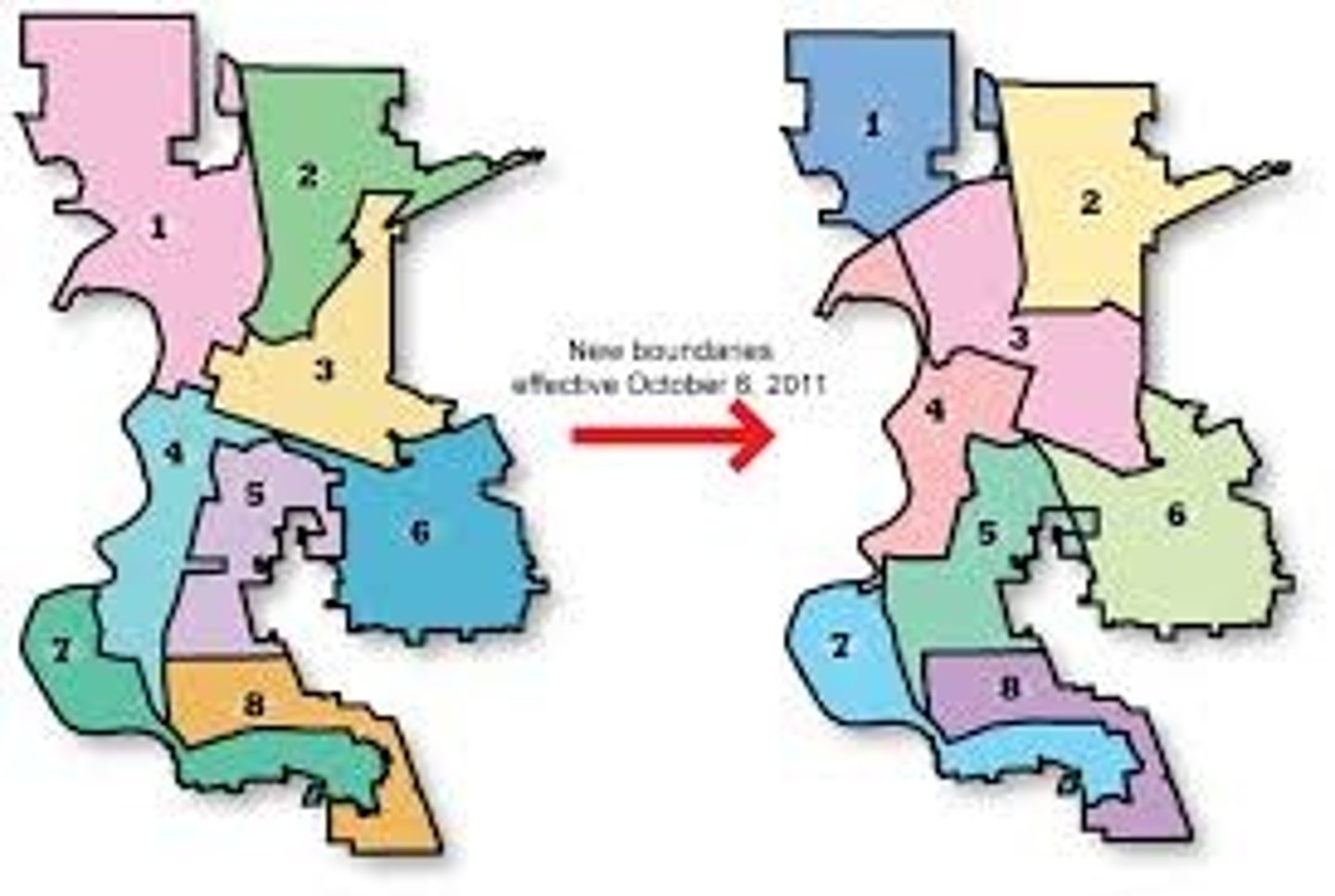
Requirements for redistricting
US constitution requires:
-Similar/equal in population size (10% variation)
-States can set additional laws on how redistricting should occur
States traditionally require:
-Contiguous
-Compactness
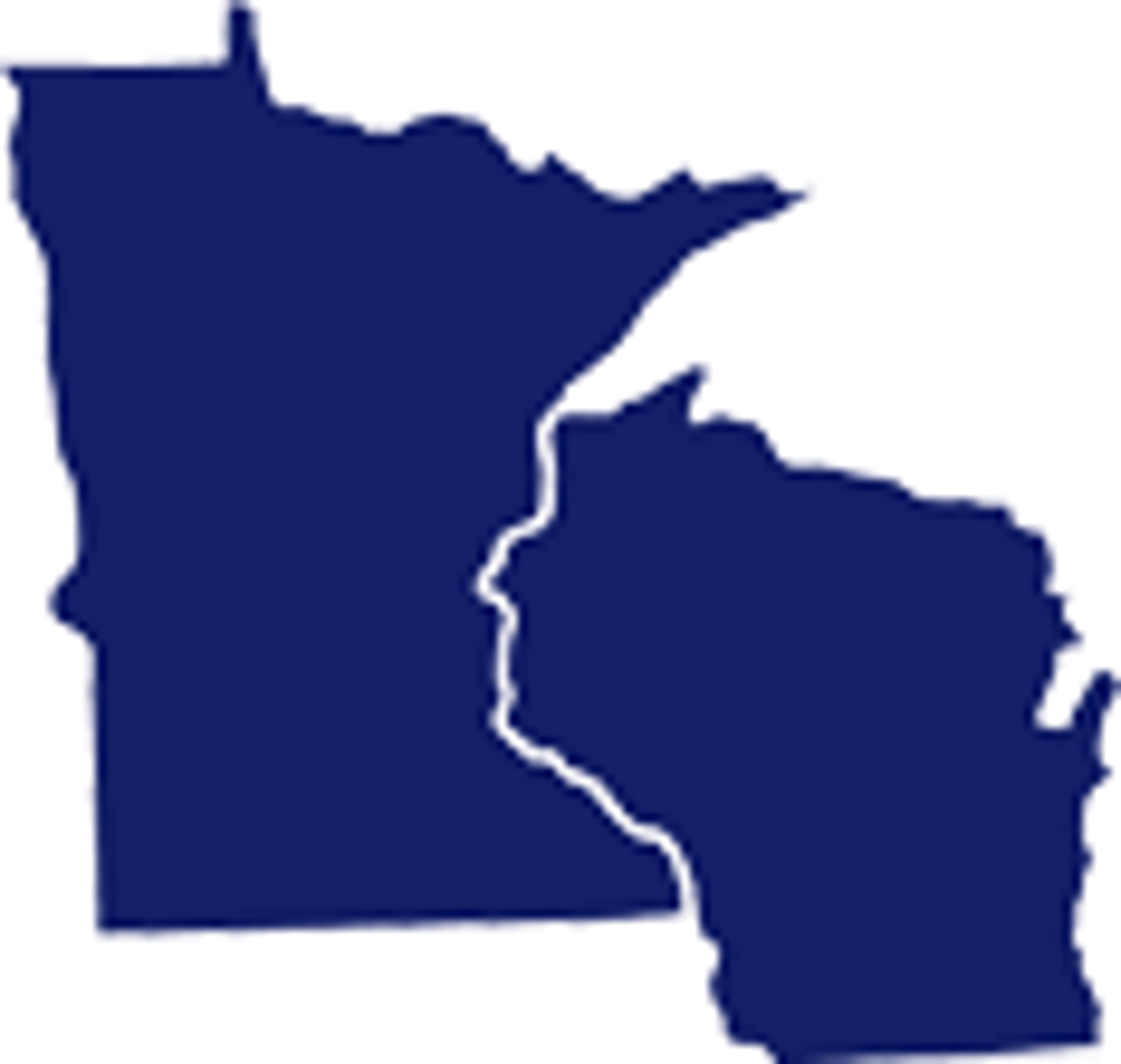
Contiguous
Next to each other, boundaries are touching. Single, unbroken shape.
Compactness
Smooth rather than contorted boundaries and should cluster around a central core, rather than dispersing outwards. (people live near each other)
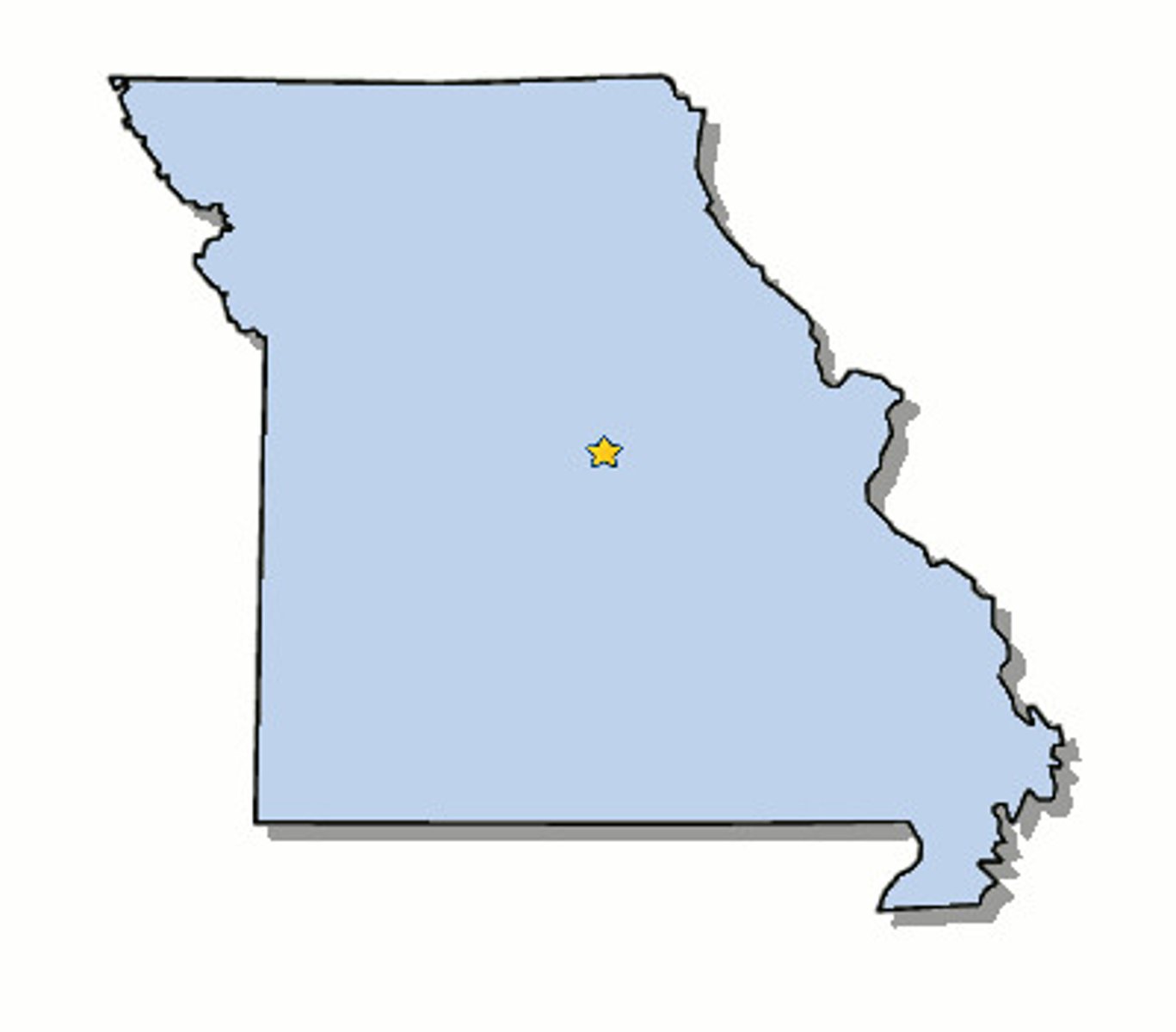
Representative districts
The ideal, in which the voting districts are equal in population, contiguous, and compact. They are truly representative of the people living in the district.
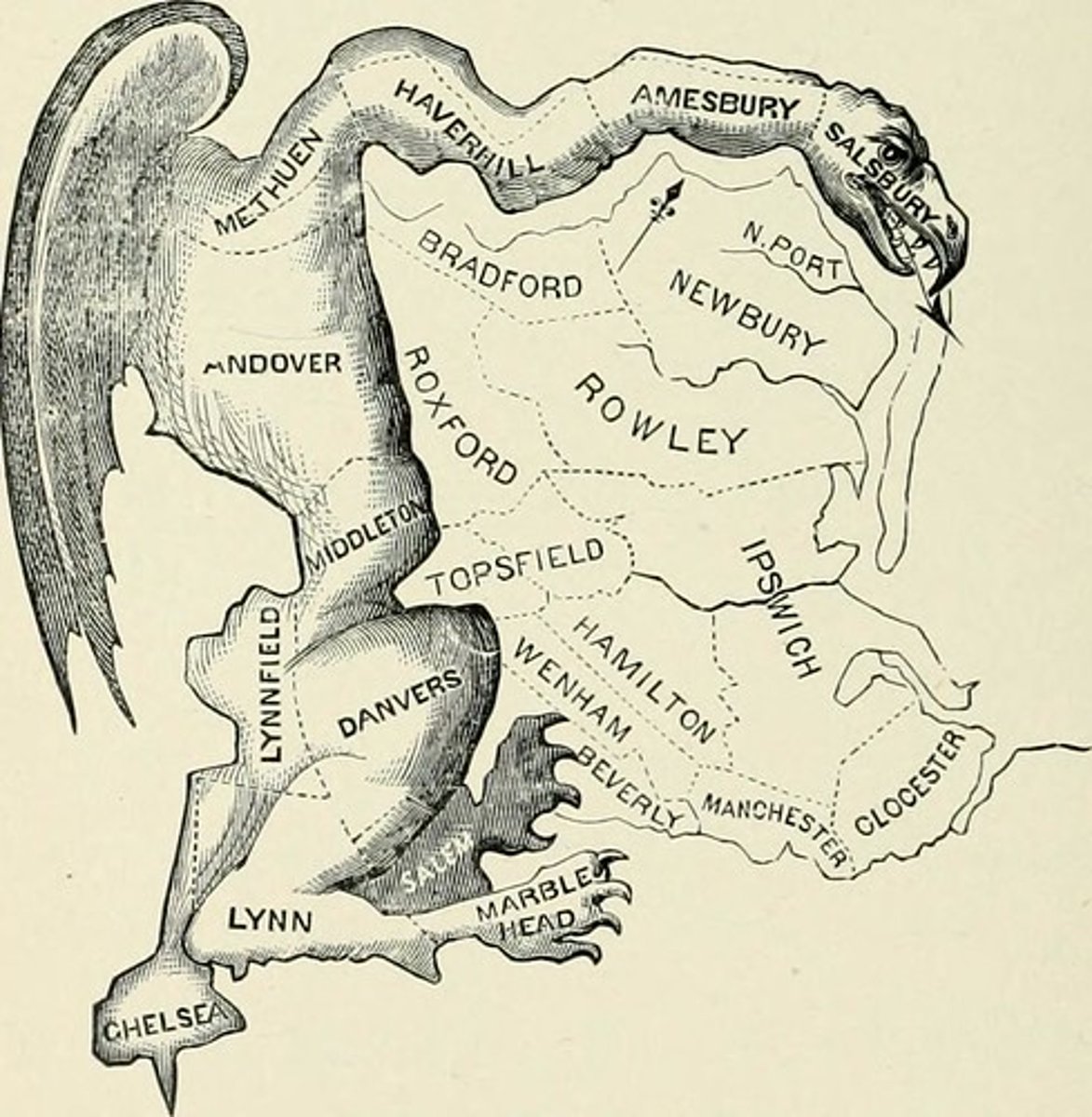
Gerrymandering
The partisan drawing of boundaries for political districts by the state legislature party of group in power to extend or cement their advantage.
Types of gerrymandering
Cracking, Packing, Stacking, Hijacking
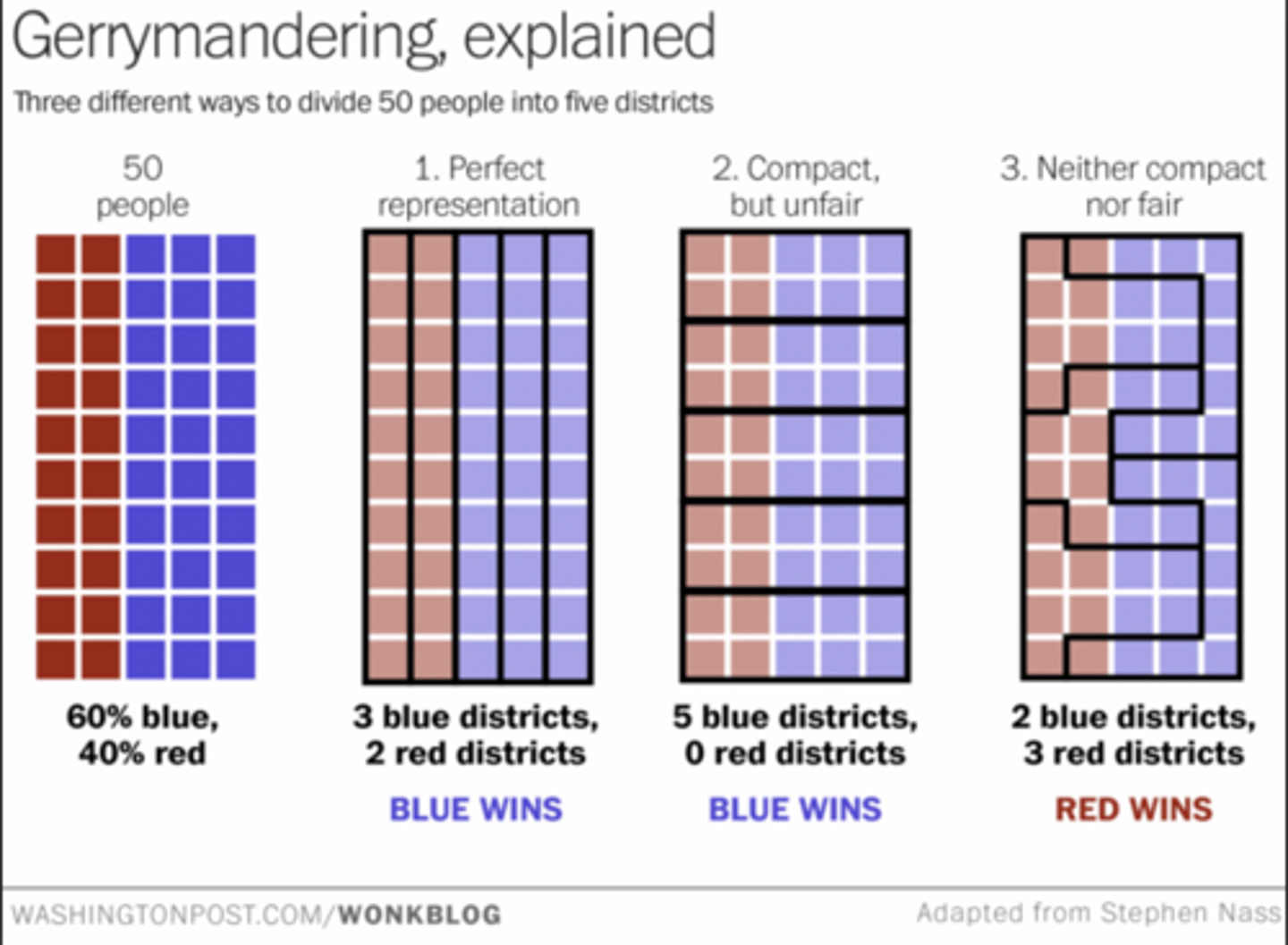
Gerrymandering (cracking)
Dispersing like-minded voters into multiple districts in order to minimize their impact and to prevent them from gaining a majority.
Gerrymandering (packing)
Clustering like-minded voters into a single district, thereby allowing the other party to win the other districts.
Gerrymandering (stacking)
Diluting a minority populated district with majority populations.
Gerrymandering (hijacking)
Redrawing 2 districts in order to force 2 elected representatives of the same party to run against one another.
Results of gerrymandering
Impacts election results at various scales (national, state, local)
Impacts of gerrymandering
Voters in opposition parties that reside in gerrymandered districts often feel disenfranchised- as they feel the districts were drawn in a way so their party cannot win.
Public good
A commodity that is provided without profit to all members of a society

Key characteristics of a public good
Nonexcludable and nonrivalrous
Nonexcludable
Costly or impossible for one user to exclude others from using a good.
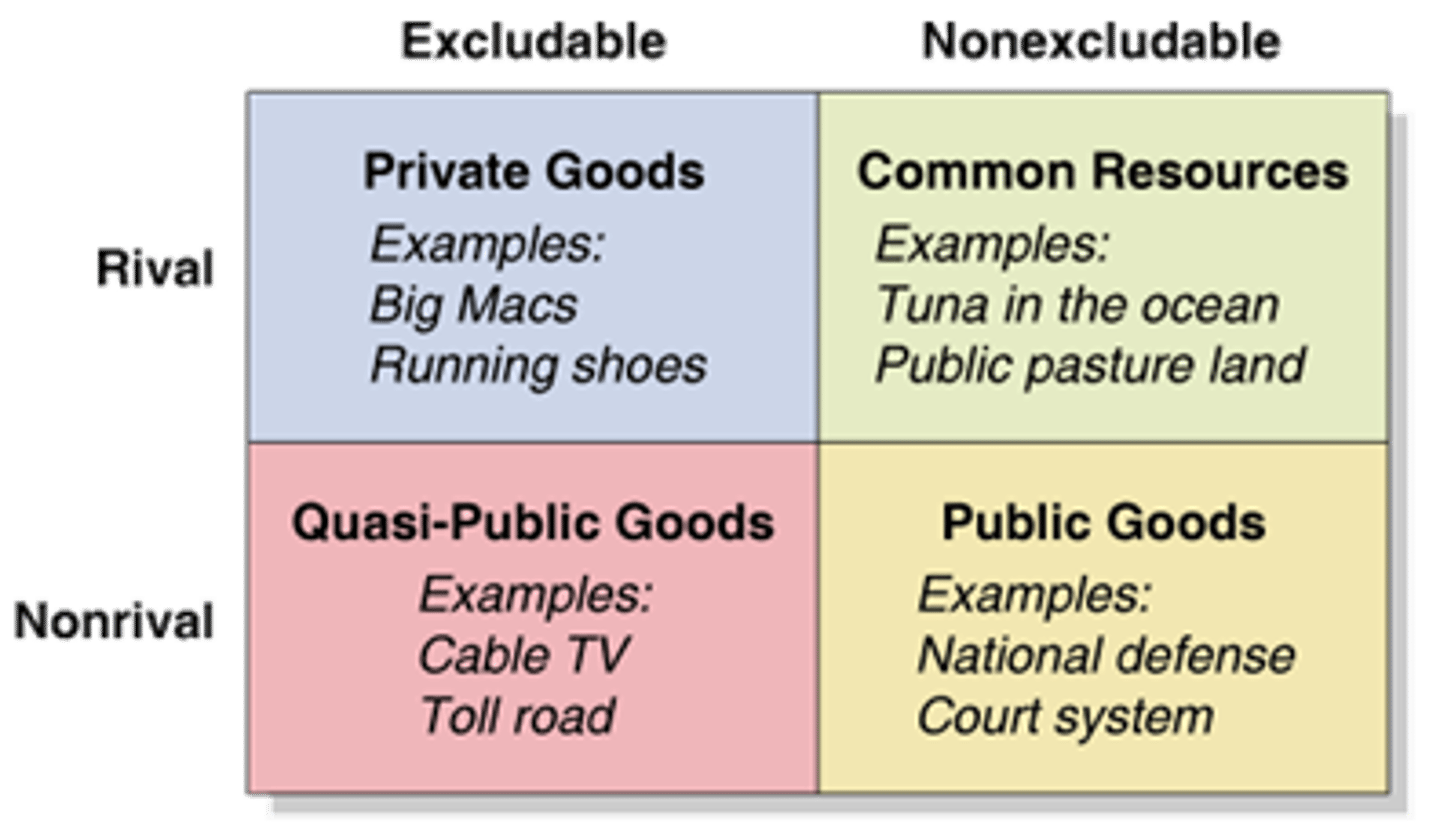
Nonrivalrous
When one person uses a good, it does not prevent others from using it.

Monarchy
The oldest form of government still found in the world today. Headed by a royal family. Usually a hereditary position. Monarchs usually claim their legitimacy as divine. Typically the state will be known as a kingdom.

Absolute monarchy
The monarch holds supreme autocratic authority, principally not being restricted by written laws, legislature, or customs.

Limited monarchy
The monarch shares power with an elected government (usually). The monarch may have limited to no actual authority in governing the state.

Dictatorship
Dictators seize their power usually through force. In a dictatorship, a dictator usually holds absolute power and authority over the state.

Democracy
Citizens hold the power wither directly or through elected representatives.

Direct democracies
Eligible citizens vote directly on initiatives facing the town or state as a whole. There is no intermediary between citizens and public policy. While no pure direct democracies exist today elements of direct democracies can be found in some countries in the form of referendums, recalls, or constitutional amendments.

Presidential democracies
Voters in presidential democracies choose a president to lead the government as the head of the executive branch. They also elect lawmakers to represent them in the national legislature. Both the president and its legislators serve a fixed term in office.

Parliamentary Democracies
Voters elect lawmakers to represent them in the nation's parliament. The party that wins a legislative majority forms a new administration. The legislative majority then selects a member to serve as the nation's prime minister, or chief executive. There is no clear-cut separation between executive and legislative branches of government.
Single-party
In a single-party, sometimes through communism, only the ruling party governs. Meaning only one political party exists and forming other political parties is forbidden. Power is exercised by the leading members of the party, who forms the political elite. (or a small group of people-oligarchy-within a larger group who have more power, more wealth, or talent than others)

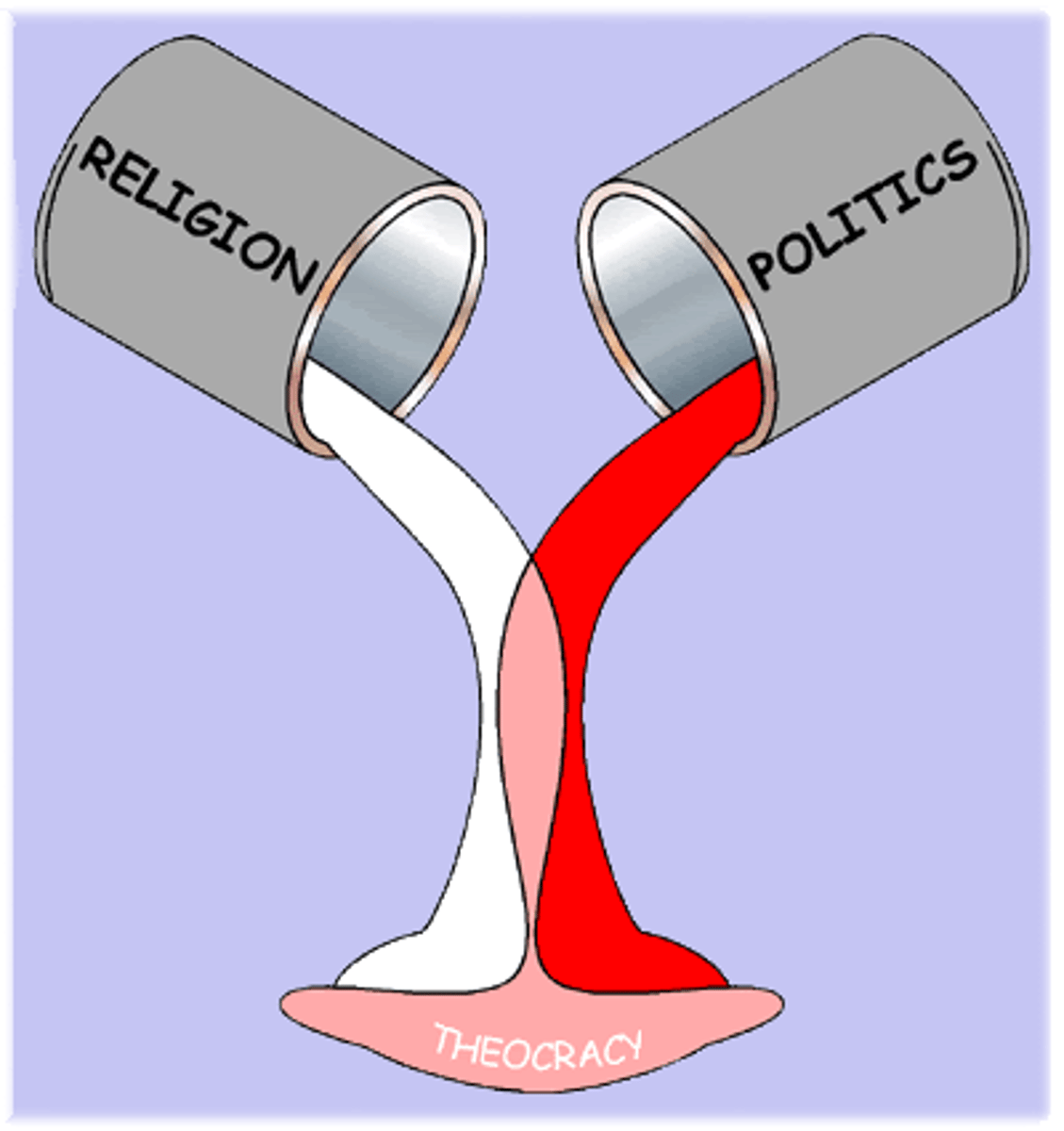
Theocracy
A form of government in which God, or a deity, is recognized as the supreme ruling authority, giving guidance to human intermediaries that manage the day to day affairs of the government. The people are governed through rule of law laid out by a religion or a religious code of laws.
Unitary state
A system of government where the central government is the supreme power. There are no states or subdivisions of land that the central government recognizes as political entities. All authority is made by the central government for all people, most countries in the world follow the Unitary system. EX: China, France, or Nation-states
Federal systems
They divide power between a central government and various constituent governments (states in the U.S.). Such systems require written constitutions to describe the respective powers of the two sets of sovereign governments, each with power to act directly on its citizens. EX: U.S, Australia, or multinational states.
Confederal state
The government is divided between national and state authorities, in which primary power rests within the individual states or semi-autonomous areas. In such systems, the national government must go through the states in acting directly on the people. The national government is typically only used to negotiate treaties, organize defense, and print currency.
Autonomy
Independence, freedom, self-governing.

Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities
Factors that lead to devolution
Physical geography, ethnic separatism, ethnic cleansing, terrorism, economic or social problem, irredentism.
Physical geography
Regions that are separated from the central state due to physical features such as mountains, deserts, or bodies of water. Fragmented states like Indonesia or the Philippines. Distance Decay: As distance increases between two locations, the quantity and quality of interactions decline.
Ethnic separatism
The advocacy or practice of separation of a certain group of people from a larger body of the basis of ethnicity, religion, or gender.
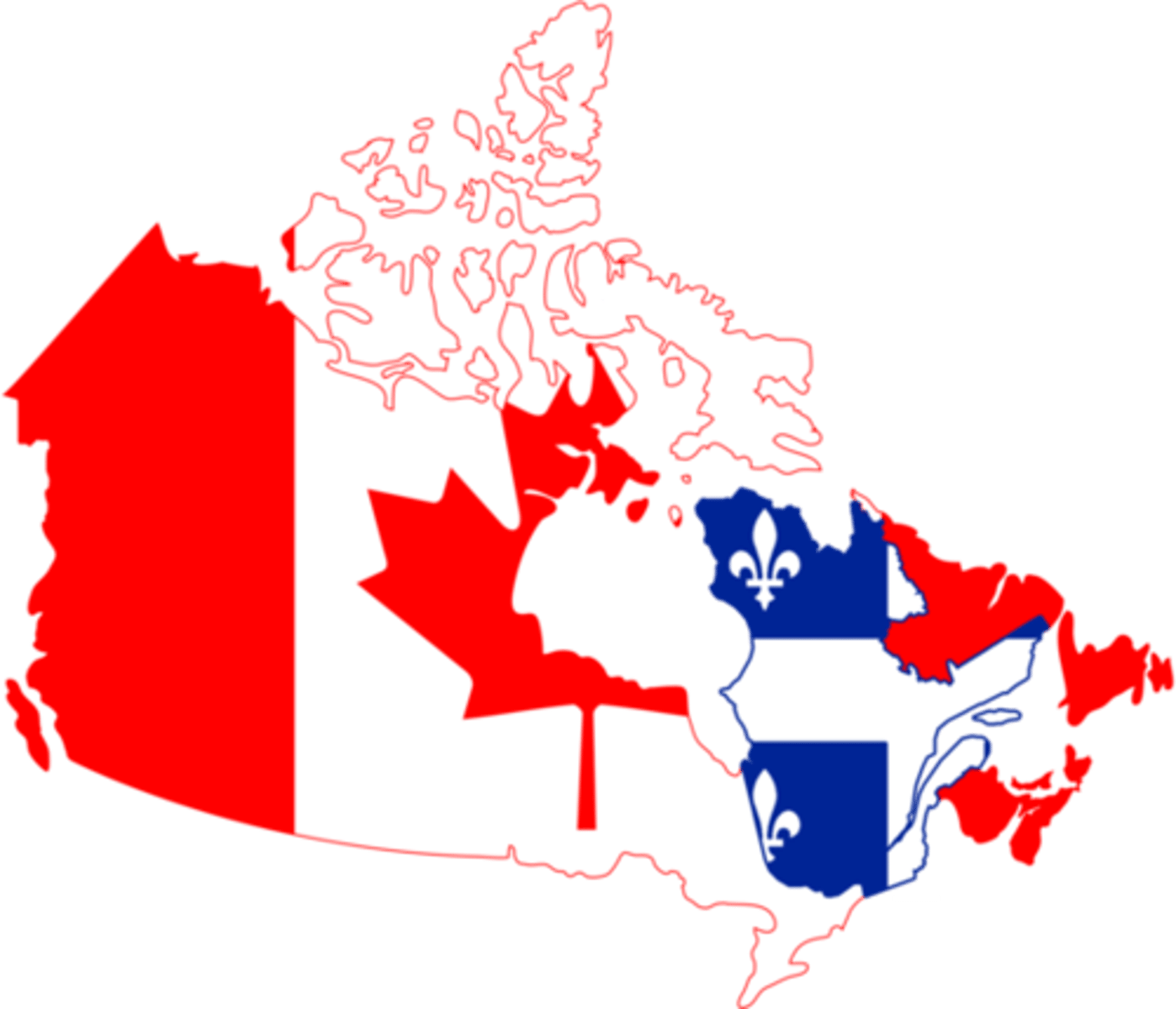
Ethnic cleansing
A process in which a more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region. Can be done through forced migration or genocide.

Terrorism
Organized violence aimed at government and civilian targets intended to create fear in order to accomplish political aims. Most commonly utilized by non-government groups with no army, (ethnic separatists) in order to achieve recognition or power.

Economic problems
Uneven development, different levels of economic activity/productivity, and conflict over the allocation of funding from the central level of government. Ex: the Catalans of Spain.

Social problems
Social problems such as discrimination against a minority group can cause rifts within a state's border and fuel devolutionary forces as well. Ex: The Welsh people of Wales.
Irredentism
A majority ethnic group wants to claim territory from a neighboring state due to a shared culture with the people residing across the border. Reunification of multistate nations
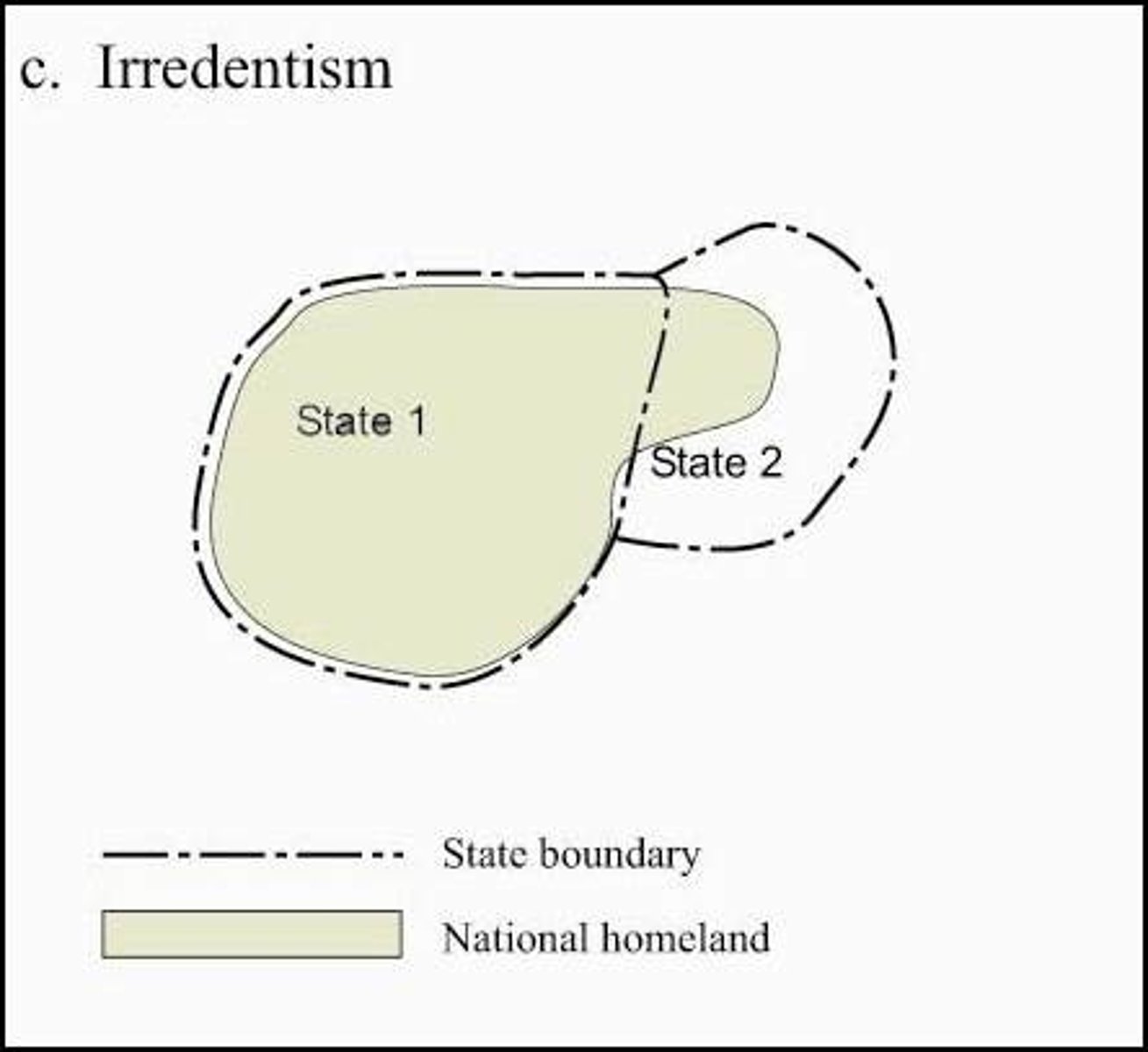
Self-determination
The right of all people to govern themselves. Usually a nation ethnicity, or former colony wants to govern themselves and establish sovereignty over their own state. Oftentimes may result in independence movements or devolution.

Devolution
Due to centrifugal forces, power is shifted from the central government or administration to regional authorities which are usually reflective of nations.

Types of political entities
State, Nation, Nation-state, Stateless Nation, Multistate Nation, Multi-nation State, Autonomous Regions.

States
Must concede some power to autonomous regions or subnational political units to avoid contact
Time-space compression
The relative distance between places has been shrinking due to modern advancements in transportation and communication technology. Increases devolutionary pressures and challenges state sovereignty, leads to social movements and democratization.
Supranationalism
An alliance of three or more states that work together in pursuit of common goals. Economic, social/cultural, political, military or environmental. Typically regional in scale, but there are some globalized -> United Nations

Benefits of supranational organizations
Decrease conflict and promote cooperation between member states. Environmental sustainability- The arctic council works together to research climate change, wildlife conservation, and ocean health. Economies of scale (more goods and services can be produced for less money on average)-Increased trade and bargaining power in order to make more money for the member nations. Collective Defense- For military organizations, an attack against one Ally is considered as an attack all Allies.
Negatives of supranational organizations
Can challenge state sovereignty by limiting the economic or political actions of member states. (the degree in which sovereignty is challenges varies based on organization) EX: European Union (High degree), Membership costs, equal participation.
Centripetal Forces
Characteristics that unify a country and provide stability.

Centrifugal Forces
Characteristics that divide a country and create instability, conflict and violence.
Results of Centripetal forces
Ethnonationalism, Equitable infrastructure development, cultural cohesion/unity/harmony
Ethnonationalism
When the people of a country identify as having one common ethnicity, language, and religion which creates a sense of pride and ties them to the territory. -Unit against one enemy.
Results of centrifugal forces
Failed states (balkanization in Yugoslavia), uneven development, stateless nations & ethnic nationalist or separist movements. Ultimately, they can lead to the balkanization, devolution, or succession of one region away from the greater state.