Joshua Hall A&P Ch. 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:28 PM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
cytosol
What is the cytoplasm made of?
2
New cards
integral
Proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane.
AKA: transmembrane
AKA: transmembrane
3
New cards
peripheral
Proteins that are anchored to either the inside or outside of the membrane.
4
New cards
receptor
A membrane protein that combines with and “reads” messengers from other cells like hormones.
5
New cards
channel
A membrane protein that is constantly open and allows solutes to pass into and out of the cell.
6
New cards
gated channel
A membrane protein that opens and closes. It only allows solutes through at certain times.
7
New cards
pseudopods
Arm structures on white blood cells that grab bacteria and bring them toward the cell to be destroyed.
8
New cards
Phagocytosis
The process by which a cell takes something into itself.
Ex: White blood cells engulfing bacteria.
Ex: White blood cells engulfing bacteria.
9
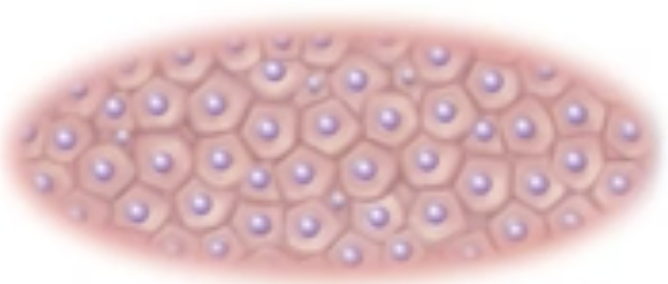
New cards
polygonal
What is this cell shape?
10
New cards
stellate
What is this cell shape?

11
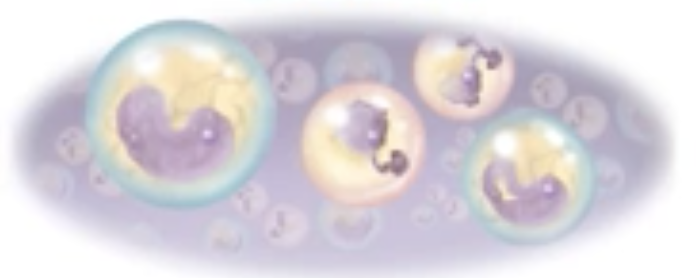
New cards
spheroidal
What is this cell shape?
12
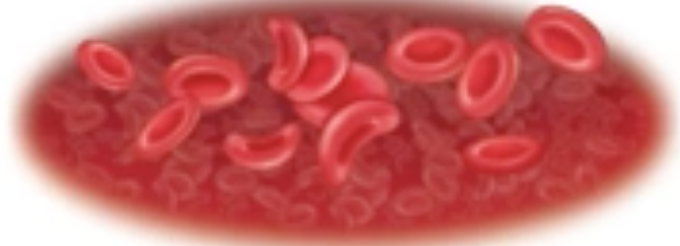
New cards
discoidal
What is this cell shape?
13
New cards
fusiform
What is this cell shape?

14
New cards
fibrous
What is this cell shape?

15
New cards
diffusion, osmosis, carrier mediated transport
What are the three types of passive transport?
16
New cards
primary active transport, vesicular transport, carrier mediated transport
What are the three types of active transport?
17
New cards
diffusion
Passive transport where particles move from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
18
New cards
osmosis
Diffusion of water down its concentration gradient.
19
New cards
aquaporins
Membrane protein that increases the speed of osmosis. (Diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.)
20
New cards
tonicity
The ability of a solution (like blood) to control the amount of water that goes into or out of the cell.
Ex: hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic
Ex: hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic
21
New cards
isotonic
Tonicity level when there is just the right amount of particles (solutes) within a cell and no water moves in or out.
22
New cards
hypertonic
Tonicity level when there are too many particles (solutes) with a cell and water is forced out of the cell.
23
New cards
hypotonic
Tonicity level when there are too few particles (solutes) within the cell and too much water moves into the cell.
24
New cards
carrier mediated transport
Type of active or passive transport where a membrane protein moves specific particle(s) across the membrane. Could also be considered facilitated diffusion.
25
New cards
uniports, symports, antiports
What are the three kinds of carriers that can perform carrier mediated transport?
26
New cards
uniport
Carrier mediated transporter that moves one type of molecule in one direction.
27
New cards
symport
Carrier mediated transporter that moves multiple types of molecules in one direction.
28
New cards
antiport
Carrier mediated transporter that moves multiple molecules in different directions.
29
New cards
primary active transport
Type of transport that uses ATP to move molecules up or against their concentration gradient. Ex: potassium pump
30
New cards
vesicular transport
Type of active transport that is used to move large particles or many particles in or out of the cell using vesicles.
31
New cards
True
Endocytosis and phagocytosis are the same thing. True or False?
32
New cards
Exocytosis
When a cell uses vesicles to move molecules out of the cell.