Sensory: Sensation Marshall 210
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
Sensation
the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
2
New cards
Transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies, such as sights, sounds, and smells, into neural impulses our brains can interpret.
3
New cards
Perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
4
New cards
sensory adaptation
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
5
New cards
psychophysics
the study of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them
6
New cards
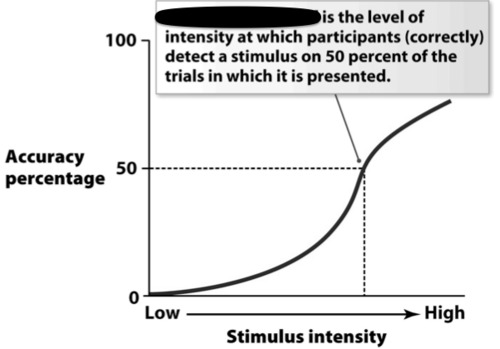
absolute threshold
the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50 percent of the time
7
New cards
supraliminal stimuli
stimuli that are strong enough to be consistently perceived
8
New cards
subliminal stimuli
stimuli that are below the level of conscious awareness
9
New cards
internal noise
the spontaneous random firing of nerve cells that occurs because the nervous system is always active
10
New cards
Sensitivity
Ability to recognize and appreciate the personal characteristics of others
Intensity of the singal
Capacity of sensory systems
Affected by noise level
From background stimulation
From random neural activity
Intensity of the singal
Capacity of sensory systems
Affected by noise level
From background stimulation
From random neural activity
11
New cards
response bias
tendency of subjects to systematically respond to a stimulus in a particular way due to nonsensory factors
12
New cards
signal detection theory
a theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise). Assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person's experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness.
13
New cards
response criterion
the internal rule a person uses to decide whether or not to report a stimulus
14
New cards
difference threshold
the minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50 percent of the time
15
New cards
sensory systems
the parts of the nervous system that provide information about the environment
16
New cards
vestibular sense
the sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance
17
New cards
kinesthetic sense
sense of the location of body parts in relation to the ground and each other
18
New cards
physical properties of light
amplitude: height
wavelength: frequency
purity: purity of wave
wavelength: frequency
purity: purity of wave
19
New cards
properties of the visual system
brightness or light intensity: amplitude
hue: wavelength or frequency
saturation: purity of wave
hue: wavelength or frequency
saturation: purity of wave
20
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
21
New cards
physical properties of a wave

22
New cards
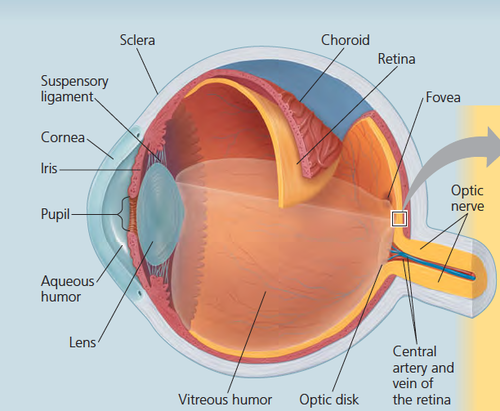
Structures of an eye
23
New cards
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
24
New cards
iris
adjustable muscle that causes pupil to dilate or constrict allows light to enter the eye
25
New cards
lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
26
New cards
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
27
New cards
Rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray; necessary for peripheral and twilight vision, when cones don't respond
28
New cards
Cones
retinal receptor cells that are concentrated near the center of the retina and that function in daylight or in well-lit conditions. The cones detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations.
29
New cards
Fovea
the central focal point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster
30
New cards
bipolar and horizontal cells
two types of cells in the intermediate layer
31
New cards
Myopia (nearsightedness)
occurs when the image is focused in front of the retina
32
New cards
hyperopia(farsightedness)
light rays focused beyond retina, corrected with convex lens
33
New cards
presbyopia
farsightedness caused by loss of elasticity of the lens of the eye, occurring typically in middle and old age.
34
New cards
astigmatism
defective curvature of the cornea or lens of the eye
35
New cards
trichromatic color theory
The theory of color vision that holds that all color perception derives from three different color receptors in the retina (red, green, and blue receptors).
36
New cards
opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, yellow-blue, white-black) enable color vision. For example, some cells are stimulated by green and inhibited by red; others are stimulated by red and inhibited by green
37
New cards
George Wald
three types of cones in the retina that are sensitive to different wavelengths
38
New cards
Frequency
number of soundwaves per time cycle
39
New cards
hertz
Unit of frequency per second
40
New cards
Amplitude
the vertical size of sound waves
41
New cards
Decibels
a measure of the physical compression of molecules that occur in an eardrum
42
New cards
pitch
frequency or wavelength
43
New cards
timbre
purity of frequency
44
New cards
auditory transduction
the process through which sound waves and sound info is passed through each part of the ear
45
New cards
middle ear bones
malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup)
46
New cards
malleus (hammer)
a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus.
47
New cards
Incus (anvil)
The middle bone which is connected to the other two, passes vibrations onto the stapes.
48
New cards
stapes (stirrup)
transmits and amplifies vibrations from the incus to the oval window
49
New cards
cochlea
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
50
New cards
basilar membrane
A structure that runs the length of the cochlea in the inner ear and holds the auditory receptors, called hair cells.
51
New cards
Organ of Corti
Center part of the cochlea, containing hair cells, canals, and membranes
52
New cards
Intensity (loudness)
Amount of energy in a wave; determined by the amplitude, relates to perceived loudness
53
New cards
conduction deafness
An inability to hear resulting from damage to structures of the middle or inner ear.
can be helped with hearing aids
can be helped with hearing aids
54
New cards
nerve deafness
Hearing loss created by damage to the hair cells or the auditory nerve fibers in the inner ear.
cannot be helped with hearing aids: bc of disease or loud sounds
cannot be helped with hearing aids: bc of disease or loud sounds