Psychophysics - Study Guide
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
How do we respond to stimuli?
detecting
perceiving magnitude
describing
recognizing
searching
Absolute threshold
smallest amount of stimulus you can detect
Difference threshold
smallest difference intensity between two stimuli
How do absolute and difference threshold differ?
the number of stimuli
absolute: 1 stimuli
difference: 2 stimuli
Classical methods of psychophysics
method of limits
adjustment
constant stimuli
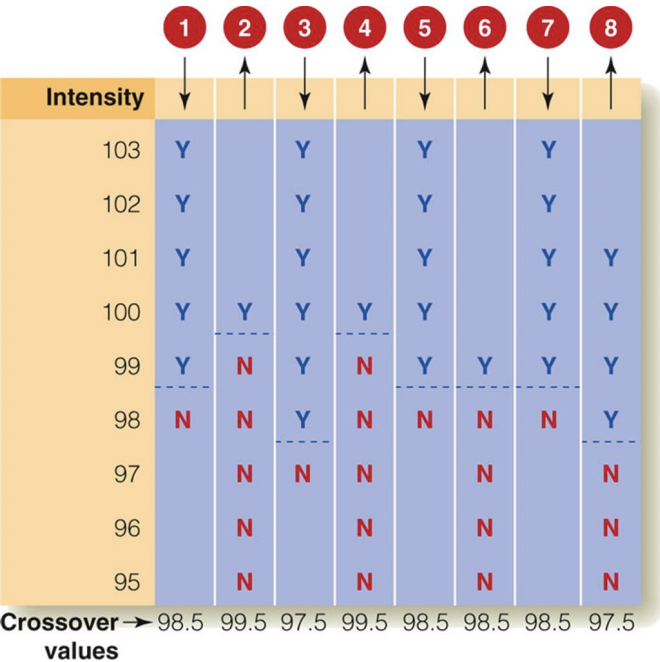
Method of limits
gradually increasing or decreasing the intensity of a stimulus over time until they can be detected
finding the point at which a stimulus becomes perceptible
goes in numerical order (increasing: 100, 101, 102… decreasing: 90, 89, 88…)
Method of adjustment
the observer/experimenter adjusts the stimulus intensity in a continuous manner until the observer can just barely detect the stimulus
the barely detectable intensity is taken as the absolute threshold
least valid but fastest
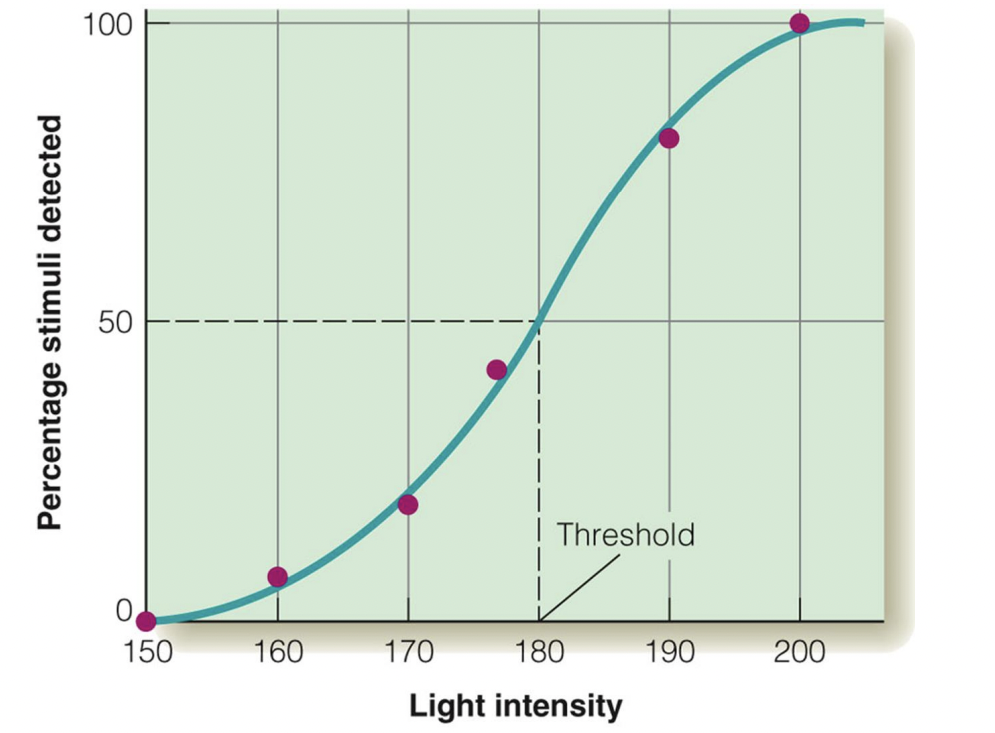
Method of constant stimuli
different intensities in random order; where it is detected half the time is threshold
slowest but most valid
What is the fundamental flaw with all of the classical methods?
they don’t look at false alarms/criterion
SDT: What/where are N distributions?
noise distribution, no signal (nothing present)
left side of SDT
SDT: What/where are S+N distributions?
signal and noise distribution, signal is present
right side of SDT
Criterion
level of evidence required to decide if signal is present (middle line)
Would someone want to be more conservative or liberal?
more liberal; more worried about misses - results in more false alarms than misses
Hits
saying something is there, and there actually is something there
Misses
saying something is not there, when something actually is there
Correct rejections
saying something is not there, and there is actually nothing there
False alarms
saying something is there, when something is actually not there
Hits + ______ = 100%
misses
False alarms + _____ = 100%
correct rejections
Hits and misses are under which distribution?
S+N Distributions
Correct rejections and false alarms are under which distribution?
N distributions
What happens to each 4 outcomes if the criterion shifts more liberal?
hits will go up
misses will go down
false alarms go up
correct rejections go down
What happens to the 4 outcomes if the criterion shifts more conservative?
hits will go down
misses will go up
false alarms go down
correct rejections go up
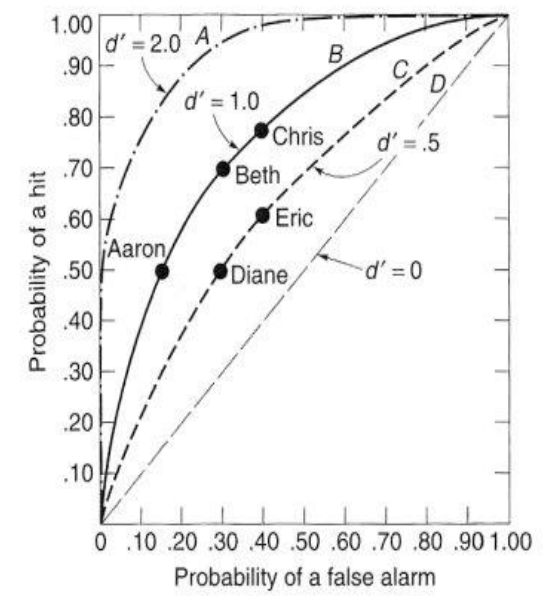
Purpose of ROC Curves
to determine and compare sensitivity levels
How is sensitivity (d’) determined?
by the distance between the peaks of the N and S+N distributions
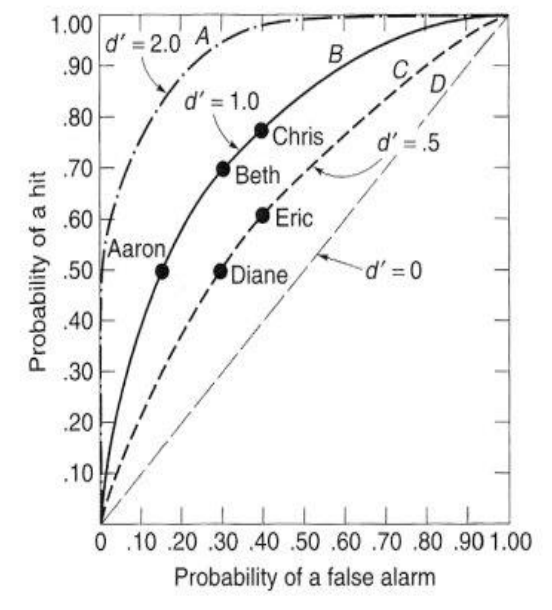
Who is the most sensitive on the ROC curve?
most bowed line
in picture: A
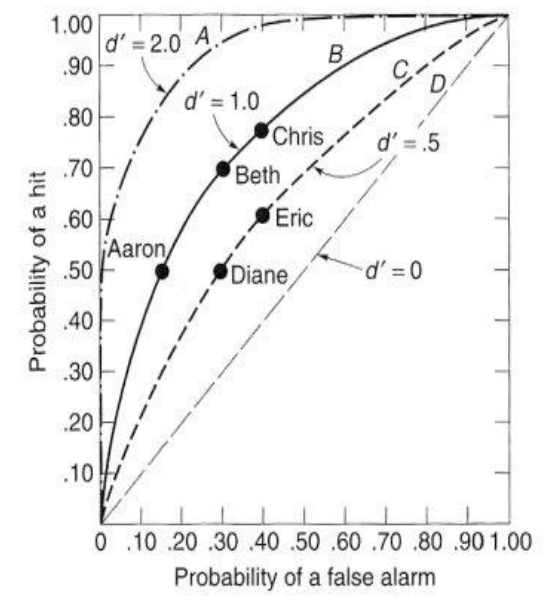
Who is more liberal/conservative if sensitivity is the same?
liberal: higher on the line
conservative: lower on the line
in picture: line B; Aaron is most conservative, Chris is most liberal
What does it mean if there are multiple points/names on one line in an ROC curve?
they have the same sensitivity but different criterion
What happens to the difference threshold as the magnitude of the standard stimulus increases?
the size of the difference threshold increases
What is Webers’s Law?
the just noticeable difference between two stimuli is a constant proportion of the original stimulus intensity
What is Weber’s fraction?
K= DT/S
K = constant
DT = difference threshold
S = standard stimulus
Magnitude estimation
the observer assigns numbers to stimuli that are proportional to perceived magnitude
Response compression
as intensity is increased, the perceptual magnitude increases, but not as rapidly as the actual intensity
ex: brightness
Response expansion
as intensity is increased, perceptual magnitude increases more than actual intensity
ex: electric shock
What is the difference between response compression and expansion?
compression = underestimation
expansion = overestimation
Search
some perceptual research uses methods that require the observer to respond as quickly as possible
ex: visual search; finding “where’s waldo”
Reaction time
the time between presentation of the stimulus and the observer’s response to the stimulus
measure from time it took to present stimulus until when it was noticed