CHAPTER 6
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Cutaneous Membrane
skin (epidermis + dermis)
Accessory Structures
hair follicles, nails & exocrine glads
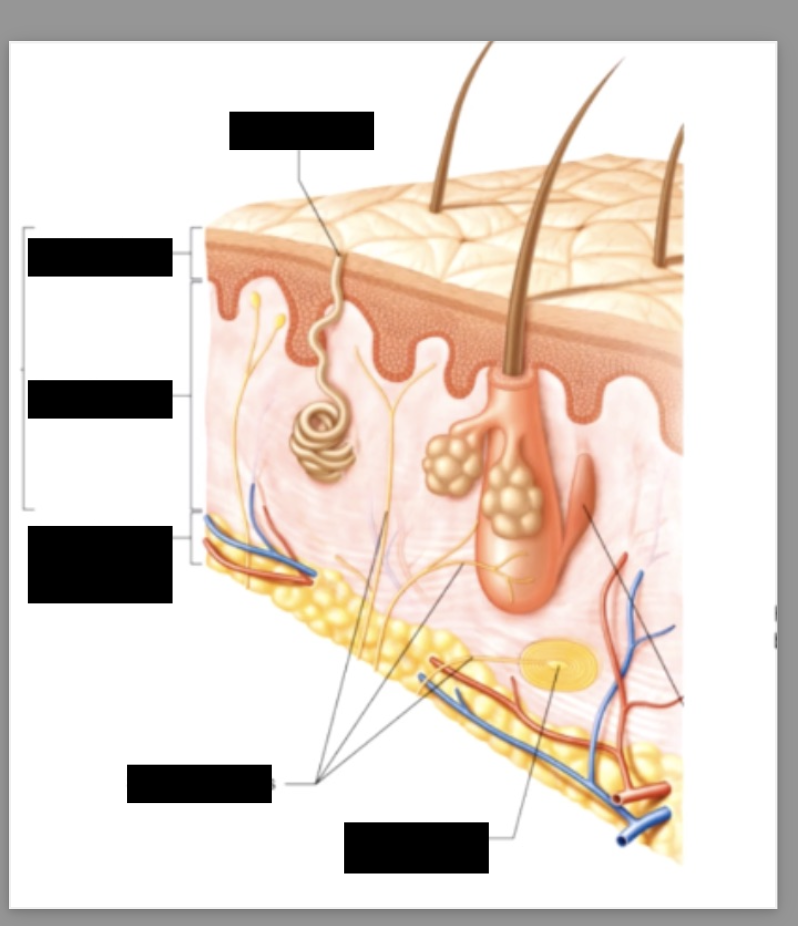
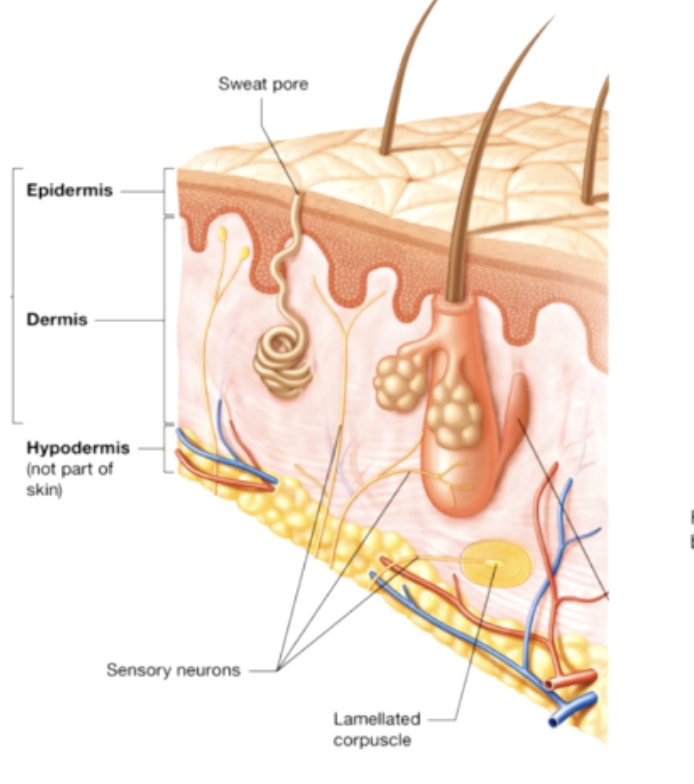
epidermis
superficial stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis
underlying areolar tissue & reticular layer of dense irregular connective tissue
integument
epidermis,demis and accessory structures
layers of the dermis
Papillary layer + Reticular Layer
hypodermis
subcutaneous layer composed of loose connective tissue, interwoven with dermis but not apart of the integumentary layer
7 functions of the epidermis
protection
Excretion
regualtion of body temp
synthesis of viatamin D
Storage of lipids
Sensation
Production of melanin
Production of karatin
epidermis
consists of stratified squamous epithelium which is avascular because superficial cells are inert/dead
main cell type of the epidermis:
keratinocytes
epidermis cell junctions
hemidesmosomes to basal lamina
keratinocytes lifespan
newly formed cells are pushed further and further toward the surface until they are eventually shed
dermal papillae
the strength of attachment is proportional to the surface area
thin epidermis
4 layers of keratinocytes that covour most the body
thick epidermis
5 layers of keratinocytes that cover palms and soles
5 layers of the epidermis
stratum corneum,stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
stratum germinativum (stratum basale)
anchored to basal lamina by hemidesmosomes
forms epidermal which interlock with dermal papillae
simple cuboidal/columnar epithelium (keratinocytes)
provides strong attachment
why do people get calluses ?
Calluses are caused by pressure and wear and tear on your skin’s surface which causes rapid mitosis of skin cells leading to the thickening of the epidermis (protective mechanism)
why do we get blisters
friction or damage to the epidermis from extreme temperatures (burns, frostbite) a blister forms to protect the underlying tissue from further harm and infection.
epidermal ridges
ridges ensure good grip of fingers and toes - creates fingerprints ridges and patterns
finger print facts
the uniqueness of everyones fingerprint is developed due to genetics in utero
everyone has different fingerprints, even identical twins
toe prints also have enough uniquness to identify someone
fingers get pruny when you’re in the water to enhance your grip strength
cell types in stratum germinativum
basal cells - germinative cells (stem cells)
melanocytes - pigment producing cells
markel cells
sensitive to touch, activate nerve endings by releasing chemicals
stratum spinosum (spiney layer)
8-10 layers joined by desmosomes
includes langerhans (dendritic) cells (phagocytes)
langerhans
play a defensive role in the stratum spinosum by defending against microorganisms and superficial skin cancer
stratum granulosum (grainy layer)
3-5 layers of keratinocytes
cells make large amounts of protein keratin (keratinocytes) and keratohyalin
Keratohyalin
accumulates in granules, promotes dehydration and cross links between karatin fibers
as cells move up through the stratum granulosum
they get thinner and less permeable creating a tightly interlocked layer of cell, cells begin to die in this layer
at what layer are the cells considered dead?
any layers superior to the stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
the clear layer only in thick skin
cells are densely packed with keratin & devoid of organelles
stratum corneum
horn
15-30 layers of keritonized, dead cells tightly interconnected by desmosomes keratinized
Water resistant, insensible water loss (500mL/day
Insensible vs sensible water loss
Sensible - evaporation
Insensible - sweating
Pigments of epithelium
Carotene
Melanin
Produced by melanocytes in stratum germinativum
Carotene
an orange/yellow pigment (also found in orange vegetables, can be converted into vitamin A)
• Humans can’t make carotene
Melanin
a yellow/brown pigment (made from tyrosine amino acid)
Melanosomes
vesicles with melanin packaged into them
Melanosomes turn into
Keratinocytes
Melasosomes in light skinned people
melanosomes get Brocken down in strata germinative and spinosum
Melanosomes in people with dark skin
melanosomes are Brocken down in strata granulosum
• Have more melanomas and larger ones
Function of melanin
protection from effects of UV radiation, and damage to stratum germinativum
What is vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a skin condition caused by the autoimmune destruction of melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color
Other effectors of skin colour
dermal circulation and melanosomes
Dermal circulation
oxygenated hemoglobin, cold temp, low oxygen
Oxygenated hemoglobin
bright red
• Noticeable in light skinned individuals especially when exercising or flushed (capillaries are dilated)
Cold temp’s effect in dermal circulation
Skin capillaries constrict making you look paler (also if blood blow is restricted = paler)
Low oxygen
deoxygenated hemoglobin
Appears dark red &
is blue when seen through pale skin (blue = cyanosis)
Cholecalciferol
(Vitamin D3) - produced by epithelial cells in status spinosum and germinativum in response to sunlight
Required for Ca absorption in the digestive tract
Liver turns cholecalciferol to a product that the kidneys turn into calcitriol
Calciteriol
product formed after the liver converts choleciferol into the product that gets transformed into calcitriol
Ricketts
caused by a vitamin D deficiency results in the bending of abnormally weak and flexible bones under our body
Vitamin
essential organic nutrient
Dermis
papillary layer and reticular layer
Papillary layer
- areolar tissue
- thrown into folds on the surface = dermal papillae
- contains capillaries, lymphatics and sensory neurons that supply the surface of the skin
Lines of cleavage
Collagen and elastin in dermis to arranged in parallel bundles
Bundles oriented to resist forces normally applied to skin
• Establishes lines of cleavage (a line of cleavage will usually remain close and heal with little scarring)
Severed elastic fibers
• Lines of cleavage that pull apart from each other making healing longer and may cause scarring
Cutaneous plexuses
• Network of arteries and veins between dermis and hypodermis
Dermal Blood supply
Dermis is well supplied with blood vessels
Network of veins between dermis and hypodermic ; cutaneous plexuses
These feed into sub capillary plexuses tat supply capillaries extending into papillae = source of O2 & nutrients for epidermis
Nerve cells
regulate blood flow, adjust gland secretion rates and monitor sensory receptors
Sensory receptors
respond to light touch, deep pressure, vibration, chemicals, temperatures & damage
appendages of the skin
hair follicles,hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, ceruminous glands
terminal hair
hair on head
specialized TH
eyelash and brow
Vellus Hair
body hair
lunugo
baby hair
hair’s function
insulates and protects scalp
protects nostrils and ear canals
detects movement through hair plexus sensory nerve
arrector pili muscle stands up + goose bumps
armpit hair
before/ during puberty - vellus hair
after puberty/adult - terminal hair
phase 1 of hair growth
the active phase lasts 2-5 years. During the active phase, the hair grows approximately 0.33mm/day
phase 2 in hair growth
the follicle begins to undergo regression and transitions to the resting phase
phase 3 of hair growth
during the resting phase the hair loses it’s attachment to the follicle and becomes a club hair
Phase 4 of hair growth
when follicle reactivation occurs, the club hair is shed and the hair matrix begins producing a replacement hair
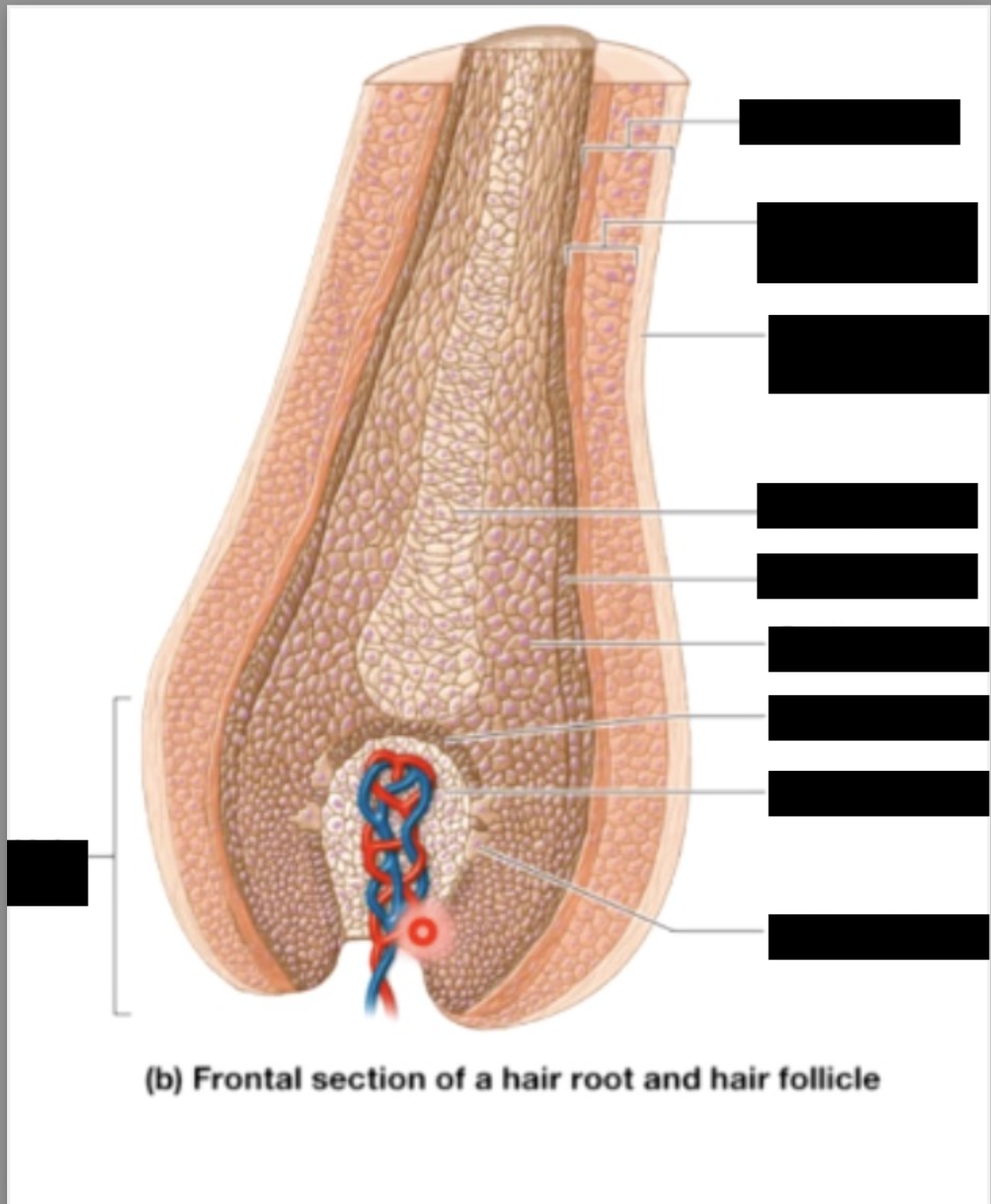
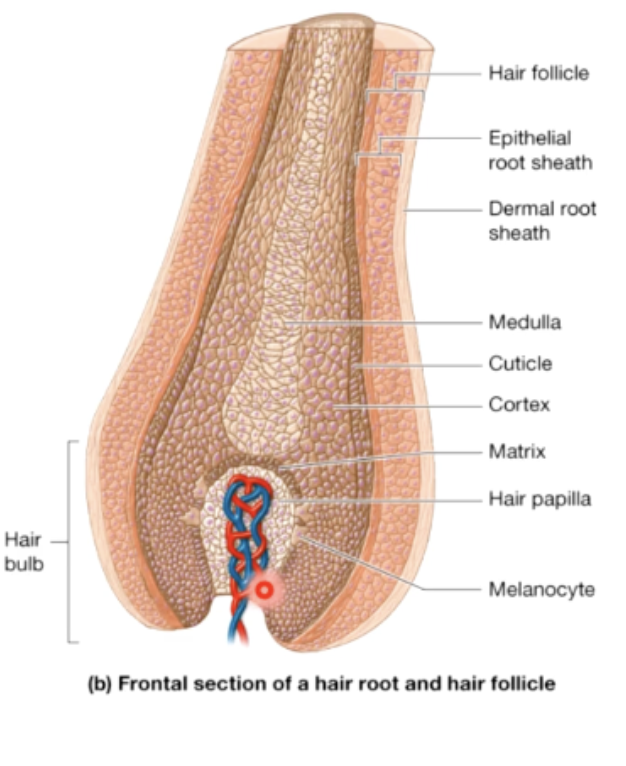
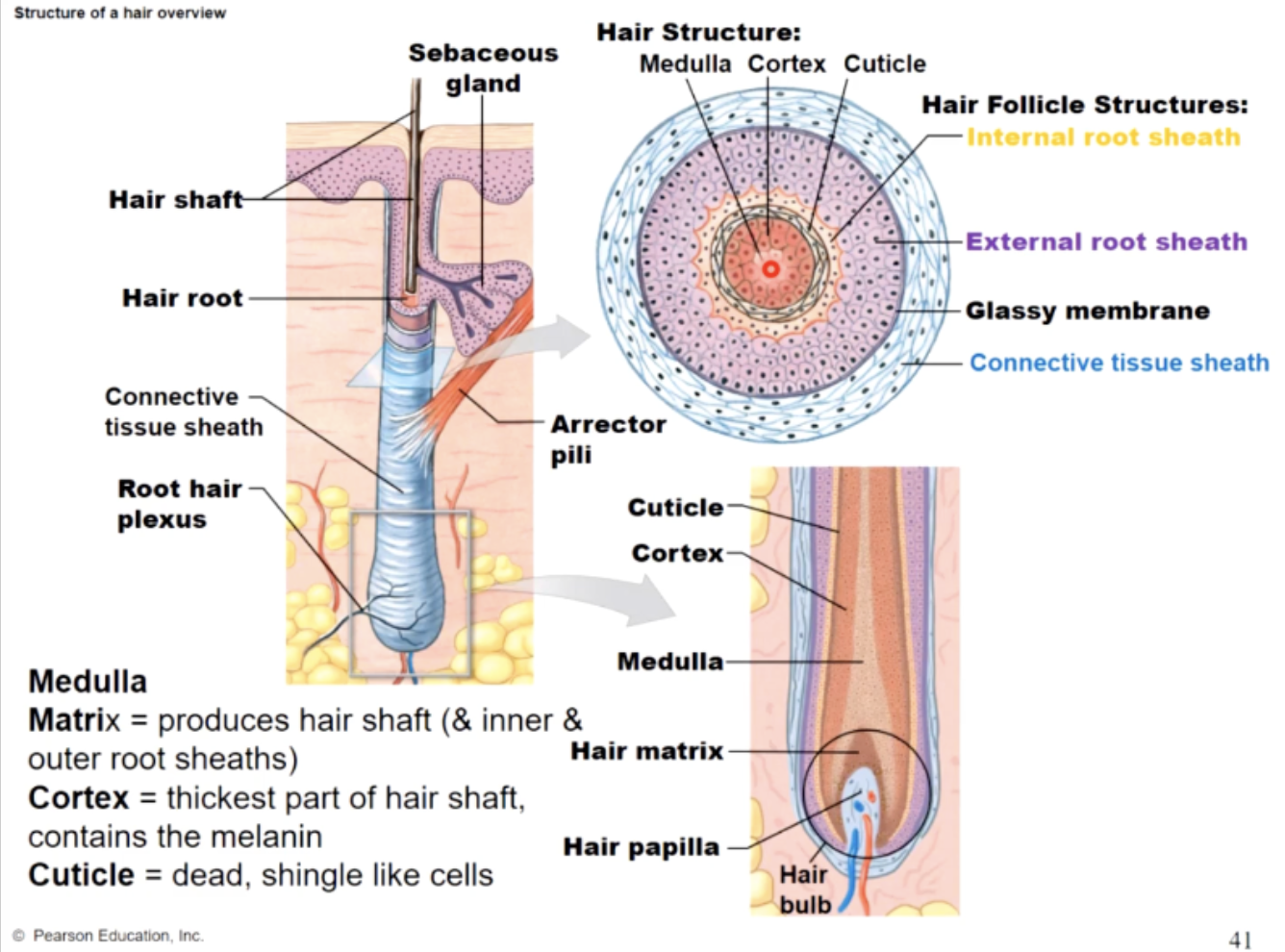
matrix
produces hair shaft (& inner root sheeths)
cortex
thickest part of the hair shaft, contains the melanin
cuticle
dead, single like cells
sebaceous glands
secrete oil through holocrine secretion
two types of holocrine secretion
simple branched alveolar glands - share duct with hair follicles & squeezed by arrector pili muscle
sebaceous Follicles - not associated with hair follicles
secretion of sebaceous glands
sebum (lipids + electrolytes + proteins + cholesterol)
functions of sebum
inhibits bacterial growth because of its acidity
lubricates & protects keratinized cells (hair & skin)
newborns vernix caseosa
acne (what is it)
a failure to discharge collected sebum in the form of white/black heads which become inflamed then cause acne


sweat glands
sudoriferous glands
merocrine
sweat glands (eccrine sweat glands)
structure - coiled tubular duct
uses exocytosis
sweat secretion is controlled by
the brain’s thermoregulatory center (hypothalamus) & emotional center (limbic center)
sweats functions
cooling surface of skin to reduce body temp
excrete water + electrolytes
flushes chemicals
contains dermicidin (antibiotic protein) to discharge microbes
aprocrine
sweat glands includes ceruminous glands of ear & mammary milk - producing glands
armpit ,pubic region,around nipples
aprocrine secretions
coiled tubular structures tat open into hair folicles
sticky, cloudy, oderous, possible sex scent (influenced by horomones)
used as a nutrient for bacteria which intensifies odour
myoepithithelial
cells that are contractile and squeeze the aprocrine gland
apocrine secretion type
merocrine secretions
ceruminous glands
modified apocrine sweat gland in the inner ear
secretes cerumen (ear wax)
helps to trap foreign particles protecting the ear drum
basal carcinoma
(most common)
stratum germinative/basale = 2/3 on areas chronically exposed to sun
cancer of keratinocytes in stratum basale, generally forms with cratered center
squamous cell carinoma
stratum spinosum sun exposed areas
cancer of keratinocytes in stratum spinosum, forms plaques that bleed or ulcerate
melanoma
least common/ most dangerous
can occur anywhere, but sun expossure increases odds
characteristics :ABCD rule
ABCD Rule for identifying cancer
Asymmetry - irregular shape
Border - irregular
Colour - mottled
Diameter - more than 5mm
burns
tissue damage caused by :intense heat, electricity radiation (including sunburn) some chemicals
first degree burn
affects only the surface of epidermis; most sunburns, usually limited to redness with minor pain
second degree burns
affects epidermis and upper portions of dermis
bloistering and swelling and pain
heals in 1-2 weeks if no infection
third degree burns
affect epidermis,dermis and sometimes hypodermis
major fluid loss (+electrolytes and proteins)
how to treat a third degree burn
within 24 hours
replace lost fluids and electrolytes
provide massive amounts of nutrients
protect to try to prevent infection
skin regeneration after injury
Inflammatory Phase -
Migratory Phase -
Proliferation Phase
Scarring Phase