Princeton Review AP Calculus BC, Chapter 9: Differential Equations
Introduction & Slope Fields
In related rates we saw how we can model the change in one thing related to another with derivatives, and differential equations are similar!
- Oftentimes, variables are not constant, so we have to represent their change using a derivative (Ex. the change in y is dy/dx)
- A differential equation models the change in one variable with respect to another
Slope fields show us what the slopes look like at points on a graph
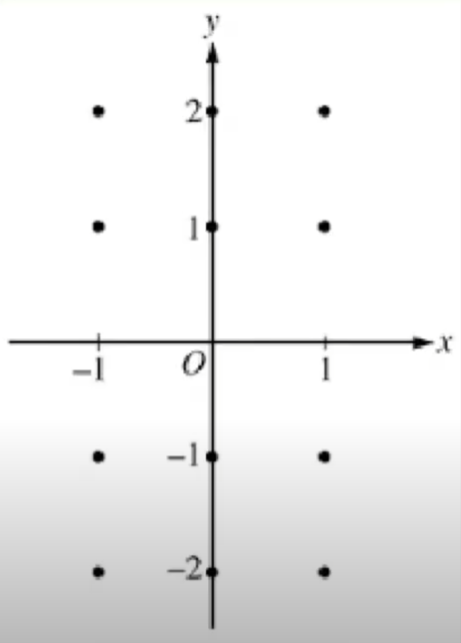
This is for the equation dy/dx = x
- Remember that this is a derivative so it will show us the slope at these points!
- All you have to do to construct a slope field is plug in your x/y (or both) values into your differential equation and draw that as your slope
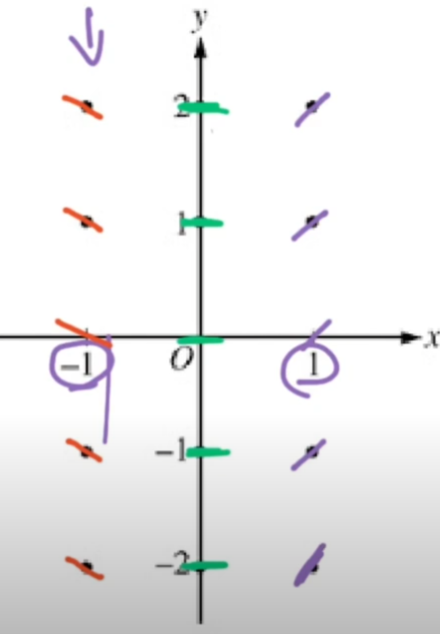
- Ex. The slope at x = -1 would be -1 (because dy/dx = x)
The AP exam might also require you to sketch a solution curve given a slope field!
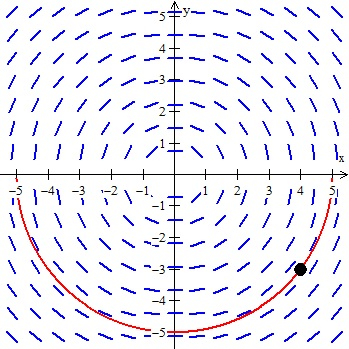
All you have to do is “flow” with the slopes
- Make sure you don’t cross abruptly or draw a line that doesn’t follow the slope
- Because this is by hand, it doesn’t have to be exact, just try and go with the tangent lines!
Differential Equations
- If you’re given a differential equation where the derivative of a function is equal to some other function, you have to solve for the original! You can do this by taking the integral (antiderivative) of both sides!
- A good memory trick is that differential equation problems will be SIPPY problems
- S: separate (dy and dx on separate sides)
- I: integrate (remove the derivative)
- P: Plus C (add your c value to your integral)
- P: Plug in your initial condition
- Y: Y equals (solve to find what y is)
- Example: If dy/dx = 4x/y and y(0) = 5 we need to solve for y
- Start by separating → ydy = 4xdx
- Then integrate → ∫ydy = ∫4xdx → y^2/2 = 2x^2 + C
- (Make sure you add C!)
- Plug in → (5)^2/2 = 2(0)^2 + C
- C = 25/2
- Now set y equals → y = 2x^2 + 25/2