Action Potential
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
An action potential is how ______________________
messages travel down the axon of neurons
Action potential is a ___________ charge created by the ___________________
positive; ratio of Na+ to K+ ions in the cell
Step 1: ___________
Resting State
Resting State Picture
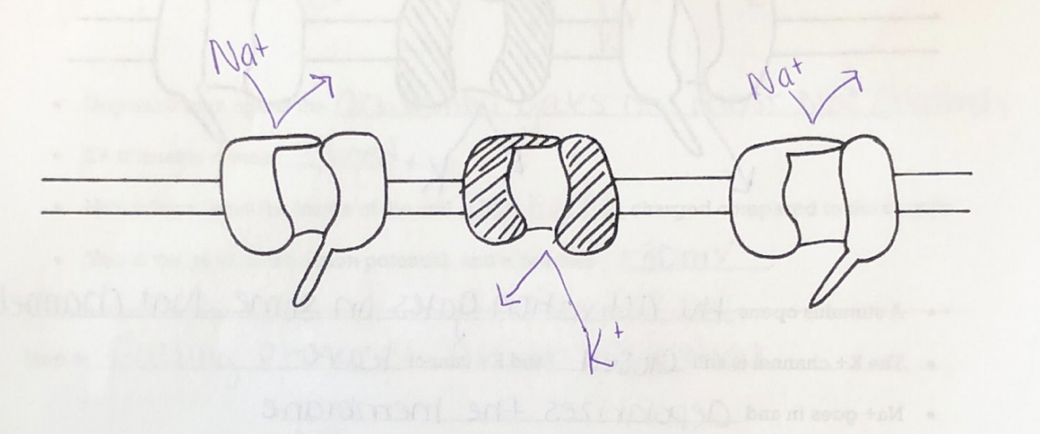
Resting State: The activation gates on the Na+ and K+ channels are _______
closed
Resting State: The charge of the cell membrane is ____________. This is called the Resting State.
Negative (-70 mv)
Resting State: Na+ is on the _________ of the cell
outside
Resting State: K+ is on the _______ of the cell.
inside
Step 2: ________
Depolarization
Depolarization Picture
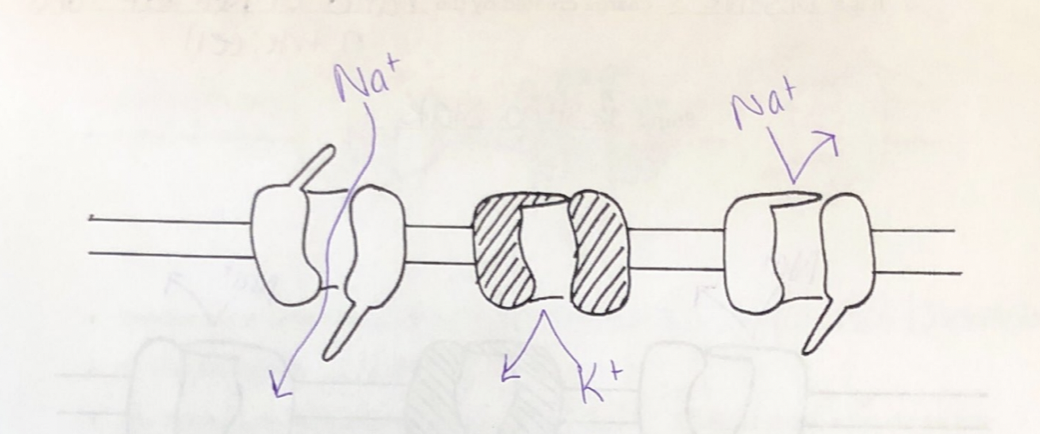
Depolarization: A stimulus opens __________________________________________
the activation goes on some Na+ channels
Depolarization: The K+ channels still __________ and K+ cannot __________
closed; leave
Depolarization: Na+ goes in and ___________________
depolarizes the membrane
Depolarization:
Depolarization
makes the charge more positive
Depolarization: If depolarization reaches the threshold _______________, it triggers an _________________. This occurs at about _________.
(if enough Na+ goes in); action potential; -55 mv
Step 3: _____________________________
Rising phase of action potential
Rising phase of action potential Picture
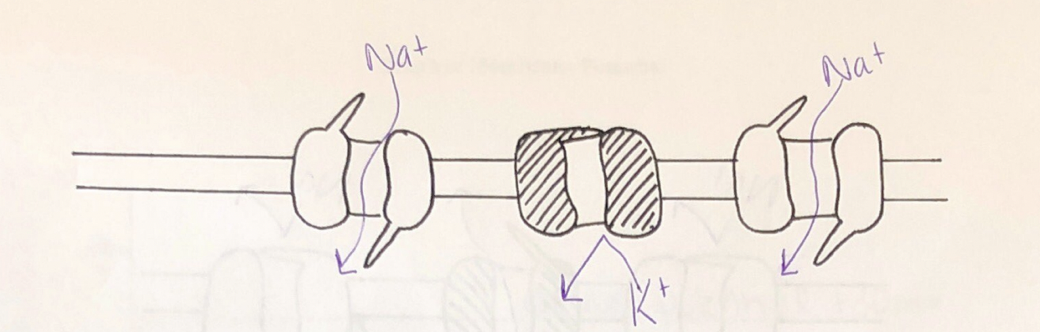
Rising phase of action potential: Depolarization opens the _____________________________________
activation gates on most Na+ channels
Rising phase of action potential: K+ channels remain ________
closed
Rising phase of action potential: Na+ influx makes the inside of the cell _____________ charged compared to the outside
positively
Rising phase of action potential: This is the peak of action potential and it reaches _______
+30 mv
Step 4: __________________________________
Falling Phase of Action Potential
Falling Phase of Action Potential Picture
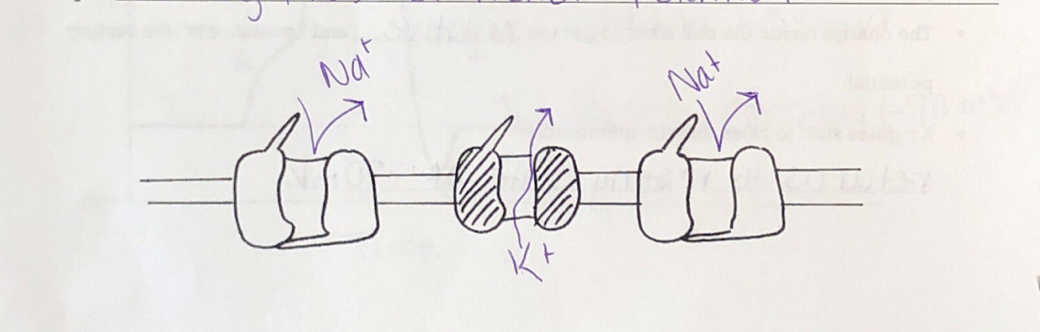
Falling Phase of Action Potential: The inactivation goes on most Na+ channels __________, so Na+ can’t go in anymore
close
Falling Phase of Action Potential: Activation goes on most K+ channels ____, and K+ can leave the inside of the cell, making the inside _______________________ again.
open; negatively charged
Step 5: ______________
Overshoot
Overshoot Picture
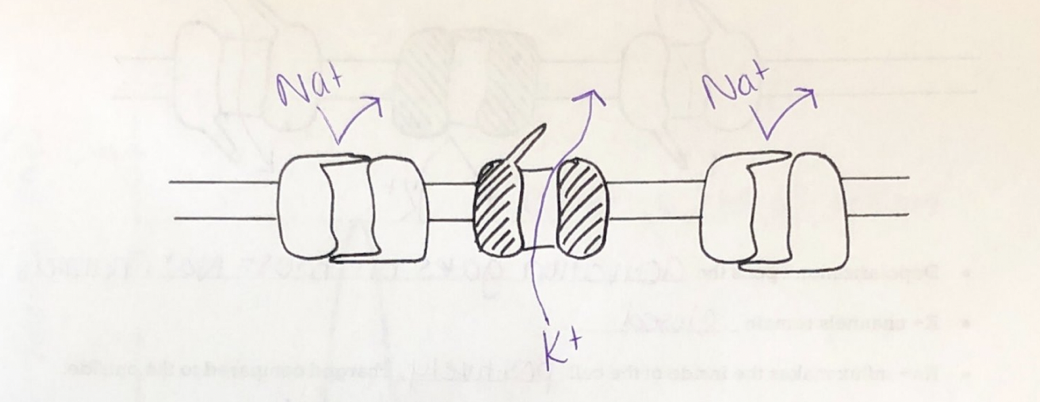
Overshoot: Both gates of the Na+ channels _________
close
Overshoot: Activation gates of some K+ channels stay ________
open
Overshoot: The charge inside the cell starts to get too __________ and “overshoots” the resting potential
negative
K+ gates start to close and the membrane _______________________________
returns to resting state of -70 mv