AP Human Geography Agriculture (copy)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
Agribusiness
System of food production involving everything from the development of the seeds to the marketing and sale of food products at the market.
2
New cards
Cash Crops
Planting large amounts of profitable crops for mass production and sell.
3
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
4
New cards
Double Cropping
Planting and harvesting a crop on a field more than once a year.
5
New cards
GMOs
Foods that\have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistant, increased productivity, or nutrients value
6
New cards
Intensive Subsistence Farming
A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land.
7
New cards
Monoculture
Dependence on a single agricultural commodity.
8
New cards
Mechanization
In agriculture, the replacement of human labor with technology or machines.
9
New cards
Primary Economy
Any economic activity pertaining to the collecting, harvesting, and obtaining of raw materials.
10
New cards
Plantation Agriculture
Raising a large amount of a 'cash crop' for local sale or export.
11
New cards
Transhumance
Movement of animal herd to cooler highland areas in the summer to warmer lowland areas in the winter.
12
New cards
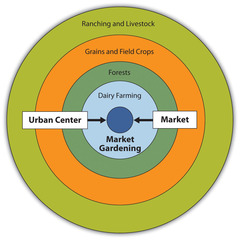
Von Thunen Model
Theory that a commercial farmer wull decide which crops to grow and which livestock to raise depending on the proximity to market.
13
New cards
Green Revolution
An outgrowth of the 3rd agricultural revolution, this effort began in the 1940s and developed new strains of hybrid seeds and fertilizers that dramatically increased the crop output possible from each farm.
14
New cards
Nomadism
Dry Areas
Same climate as livestock ranching(commercial farms in MDCs)
Marginalized land
Same climate as livestock ranching(commercial farms in MDCs)
Marginalized land
15
New cards
Mixed livestock and grain
Raise domesticated animals and growing feed
16
New cards
Commercial Grain Farming
Wheat belt
Bread-basket US
Corn belt
Bread-basket US
Corn belt
17
New cards
Mediterranean Agriculture
An agricultural system practiced in the Mediterranean-style climates of Western Europe, California, and portions of Chile and Australia, in which diverse specialty crops such as grapes, avocados,
18
New cards
Double cropping
Harvesting twice in one year
Employ crop rotation
Employ crop rotation
19
New cards
Truck Farms
Farm where farmers produce fruits for the market
Use mechanization to produce large quantities of fruits and veggies
Use mechanization to produce large quantities of fruits and veggies
20
New cards
Agrarian
relating to land; relating to the management or farming of land
21
New cards
Agricultural Industrialization
The use of machinery in agriculture, like tractors etc. - makes it easier for farmers to have higher crop yields.
22
New cards
Agricultural Landscape
The land that we farm on and what we choose to put were on our fields.
23
New cards
Agricultural Location Model
An attempt to explain the pattern of agricultural land use in terms of accessibility, costs, distance, and prices.
24
New cards
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
25
New cards
Cultivation Regions
Regions were there is agricultural activity. Know these specifically! (ie. Southwestern US is cattle ranching, Mediterranean is crop trees).
26
New cards
Dairy Farms
specialized in dairy products, N. America, Europe, NOT Africa, South America, Asia
27
New cards
Desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
28
New cards
Extensive Commercial Agriculture
A crop or livestock system in which land quality or extent is more important than capital or labor inputs in determining output
29
New cards
Feedlot
a plot of land on which livestock are fattened for market
30
New cards
Food Manufacturing
The processes that are used to convert raw materials into finished food products
31
New cards
Growing Season
The season in which crops grow best. Growing season can vary by location, societies rely on their growing season to which crops they can or can't grow at their latitude.
32
New cards
Hunting and Gathering
the killing of wild animals and fish as well as the gathering of fruits, roots, nuts, and other plants for sustenance
33
New cards
Intensive Commercial Agriculture
Intensive farming in a commercial economy, crops have high yields and market value
34
New cards
Livestock Ranching
an extensive commercial agricultural activity that involves the raising of livestock over vast geographic spaces typically located in semi-arid climates like the American West
35
New cards
Long-Lot Survey System
A distinct regional approach to land surveying whereby land is divided into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers, roads, or canals
36
New cards
Luxury Crops
Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee, and tobacco
37
New cards
Metes and Bounds System
a system of land surveying east of the Appalachian Mountains. The system relies on descriptions of land ownership and natural features such as streams or trees.
38
New cards
Pastoralism
A type of agricultural activity based on nomadic animal husbandry or the raising of livestock to provide food, clothing, and shelter.
39
New cards
Organic Agriculture
Approach to farming and ranching that avoids the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones, and other similar synthetic inputs.
40
New cards
Pesticides
Chemicals used on plants that do not harm the plants, but kill pests and have negative repercussions on other species who ingest the chemicals.
41
New cards
Plant Domestication
genetic modification of a plant such that its reproductive success depends on human intervention
42
New cards
Rectangular Survey System
A system used to divide public domain lands in the United States in which land is divided into 6-mile square townships and subdivided into sections, portions of sections, or irregular lots.
43
New cards
Root Crops
crop that is reproduced by cultivating the roots of or the cuttings from the plants
44
New cards
Carl Sauer
Defined the concept of cultural landscape as the fundamental unit of geographical analysis.
45
New cards
2nd Agriculture Revolution
Innovations led to agricultural surpluses, food surpluses, let people move from farms to factories, growth of cities increased.
46
New cards
Seed Crops
crop that is reproduced by cultivating the seeds of the plants.
crop that is reproduced by cultivating the seeds of the plants.
crop that is reproduced by cultivating the seeds of the plants.
47
New cards
Specialization
The concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities
48
New cards
Slash and Burn Agriculture
a farming technique in which trees are cut down and burned to clear and fertilize the land
49
New cards
Township and Range System
A rectangular land division scheme designed by Thomas Jefferson to disperse settlers evenly across farmlands of the U.S. interior.
50
New cards
Third Agriculture Revolution
'green revolution' rapid diffusion of new ag techniques between 1970's and 1980's, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers
51
New cards
Soil Erosion
the wearing away and removal of rock and soil particles from exposed surfaces by agents such as moving water, wind, or ice
52
New cards
scale economies
cost advantages due to the size of a retailer
53
New cards
Terrace Farming
The cutting out of flat areas (terraces) into near vertical slopes to allow farming. Terrace farms appears as steps cut into a mountainside.
54
New cards
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
55
New cards
fair trade movement
an effort to promote higher incomes for producers and for more sustainable farming practices
56
New cards
commodity chain
series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution and resulting in a commodity that is then exchanged on the world market