PSYC 301 - Structural Anatomy
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
major divisions of the nervous system
peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS)
how is the PNS further divided into
somatic nervous system (SNS) and autonomic nervous system (ANS)
SNS
component that interacts with the external environment
differences between afferent nerves and efferent nerves
afferent nerves carries towards the CNS but efferent nerves carries away from the CNS
what does the afferent servers in SNS carry
it carries sensory signals in from the world around us towards the CNS using sensory neurons
what is an example of afferent nerves in the SNS
detecting lights, sounds, smells etc
what does efferent nerves in SNS carry
it carries motor signals from the CNS out to the skeletal muscles using motor neurons
what is an example of efferent nerves in the SNS
information from the brain to cause muscle to contract or flex
ANS
nerves that participate in the regulation of the internal environment of the body and its internal processes
what does the afferent nerves in ANS carry
it carries sensory signals from the internal organs to the CNS
what is an example of afferent nerves in the ANS
when stomach is full, information gets sent to the brain to stop eating
what does the efferent nerves in the ANS carry
it carries motor signals from the CNS to the internal organs
what is an example of efferent nerves in the ANS
heart rate should increase so it causes the heart to beat faster
what are the two types of nerves in efferent nerves
sympathetic nerves and parasympathetic nerves
sympathetic nerves
mobilises energy in threatening situations causing physiological arousal that acts via glands or organs
example for sympathetic nerves
inhibiting saliva and increase in heart rate in threatening situations
parasympathetic nerves
act to conserve energy or “rest and digest”
example of parasympathetic nerves
stimulating digestion
what are we always in a state of
in a state of balancing sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves
what are clusters of cell bodies in the PNS called
ganglion
what are bundles of axons called in the PNS
they are called a nerve and axons are often called nerve fibres
what is the CNS composed of
brain and spinal cord
what are clusters of cell bodies called in the CNS
nucleus
what are bundles of axons called in the CNS
tract
label spinal cord
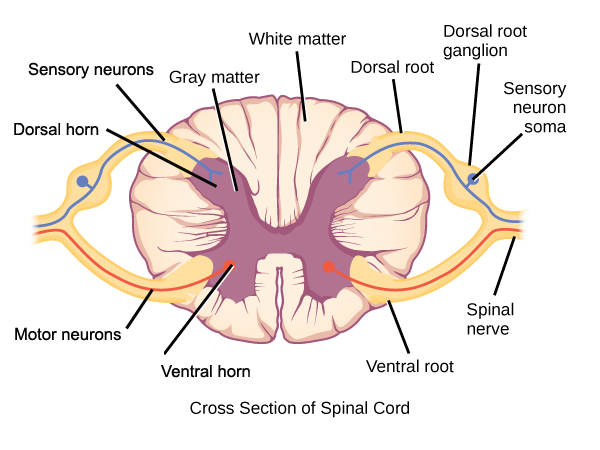
what is the inner h shaped of the spinal cord made up of
gray matter
what is the gray matter of the spinal cord made up of (3)
cell bodies, unmyelinated axons and capillary blood vessels
what is the surrounding area of the spinal cord made up of
white matter
why is the surrounding spinal cord area white
due to myelinated axons wrapped in fats that carries messages very quickly
why do we need the both grey and white matter (2)
to carry information long distance very quickly that is supported by white matter
to process information supported by grey matter
how does grey matter and white matter differ in the thoracic curve (upper back)
more white matter than grey matter due to more information passing through at this part of the spine
how does grey matter and white matter differ in the sacral curve (lower back)
more grey matter than white matter as it receives and processes more information than passes information
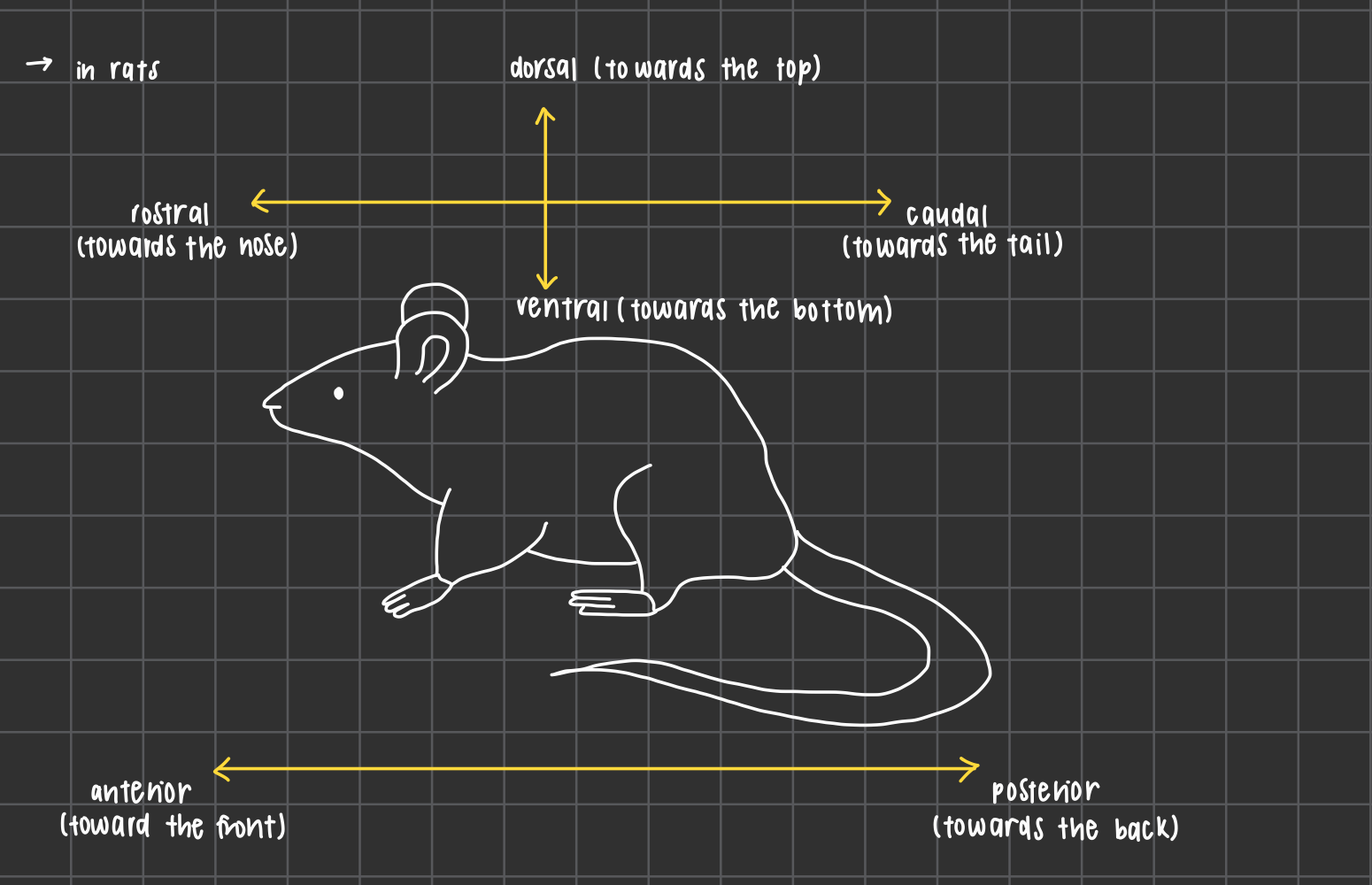
neuroanatomical directional terms in rats (6)
dorsal: towards the top
ventral: towards the bottom
rostral: towards the nose
caudal: towards the tail
anterior: towards the front
posterior: towards the back
neuroanatomical directional terms in humans head (4)
dorsal: top of head
ventral: bottom of head
anterior: towards face
posterior: towards back
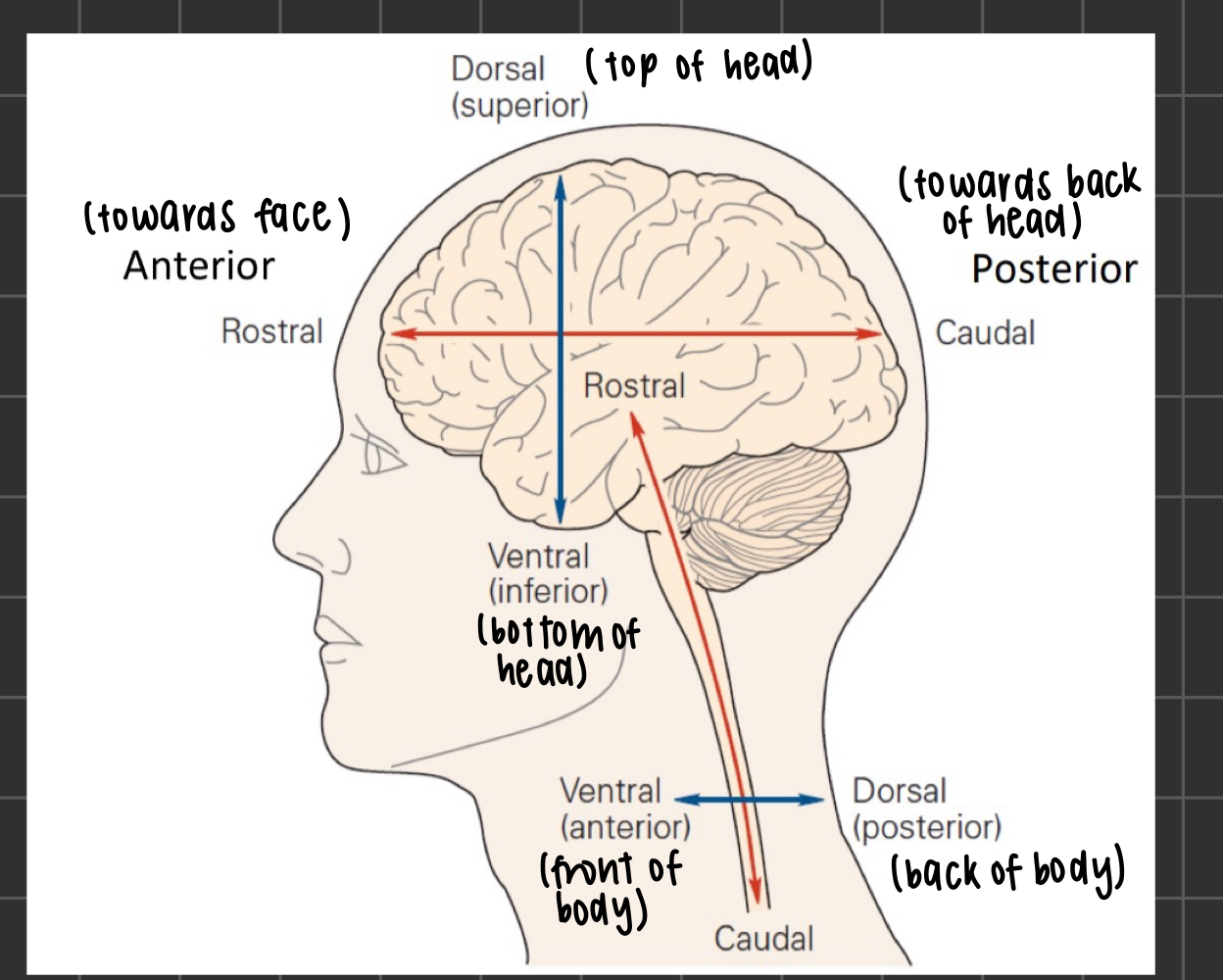
neuroanatomical directional terms in humans spinal cord (2)
ventral (anterior): front of the body
dorsal (posterior): back of the body
left and right neuroanatomical terms (3)
lateral: out to the side
medial: middle of the person
always view L and R from the POV of the patient
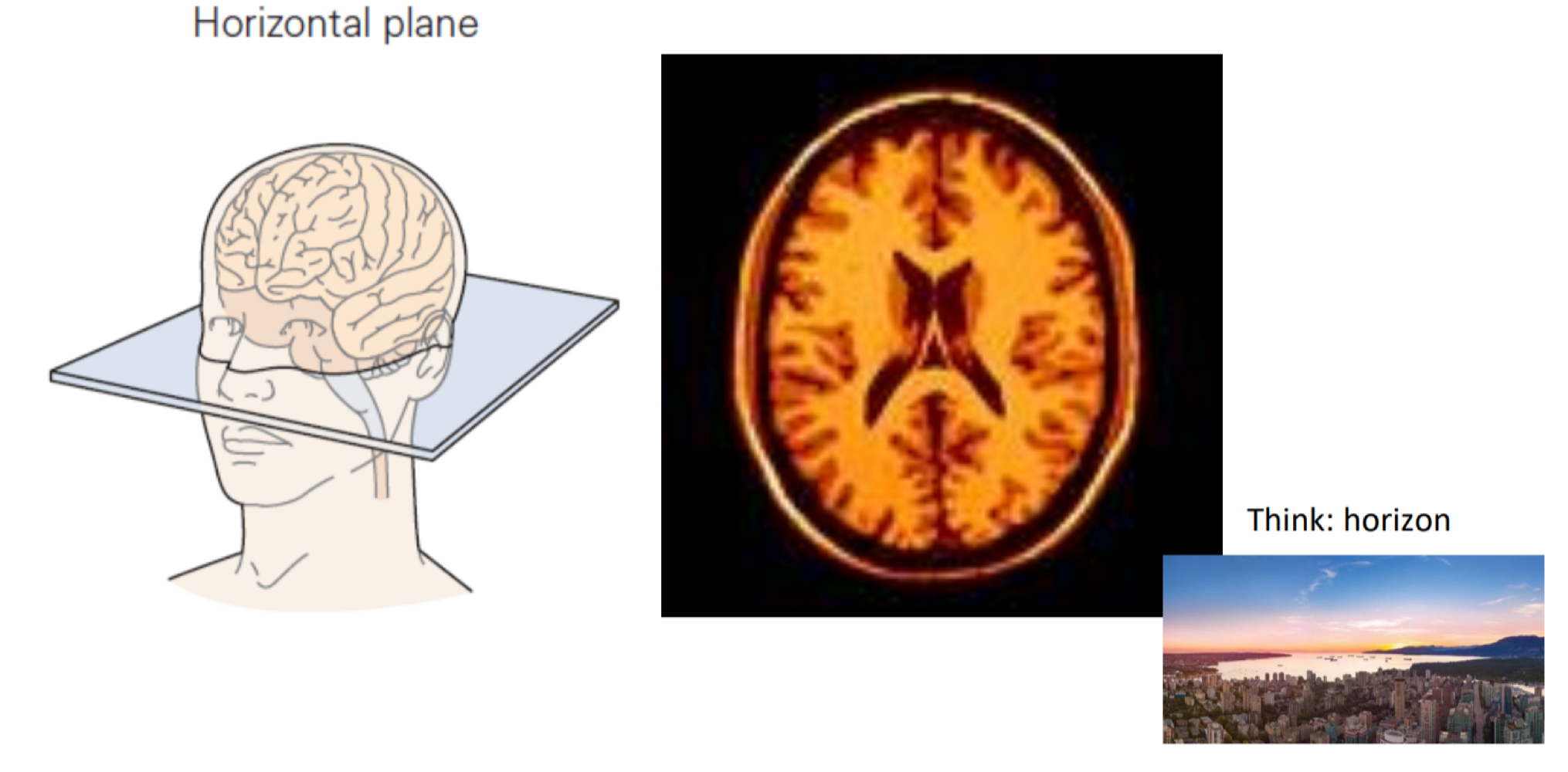
what are the 3 different sectional planes
horizontal plane
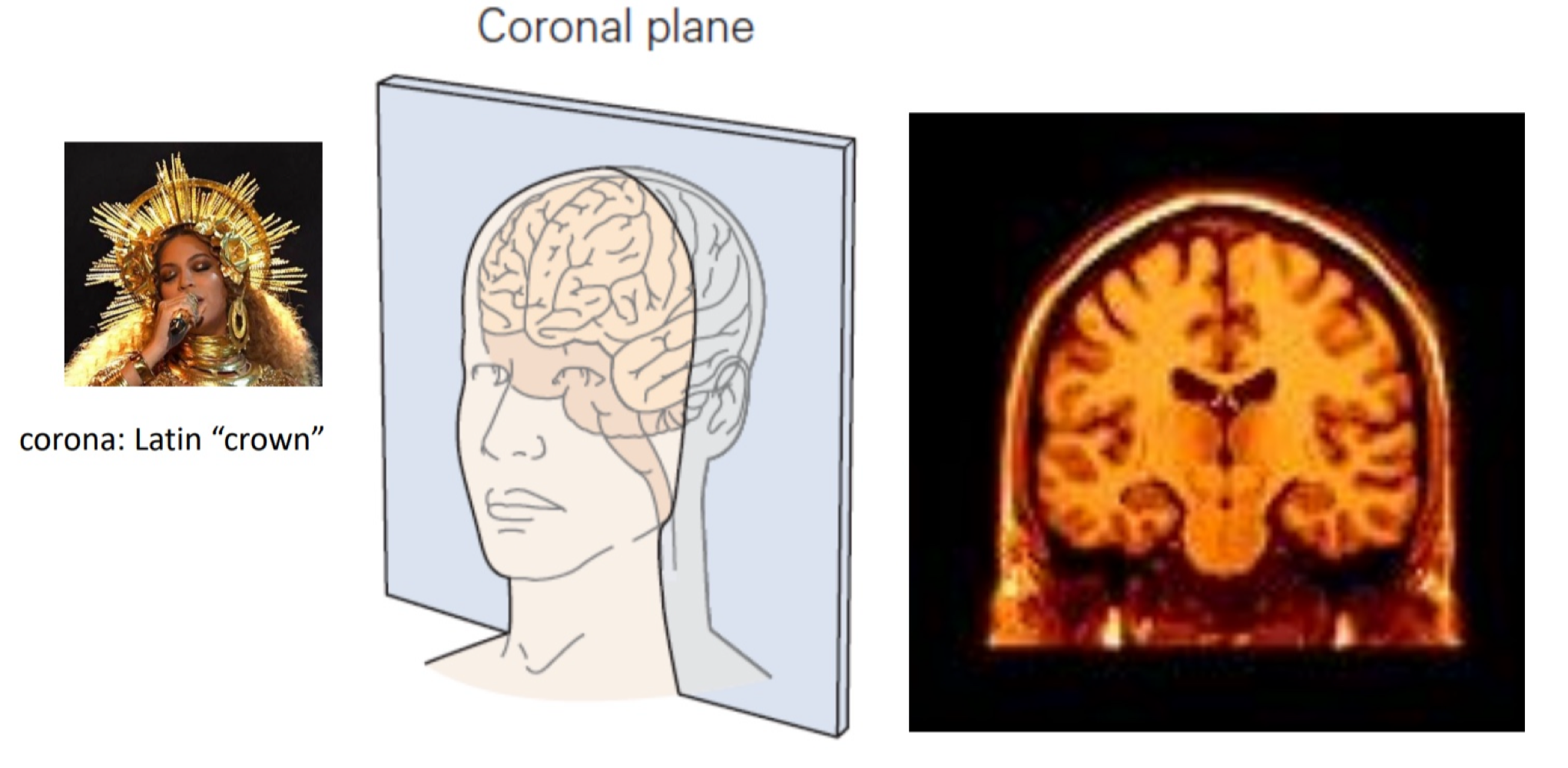
coronal plane
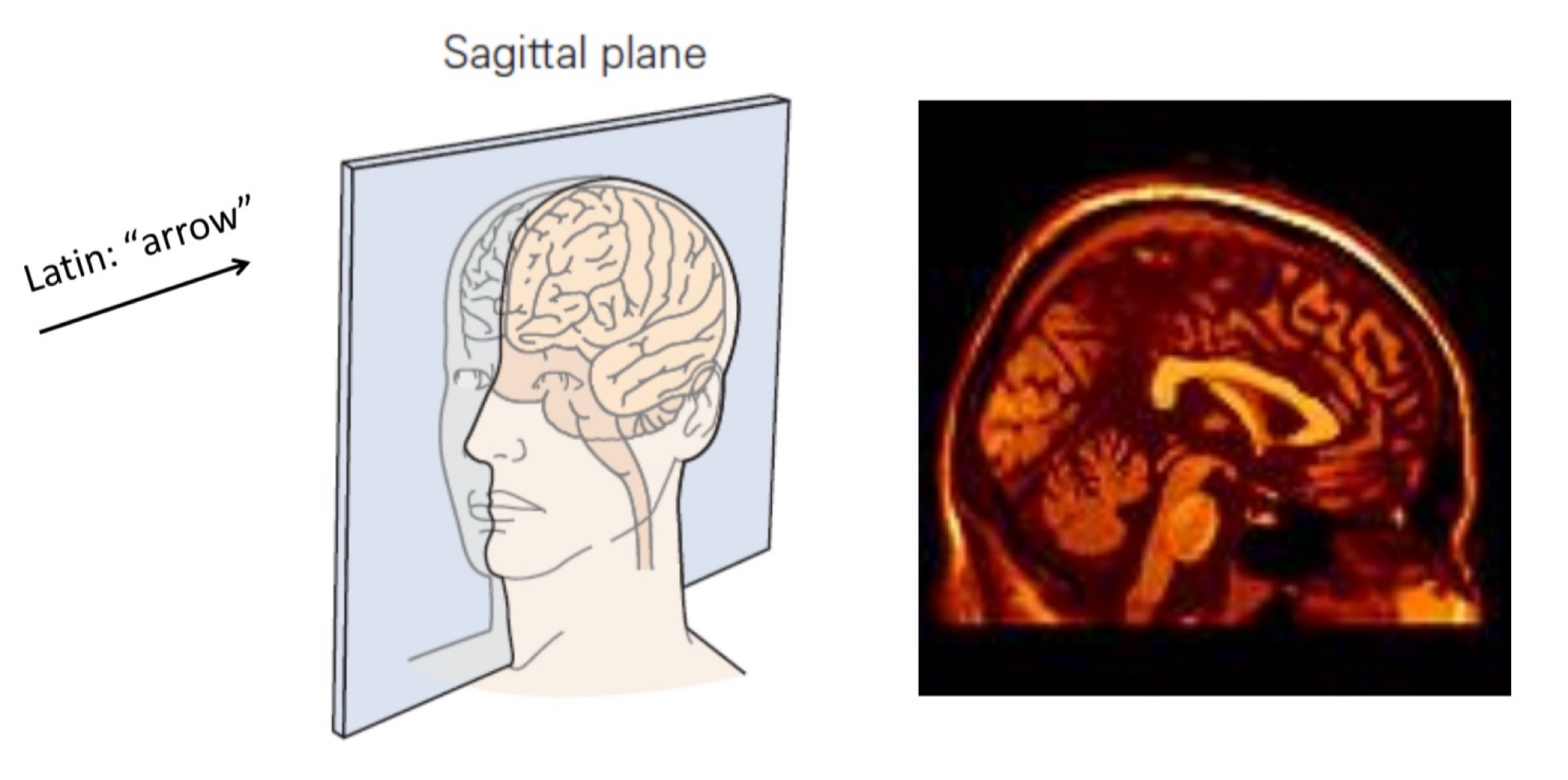
sagittal plane
horizontal plane
oval- like, symmetrical
coronal plane
like a latin crown, can see top of person’s head and maybe their neck
sagittal plane
“arrow”, not symmetrical
very early in development, 18-21 days old human embryo, what are the 3 divisions of the brain that can be seen
hindbrain
midbrain
forebrain
before birth, these 3 swellings become what five structures
telencephalon
diencephalon
mesencephalon
metecephalon
myelencephalon
what is part of the forebrain
telencephalon and diencephalon
what is part of the midbrain
mesencephalon
hindbrain
metecephalon and myelencephalon
myelencephalon (2)
aka medulla
composed largely of tracts carrying signals between the rest of the brain and the body
what are the two part composed of the metecephalon
pons and cerebellum
pons (3)
houses many fibre tracts
part of reticular formation
has lots of white matter
what is reticular formation (2)
network of nuclei that play roles in arousal, attention, cardiac and respiratory reflexes
in myelcenphalon, metecephalon and mesencephalon
cerebellum (3)
“little brain”
massively connected to cortex, multiple cerebro- cerebellar systems
involved in movement and timing - matching motor signal and sensory feedback
is the cerebellum part of the brainstem
no
what are the 2 components of mesencephalon
tectum and tegmentum
tectum
“roof”
contains nuclei that receive and relay visual and auditory information
what is the nuclei that relay visual information
superior colliculi
what is the nuclei that relay auditory information
inferior colliculi
tegmentum (2)
“floor”
contains nuclei related to motor function and processing pain
what is the nuclei that is related to motor function
subutancia nigra and red nucleus
what is the nuclei related to processing pain called
periaqueductual grey
are the abilities in the mesencephalon common across all vertebrate
yes it is not uniquely human and it is conserved evolutionarily
injuries to which regions of the brain are less survivable
injuries to mid and hindbrain due to them being involved in heart rate, breathing, being alert etc
what are the 3 disorder of mid and hindbrain learnt in class
Dejerine syndrome
Chiari malformation
pontine tegmental cap dysplasia
dejerine syndrome (4)
bilateral medial medullary
respiratory failure
paralysis of all four limbs
includes tongue dysfunction
chiari malformation (2)
compression and distortion of cerebellum due to skull shape causing it to make its way down the spinal cord
surgery can be done to relive pressure
what are the symptoms of chiari malformation (5)
headaches
neck pain
coordination issues
swallowing issues
can be asymptomatic
pontine tegmental cap dysplasia (2)
rare genetic disorder of pons and cerebellum formation due to developmental error in axon growth and guidance
affects hearing, gaze, swallowing and facial movements
what is the diencephalon composed of
thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus (2)
2 lobed structure, bilateral
made up of many different types of nuclei - some process and relay sensory information between the receptors and cortex
nuclei in the thalamus
may be specific to one sense or non specific and involved in multimodal integration simultaneously
thalamo- cortical loops and consciousness (3)
relationship between the thalamus and the cortex is important to have a subjective experience of consciousness
general anaesthetics tend to act upon the non specific nuclei of the thalamus
abnormal synchronisation in the thalamo cortical network can cause absence seizures, moments of unconsciousness
hypothalamus (2)
plays an important role in autonomic type functions such as feeding, sex, sleeping, temperature, emotion and movement
also bilateral and symmetrical
what does the hypothalamus act upon
acts upon the body’s endocrine system via the pituitary gland - sends messages to pituitary glands to release different
hypothalamic and pituitary tumours symptoms (5)
headache, seizures
feedings and weight changes
energy and mood changes
cognitive changes
hormonal changes
telencephalon
largest division of the brain
what are the 3 structures that make up the telencephalon
basal ganglia
limbic system
cerebral cortex
basal ganglia (2)
collection of nuclei highly connected to the cortex, thalamus and midbrain
involved in movement and learning, esp recognising patterns
what 2 structures are composed of the limbic system
hippocampus and amygdala
hippocampus
plays a role in spatial memory and episodic memory
amygdala
plays a role in emotion
cortex (3)
also known as cerebral cortex
outer surface of the brain
it is highly folded and convoluted in order to get max surface area into a finite volume
do different animals have different folding of the cortex
yes
what is a gyrus
the top of the folds
what is a sulcus
the bottom valley of the folds
if a sulci is deep enough to indent the ventricles what is it called
fissures
90% of the human cerebral cortex is…
isocortex or neocortex, means that there is 6 layers
10% of the human cerebral cortex is…
allocortex, less than 6 layers
what the different layers specialised to do
either to receive information from other brain structures, output information or process information
why is it important that during development the layers are formed properly
as if the cells do not migrate normally, folding is interrupted which can lead to Lishencephaly, a smooth brain
Lishencephaly (4)
happens between 12-40 per million birth
symptoms can include seizures, muscle spasm, developmental delays etc
many children with Lishencephaly will die before the age of 10 due to seizure ore respratory function
can be genetic or non genetic
the cerebral hemisphere are connect by a few tracts called
the cerebral commissures
what is the largest track
the corpus callosum
what are the 4 parts of the cortical lobes
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
all bilateral
what are the landmarks used to delineate between the lobes called
sulcus and fissures
what is the sulcus distinguishing the frontal and parietal lobe
central sulcus
what is the sulcus distinguishing the frontal and temporal lobe
lateral sulcus
what is the sulcus distinguishing the left and right side
longitudinal sulcus
what is part of the brain stem
mesencephalon, metencephalon (pons) and myelencephalon
what are fluid filled spaces in the brain called and what do they contain
they are called ventricles and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
what are the 3 main roles CSF play
buoyancy
protection
chemical stability
buoyancy (2)
dense brain is suspended in fluid, reduces its effective weight
does not interfere with blood supply or put pressure on lower structures
protection
reduces injury upon head impact