Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics, Antivirals, and Antifungals: Uses, Side Effects, and Nursing Implications
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the action of Acyclovir?
Inhibits DNA replication, used for Herpes simplex virus.
What are common side effects of Acyclovir?
Renal failure, especially in patients with decreased renal function.
What is the primary use of Amphotericin?
Treatment of potentially fatal fungal infections.
What are the side effects of Amphotericin?
Renal failure, organ failure, and cardiac arrest.
What is the mechanism of action for Beta-lactam antibiotics?
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Name a common Beta-lactam antibiotic.
Penicillin G.
What is the action of Cephalosporins?
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
What are the generations of Cephalosporins?
First, Second, Third, Fourth, and Fifth generations.
What is a common side effect of Penicillins?
Maculopapular rash.
What does 'bactericidal' mean?
It refers to antibiotics that kill bacteria.
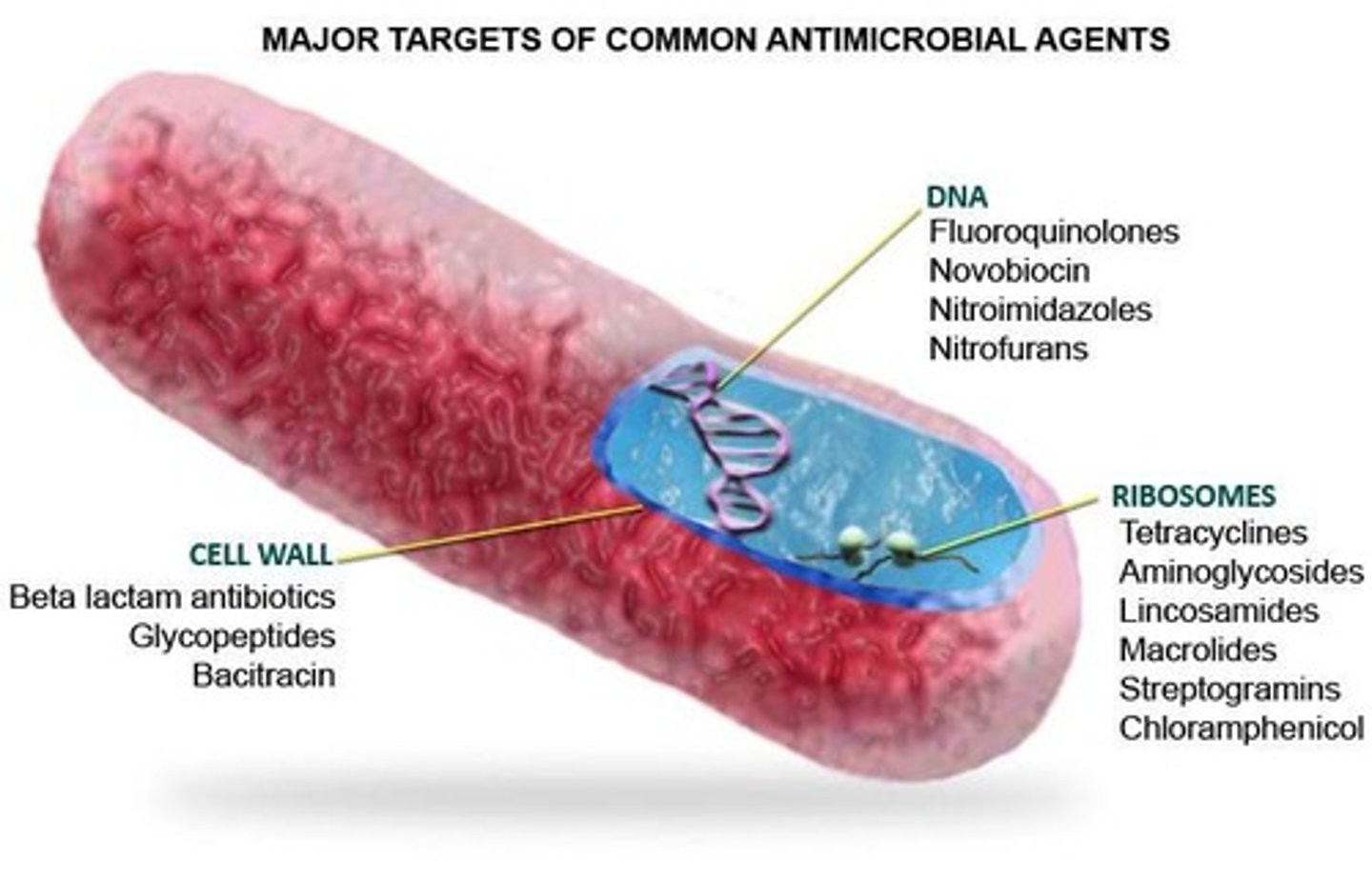
What does 'bacteriostatic' mean?
It refers to antibiotics that inhibit bacterial growth.
What is the significance of Peak and Trough levels?
Peak is the highest drug level, and Trough is the lowest drug level in the bloodstream.
What are common resistant pathogens?
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and VRE (Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci).
What is the role of Probenecid in antibiotic therapy?
It is used to prolong the effects of certain antibiotics.
What is the primary use of Gentamicin?
Treatment of serious Gram-negative infections.
What is a common adverse effect of Fluoroquinolones?
Tendonitis and tendon rupture.
What is the action of Fluoroquinolones?
They interfere with bacterial enzymes required for DNA synthesis.
What is the primary use of Nystatin?
Treatment of oral thrush and other fungal infections.
What is a common side effect of Fluconazole?
QT prolongation and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
What is the incubation period in infection?
The time between exposure to a pathogen and the onset of symptoms.
What is a nosocomial infection?
An infection acquired in a healthcare setting.

What is the difference between broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antibiotics?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics affect a wide range of bacteria, while narrow-spectrum antibiotics target specific types.
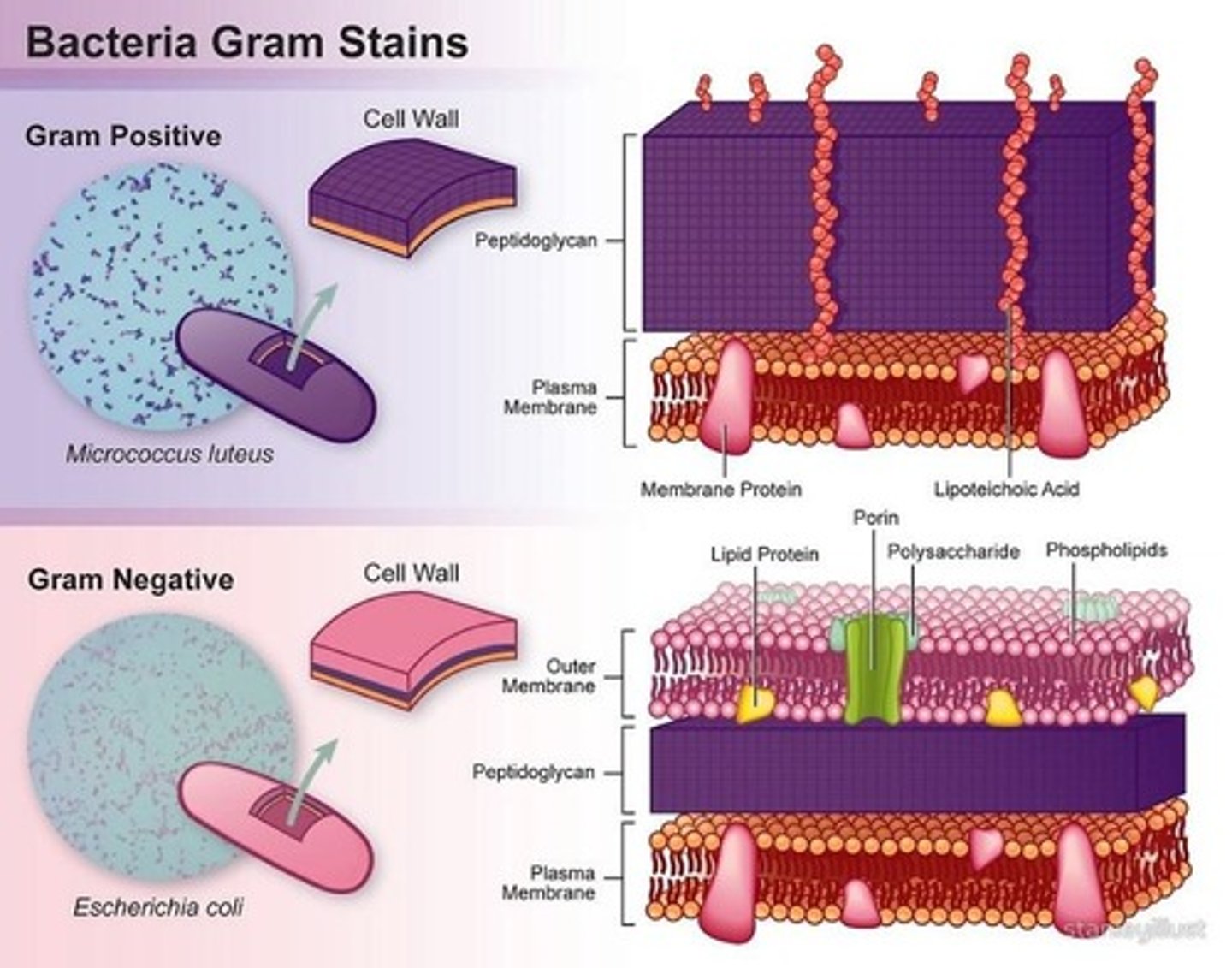
What is the role of culture and sensitivity testing?
To identify the specific bacteria causing an infection and determine the most effective antibiotic.
What is the significance of the term 'opportunistic pathogen'?
Pathogens that cause disease in individuals with weakened immune systems.
What are the common causes of fungal infections?
Molds and yeasts, often found in warm and moist environments.
What is the mechanism of action of aminoglycosides?
They are bactericidal and inhibit bacterial protein synthesis.
What are the indications for using Ciprofloxacin?
Urinary tract infections, bone and joint infections, and skin infections.
What is the treatment for C. difficile infections?
Antibiotic therapy and sometimes fecal microbiota transplantation.
What is the significance of monitoring renal function in patients on antibiotics?
To prevent nephrotoxicity and ensure proper dosing.