Properties of alkanes
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Basics of alkanes
General formula- CnH2n+2
Saturated
Single covalent bonds
Non-polar
Bonding of alkanes
All alkanes are S-orbitals and form sigma bonds, which are directly between atoms, so are strong
C-C and C-H bonds are strong and C-C are non-polar as both electronegativity are similar
Shapes of alkanes
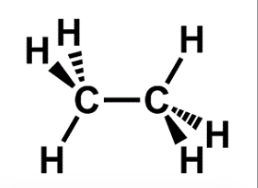
A 3D tetrahedral shape forms around alkanes at 109.5o due to electron repulsion theory.
Electron repulsion theory
Electrons/ areas of electrons density will repel each other and hence bonds will try to push themselves as far away from each other as possible.
Boiling points of alkanes
As chain length increase, number of atoms increases, meaning there is more close surface contact area between atoms, so there is greater London forces, so more energy is required to overcome them.
Boiling point will decrease if branching increases as there us less surface area contact, so weaker London forces.