Integumentary additional medical terms
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
abrasion
scraping or rubbing away of a surface, such as skin, by friction
abscess
localized collection of pus at the site of an infection (staphylococcal infection)
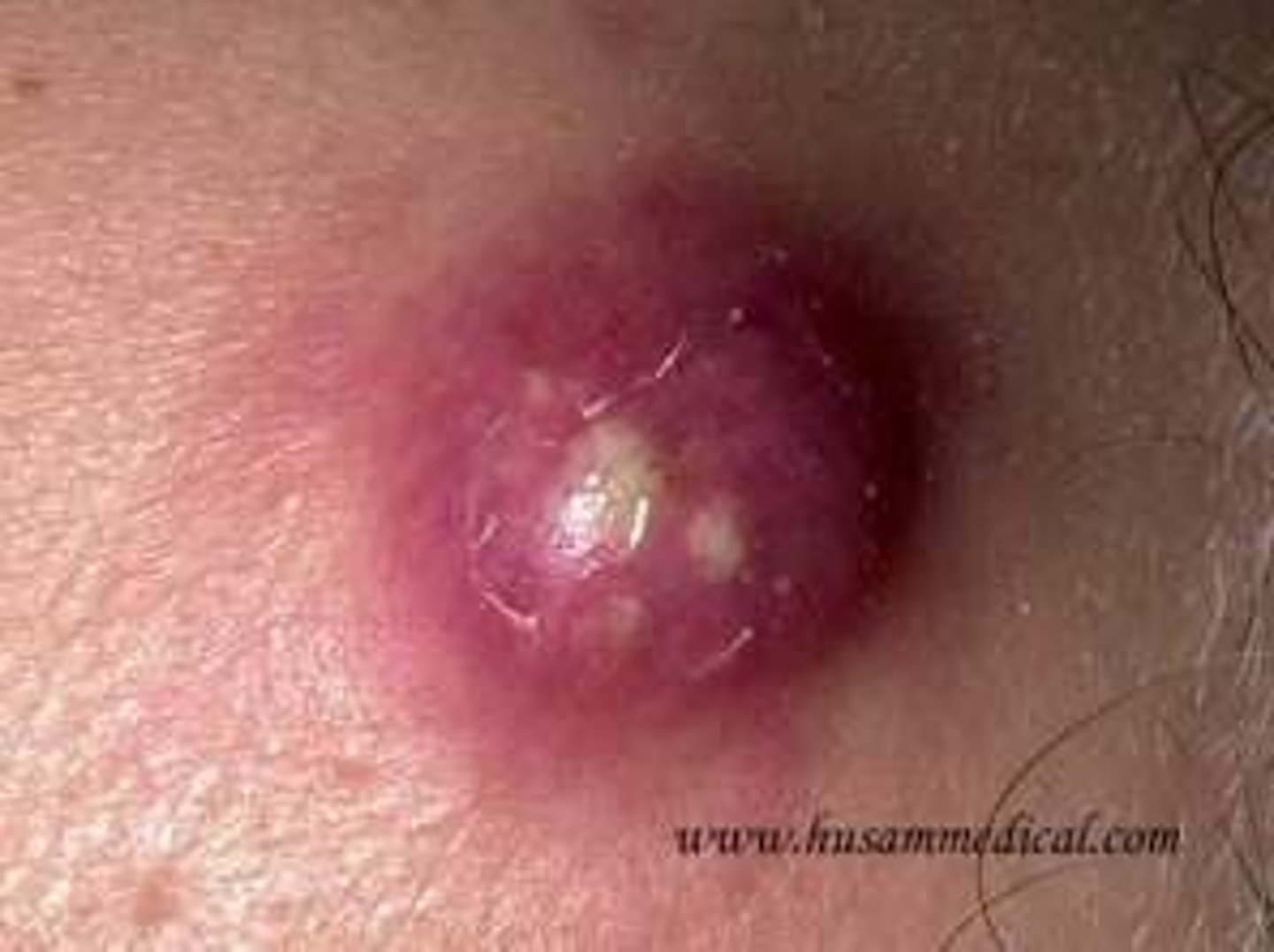
furuncle
boil; suppurative inflammatory skin lesion due to infected hair follicle
carbuncle
a cluster of connected furuncles (boils)
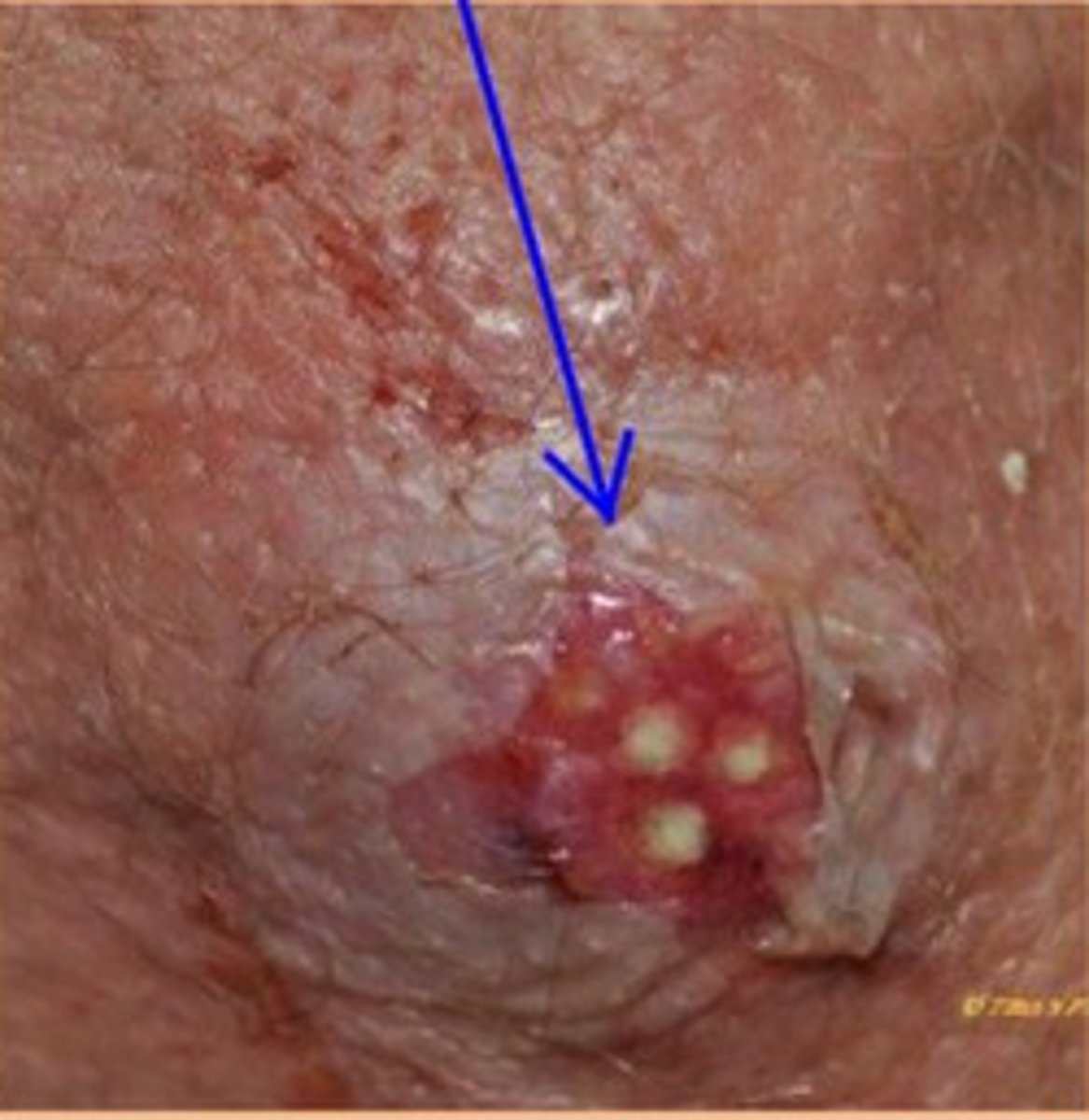
acne
inflammatory disease of the skin involving the sebaceous glands and hair follicles
- characterized by comedos (blackheads), papules, and pustules
papules
a small, raised, solid pimple or swelling, often forming part of a rash on the skin and typically inflamed but not producing pus.
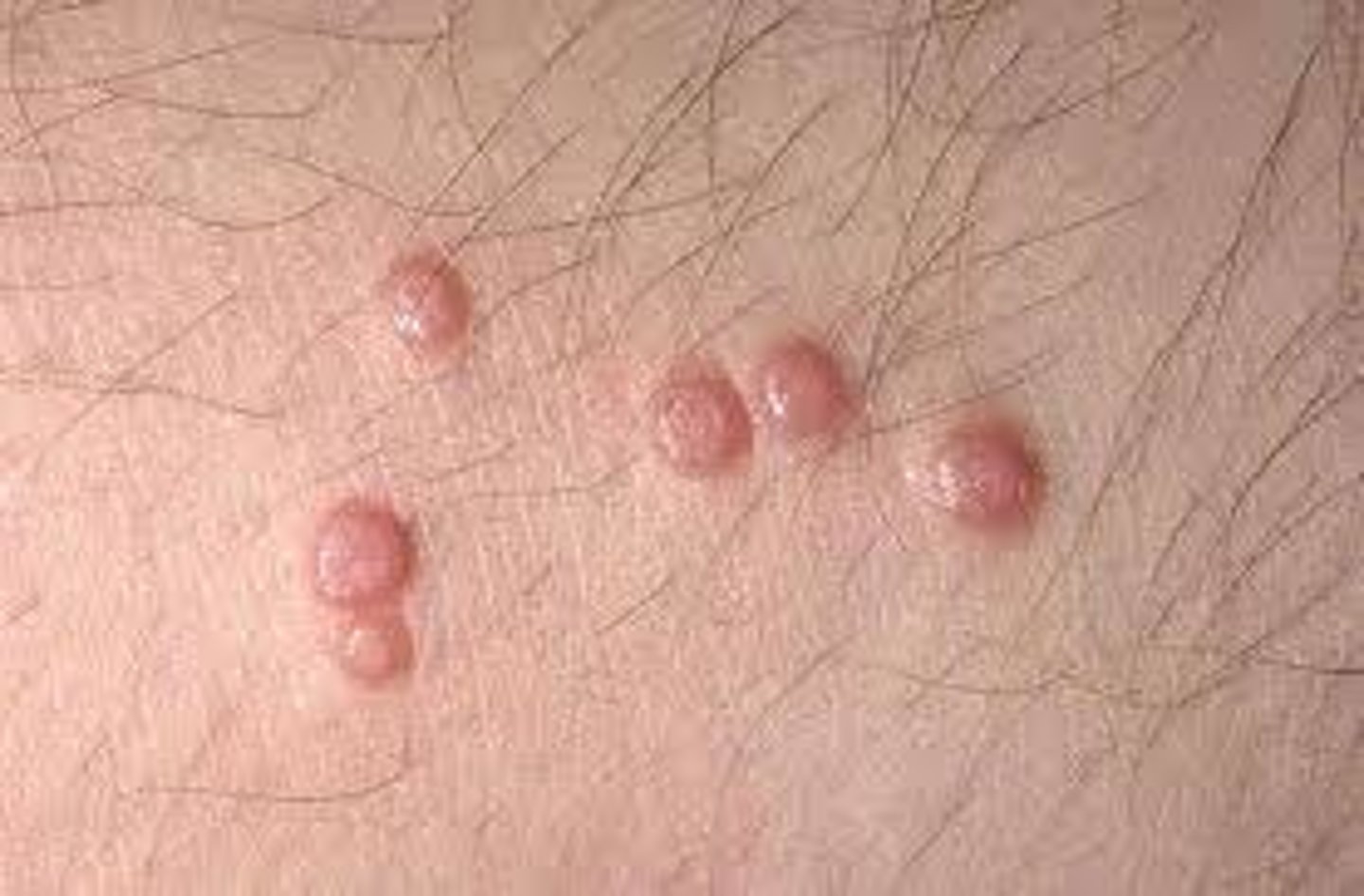
alopecia
loss of hair
cyst
closed sac or pouch in or under the skin with a definite wall that contains fluid, semifluid, or solid material
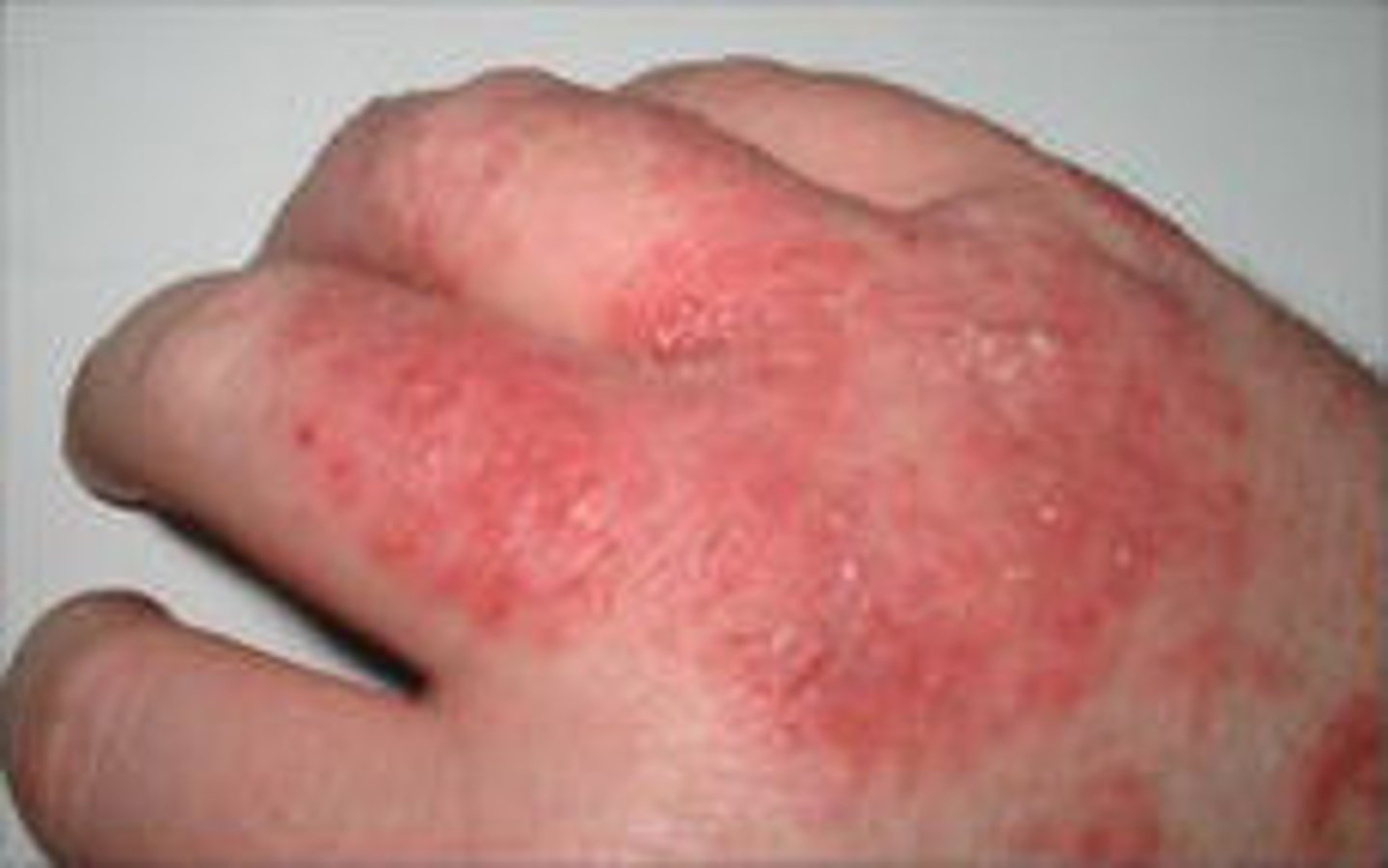
eczema
redness of the skin caused by swelling of the capillaries
hemorrhage
loss of a large amount of blood in short period, externally or internally
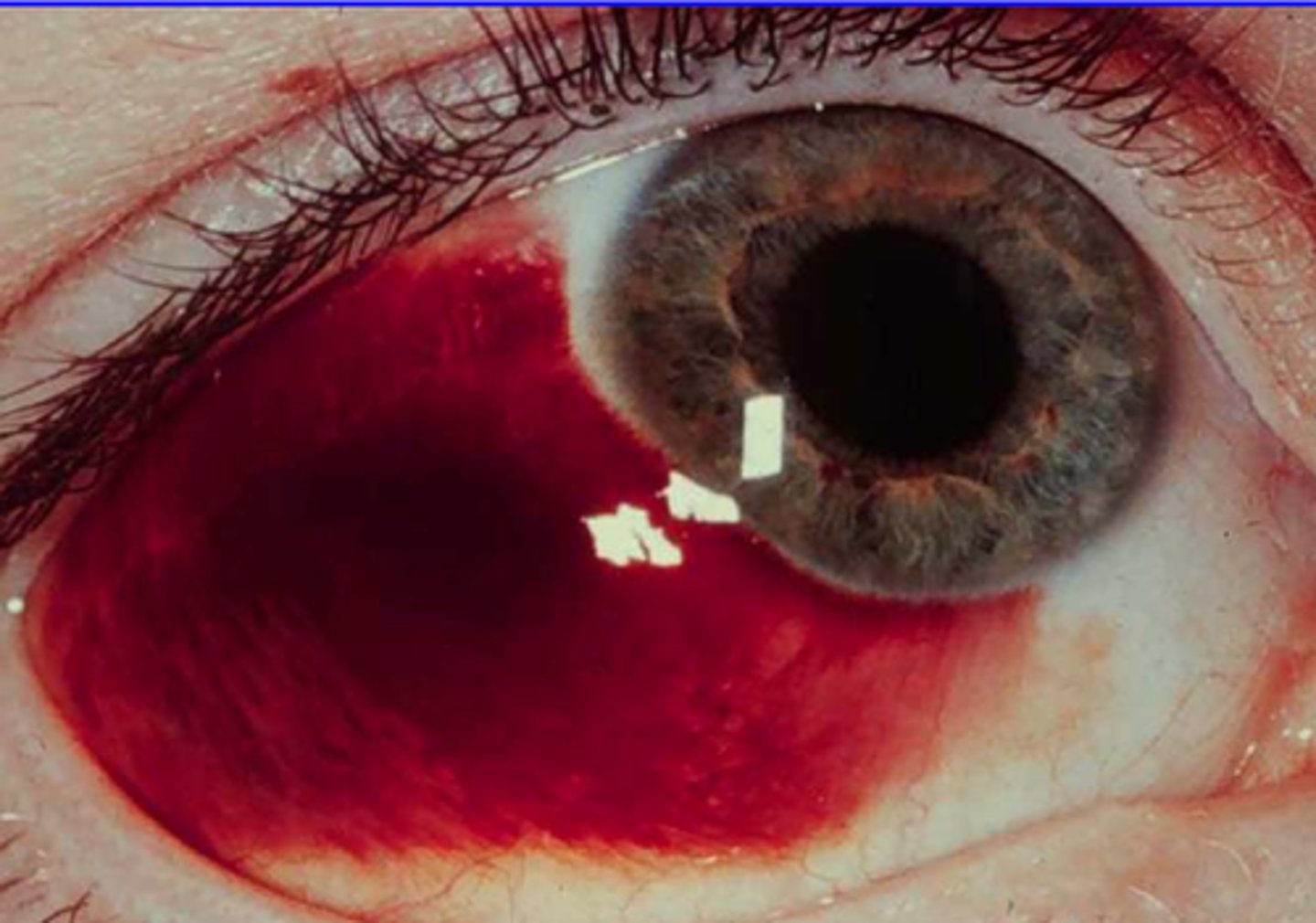
contusion
hemorrhage of any size under the skin in which the skin is not broken, also known as a bruise
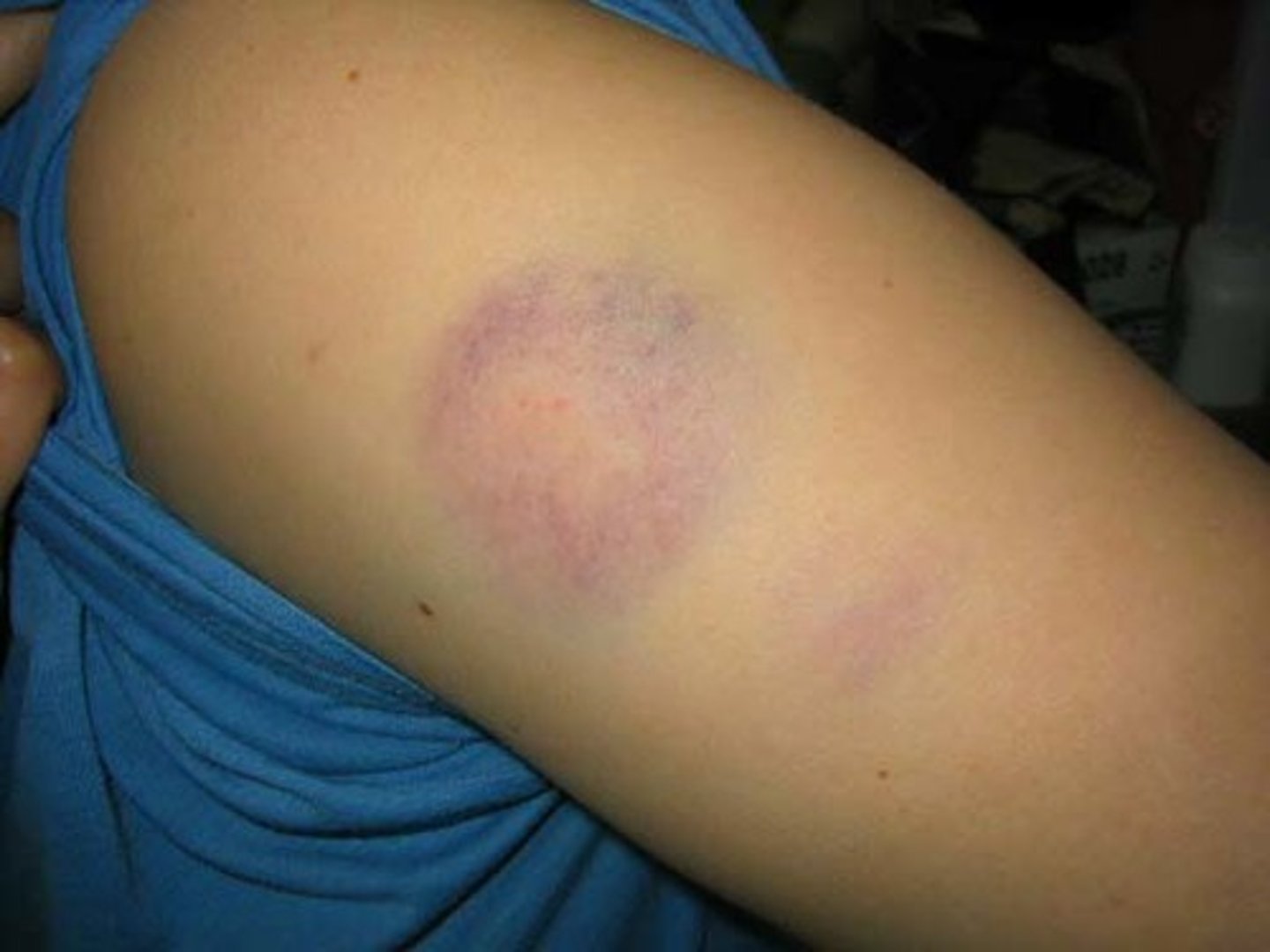
Ecchymosis
skin discoloration consisting of a large, irregulary formed hemorrhagic area with colors changing from blue-black to greenish brown or yellow, commonly called a bruise
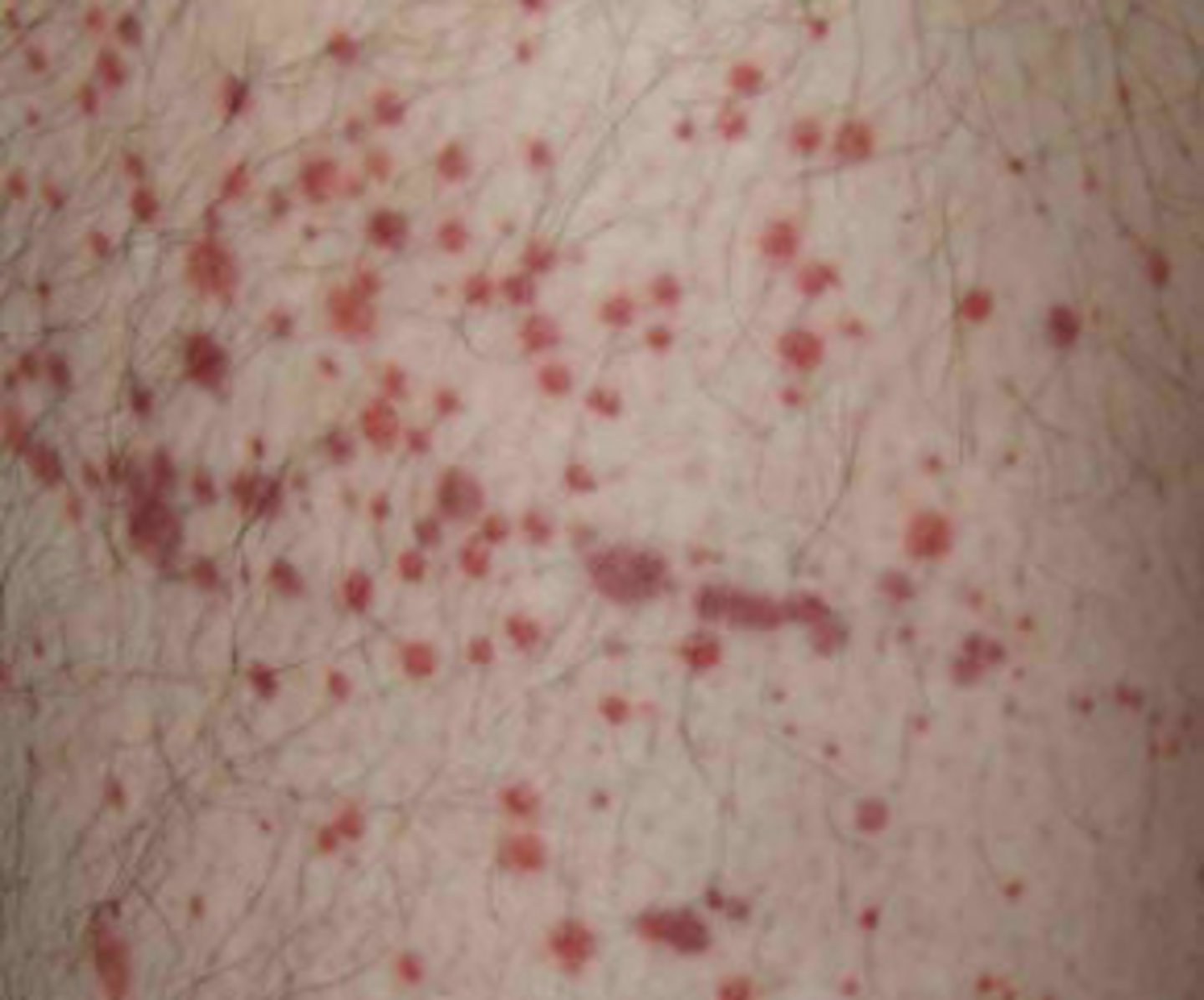
petechia
minute, pinpoint hemorrhage under the skin
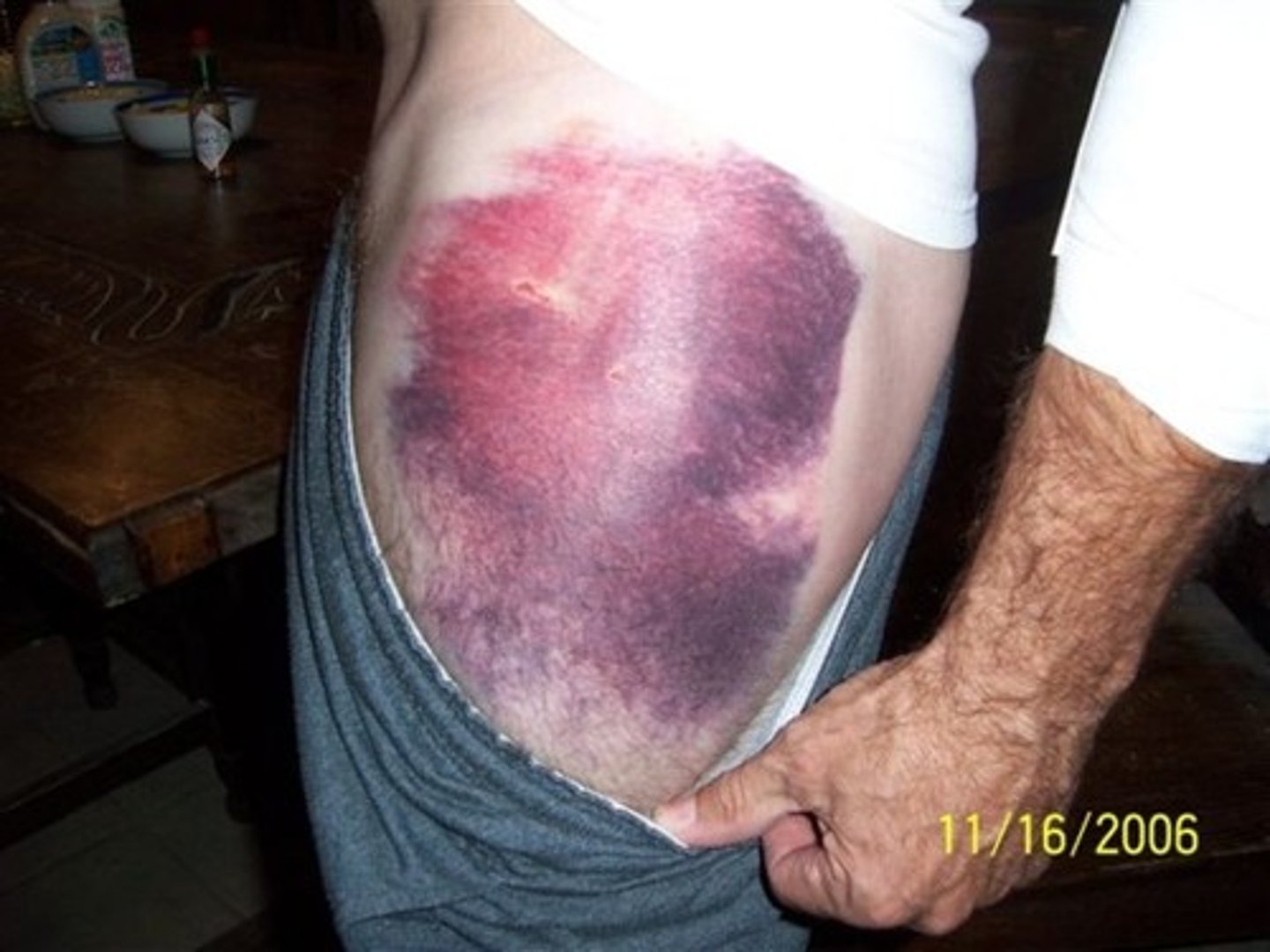
hematoma
elevated, localized collection of blood trapped under the skin that usually results from trauma
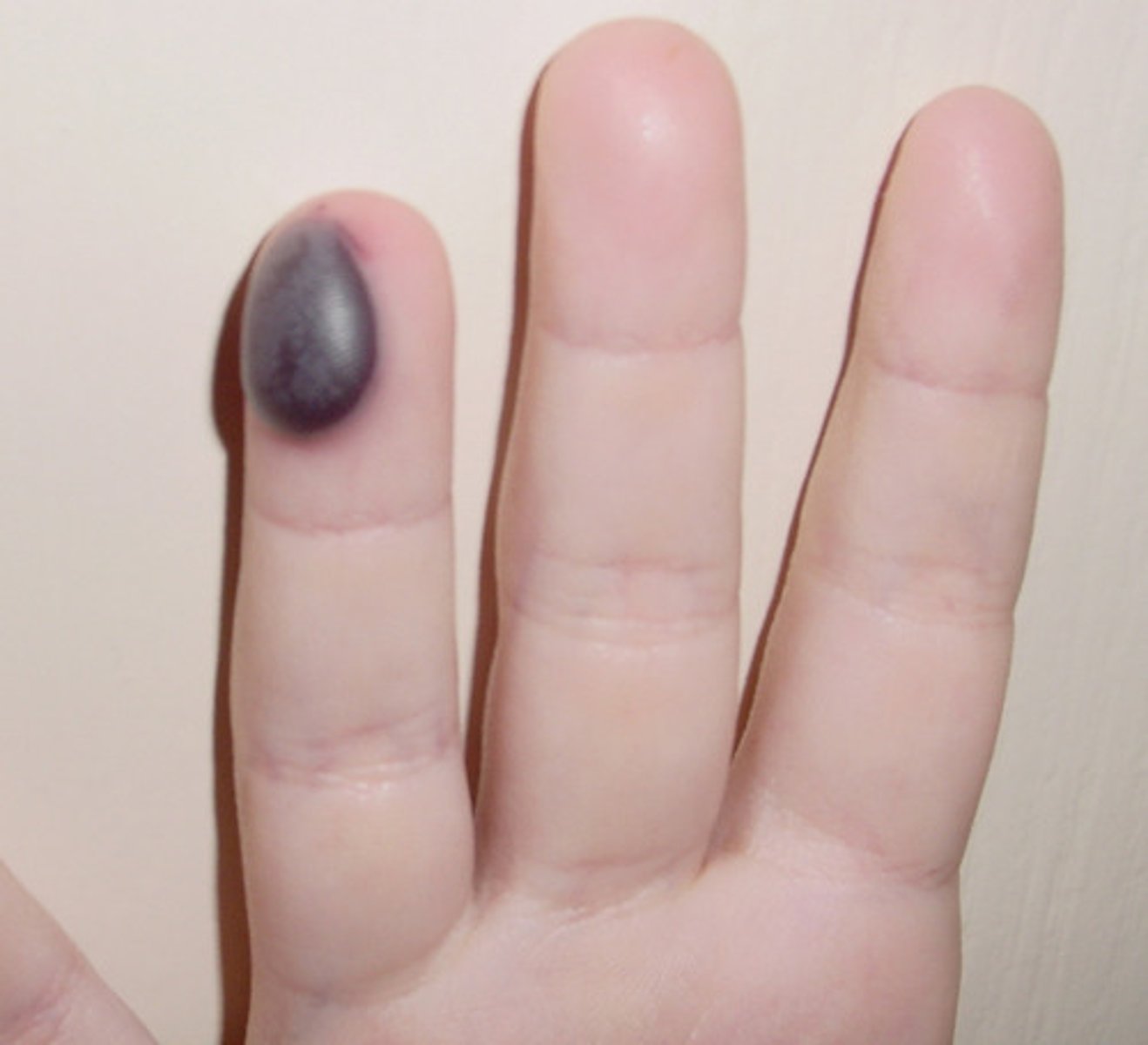
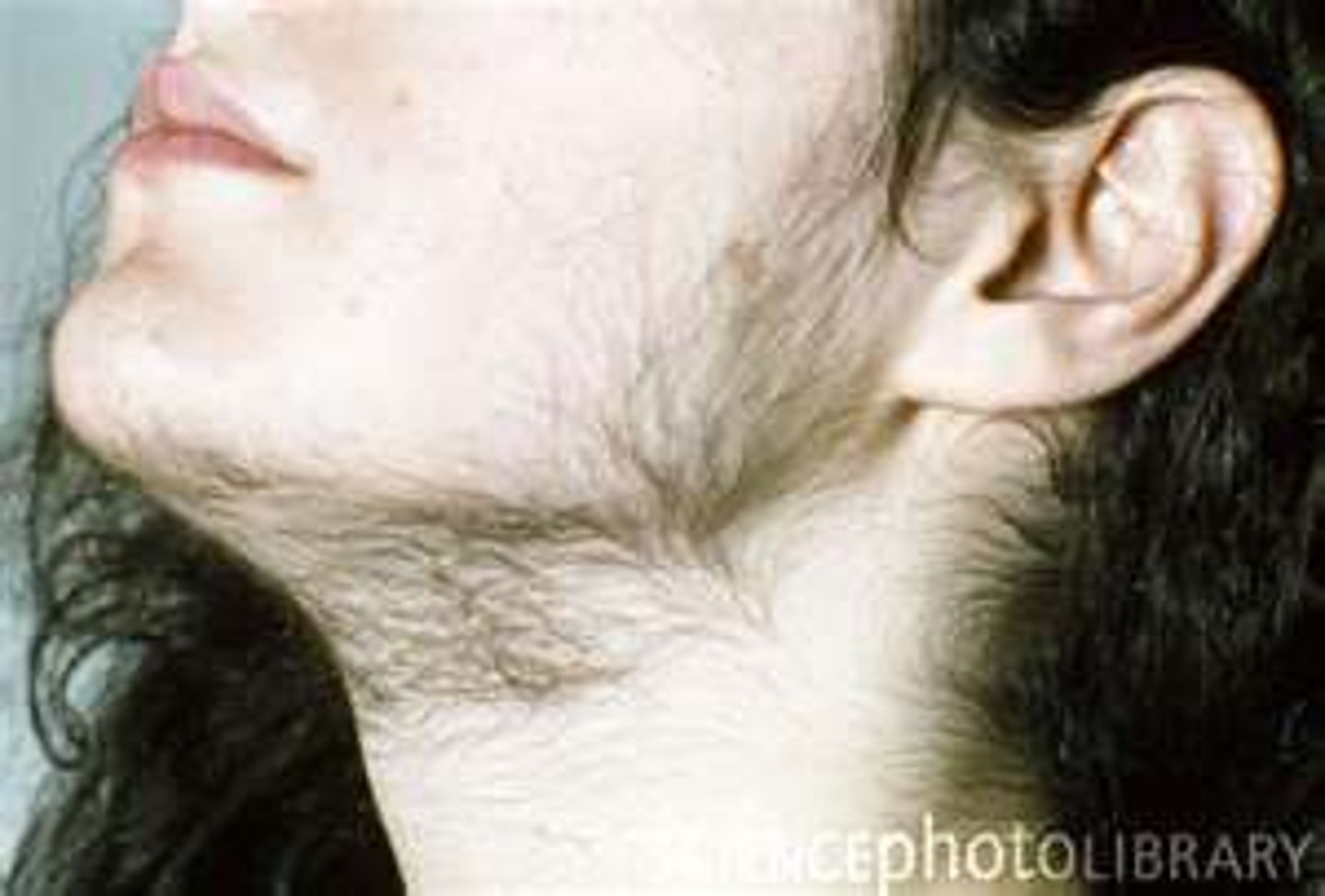
hirsutism
Condition pertaining to an excessive growth or cover of hair, especially in women. in unusual locations
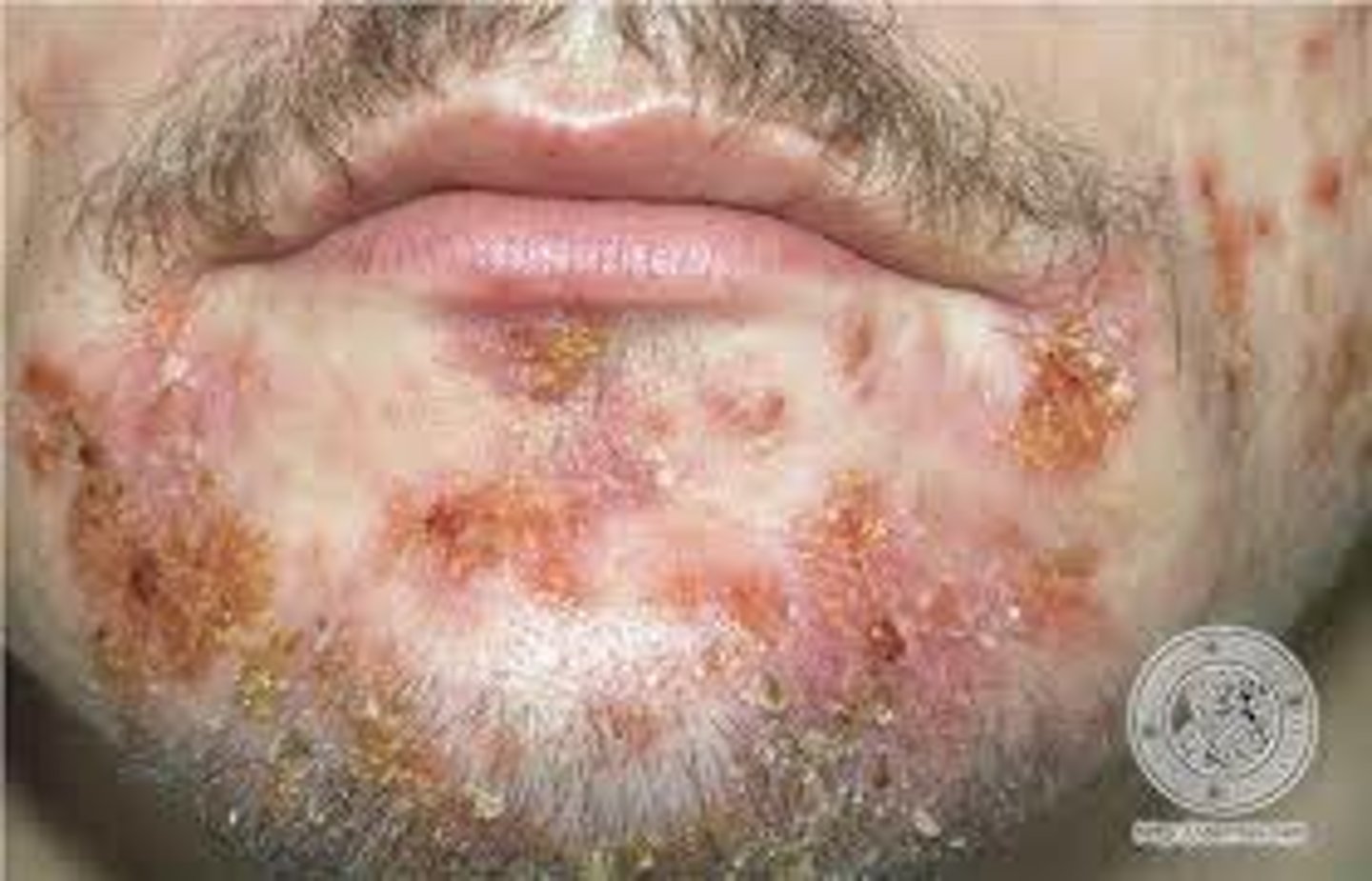
impetigo
bacterial skin infection characterized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture
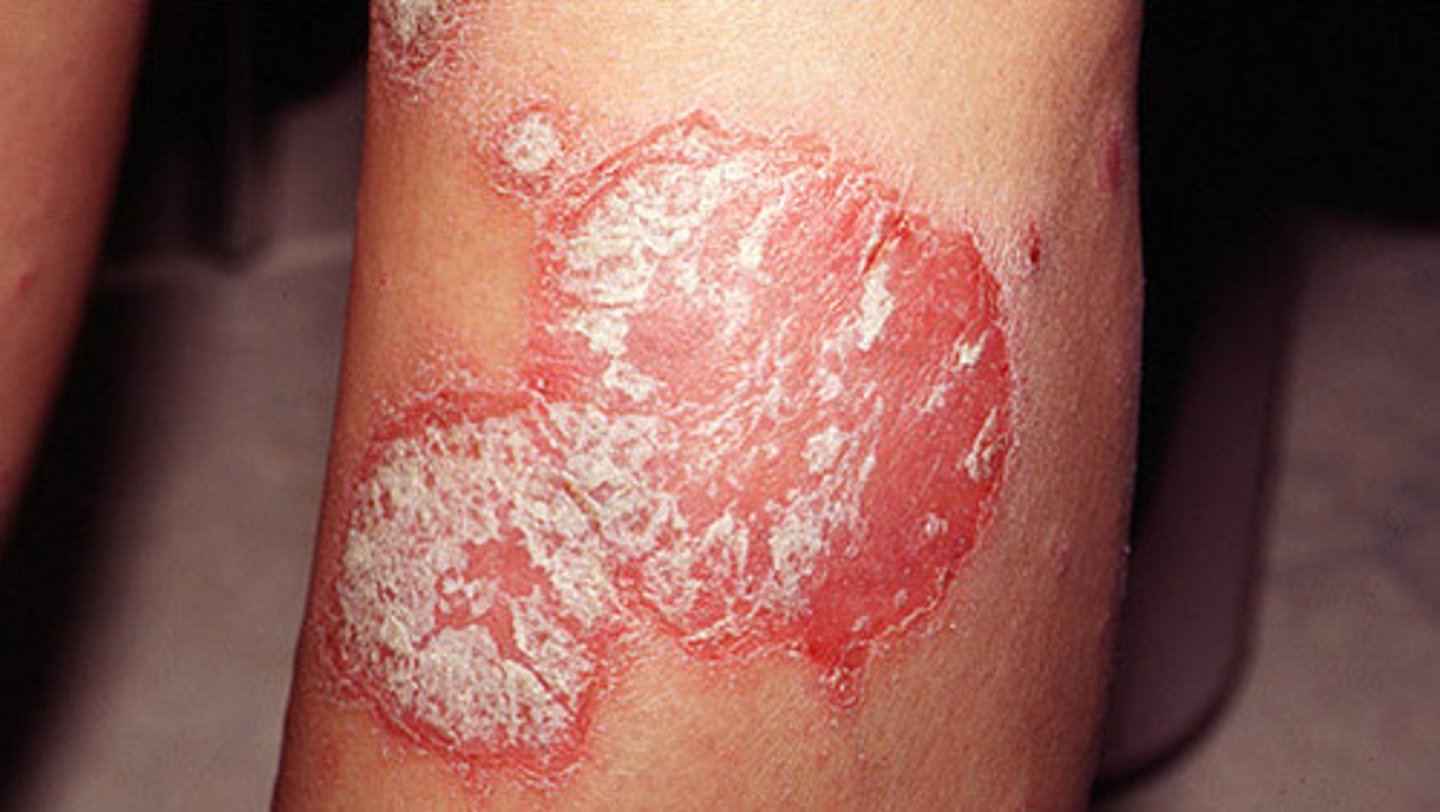
psoriasis
chronic skin condition producing red lesions covered with silvery scales
Scabies
contagious skin disease transmitted by the itch mite
skin lesions
areas of pathologically altered tissue caused by disease, injury or a wound due to external factors or internal disease
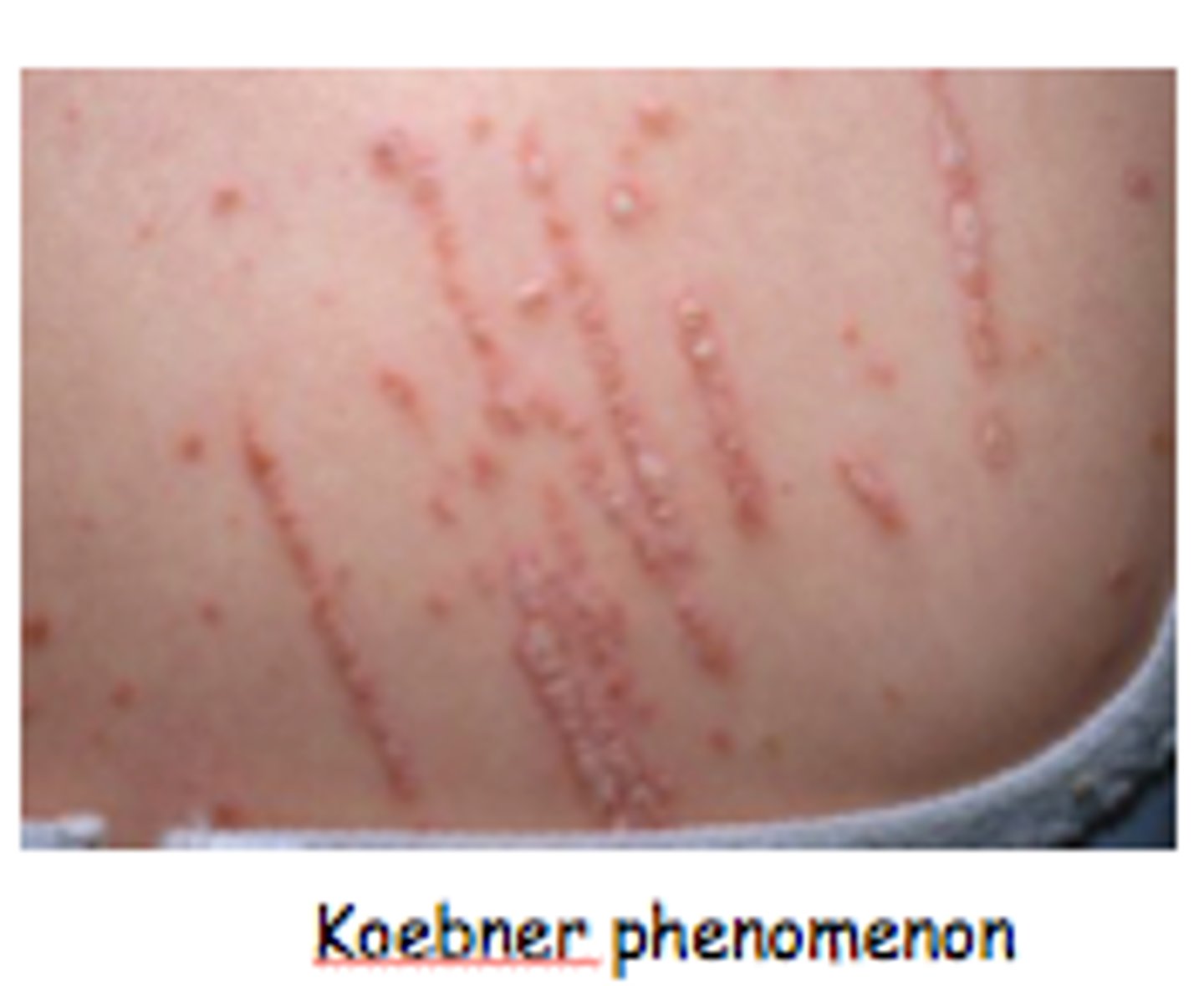
primary lesion
initial reaction to pathologically altered tissue that may be flat or elevated
secondary lesions
result from the changes that take place in the primary lesion due to infection, scratching, trauma, or various stages of a disease
tinea
fungal infection whose name commonly indicates the boy part affected, also called ringworm
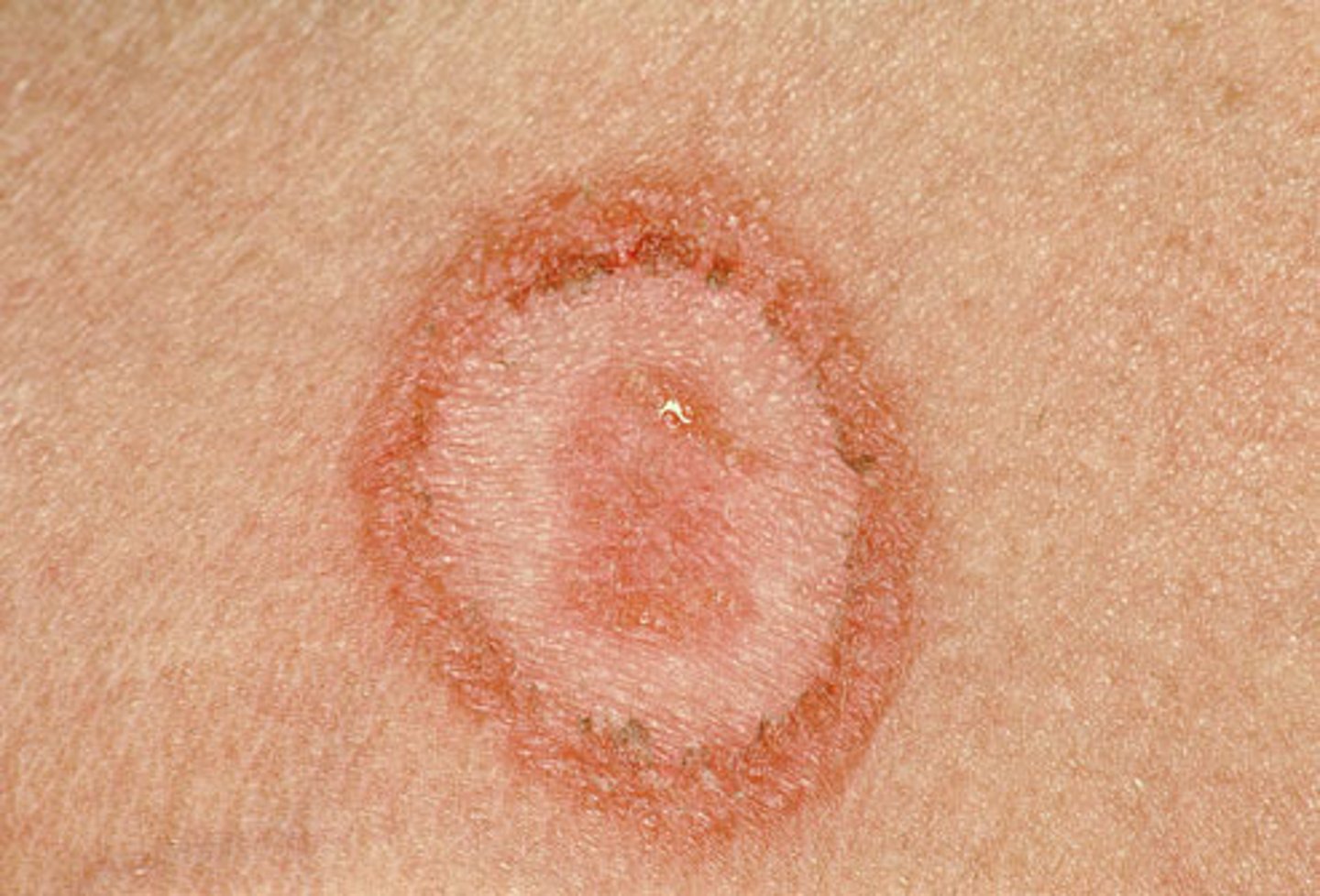
ulcer
lesion of the skin or mucous membranes marked by inflammation, necrosis, and sloughing of damaged tissues
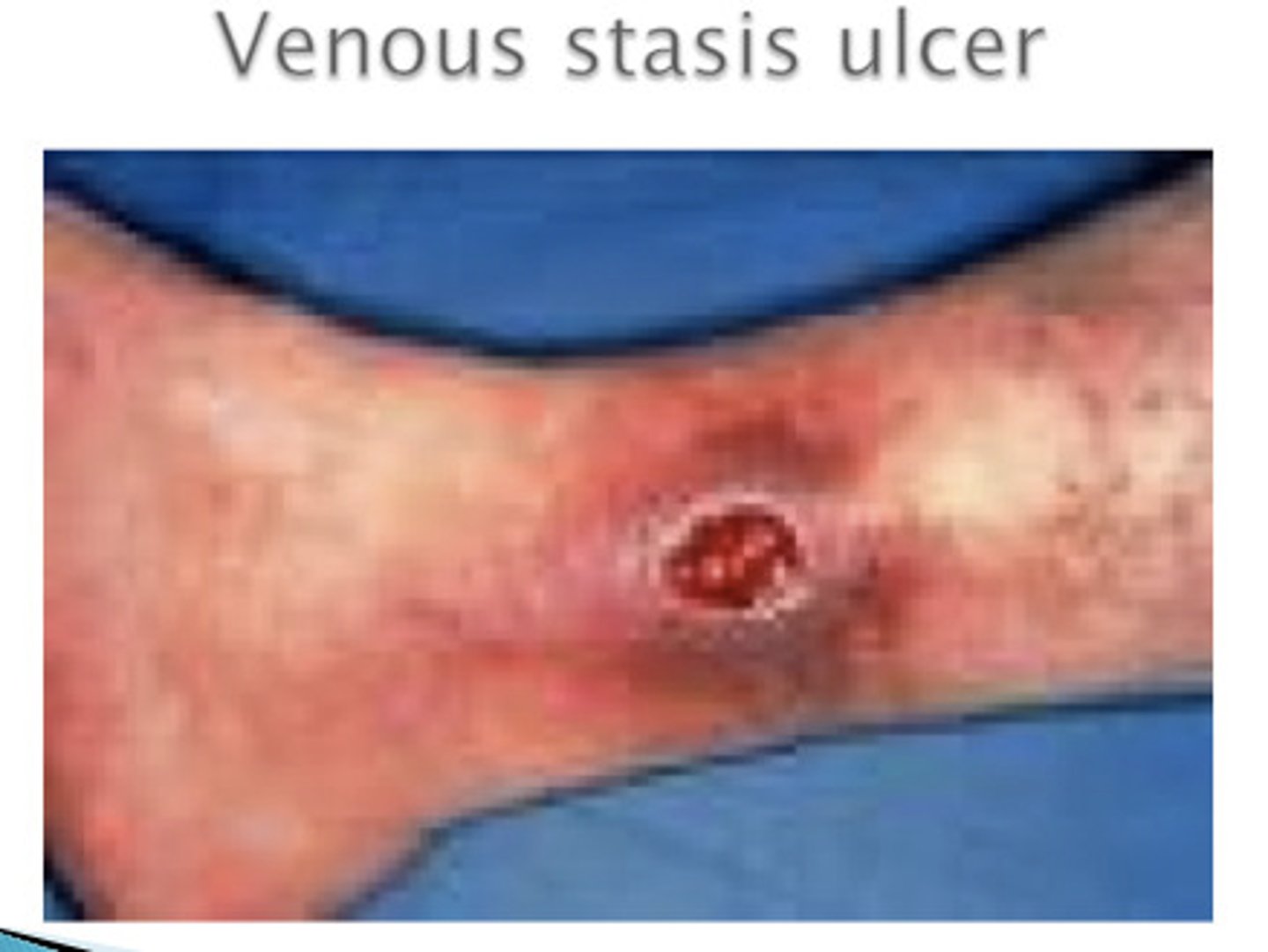
pressure ulcer
caused by prolonged pressure on an area of the body that interferes with circulation
- ex: bed sore
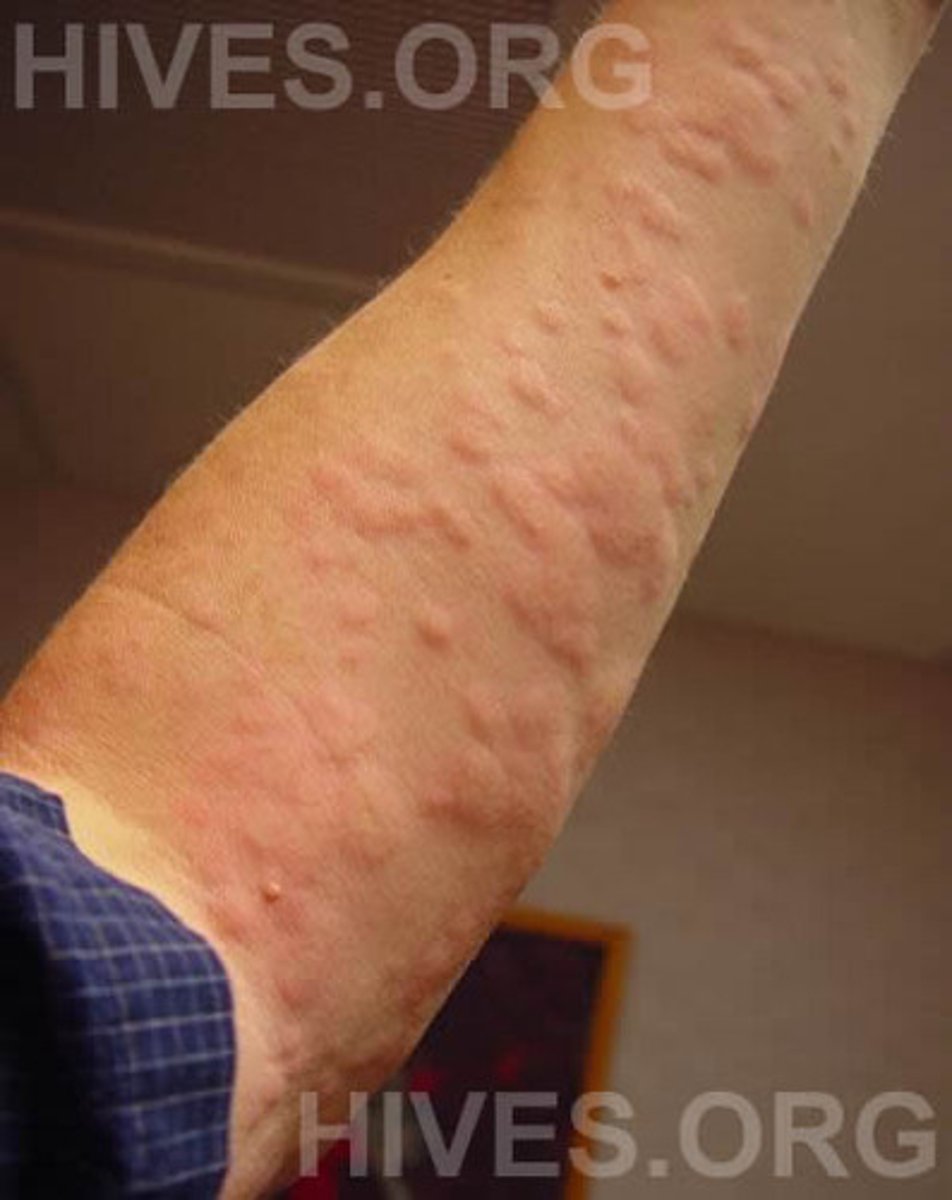
urticaria
allergic reaction of the skin characterized by eruption of pale-red elevated patches that are intensely itchy, also called wheals or hives
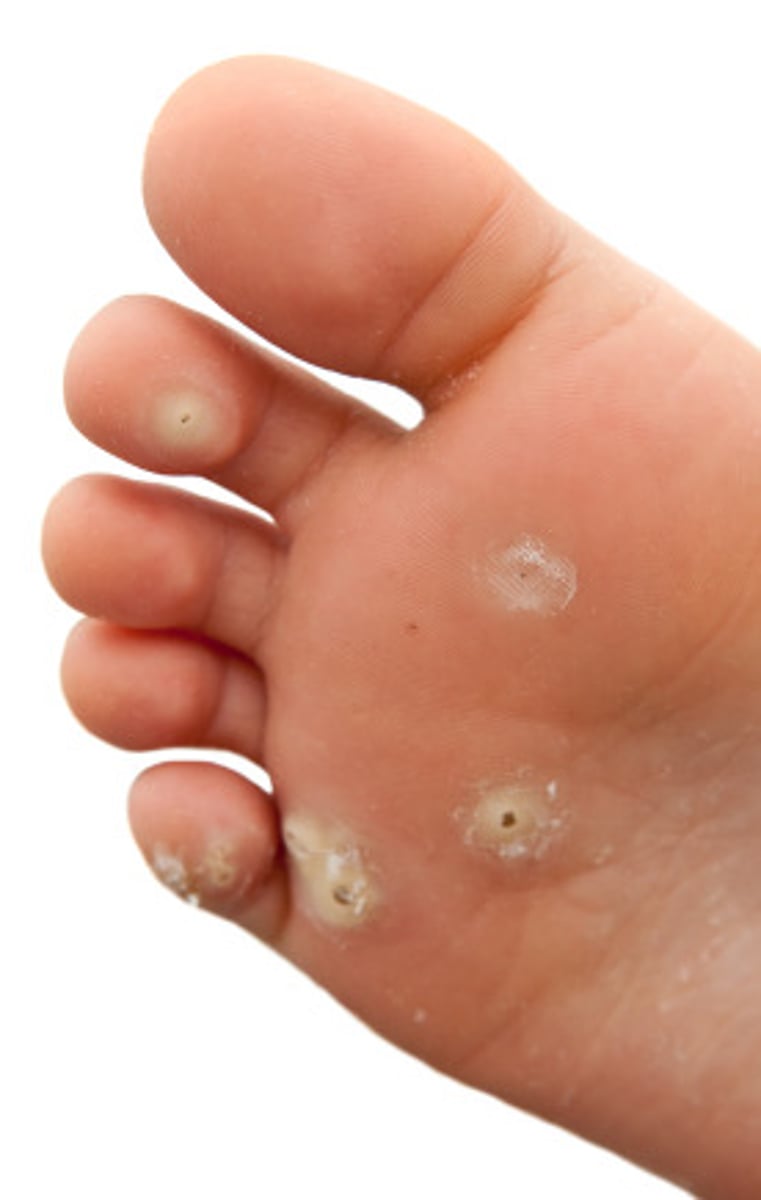
verruca
rounded epidermal growths caused by a virus; also called wart
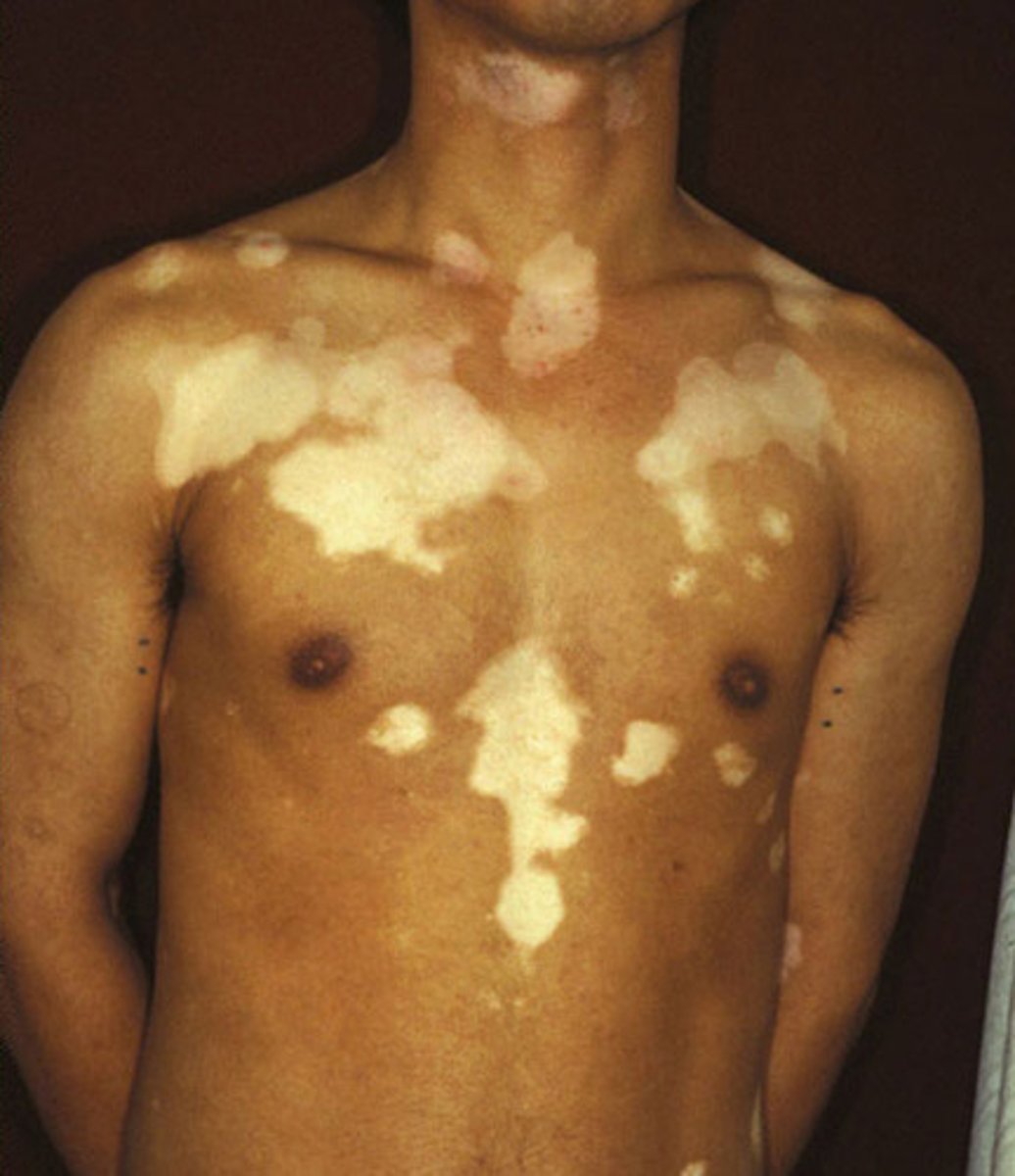
vitiligo
localized loss of skin pigmentation characterized by milk-white patches
- also called leukoderma
skin test
diagnostic procedure for determining allergies by applying inoculating or suspected allergern or sensitizer into the skin and determining sensitivity (allergry) to the speicifc antigen by an infalmmatory skin reaction to it.
- ex: scratch tests or intradermal (little bumps raised on arm)