Structure, electronic effects, bonding and moles
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the pKa value?
Negative log10 of Ka
The smaller the value of pKa…
…the stronger (more likely to lose H+) the conjugate acid is in the equilibrium, and the weaker (less likely to gain H+) is the conjugate base.
Does the pKa value refer to an equilibrium or a substance?
Equilibrium
For acidic compounds, the pKa for dissociation into a proton and the conjugate base will depend on factors which what?
Lower the energy of the anionic conjugate base, for example, factors which “spread out” the negative charge over several atoms.
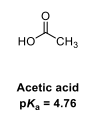
Draw the equilibria for the ionisation of this acid
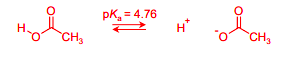
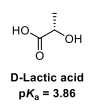
Draw the equilibria for the ionisation of this acid
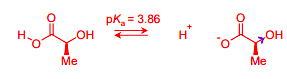
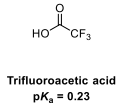
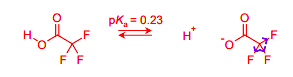
Draw the equilibria for the ionisation of this acid
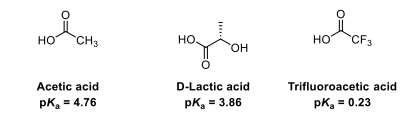
Explain the differences between the pKa values
In acetic acid, the energy of the COO- anion is lowered by the delocalisation of the negative charge across both oxygens
In D-lactic acid, the energy of the COO- anion is lowered by delocalisation of the charge across both oxygens and by the presence of an inductively electron withdrawing oxygen in the OH
In trifluoroacetic acid, the energy of the COO- anion is lowered by delocalisation of the charge across both oxygens and by the presence of three inductively electron withdrawing fluorine atoms
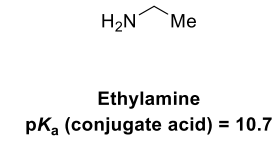
Draw the equilibria for the protonation of this amine base
The pKa of bases refers to the pKa of the conjugate acid. The conjugate acid is NH3. pKa is always acid → base, so the LHS has to have the NH3 one, rather than the base.
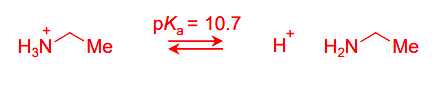
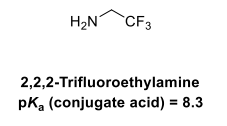
Draw the equilibria for the protonation of this amine base
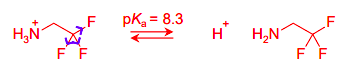
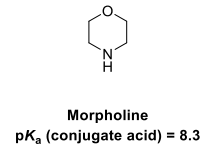
Draw the equilibria for the protonation of this amine base
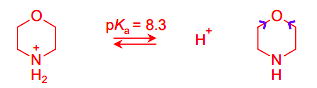
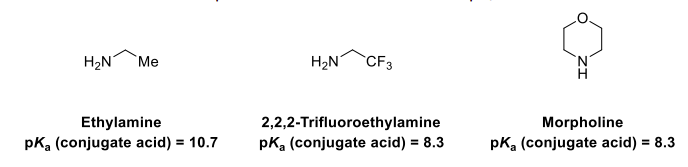
Explain the differences between the pKa values
In 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine, the energy of the cation (conj acid) is raised by the inductive effect of the 3 F withdrawing electron density from the cationic nitrogen
The energy of the cation (conj acid) is raised by the inductive effect of the oxygen withdrawing electron density from the cationic nitrogen