Chapter 4: Carbon and Molecular Diversity of Life
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Stanley Miller's experiments were significant because he demonstrated that __________.
a variety of simple organic compounds could be spontaneously synthesized from components in Earth's primitive atmosphere
Biologically important chemical groups include all of the following except __________.
water (H2O)
Which of the following are properties of hydrocarbons?
Hydrophobic, nonpolar, and a good source of stored energy
Pharmaceutical companies are selling close to $200 billion worth of single-enantiomer drugs. Why might it be important to use only one form of an enantiomer?
One enantiomer may provide an effective treatment whereas the other may be ineffective or even toxic.
When a double bond joins two carbon atoms, __________ can form.
cis-trans isomers
What are the six most important chemical elements of life?
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphate, and sulfur
Structural isomers have __________.
the same molecular formula but different covalent arrangements of their carbon skeletons
Although the structures of the functional groups that are most important to life vary, they share one thing in common: They __________.
all help give each biological molecule its unique properties
Choose the pair of terms that completes this sentence about functional groups in organic chemistry: Carboxyl is to __________ as __________ is to base.
acid; amino
Which element is always associated with organic chemistry?
Carbon
What is ATP's importance in the cell?
ATP stores the potential to react with water, thereby removing a phosphate group and releasing energy for cellular processes.
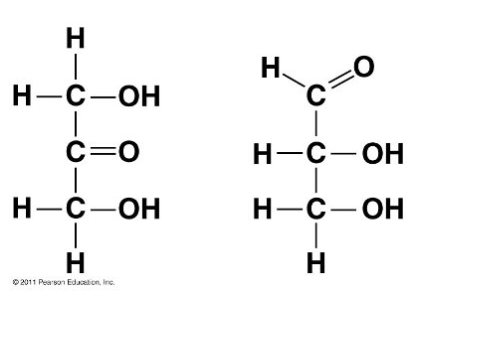
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between these two sugar molecules:
Structural isomers
Which of the following molecules is a weak acid?
R-COOH
Inorganic carbon such as CO2 differs from organic carbon because __________.
organic carbon always has a hydrogen atom covalently attached to it
Molecules that contain only carbon and hydrogen are __________.
called hydrocarbons
The carbon atom is tetravalent; this means that __________.
a carbon atom can complete its valence shell by forming four covalent bonds
In the pharmaceutical industry, two enantiomers of a drug __________.
may not be equally effective
The carbon skeleton can vary in all of the following except __________.
lacking hydrogen atoms
In Miller’s 1953 laboratory experiment, __________.
abiotic compounds cycled through the apparatus and were sampled for organic compounds
Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
Amino
The chemical group that helps stabilize protein structure is the __________.
sulfhydryl group (-SH)
Chemical groups are significant because __________.
they contribute to the molecular shape of a molecule and its unique properties
Enantiomers are __________.
mirror-image isomers of a molecule
Carbon’s atomic number is 6. This means that it has __________ electrons. After completing the first energy level, carbon has __________ valence electrons and can form __________ bonds.
6; 4; 4
The chemical group that acts as an acid is the __________.
carboxyl group (-COOH)
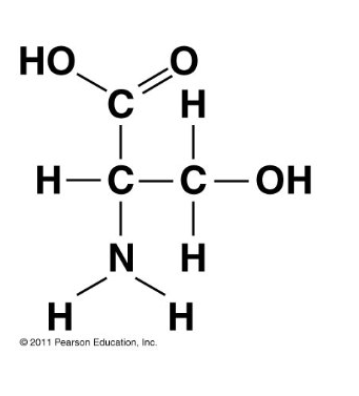
Which functional group is not present in this molecule?
Sulfhydryl
Which of the following is found in all amino acids?
Both -COOH and -NH2
When three phosphate groups are covalently attached to adenosine, __________ is formed.
ATP
The chemical group that is involved in regulating DNA is the __________.
methyl group (-CH3)
Which of the following molecules is a weak base?
R-NH2
________ is the study of compound that contain carbon
Organic chemistry
Stanley Miller’s classic experiment_________________
demonstrated the abiotic synthesis of organic compounds
Major elements of life
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur
_____________________ determines the kinds and number of bonds an atom will form with other atoms
The number of unpaired electrons in the valence shell of an atom is generally equal to its ______.
Four ways that carbon skeletons can vary?
1: Carbon Skeletons vary in length
2: Skeletons may be unbranched or branched
3: The skeleton may have double bonds, which can vary in location
4: Some carbon skeletons are arranged in rings
_______________ are organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that _________
release a large amount of energy
________ are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
Isomers
What are the different type of Isomers?
Structural isomers, Cis-trans isomers, and Enantiomers
Structural isomers
Have different covalent arrangements of their atoms
Cis-trans Isomers ( also called geometric isomers)
Have the same covalent bonds but differ in their spatial arrangements
Enantiomers
Are isomers that are mirror images of each other
Two enantiomers of a drug ________
may have different effects
Distinctive properties or organic molecules depend on what?
The carbon skeleton and the chemical groups attached to it
__________ are the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
Functional groups
What gives each molecule their own unique properties?
The number and arrangement of functions groups
The seven most important functional group
1: Hydroxyl group
2: Carbonyl group
3: Carboxyl group
4: Amino group
5:Sulfhydryl group
6:Phosphate group
7:Methyl group