Magnesium and Sulfur
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
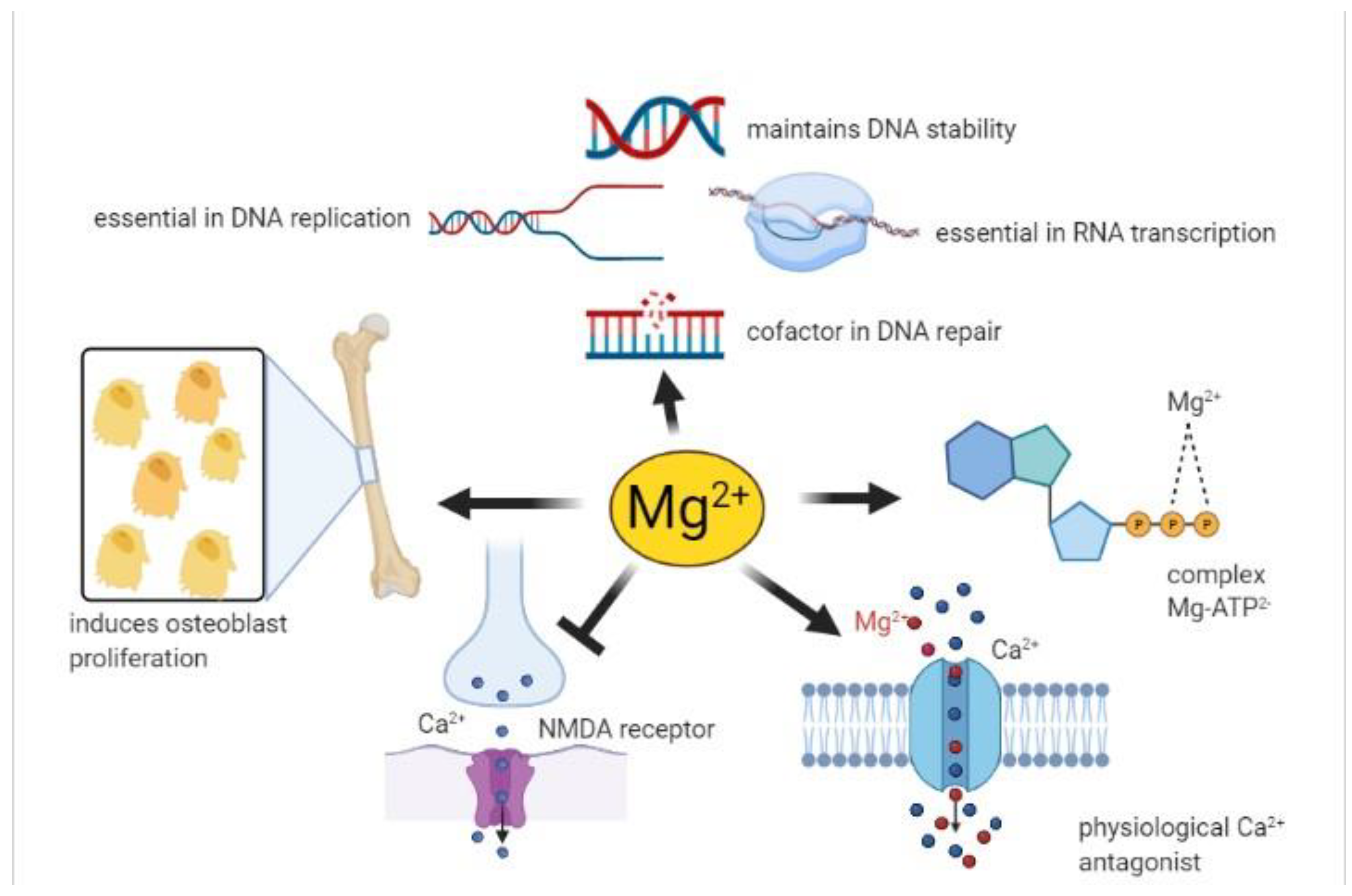
Magnesium is involved in what functions?
Bone, oxidative phosphorylation, enzyme activator (involve phosphatases, ATP)
Where can sources of magnesium be found?
Grasses such as alfalfa
Animal protein supplements
MgO (55%)
Grains (low in Mg)
Half of body Mg is found where?
In the bone
Magnesium can be found in cells where?
Liver cells
Skeletal muscle
RBC
Where is magnesium absorbed?
Absorbed passively primarily in the ileum
A great percentage of Mg is excreted via _______.
Urine
What are the signs of a magnesium deficiency?
Hyperirritability, muscle twitching, weak and crooked eggs, tetany, mitochondrial swelling, reduced enzyme activity, necrosis of kidney, death
What occurs when there is a toxicity of magnesium?
Decreases acetylcholine, drops blood pressure, stops the heart while in diastole, excess Mg interferes with Ca and P

Why does magnesium cause a decrease in acetylcholine?
Excess magnesium paralyzes skeletal muscles by competing with calcium on the presynaptic membrane and inhibits calcium-dependent acetylcholine release
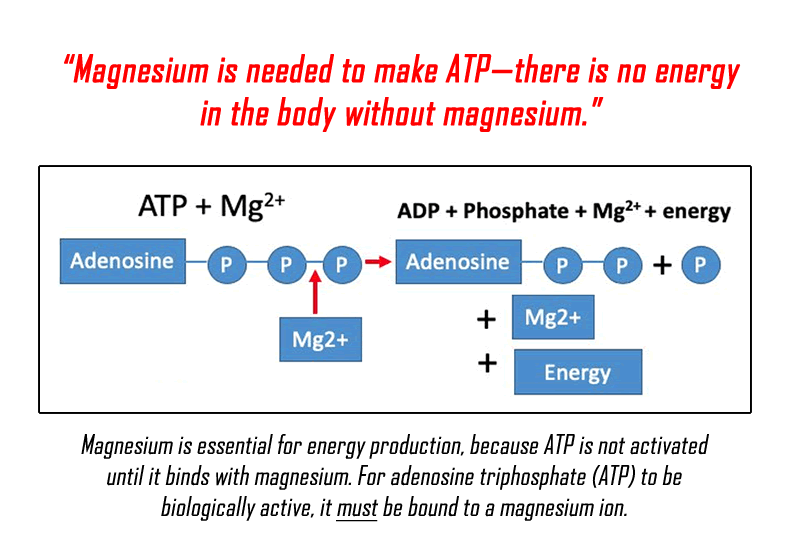
Magnesium in the _______ involved in phosphate transfer reactions
Co-factor
Magnesium chelates with what to form insoluble magnesium-phytate salt
Phytate
About _____ of the magnesium body supply is in the skeleton
70%
What percent of magnesium is distributed in body fluids/tissues?
30%
How much magnesium is found in blood?
2-3 mg/100 mL
How much skeletal magnesium can be mobilized to blood in case of reduction in dietary supply?
1/3
Magnesium helps with bone _______.
Formation
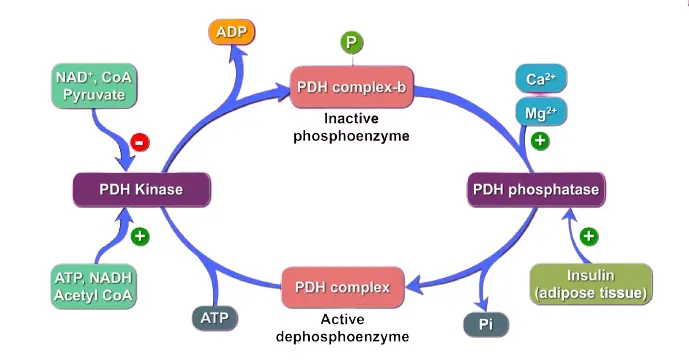
Magnesium is a cofactor used to change pyruvate to what during cellular respiration?
Acetyl CoA
Magnesium helps to _______ nerve irritability (similar to calcium)
Decrease
Where does absorption of magnesium occur in ruminants v.s. Non-ruminants?
Non-ruminants: Ileum of small intestine
Ruminants: Rumen
Soluble magnesium salts use what mechanism during absorption?
Active transport
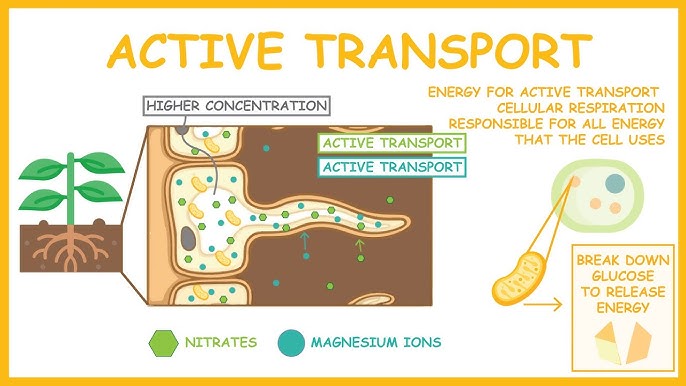
High levels of ammonia (NH3) (from grazing lush spring grass) can _______ absorption of magnesium.
Dcrease
A ____ level of ammonia is favored for magnesium absorption.
Low
High nitrogen amounts in blood will ______ urinary magnesium excretion, while high potassium _______ absorption.
Increase; Decreases
Grass tetany is characterized by what 5 things?
low Mg levels in blood
Nervousness
Loss of appetite
Trembling (titanic muscle spasms)
Convulsions, coma, death
When does grass tetany occur and in who?
Occurs in cows and ewes who are turned out on lush pasture in the spring
Grass tetany is also known as:
Hypomagnesemia
How do you cure a magnesium deficiency?
IV Ca and Mg-gluconate
Feeding/supplying Mg
A magnesium deficiency in swine showed stepping syndrome. What is this?
The pig steps continuously while standing. Weakness of patterns was apparent. Due to neuromuscular hyperexcitability. Calcium will not properly be blocked, leading to overactive muscle contractions.
magnesium deficiency in lambs illustrated _________, causing stiff legs.
Unthriftiness
Convulsive seizure is characterized by what?
Magnesium “tetany”/ deficiency. Animal first illustrates hyperextension then by relaxation to rigidity and opisthotonos.
The body contains what percentage of sulfur?
0.15%
What two amino acids are involved in organic sulfur bonding?
Cystine and methionine
Wool is what percentage of sulfur due to sulfur contains amino acids?
4%
Majority of sulfur found in blood is found where?
In plasma proteins
Free amino acids (CYS and MET)
Sulfur is present in which 2 vitamins?
Thiamine
Biotin
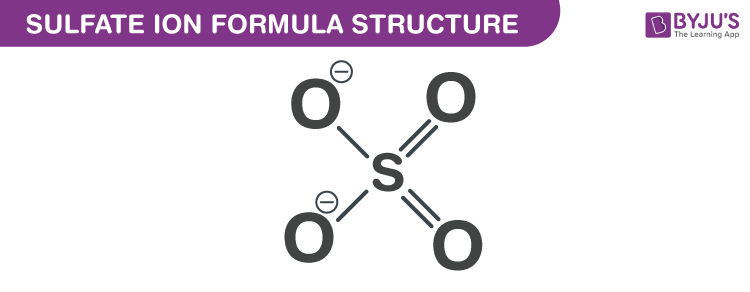
A smalls mount of sulfur is found in what ion?
Inorganic sulfate ion (SO4-)
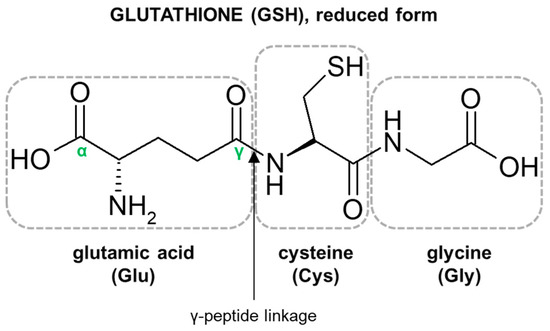
Besides amino acids, what other 2 organic compounds contain sulfur?
Insulin: Hormone that regulates blood sugar)
Glutathione (a reducing agent in metabolism)
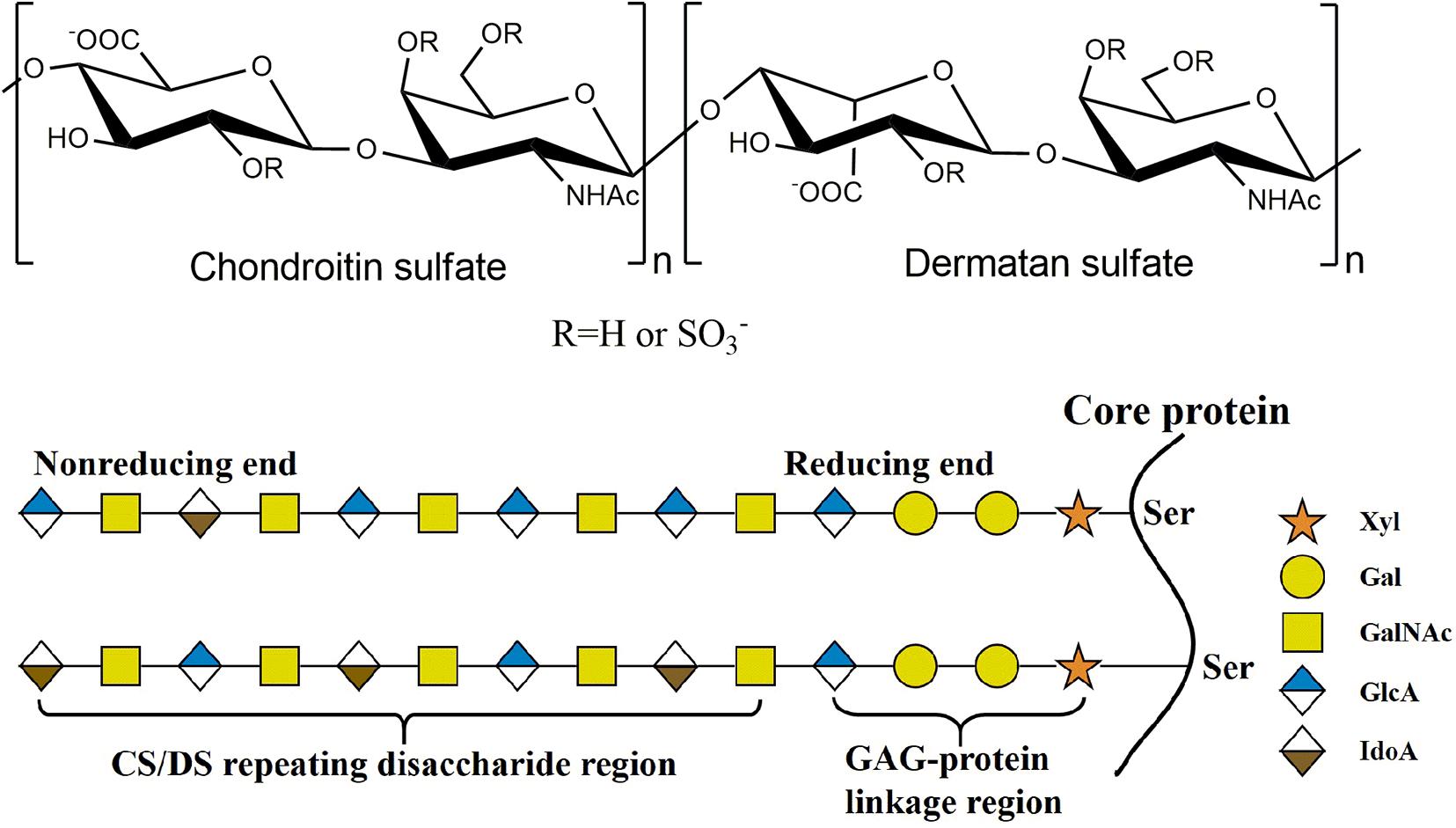
Sulfur is present in chondroitin sulfate. What is this?
A constituent of cartilage
Sulfur nutrition is primarily a matter of _____ ______ nutrition.
Amino acid
Sulfur is typically absorbed in what form?
Absorbed in organic form as cystine and methionine
Some may occu as the sulfate form nd hydrogen sulfide
Where is sulfur absorbed?
Small intestine
What are the two ways sulfur is excreted?
Urine
Feces
What is the form of sulfur that is excreted in feces?
Organic sulfur; amino acids
What is the primary form of sulfur as it is excreted in urine?
Excreted as inorganic sulfate (SO4-). This is the final oxidation product of organic sulfur
What are the 3 forms of sulfur that is exerted in the urine?
Inorganic sulfate (SO4-)
Ethereal sulfur
Neutral Sulfur
Ethereal sulfur is excited in urine. What is this compound present in?
Ethereal sulfur is present in complex detoxification compounds
What 3 neutral sulfur compounds are excreted in urine?
Cystine
Taurine
Thiosulfates
Why do you not have to consider S when feeding natural proteins to ruminants?
Due to the high content of sulfur containing amino acids in their diet
Other sulfur forms in the body can be derived from what?
Amino acid metabolism
In general is sulfur supplemented?
No, sulfur is not considered when supplementing rations
Providing what amino acid provides for the total sulfur needs since most of it is used as amino acids
Methionine (MET)
Additional sulfur will be beneficial for microbial synthesis of sulfur amino acids in what diet and in what species?
NPN (urea) for ruminants