L27-kidney: regulation of water and salt balance
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
where does salt reabsorption occur in the nephron
proximal convoluted tubule
loop of Henle- ascending
collecting duct
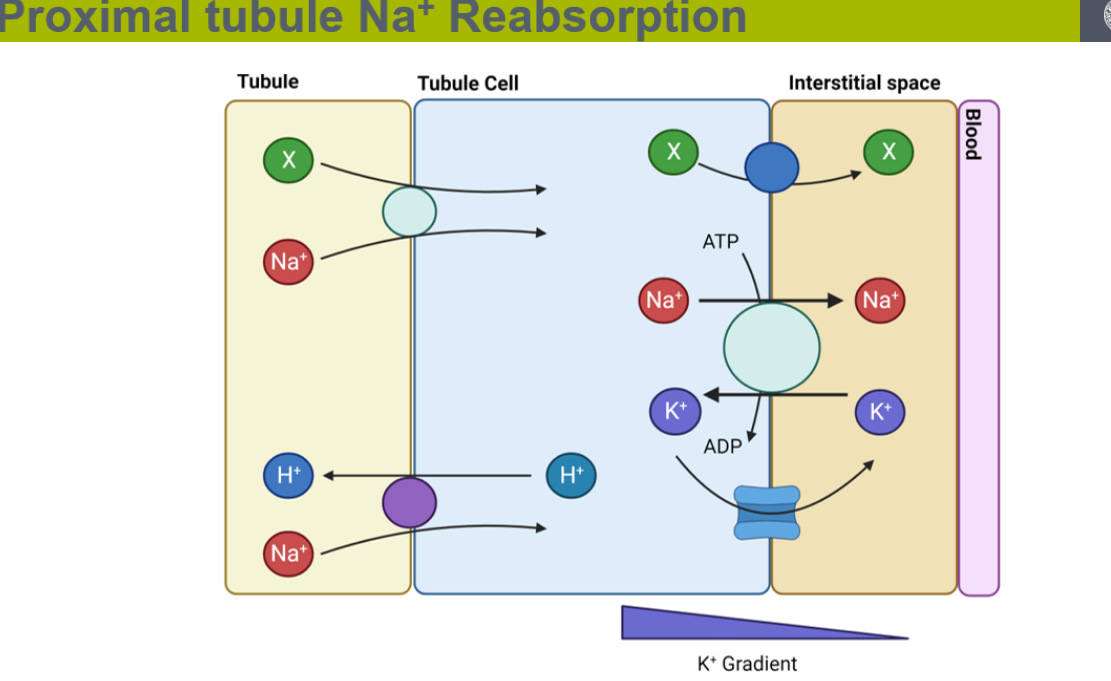
explain how salt reabsorption happens in the proximal convoluted tubules
NA+ is moved from the tubules into the tubule cells through co- transport ( with other molecules like glucose ) and counter- transport ( hydrogen ions retuning into tubule )
once in the tubule cells the sodium ions move into the interstitial space by active transport
the sodium/potassium ATPase pump, pumps sodium into the space and potassium goes back into the cell down a concentration gradient
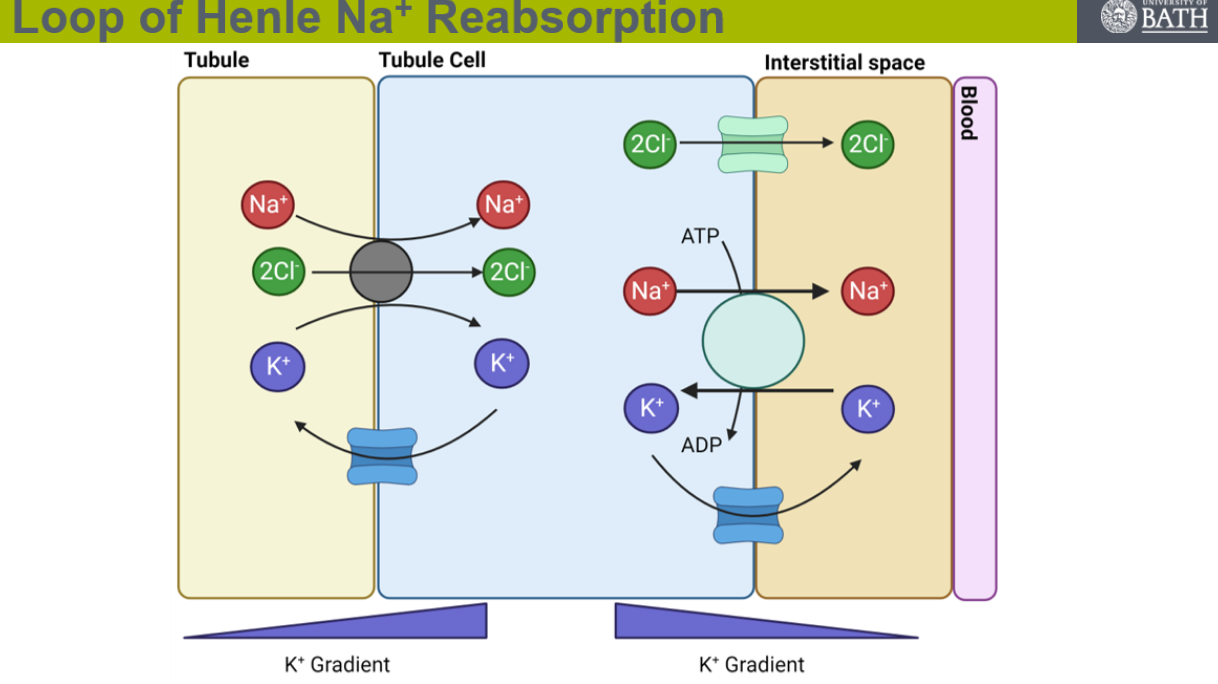
explain salt reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle
the sodium moves from inside the tubules into the cells through co transport with K+ and Cl-
this happens through NA-K-CL cotransporters
potassium moves back into the tubule via ion channels down a concentration gradient
once in the tubule sodium/ potassium ATPase moves the sodium ions out into the interstitial space and the potassium out into the cell down a concentration gradient
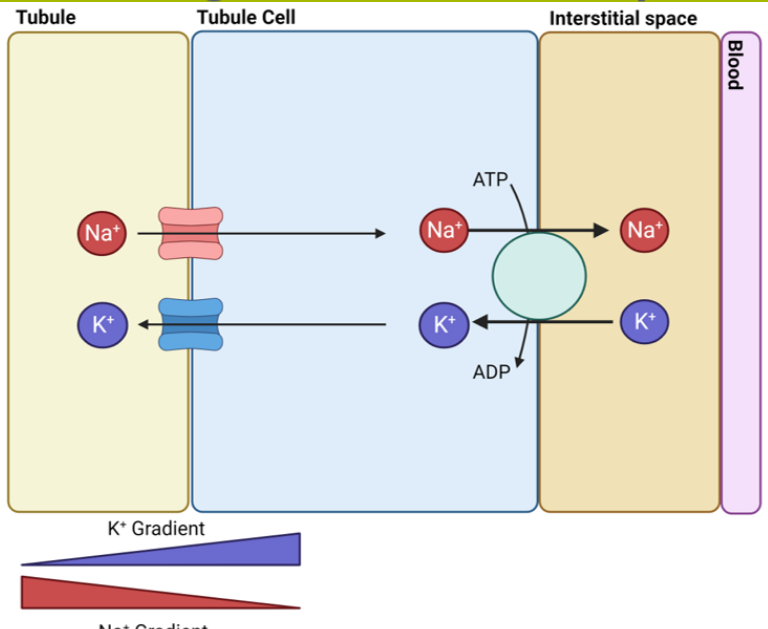
explain how salt reabsorbtion occurs in the colecting duct
between the tubule and the tubule cells there are ion channels one specific for sodium ions and one for potassium ions
the sodium moves into the cell whilst the potassium moves out down a concentration gradient
the sodium/potassium ATPase moves sodium out to the interstitial space and potassium ions back into the cell
what is the function of aldosterone in salt reabsorbption
its a steroid hormone that regulates sodium ion reabsorption and blood pressure
it acts in the collecting duct and tubule cells
it is able to enter the tubule cells from the blood, bind to a receptor ( nuclear receptor) and enter the cell nucleus of the tubule cells
it cause the expression of the ion channels and sodium/potassium ATPase
its effects cause more salt reabsorption but it takes hours for the proteins to be made
where does water reabsorption take place in the nephron
descending loop of Henle
collecting ducts
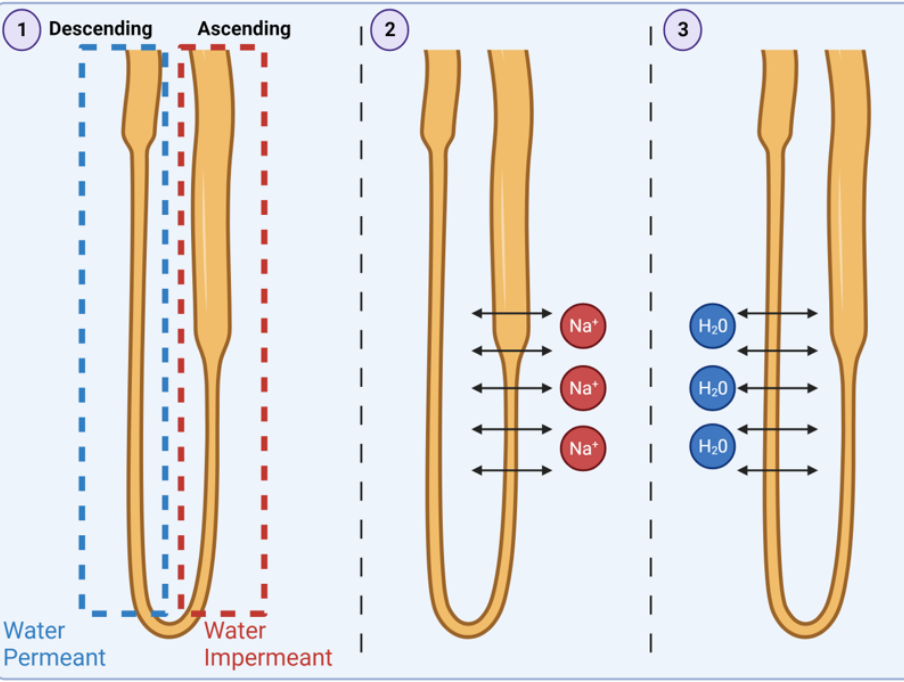
explain how water reabsorption occurs in the descending loop of Henle
only the the descending loop of Henle is permeable to water
as the ascending loop of Henle reabsorbs salts it creates a hypertonic solution in the fluid around the loop
this causes water to diffuse out of the loop in the descending
the blood flow around the loop help drive the water abs option through counter current flow
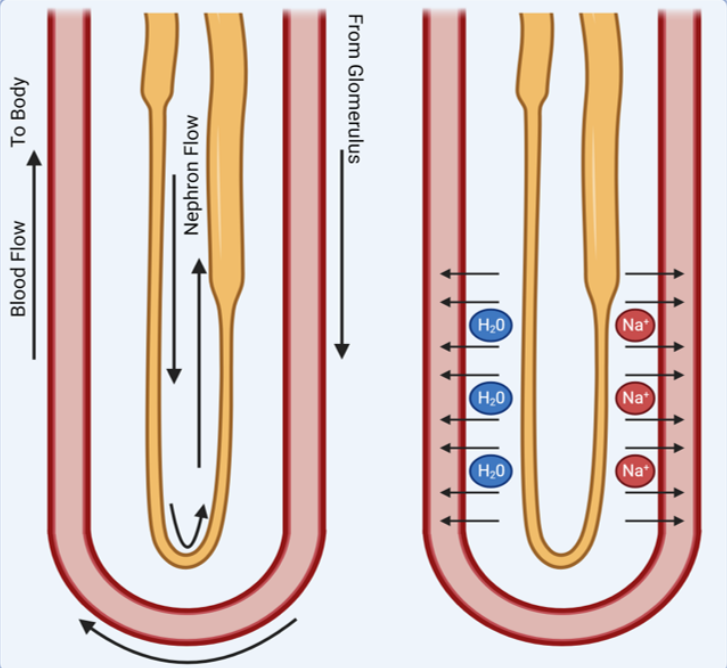
explain counter current flow
freshly filtered blood (low in salt ) first encounters the ascending loop of Henle
which encourages salt reabsorption from a high concentration inside the loop to a low one in the blood
the salt rich blood then circulates around the descending loop and water then moves from high concentration in the loop to a lower one in the blood.
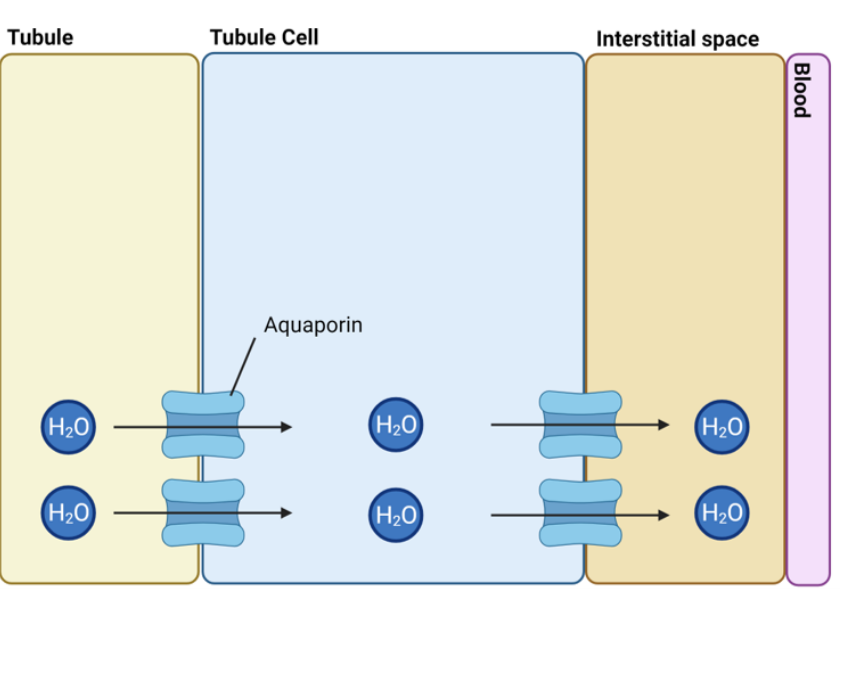
explain how water reabsorption occurs in the collecting duct
the collecting duct tubule contains lots of water channels- aquaporins
as the interstitials space is full of salt from the reabsorption
this allows the water to diffuse down the concentration gradient into the fluid/space through the aquaporins
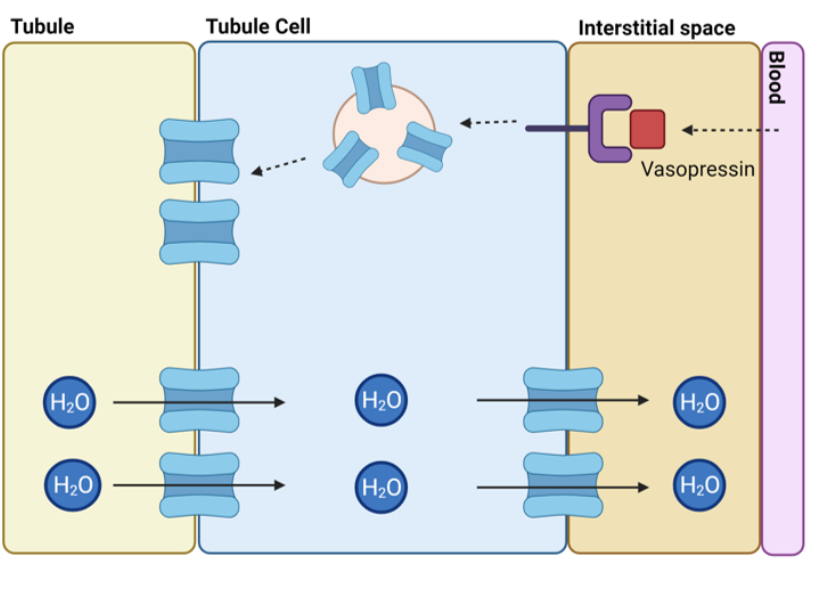
explain the function of vasopressin in water reabsorption
its the hormone that controls water reabsorption
it is released from the blood
it acts on the receptors that’s on the collecting duct cells
it causes aquaporin rich vesicles inside the cells to fuse with the cell membrane
this increases the number of channels water can use to cross
as the channels are already made and just waiitng its a qucik process