Preventive Exam 3 [Periodontal Examination and Clinical Parameters: Spector]
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Always _____ before treating
Diagnose
Proper diagnosis is essential to
efective treatment
Periodontal diagnosis is primarily aimed at determining whether the disease is
present, as well as its severity and extent
An accurate perio diagnosis can provide valuable information pertaining to the
underlying pathologic processes and their causes, which is fundamental to formulating a personalized treatment
From the first interaction, the clinician should attempt to make overall appraisal of the patient. Including consideration of patient's
mental and emotional status, temperament, attitude, and physiologic age.
ex. observation of a patient's gait when walking in the clinic. This observation could provide valuable information on the patient's neurological status and the existence of physical inabilities that could potentially affect the patient's oral hygiene practices
Health history: A thorough health/medical history should be obtained
At the first visit and can be supplemented and updated by questioning on subsequent visits.
Health history: Can be obtained
verbally by questioning the patient and recording his or her responses in the patient's health record or by means of a questionnaire that the patient completes prior to the appointment and then you discuss with the patient.
Health History: The patient should be made aware of the following
1. possible impact of certain systemic diseases, conditions, behavior factors, and medications on periodontal diseases and conditions, their treatment, and treatment outcomes
- Smoking
- Diabetes
2. Certain conditions may require special precautions or modifications of the treatment procedures
- Bad asthema brought on by stress
3. The impact that oral infections may have on systemic health
- Cleared oral infection before major operations
Extraoral and Intraoral Examination
- Temporomandibular joint
- Oral mucosa
- Muscles of mastication
- Lymph nodes
- lips
- Floor of mouth
- Tongue
- Salivary glands
- Palata
- Oropharynx
Dental examination
- Missing teeth and their replacements
- Status of existing restorations
- Caries
- Incisal and occlusal wear
- Pulpal status
Periodontal examination
- Appearance of the tissue
- Presence of plaque/calculus
- Probing depths
- Bleeding on probing (BOP)
- Suppuration
- Position of gingival margin
- Width of keratinized gingiva
- Furcation involvement
- Mobility
- Occlusal interferences
BOLD = Focus on this lecture
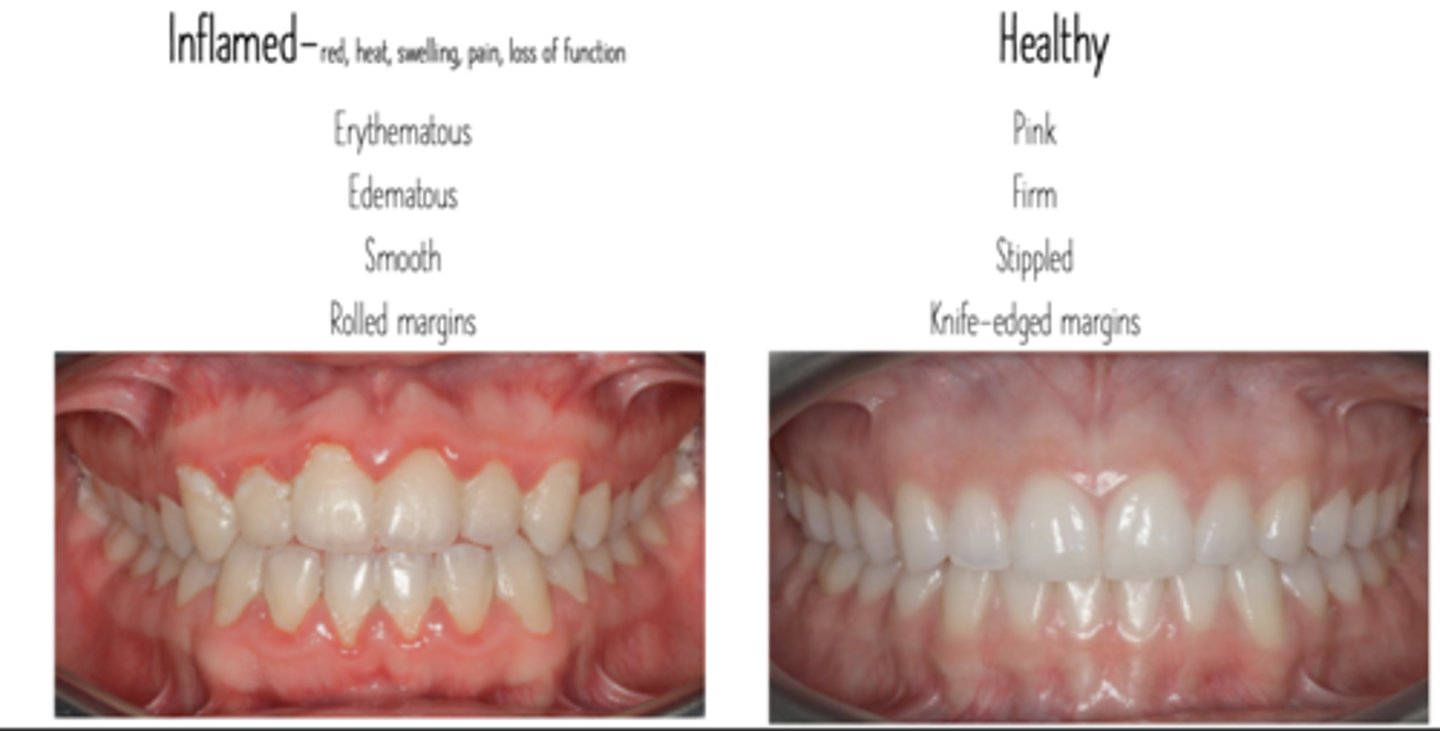
Appearance of the tissue: Clinical signs of inflammation
Red
Heat
Swelling
Pain
Loss of function
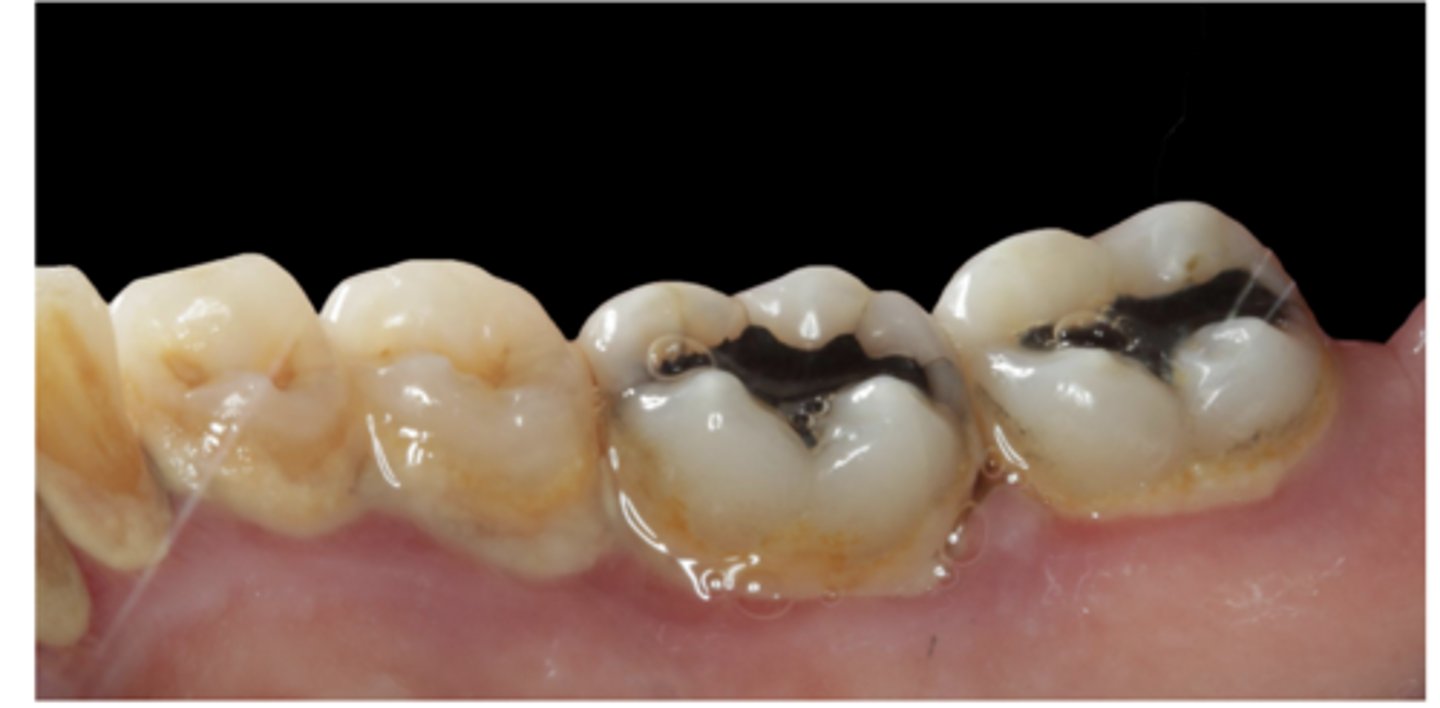
Presence of Plaque and Calculus: Visual examination begins with the ____ of the tissue and taking a survey of ____ and _____ accumulation to assess oral hygine
drying, biofilm, calculus
Probing Depth is the
The distance from the gingival margin to the bottom of the probeable crevice
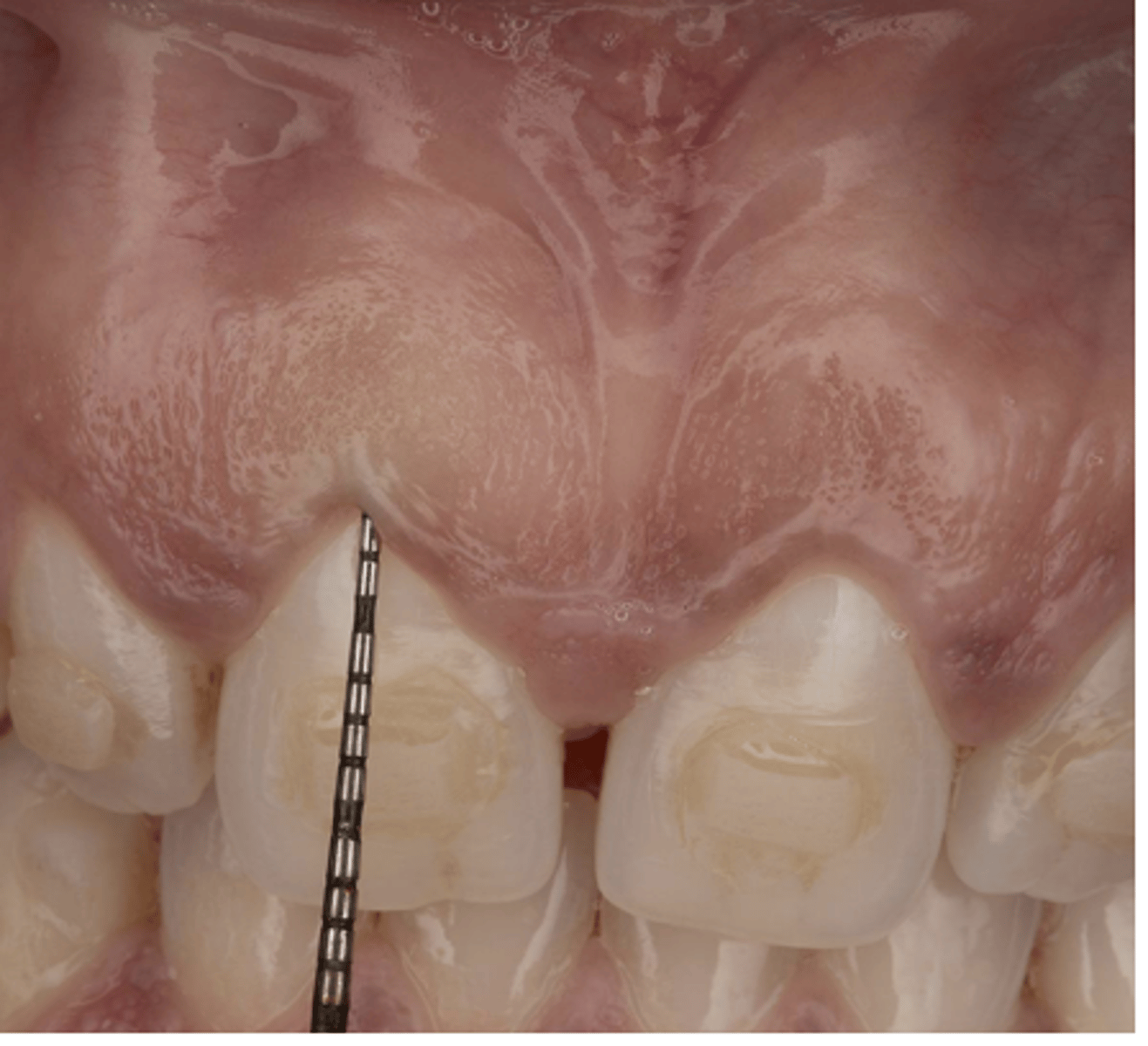
Healthy probe depth =
1-3 mm
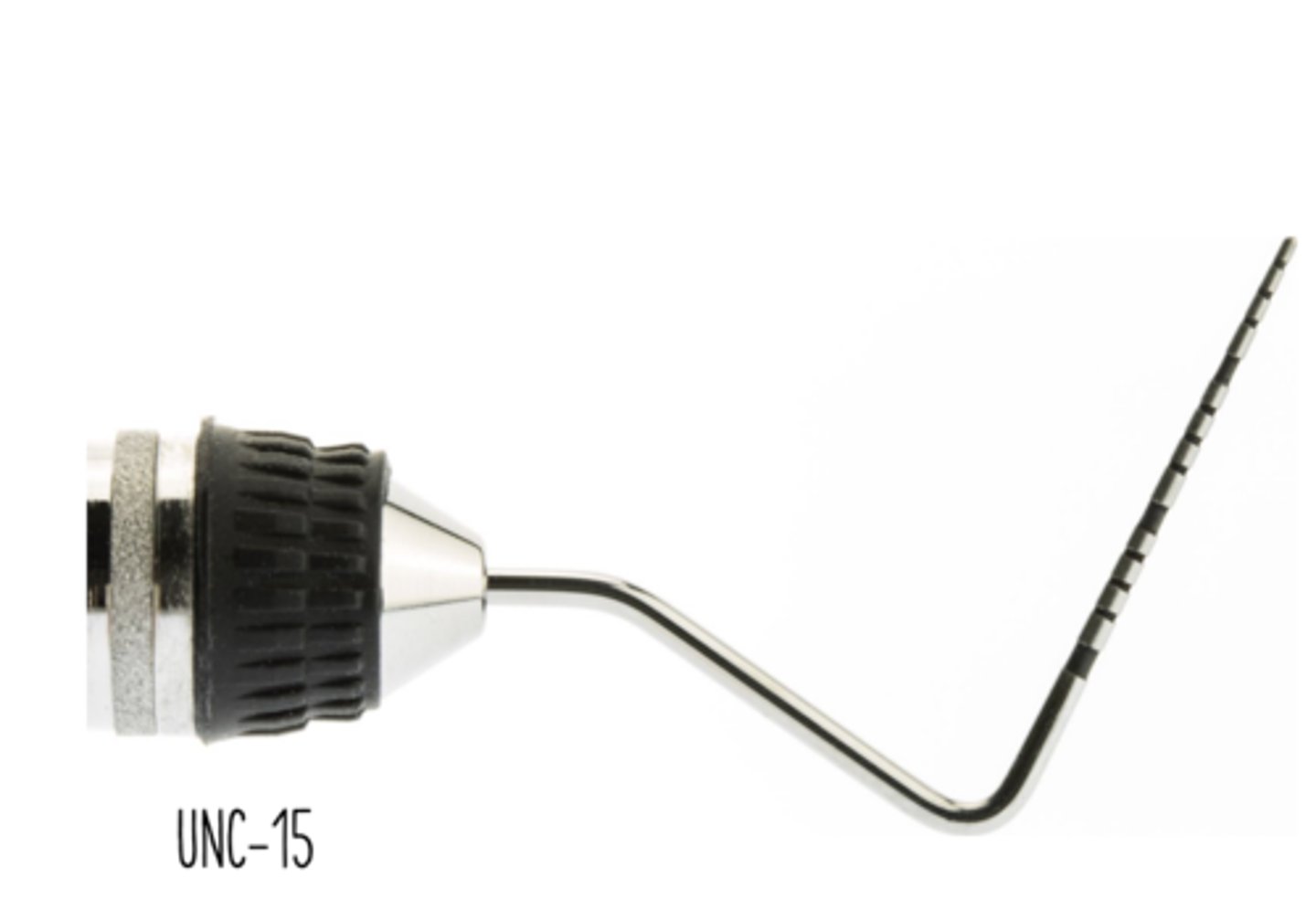
The Periodontal probe we will mostly be using
UNC-15
- 15 bc 15mm

Appearance of the tissue: Phenotype (thin)
Triangular or oval shaped teeth
Highly scalloped gingival margin
Delicate and friable tissue
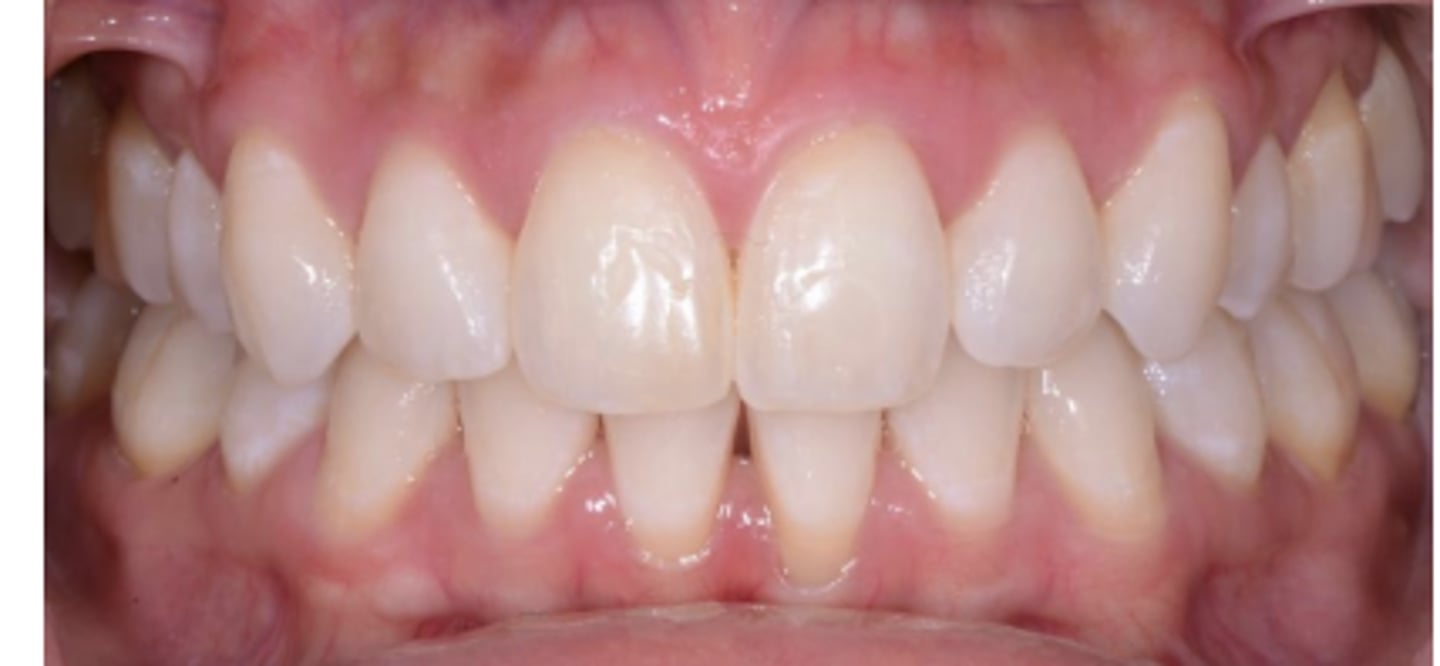
Appearance of the tissue: Phenotype (Thick)
Square-shaped teeth
Flat gingival margin
Dense and fibrotic tissue
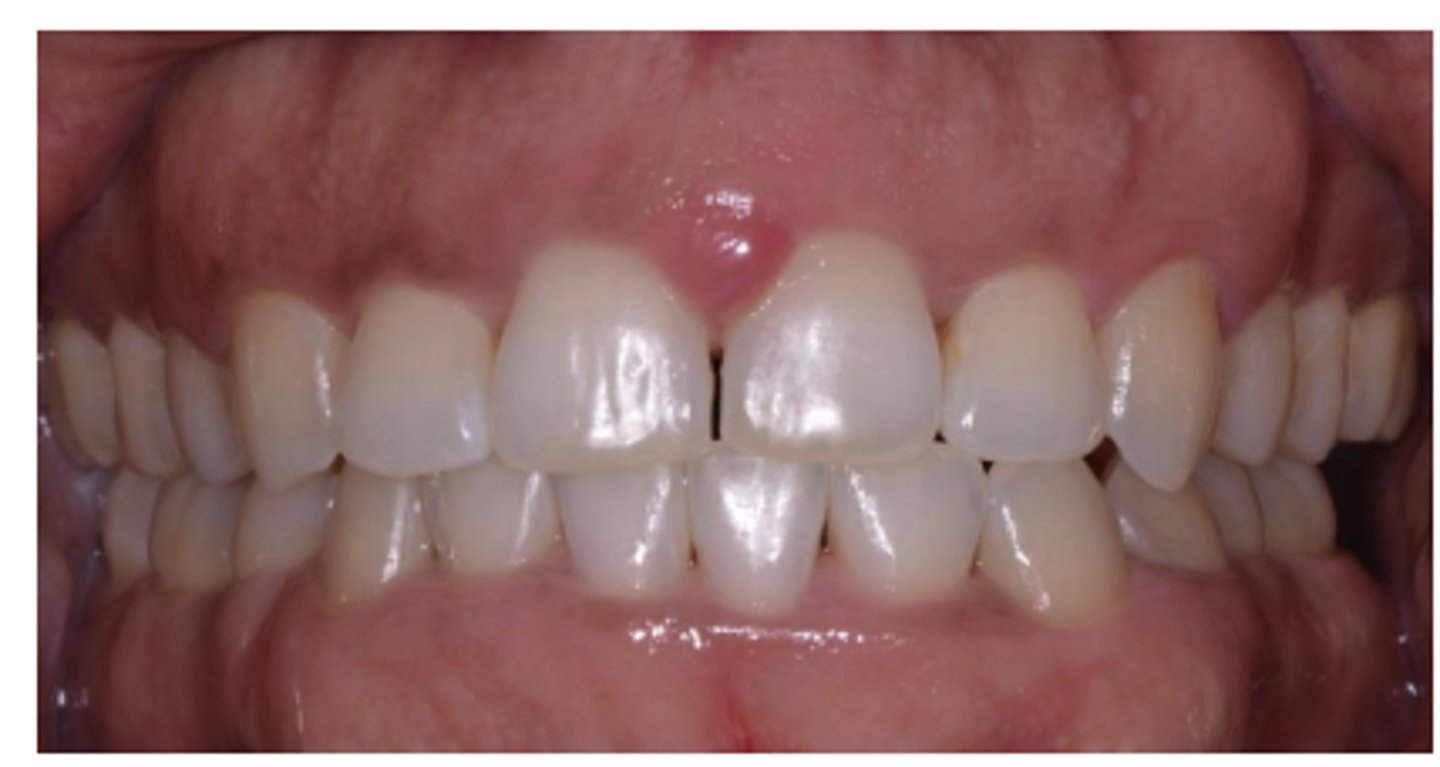
Appearance of the tissue: Phenotype (Comparison)
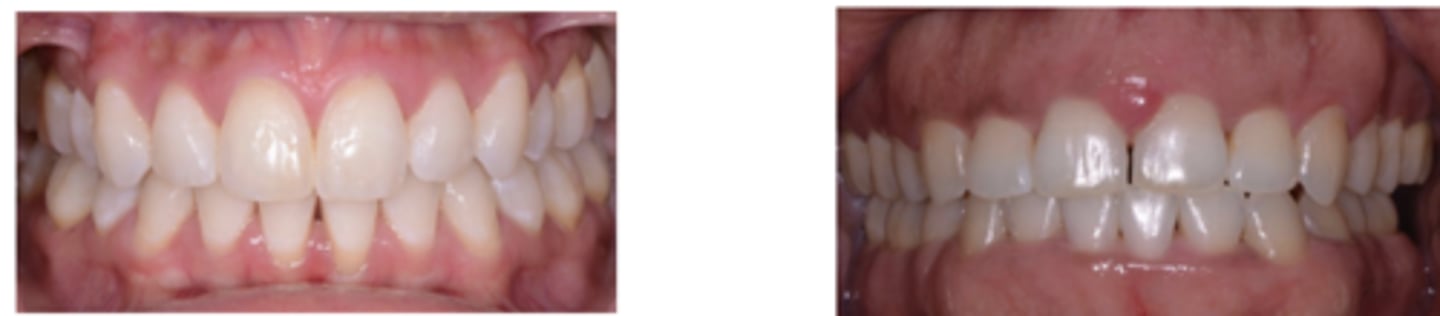
Bleeding on Probing is associated with
inflammatory changes in the marginal gingiva
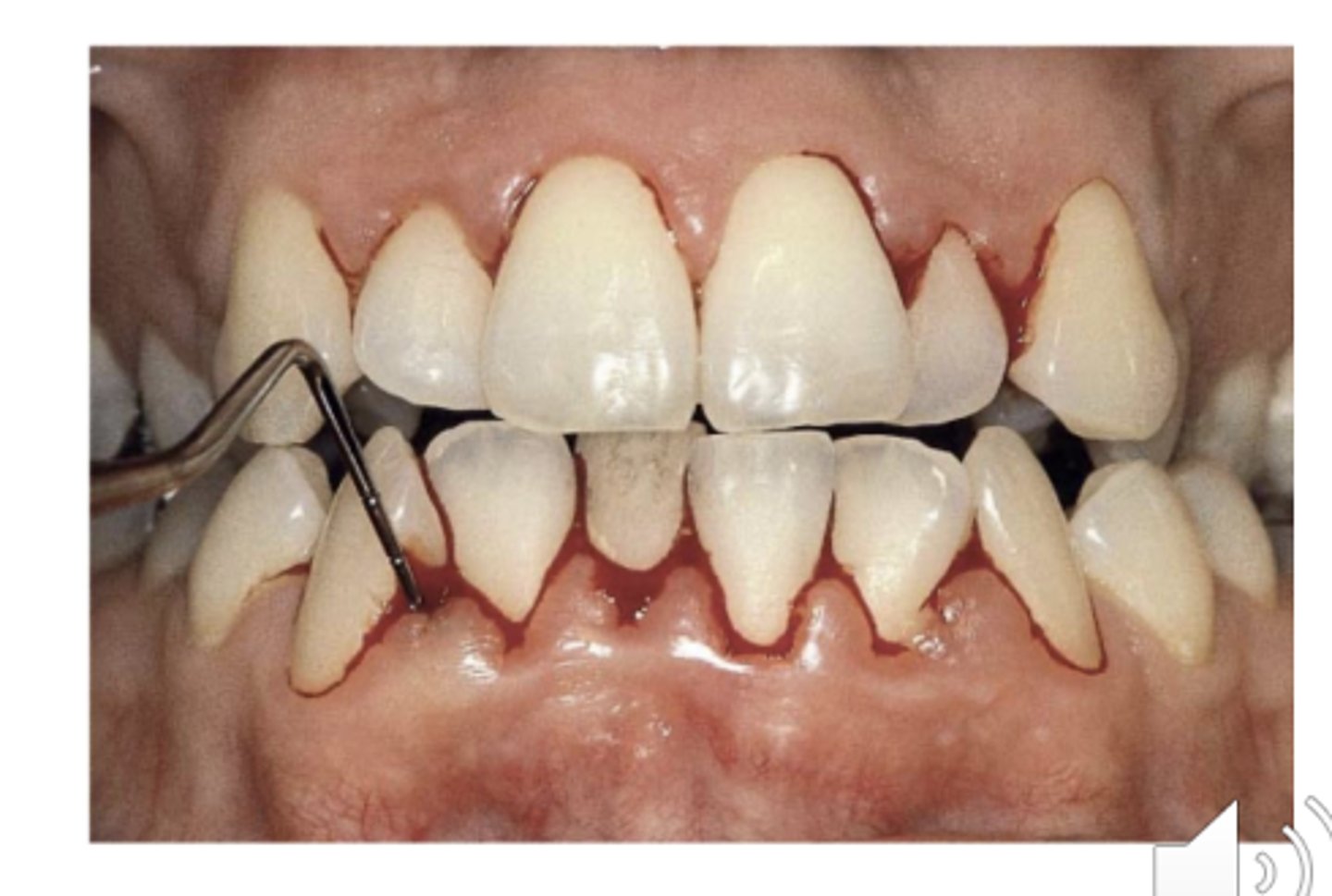
Rule of thumb: If more than 10% of the sites BOP then
it is an -itis (gingivitis or periodontitis)
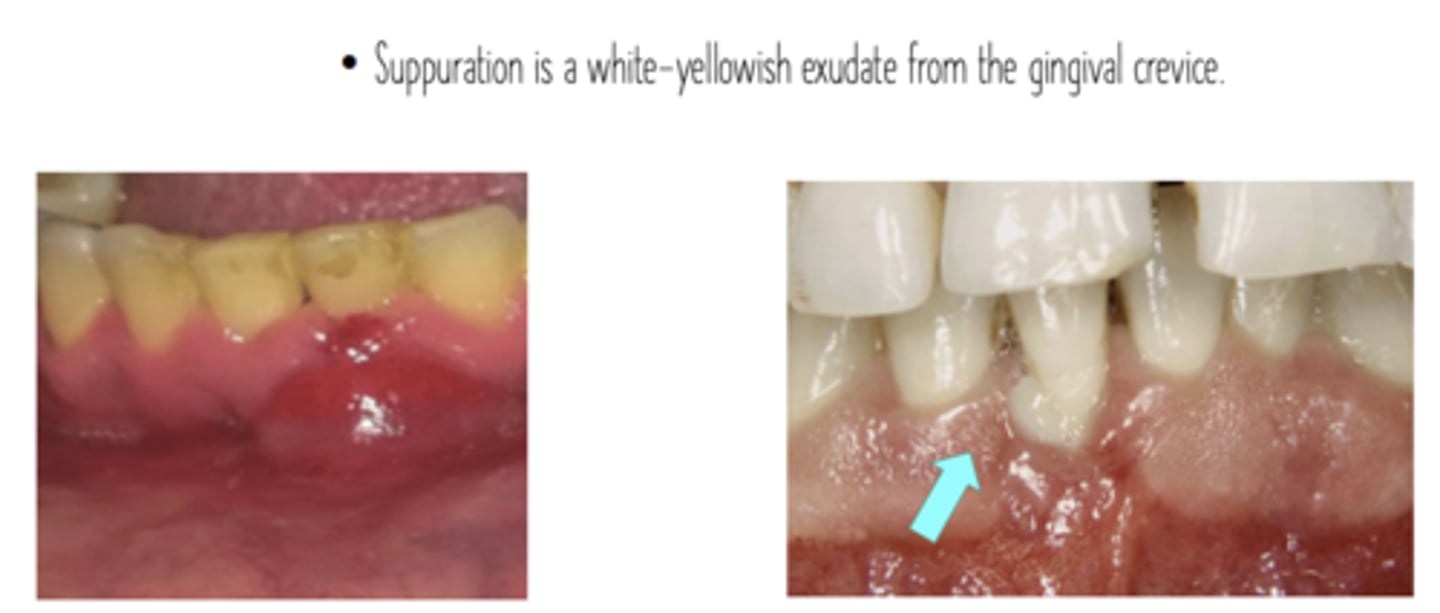
Suppuration definition
The palpation of the marginal gingiva with a probe or digitally, by placing the ball of the index finger on the gingiva apical to the margin and pushing coronally toward the gingival margin, may trigger the release of a white-yellowish exudate from the gingival crevice. The presence of an abundance of neutrophils in the gingival fluid transforms it into a purulent exudate
BOP and SUPPURATION
Critical applications of periodontal probe
1. Determine the level of the epithelial attachment (JE) on the tooth
2. Determine the depth of gingival or periodontal pockets
3. Determine the presence of bleeding on gentle application
4. Determine if suppuration is present
5. Determine the presence of subgingival deposits of calculus
6. Determine the amount of visible recession
7. Determine the amount of attachment loss (probing depth + recession)
Mobility definition
The movement of a tooth in its socket resulting from an applied force
Mobility: is measured by
pushing the tooth gently in a buccolingual direction using the handle ends of two metal instruments
Mobility: can tell us
loss of tooth support/periodontal disease
Traumatic occlusion
Occlusal Interference
Trauma from occlusion
Premature contacts
- more depth in this in future lectures
At the end of the day we want you to know the difference between
Gingival health
Gingivitis
Periodontitis
- Mild to moderate (stage 1-2)
- Moderate to advanced (stage 3-4)
[At the end of your four years]
Gingival Health on an intact Periodontium
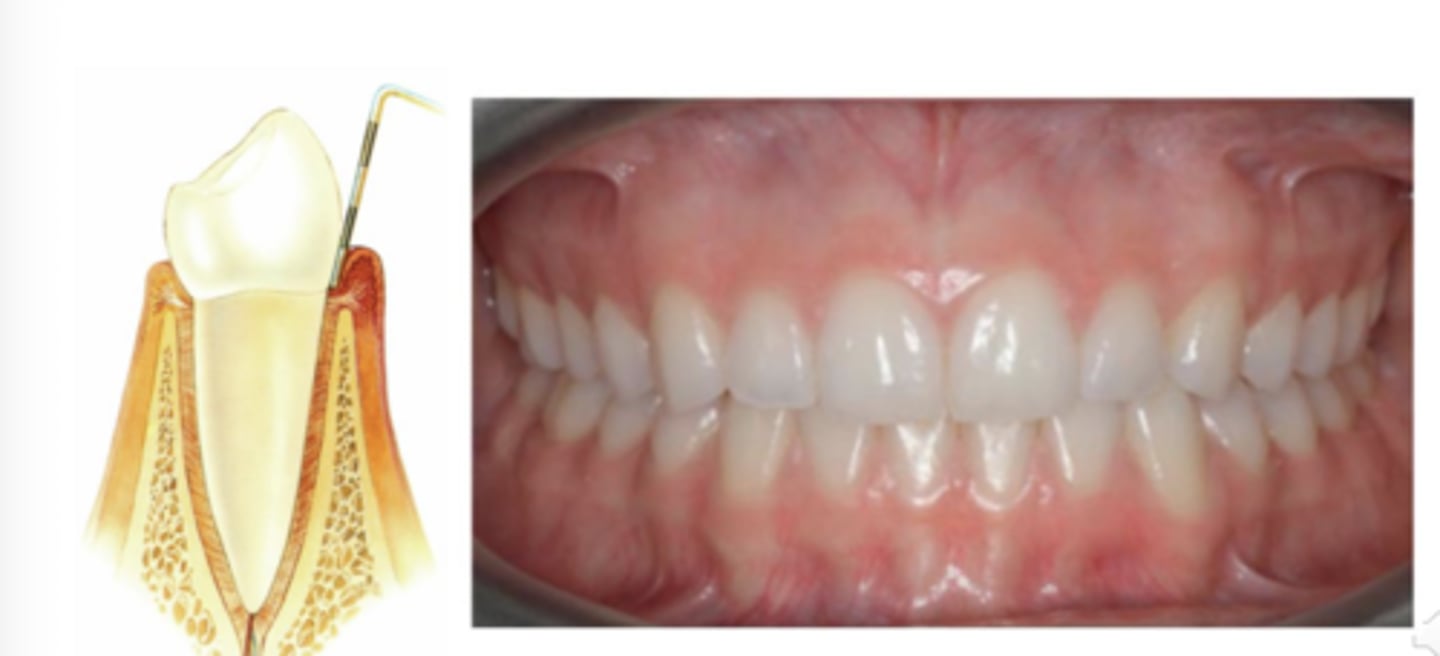
Gingivitis-Inflammation that is reversible-no bone loss
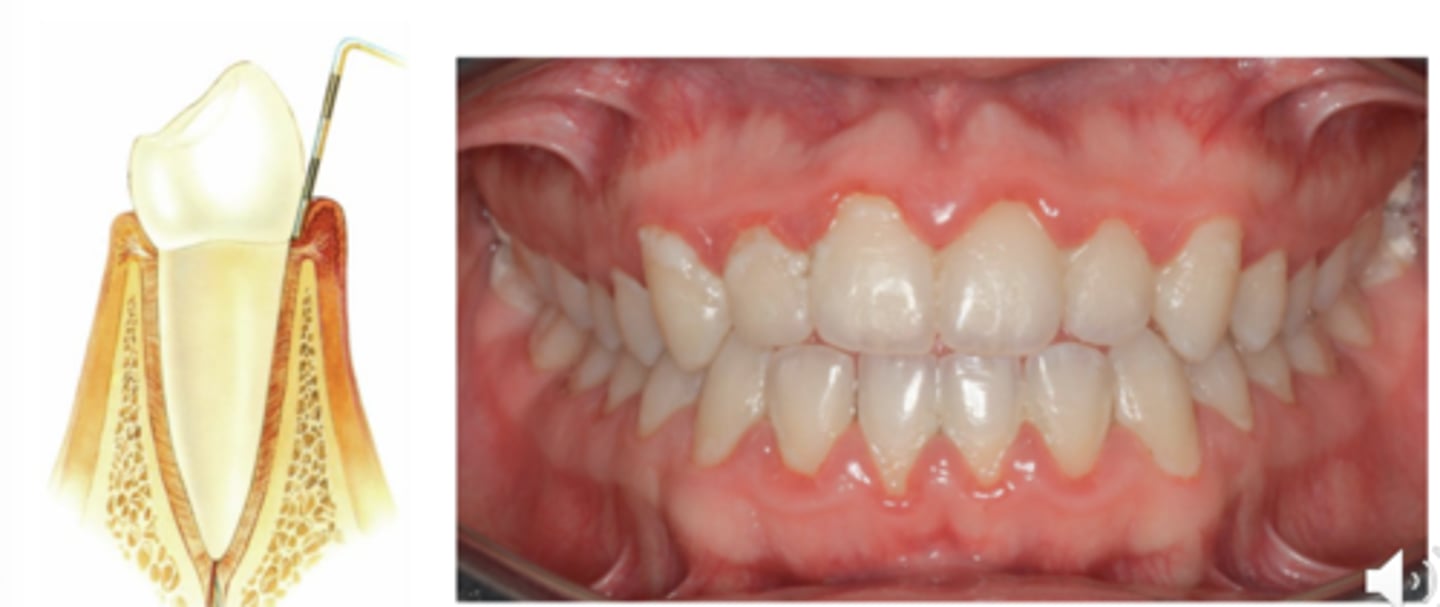
Periodontitis- Presence of inflammation sites where their is loss of connective tissue and alveolar bone, NOT reversible
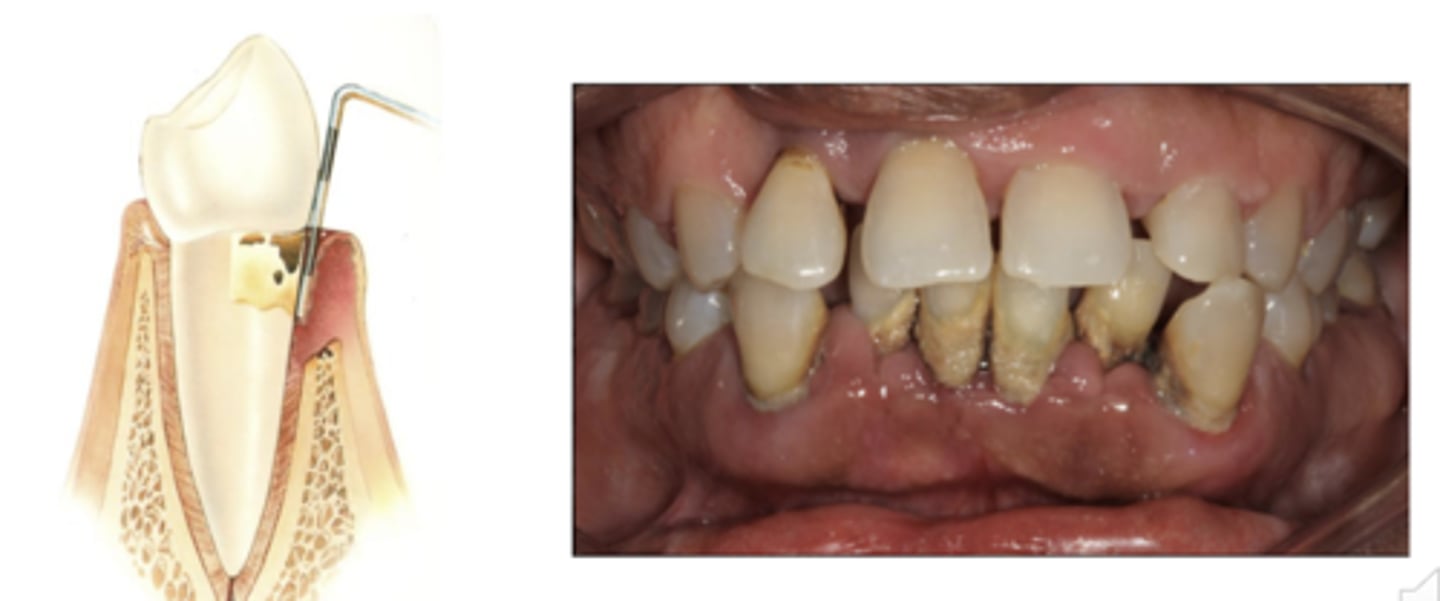
Staging
Used to classify the severity and extent of a patient's disease based on the measurable amount of destroyed and/or damaged tissue as a result of periodontitis and to assess the specific factors that may attribute to the complexity of long-term case management
What to know:
- classify things by stages of severity
Grading
Indicates the rate of periodontitis progression, responsiveness to standard therapy and potential on systemic health
What to know:
- Grading is to classify rate