Chapter 18 — Multimodality Imaging
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Which one of the following statements is true about hybrid PET/CT or SPECT/CT imaging systems?
The CT provides anatomic correlation for the SPECT or PET.
Which one of the following statements is true about the CT in SPECT/CT or PET/CT?
CT images must be scaled and smoothed before being used for attenuation correction.
Which of the following is not a potential source of artifacts in PET/CT or SPECT/CT imaging?
Anatomic coverage
Which of the following is not a barrier to combining an MRI system with either a SPECT or PET system?
MRI scanners do not produce ionizing radiation
If performing a CT for attenuation correction only, why would the CT parameters be significantly altered from those for a diagnostic CT scan?
To reduce the radiation exposure to the patient.
A CT scan to define the area of the body to be scanned is called a:
Scout scan and topogram
CT artifacts can be caused by:
All of the above
How often should the CT calibration be checked and a tube warm-up performed?
Daily
IV contrast must always be administered during a PET/CT scan.
False
Artifacts due to respiration mismatch between CT and SPECT or PET are most likely to be seen near:
Dome of the diaphragm/liver
If a patient moves between the CT and the SPECT or PET, which two of the following corrections will be affected?
Attenuation and scatter
Select two reasons that metal implants in patients create prob lems for SPECT/CT and PET/CT systems:
Both
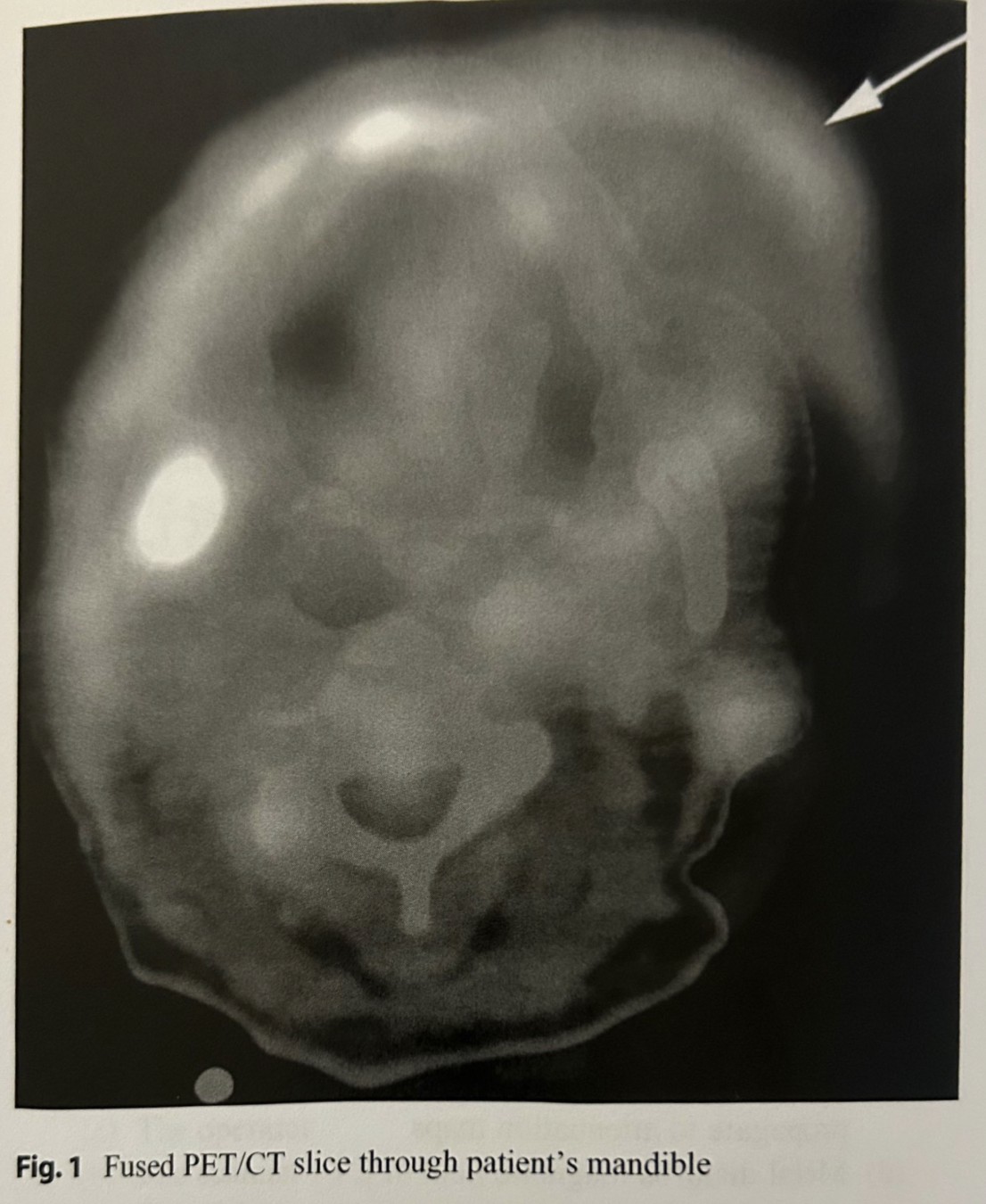
Refer to Fig. 1. In this fused PET/CT transaxial slice through the mandible, what is the likeliest explanation for the area of activity extending outside the boundary of the CT (see arrow)?
Patient tilted head between CT and PET