Thermoregulation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Thermoregulation
Maintenance of a relatively constant core body temp. to maintain optimum enzyme activity
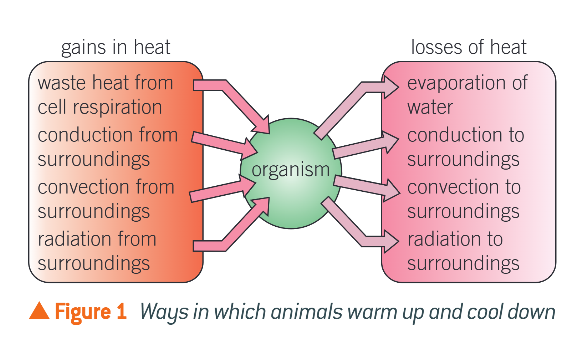
Ways of losing heat
Evaporation of water
latent heat lost from surface (mouth /sweat)
Radiation to surroundings
IR from skin → surroundings absorb it
Convection to surroundings
Convection currents form from skin (warm air rises, cooler air sinks)
Conduction to surroundings
Passes thermal energy between particles as they vibrate more
Ectotherms
Use surroundings to warm bodies
Coe body temp. heavily dependent on environment
Invertebrate animals
Those in water don’t need to thermoregulate
Why do ectotherms in water not need to thermoregulate
Water has high heat capacity, temp doesn’t change much
Endotherms
Mammals and birds
Rely on metabolic processes to warm up, usually maintain v. stable core
Use heat produced internally to maintain body temperature
Endo and Ecto metabolic rates
Endo metabolic rate 5x higher than ecto
Endo need to consume more food to meet metabolic needs
Ecto use less of their food in resp. , need to find less food, can last long w.out food
Ectotherm behavioural responses (increase temp.)
Bask in sun
Orientate / Change bodies so that max. SA exposed to sun
Press bodies against warm ground
Exothermic metabolic reactions (vibrate wings, contract muscles & vibrate)
Ectotherm behavioural response (decrease temp)
Shelter from sun
Press bodies against cool, shady surfaces
Move into water or mud
Orientate bodies so minimum SA exposed to sun
Minimise movement to reduce metabolic heat generated
Ectotherm physiological
darker colours tend to live in colder areas (absorb more radiation)
Alter heart rate to increase or decrease metabolic rate and to affect warming or cooling across body surfaces
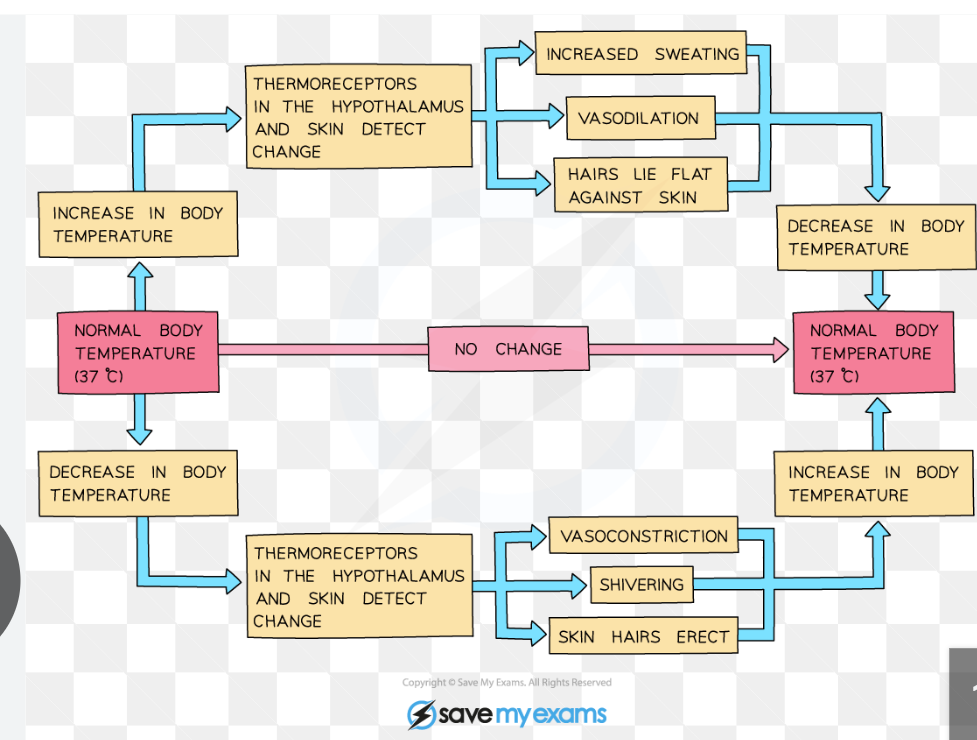
Endotherms thermoregulation
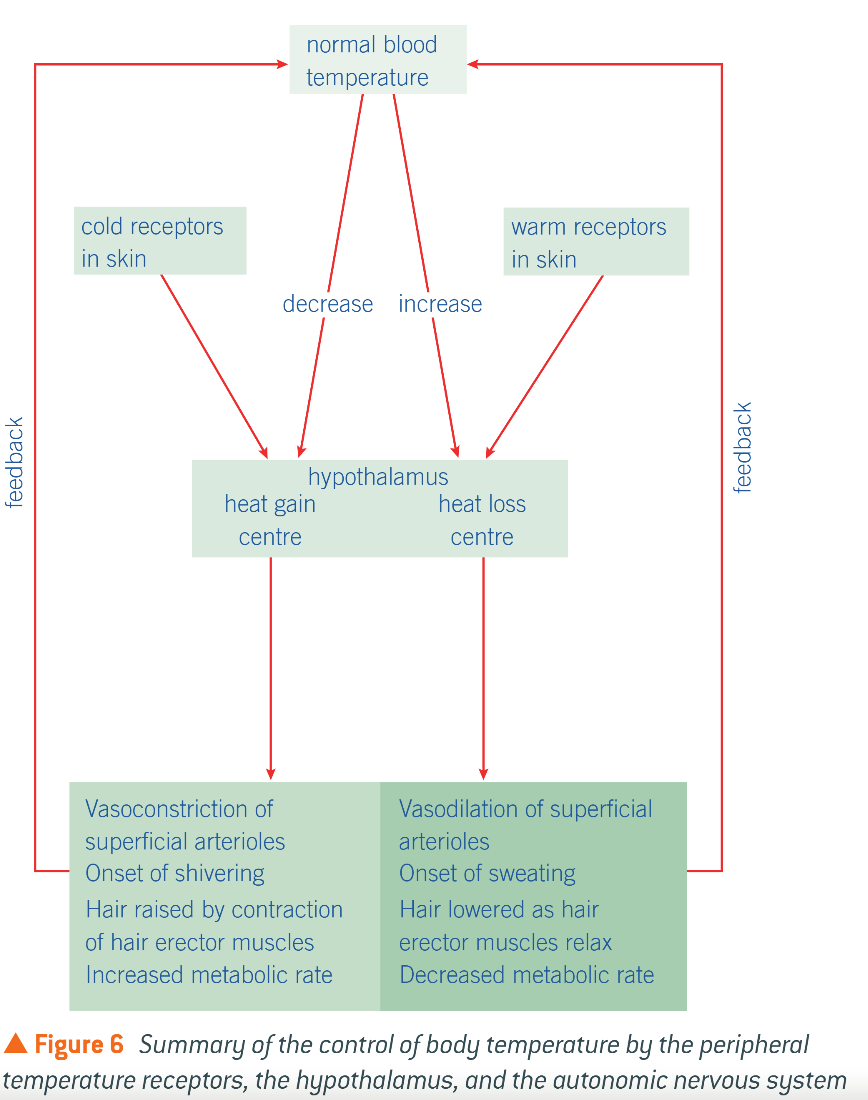
Hypothalamus and body temp
Receives info about temp from thermoreceptors
Thermoreceptors send impulses along sensory neurones to hypothalamus, sending impulses along motor neurones to effectors
E.g. skeletal muscles, sweat glands, erector pili muscles, smooth muscles of shunt vessels