Joints of the Skeleton
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is a joint
a location where two or more bones come together
What is the joint also known as
articulation
What are the two roles of joints
allows us to move and holds our skeleton together
how many types of joints are there
3
How many types of names do joints have
2
what is the anatomical name
based upon what separates the bones
what is the physiological name
based upon how well the joint moves
what is the fibrous joints physiological name
synarthrosis
what is the cartilaginous joints physiological name
amphiarthrosis
what is the synovial joints physiological name
Diarthrosis
what is the fibrous joint
it is immovable
what is the cartilaginous joint
it is slightly moveable
what is the synovial joint
it is freely moving
what is the fibrous joint separated by
Fibrous connective tissue
what is the cartilaginous joint separated by
cartilage
what is the synovial joint separated by
synovial fluid
what are examples of the fibrous joint
cranial sutures and teeth in sockets
what are examples of the cartilaginous joint
pubic symphysis, intervertebral disc
what are examples of the synovial joint
knee joint and shoulder joint
what are the hinge joint
most common type of joint, allows one type of movement, allows a joint only to bend and straighten (flex and extend)
what are examples of hinge joints
femur-tibia, phalanges-phalanges, temporomandibular joint
what is the pivot joint
allows only 180 degree rotation, one bone rotates around another
what is the saddle joint
allows two types of movement, allows a joint to bend and straighten, also allows a joint to move side-side
What is the plane joint
bones side against each other like blocks gliding against each, common in short bones
what is ball and socket joints
allows many different types of movements, most moveable type of joint
what is a condyloid joint
allows two types of movements, allows a joint to bend (flex) and straighten (extend) allows a joint to slightly shift side-to-side, a modified ball and socket joint
examples of hinge joints
femur-tibia, phalanges-phalanges, temporomandibular joint
what is examples of pivot joint
atlas-axis, radius-humerus
examples of saddle joints
metacarpal of the thumb-trapezium
example of the plane joints
carpals and tarsals
what are examples of ball and socket joints
humerus-scapula, femur-pelvis
what are examples of condyloid
proximal Phalanges-metacarpals
what is flexion
decreasing an angle between two bones (bending)
what is extension
increasing an angle between two bones (straightening)
what is hyperextension
extending beyond a straight line (back bend or looking up)
what is dorsiflexion
toes/foot pointing upwards
what is plantarflexion
toes/foot pointing downwards
what is abduction
pulling limbs from the midline
what is adduction
bringing limbs back towards the midline
what is circumduction
circular motion at a ball and socket joint not twisting (shoulder circles or hip circles”
what is Rotation
180-degree rotation (twisting) (neck wrist shoulder, hip)
what is Lateral rotation
rotating out to the side (head turned out)
what is medial rotation
rotating in toward midline (bringing head back)
what is supination
palm rotates up
what is pronation
palm rotates down
what is eversion
elevating your lateral soles (big toe side down)
what is inversion
elevating your medial soles (pinkie toe side own)
what is protraction
to stick out
what is retraction
to pull back in
what is elevation
to raise up
what is depression
to lower
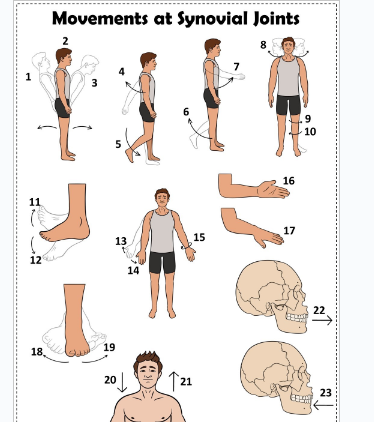
what is 1
Hyperextension the back
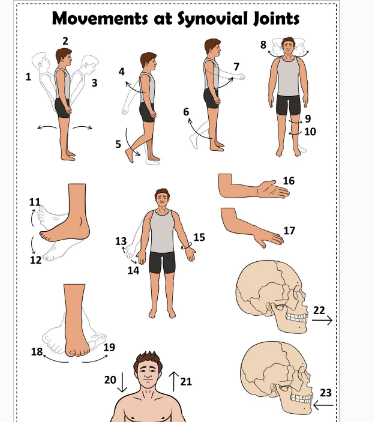
what is 2
extension of the back
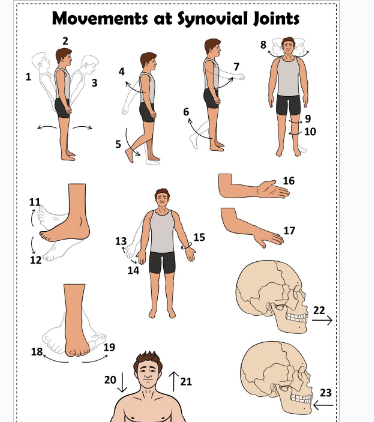
what is 3
flexion the back

what is 4
extension of the upper limb at the shoulder joint
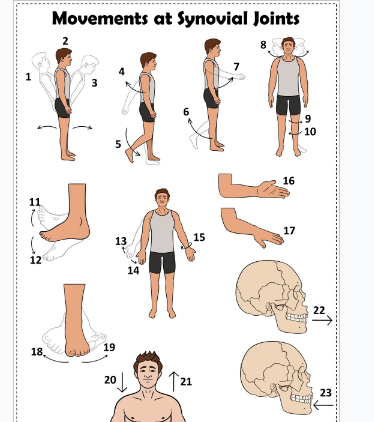
what is 5
extension of the lower limb at the knee joint
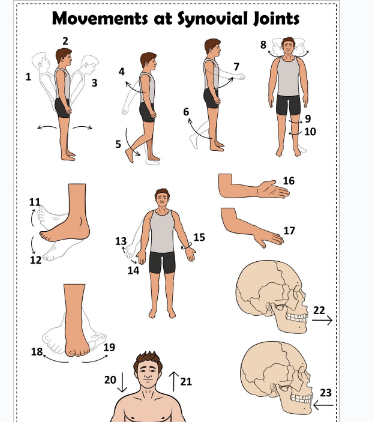
what is 6
flexion of the lower limb at the knee joint
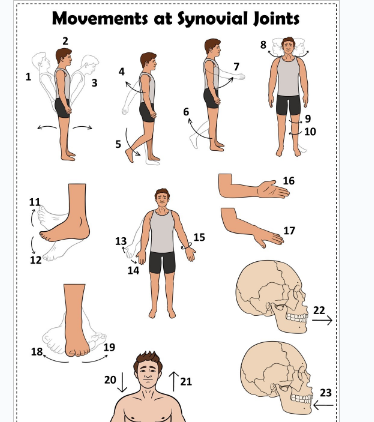
what is 7
Flexion of the upper limb at the shoulder joint
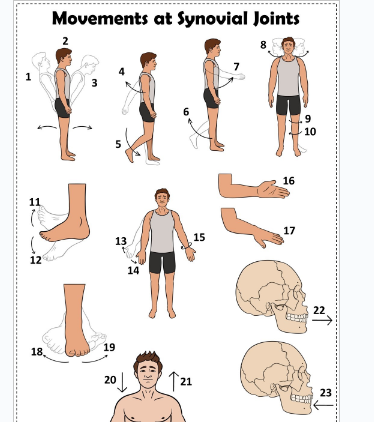
what is 8
lateral rotation of the head
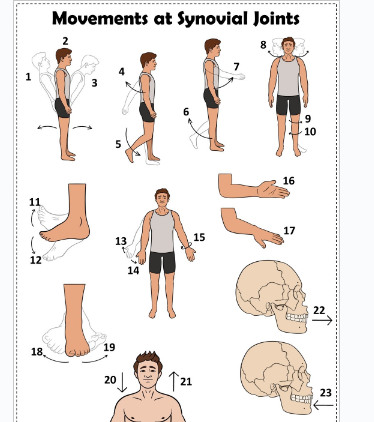
what is 9
lateral rotation of the lower limb
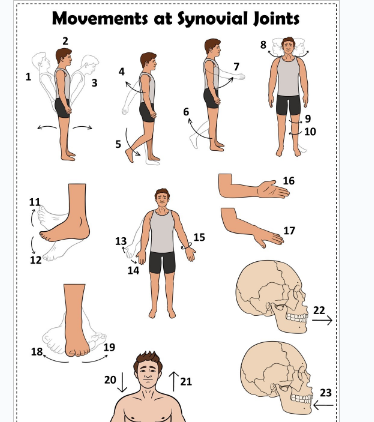
what is 10
medial rotation of the lower limb at the hip joint
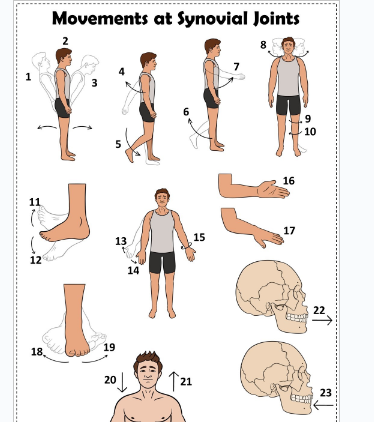
what is 11
dorsiflexion
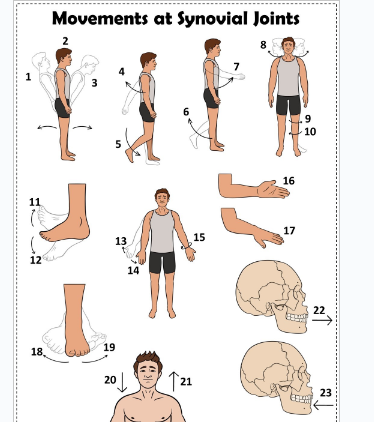
what is 12
plantarflexion
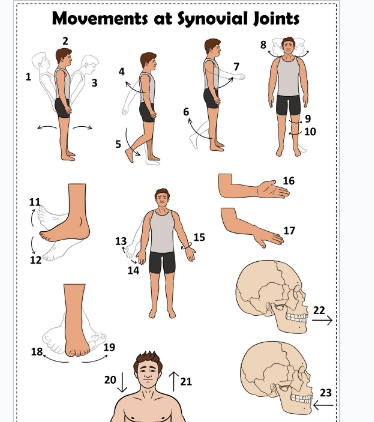
what is 13
abduction of the upper limb
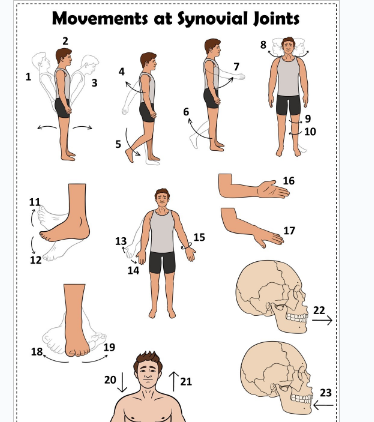
what is 14
adduction of the upper limb
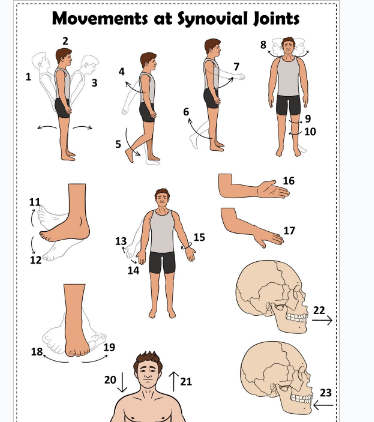
what is 15
circumduction of the upper limb
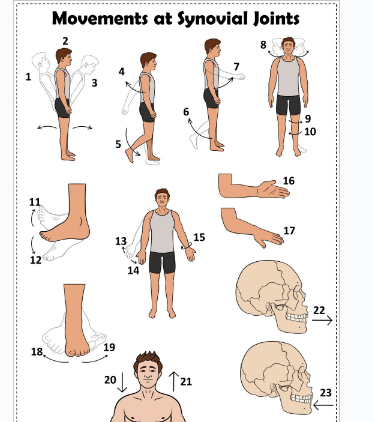
what is 16
supination
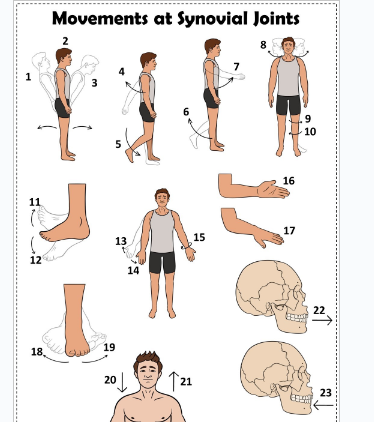
what is 17
pronation
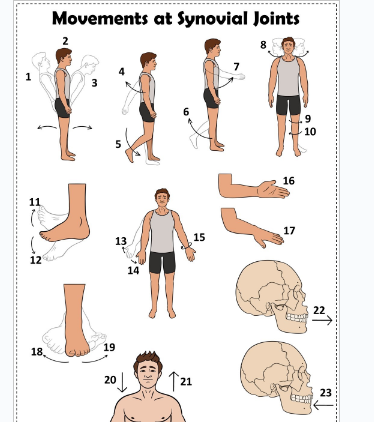
what is 18
inversion
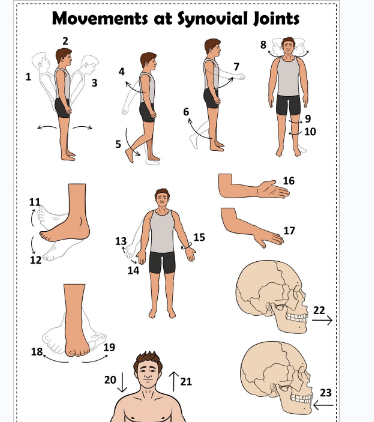
what is 19
eversion
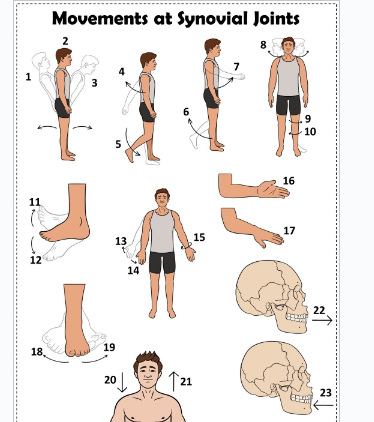
what is 20
depression of the shoulder
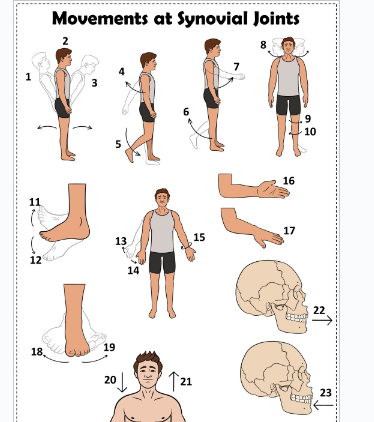
what is 21
elevation of the shoulder
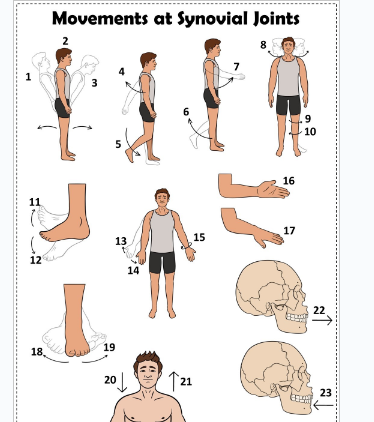
what is 22
protraction of the jaw
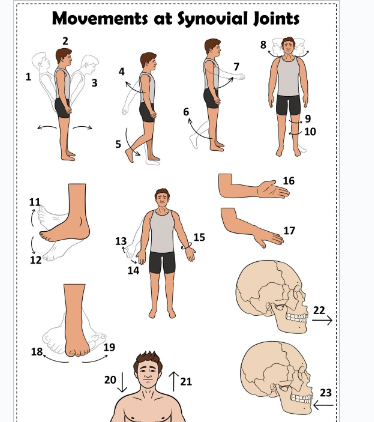
what is 23
retraction of the jaw
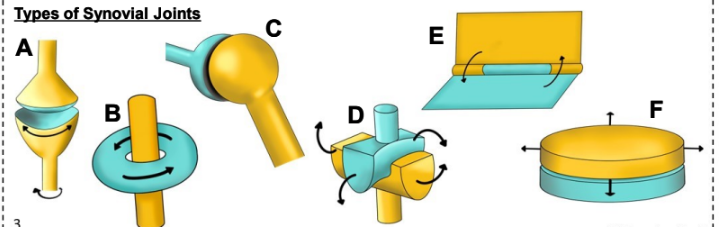
what is A
Condyloid joint
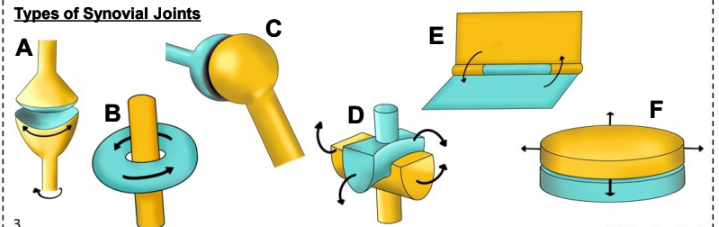
what is B
Pivot Joint
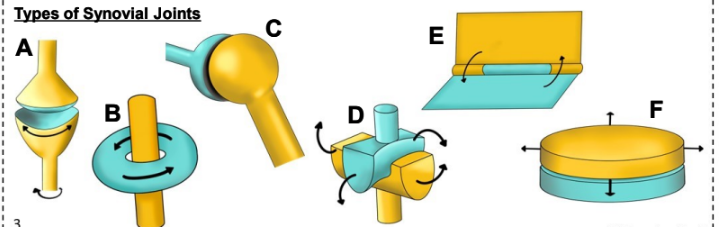
what is C
Ball and socket joint
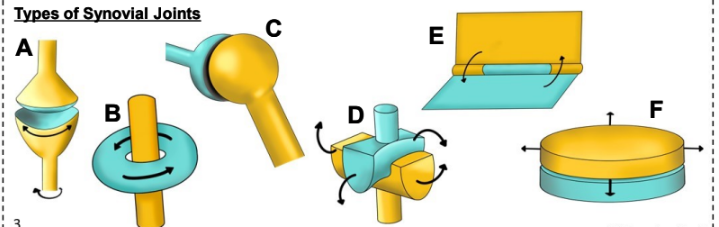
what is D
Saddle joint
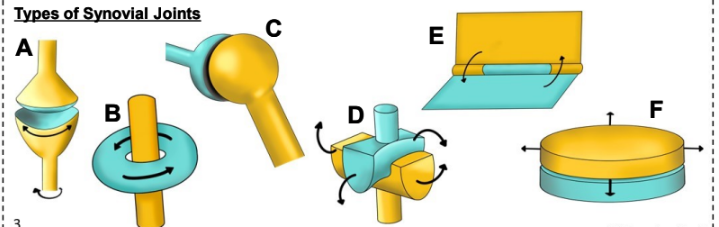
what is E
Hinge Joint
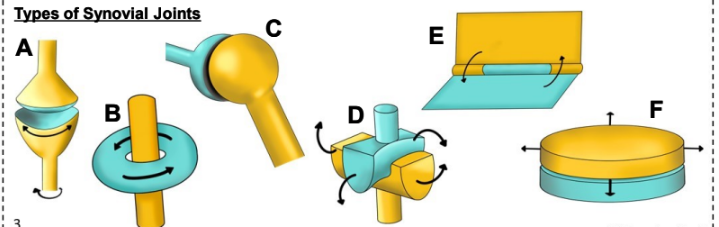
what is F
Plane Joint
what kind of synovial joint is the atlas-axis
pivot joint
what kind of synovial joint is the humerus-scapula
ball and socket
what kind of synovial joint is the radius-humerus
pivot joint
what kind of synovial joint is the carpal bones
plane joint
what kind of synovial joints are the wrist joints (radius/ulna-carpals)
condyloid
what kind of synovial joint is femur-tibia
hinge
what kind of synovial joint is temporal bone -parietal bone
not a synovial joint (fibrous)
what kind of synovial joint is tarsal bones
plane joint
what kind of synovial joint is femur-pelvis
ball and socket
what kind of synovial joint is metacarpal of thumb-trapezium
saddle joint
what kind of synovial joint is tempormandibular joint
hinge
what kind of synovial joint is proximal phalanx-metacarpal
condyloid