RD20: Memory Allocation I
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How many types of allocators are there?
2 allocators: An implicit allocator and an explicit allocator
What is an implicit allocator?
Where the programmer is only responsible for allocations, and the allocator implicitly handles the deallocations.
What is an explicit allocator?
Where the programmer is responsible for both allocations and deallocations.
What is the first thing the application must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Can issue an arbitrary sequence of allocation and deallocation.
What is the second thing the application must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Must never access memory that is not currently allocated.
What is the third thing the application must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Must never try to deallocate memory that is not currently allocated.
What is the first thing the allocators must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Can't control the number or size of allocated blocks.
What is the second thing the allocators must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Must respond immediately to allocation requests.
What is the third thing the allocators must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Must satisfy alignment requirements during allocation.
What is the fourth thing the allocators must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Can only allocate from freed memory.
What is the fifth thing the allocators must adhere to to follow the interface contract?
Can't move allocated blocks.
What are the two dynamic memory allocator performance goals that frequently conflict with each other?
1. Throughput
2. Memory Utilization
What is Throughput as a performance goal?
The allocator wants to complete as many allocation and dealllocation requests as possible per unit time.
What is Memory Utilization as a performance goal?
Using the heap space as efficiently as possible.
What is an implicit free list?
An allocator implementation that traverses its blocks via arithmetic by using the size of each block.
What is an explicit free list?
An allocator implementation that traverses its free blocks using a linked list data structure.
What causes poor memory utilization?
Fragmentation: all the parts of the heap that are not currently being used to store program data.
What is internal fragmentation?
The "wasted" space inside of allocated heap blocks.
What is external fragmentation?
The unused space between allocated heap blocks.
What must the dynamic memory allocator do to manage the heap?
The allocator must always allocate a block sizze that is greater than the requested space.
What is the payload?
The requested space, space requested by the allocator.
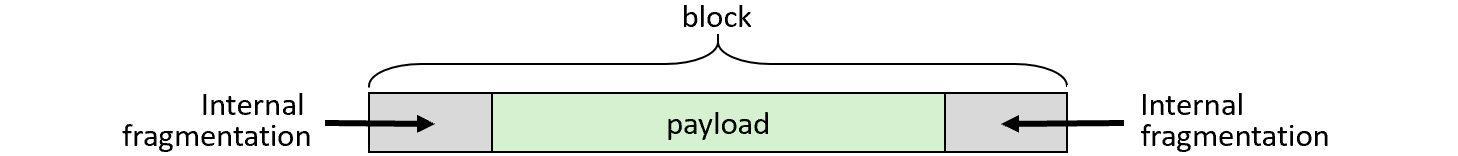
What is internal fragmentation in relation to the payload?
All of the space within a block that is NOT the payload.
What are the sources of internal fragmentation?
Heap data structures and alignment padding.
What does external fragmentation consist of?
All the holes between allocated blocks.
What’s the cause of external fragmentation?
The specific pattern of allocation/deallocation requests.
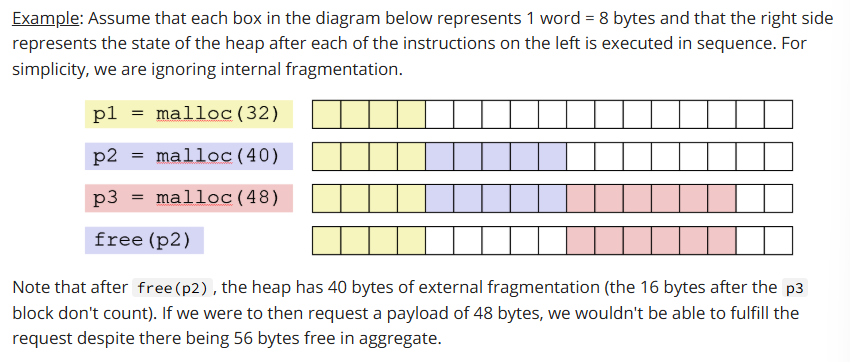
What’s a potential problem with allocation/deallocation requests?
Sometimes an allocation request cannot be satisfied despite there being enough total free heap memory.
An example of allocation/deallocation request issues.