CIT 300 chapter 2 notes / identifying competitive advantages
learning outcomes:
explain why competitive advantages are temporary
what are the 4 key areas of a SWOT analysis
describe porter’s five forces model and explain each force
compare porter’s 3 generic strategies
demonstrate how a company can add value using porter’s chain value analysis
identifying competitive advantages
business strategy: a leadership plan that achieves a specific set of goals/objectives such as increasing sales, decreasing costs, entering new markets, or developing new products or services
stakeholder: a person or group that has an interest or concern in an organization. stakeholders drive business strategies, and depending on the stakeholder’s perspective, the business strategy can change
competitive advantage: a feature of a product or service on which customers place a greater value than they do on similar offerings from competitors
example: raising canes and kfc. in certain places, canes may have a competitive advantage over kfc because of their cane’s sauce being close in price value to regular kfc sauces.
first-mover advantage: occurs when a company can significantly increase its market share by being first with a new competitive advantage
example: when apple introduced itunes with the ipod before other companies included software with their mp3 players
competitive intelligence: the process of gathering information in a competitive environment in order to increase a businesses chance at succeeding
different stakeholders found in businesses
partners/suppliers
reliable contracts
ethical materials handling
responsible production
shareholders/investors
maximize profits
grow market share
high return on investment
community
professional associations
ethical recycling
increase employment
employees
fair compensation
job security
ethical conduct/treatment
customers
exceptional costumer service
high-quality products
ethical dealing
government
adhere to laws and regulations
increase employment
ethical tax reporting
business tools for analyzing business strategies
SWOT analysis: evaluates project position
evaluates an organization’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to identify things that work for or against business strategies
potential internal strengths: strengths associated with the competitive advantage
potential internal weaknesses: areas that require improvement
potential external strengths: trends that the organization can benefit from
potential external weaknesses: outside risks detrimental to an organization
—
the five forces model: evaluates industry attractiveness
analyzes the competitive forces within the environment in which a company operates to access the potential for profitability in an industry
threat of substitute products/services:
power of customers to buy alternatives
becomes high when there are many alternatives, and low when there are few
buyer power:
power of customers to drive down prices
switching costs: costs that make customers reluctant to switch to different products/services
loyalty programs: rewards customers based on their spending
threat of new entrants:
power of competitors to enter a new market
high when there are few entry barriers to enter a new market and low when there’s many
entry barrier: a feature of a product or service that customers have come to expect and that new competitors must offer in order to survive in the market
supplier power:
power of suppliers to increase the price of materials
supplier can increase power by:
charging higher prices
limiting services or quantity
shifting costs
and this power can be decreased by:
using MIS to find alternative products
supply chain: consists of all parties involved in getting raw materials or a product
rivalry among existing competitors:
high when competitive is fierce in a market and low when there’s less competition
product differentiation: occurs when a company develops unique differences in its product/services in order to influence demand
—
portner’s three generic business strategies: chooses business focus
generic business strategies that are neither organization nor industry specific and can be applied to any business, product, or service
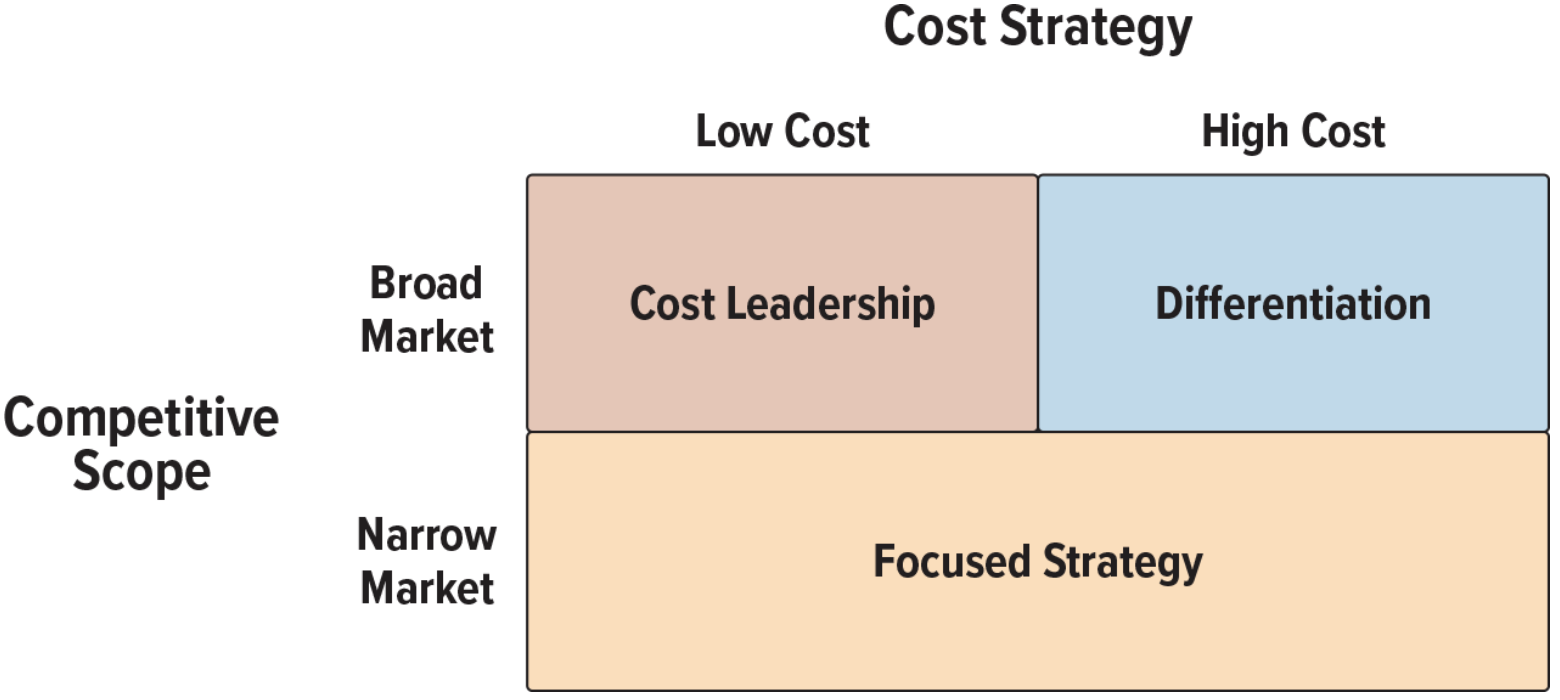
broad market, low cost: loads of different products at low costs
example: walmart
broad market, high costs: loads of different products at high costs
example: erewhon
narrow market, low costs: a specific product at low costs
example: payless shoe stores, cheap shoes
narrow market, high costs: a specific product at high costs
example: jimmy choo, expensive shoes
—
value chain analysis: executes business strategy
views a firm as a series of business processes that each add value to a product or service
business process: a set of activities that accomplish a certain task
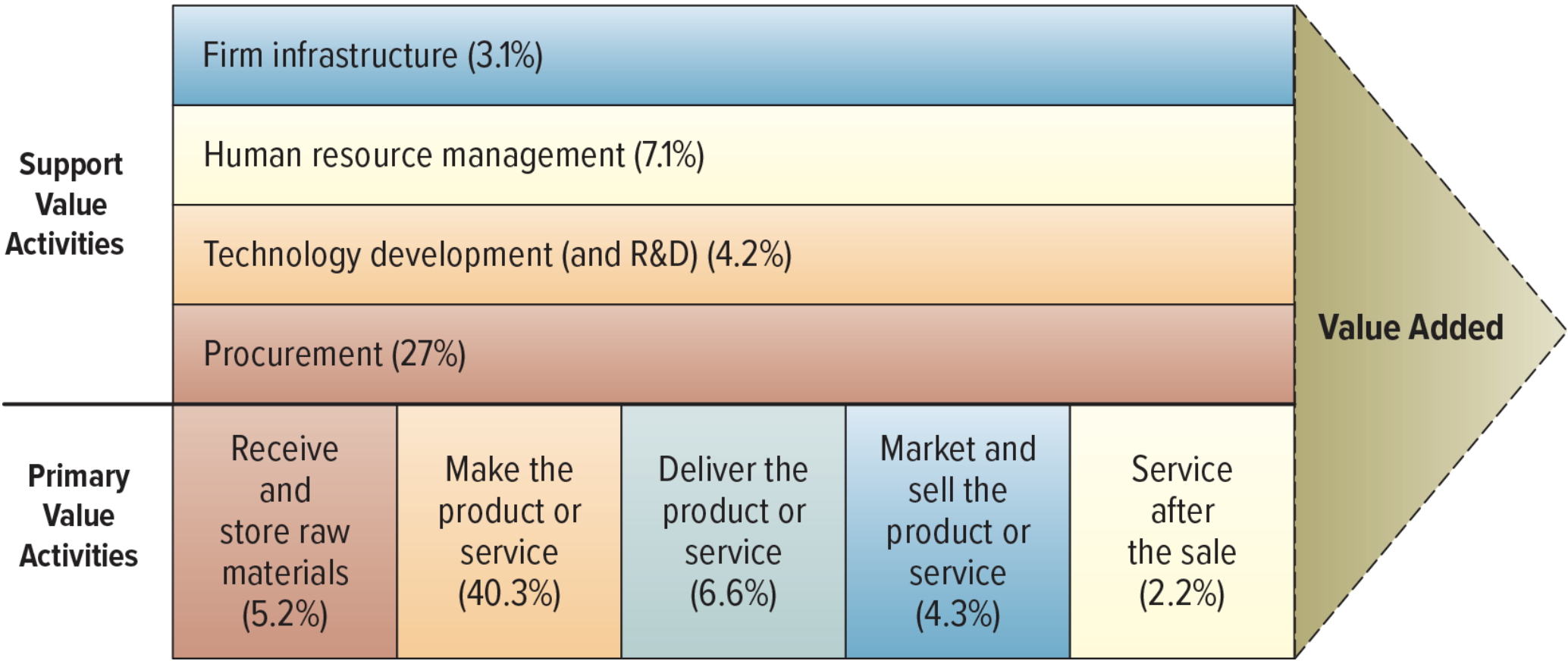
primary value activities: acquire materials, and manufacture, deliver, market, sell and provide after-sales services
inbound logs
operations
marketing and sales
service
support value activities: help with firm infrastructure, HR development, tech. development, and procurement
firm infastructure
HR
tech dev.:
procurement
digital value chain: digitizes work across primary and supporting activities
case study questions:
porter’s five forces evaluate how “attractive” a market could be to a business, i.e, how profitable that market could be. this “attractiveness” is calculated using “five forces,” which are: the threat of alternative products, the threat of new entrants, the threat of existing competition in the market, and buyer and supplier power
so, if you’re planning on opening a coffee shop in a small town, you could think about the alternative to your place that people could go to get coffee for cheaper, how many new coffee shops may enter the market where you live, if you already have coffee shops in your town, and you could think about how you could get buyer and supplier power on your side, possibly by making a rewards program or by up charging on your coffee
it would be difficult to operate in more than one of porter’s generic strategies because each business strategy operates in a specific market with specific prices
learning outcomes are on page 30
review questions on page 31
 Knowt
Knowt