Period 5: 1844-1877
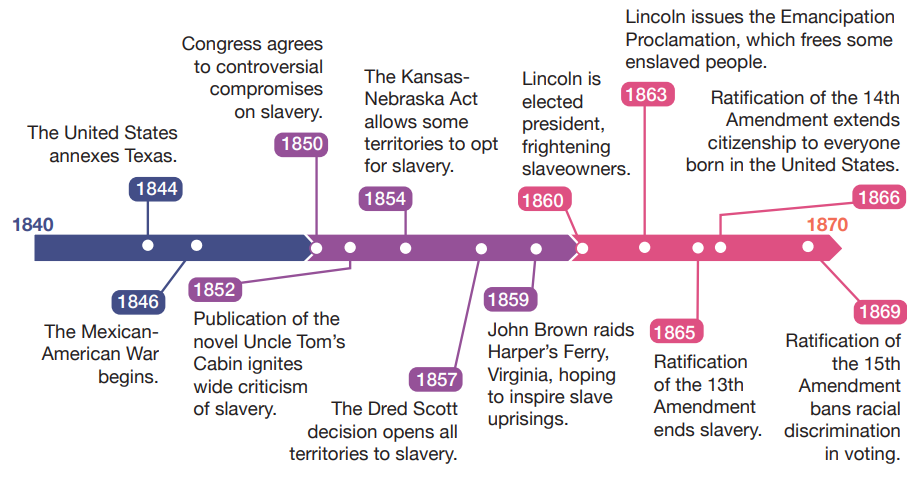 5.1 Contextualizing Period 5
5.1 Contextualizing Period 5
Continuity b/t 1844-1877: Racism remained & expansion of voting rights
Change b/t 1844-1877: Territory expansion to the Pacific Ocean, federal gov’t power expanded & slavery ended, new technology + transportation → another Market Revolution
Growth in Land and Population:
U.S. expansion westward → citizens = destiny to control all land to the Pacific Ocean
Land acquisition from Mexican War; U.S. established Southern border
Rapid expansion = new immigrants (left Europe due to famine, poverty, & political turmoil)
Political orgs to restrict immigration & citizens
Political Conflicts over Slavery
Expansion + sectionalism → intensified differences over politics, economics, & slavery
Slaveholders argued for federal laws to return enslaved people who had escaped
Free-soilers believed slavery shouldn’t be allowed in territories
“Underground railroad” established to help fugitives escape from slavery
The Civil War and Reconstruction
Abraham Lincoln was elected → 11 states left the Union & a 4 year civil war took place
Lincoln opposed slavery, but didn’t want immediate abolition; slaveholders = frightened
Union victory in war ended slavery & gave federal gov’t more power
Reconstruction = the 12 years after the Civil War
Reshaped federalism & power among branches of gov’t
Racism & Discrimination
Black codes were passed that restricted the basic rights of Black citizens
Sharecropping emerged in place of slavery
White Americans killed thousands of black citizens to maintain racial supremacy
5.2 The Idea of Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny expressed the belief that the U.S. had a mission to extend its power and civilization across the breadth of North America
Driven by: nationalism, population increase, rapid economic development, technological advances, & reform ideals
Conflicts over Texas, Maine, and Oregon
Texas
Mexico won independence from Spain (1823) — hoped to attract settlers to Texas
Stephen Austin brought 300 families to Texas & began the migration of Americans to frontier territory
1830: Americans outnumbered Mexicans by 3:1
Tensions increased (1829): Mexico outlawed slavery & forced immigrants to become Roman Catholics
Many settlers refused → Mexico closed Texas to add’l American immigrants
Land hungry Americans ignored & streamed into Texas
General Santa Anna made himself the dictator of Mexico (1834) — he attempted to enforce Mexico’s laws in TX
American settlers led by Sam Houston revolted & declared TX an independent republic in March 1836 — made slavery legal again
Santa Anna led a Mexican army → captured the town of Goliad & attacked the Alamo
Battle of San Jacinto River: Sam Houston’s army captured Santa Anna
The Mexican leader signed a treaty that recognized Texas as independent & granted the U.S. all territory N. of the Rio Grande
The Mexican legislature rejected the treaty
Sam Houston applied to the U.S. gov’t for the Lone Star Republic to be annexed to the U.S. as a new state
Presidents Jackson & Van Buren put off the request due to opposition from Northerners about slavery expansion
TX might’ve been divided into 5 new states = 10 pro-slavery Senate members
President John Tyler worked to annex TX; Senate rejected his request in 1844
Boundary Dispute in Maine
A conflict b/t rival groups of lumber workers on the Maine-Canadian border erupted into open fighting
Webster-Ashburton Treaty(1842): disputed territory was split b/t Maine & British Canada + settled the boundary of the Minnesota territory
Boundary Dispute in Oregon
Britain based its claim to Oregon on profitable fur trade with the American Indians of the Pacific Northwest
U.S. based its claim on:
The exploration of the Columbia River in 1792
The overland expedition to the Pacific Coast by Lewis & Clark in 1805
The fur trading post + fort in Astoria, Oregon, that was established in 1811
Protestant missionaries + farmers settled in Willamette Valley in the 1840s & had major success in farming
5k+ Americans caught “Oregon fever” & traveled 2k+ miles over the “Oregon trail” (S. of the Columbia River)
The Election of 1844
The possibility of annexing TX + the expansion of slavery split the Democratic Party
N. wing: opposed annexation + wanted to nominate Van Buren again
S. wing: proslavery + proannexation wanted John C. Calhoun
At the Democratic convention James K. Polk was nominated — he was firmly committed to Manifest Destiny:
Favored the annexation of TX
Acquisition of California
Reoccupation of Oregon territory to the Russian Alaska border (latitude 54 40’)
“Fifty-Four Forty or Fight!” — appealed to American Westerners + Southerners
Polk won the close election due to the Whigs’ (Henry Clay) loss of NY’s electoral votes
Democrats aimed to add TX to the Union
Polk kept his promises like:
Acquiring California from Mexico
Settling the Oregon dispute
Lowering the Tariff
Establishing a sub-treasury
Retire from office after 4 years
Annexing Texas & Dividing Oregon
Outgoing president John Tyler pushed the annexation of TX by passing a joint-resolution for annexation in both houses of Congress
Left Polk to deal with Mexico’s reaction
Polk signed an agreement to divide the Oregon Territory at the 49th parallel w/Britain
This issue was finally settled when the U.S. agreed to grant Vancouver Island & the right to sail the Columbia River to Britain
Settlement of the Western Territories
As Oregon + California were acquired, many Americans migrated to these areas
They passed over the Great American Desert (arid region b/t the Mississippi Valley & Pacific Coast) to reach the inviting lands of the West Coast
Fur Traders’ Frontier
Fur traders (mountain men) were the earliest nonnative ppl to open the Far West
Ppl like James Beckwourth & Jim Bridger helped provide early information about the trails + frontier conditions
They held annual meetings w/American Indians to trade for Animal skins
Overland Trails
Hundreds of thousands followed the California, Oregon, Santa Fe, or Mormon trails
Hoped to clear forests + farm fertile valleys of California & Oregon
Journeys typically began in Missouri or Iowa & went through the Great Plains
Travelled ~15 miles per day
Hardships include: passing through the Sierras & Cascades before the 1st heavy snow, attacks by American Indians, disease & depression from harsh conditions (most common)
Mining Frontier
Gold = discovered in California (1848) → set off migrations to mountains of the West
Gold/silver rushes often in: Colorado, Nevada, & the Black Hills of the Dakotas
Mining camps & towns (often short-lived) sprang up wherever a discovery was reported
California’s population: 14k (1848) → 380k (1860)
1/3 of Western miners were Chinese
Farming Frontier
Congress’s Preemption Acts (1830s+40s): allowed squatters to settle public lands & purchase them for low prices as the gov’t put them up for sale
A family needed $200-$300 to travel westward — mostly middle class
Rural communities developed based on Eastern ideals or from immigrants’ native lands
Urban Frontier
Western cities arose due to: railroads, mineral wealth, & farming
Attracted professionals & business owners
San Francisco + Denver grew due to gold & silver rushes
Salt Lake City grew due to its fresh supplies to travelers
Foreign Commerce
Growth in manufactured & agricultural goods (e.g. Western grains & Southern cotton) → more exports and imports
Other factors of U.S. expansion:
Shipping firms had scheduled departures → encouraged trade + travel across the Atlantic
Greater demand for whale oil from middle class; N. England merchants took the lead
Improvements in ship design
Steamships gained popularity (large storage capacity, low maintenance cost, & followed a schedule)
U.S. expanded trade to Asia (N. England merchants traded for silk, tea, & porcelain w/China)
Kanagawa Treaty (1854): allowed U.S. vessels to enter 2 Japanese ports for coal
Led by Matthew C. Perry
Expansion After the Civil War
Issues of union, slavery, civil war, & reconstruction would overshadow the drive to acquire new territory — but Manifest Destiny still helped to shape U.S. policy
e.g: Sec. of State William Seward purchased Alaska (1867) when the U.S. was recovering from Civil War
5.3 Manifest Destiny & the Mexican-American War
The U.S. annexation of TX + President Polk’s desire to expand the nation to the Pacific Ocean increased tensions for war
Conflict with Mexico
Slidell’s Mission
Polk dispatched John Slidell as an envoy to the Mexican Gov’t, he wanted him to:
Persuade Mexico to sell the California + New Mex. territories to the U.S.
Settle the disputed Mexico-TX border
The Mex. gov’t refused to sell California & insisted Texas’s S. border was on the Nueces River
Slidell believed TX’s border lied further S, on the Rio Grande
Immediate Causes of the War
Polk ordered Zachary Taylor to move his army to the Rio Grande, over territory claimed by Mexico, while waiting on Mexico’s response to Slidell
In 1846, a Mexican army crossed the Rio Grande, captured an American army patrol, & killed 11
Polk used this incident to justify war to Congress
Many Whigs opposed, but a large majority in both houses approved the war resolution
Military Campaigns
Most of the war = fought in Mex. territory by small American armies
Stephen Kearney took N. Mexico & California territory & led a force that didn’t exceed 1.5k soldiers
John C. Fremont overthrew Mexican rule in California (1846)
Declared California the Bear Flag Republic
Z. Taylor’s force of 6k soldiers drove the Mex. army from TX & into N. Mexico
Victory of Buena Vista (Feb. 1847)
Polk had Winfield Scott invade central Mex. with 14k soldiers
Captured Mexico City in Sept. 1847
Consequences of the War
After the fall of Mex. City, the gov’t had to agree to U.S. terms
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848): negotiated by Nicholas Trist w/terms favorable to U.S.
Mex. recognized Rio Grande as S. border of TX
Mexican Cession: U.S. took California & N. Mexico for $15 million and took responsibility for any claims of American citizens against Mexico
Whigs opposed treaty → opportunity to expand slavery
Democrats wanted to take all of Mex, since the land was below the line of the Missouri Compromise
Wilmot Proviso:
David Wilmot proposed that slavery be banned in any territory acquired from Mexico
Appealed to those who wanted to preserve land for White settlers & protect them from having to compete w/enslaved labor
Ultimately defeated in the Senate where the S. had more power
Prelude to Civil War
The acquisition of these western land renewed the debate over the expansion of slavery
Many Northerners viewed the war as a Southern plot to expand slavery
Wilmot Proviso escalated political conflict that led to the Civil War
5.4 The Compromise of 1850
Manifest Destiny + expansion intensified the debate regarding slavery because abolitionists wanted to settle W. land w/o slave labor, but slaveowners wanted slavery to grow
Most Americans still wanted a compromise to keep the Union together
Southern Expansion
Southerners = disliked Missouri Compromise; it limited slavery in Louisiana Purchase lands
Felt territorial gains from Mexican Cession weren’t large enough
Overall, they were eager to find new land for cultivation w/slave labor
Manifest Destiny in the South
In the early 1850s, many slaveowners wanted new land — esp. in Latin America
Southern expansionists sought to acquire Cuba
Ostend Manifesto
Polk offered to purchase Cuba for $100 million; Spain refused
Some Southern adventurers led small expeditions, to take the island by force - easily defeated
President Pierce adopted pro-Southern policies & dispatched American diplomats to Belgium, where they negotiated to buy Cuba from Spain — Ostend Manifesto
It was leaked to the press & antislavery members of Congress were angry
Walker Expedition
William Walker attempted to take Baja California in 1853 — failed
He led a force of mostly southerners & seized power in Nicaragua in 1855
Gained temporary recognition from the U.S. gov’t in 1856
His scheme for a proslavery Central American empire ended when Central American countries invaded his country & defeated him — he was executed in 1860
Clayton-Bulwer Treaty (1850)
Some Americans & Great Britain wanted a canal through Central America, to allow ships to sail from the Atlantic to the Pacific w/o having to go around S. America
Clayton-Bulwer Treaty: prevented GB & the USA from seizing this opportunity & established that neither nation would attempt to take exclusive control of the canal
Lasted until 1901
Gadsden Purchase
President Pierce bought a small strip of land from Mexico in 1853 for $10 million
This land was the best route for a railroad in this region
Conflict Over Status of Territories
New territories gained in the Mexican War → sectional differences in the late 1840s
Wilmot Proviso would’ve upset the Missouri Compromise’s balance of 15 free & 15 slave states
It’s defeat increased sectional feelings
Three Conflicting Positions on Slavery Expansion
Free-Soil Movement
N. Democrats + Whigs supported the Wilmot Proviso & that all African Americans should be excluded from the Mexican Cession
Didn’t oppose S. slavery; they sought to keep the West a land of opportunity for Whites only
Organized the Free-Soil Party
This party aimed to prevent the extension of slavery & advocated for internal improvements
Consisted of Conscience Whigs (opposed slavery) & antislavery Democrats
“Barnburners” — their defection threatened to destroy the Democratic Party
Southern Positions
Southern plantation owners viewed attempts to restrict the expansion of slavery as a violation of the their right to take property wherever they wished
Saw Free-soilers + abolitionists as intent on the destruction of slavery
Some southerners were moderate & wanted to expand the Missouri Compromise westward
Popular Sovereignty
Lewis Cass proposed a compromise solution that moderates across the country supported
Suggested determining whether to allow slavery in a western territory/state should be voted on by ppl who settled in this area → popular sovereignty
The Election of 1848
The expansion of slavery was vital in the presidential election of 1848
Democrats: nominated Senator Cass & pledged to popular sovereignty
Whigs: nominated Zachary Taylor (never been involved in politics & had no position on slavery in the W. territories)
Taylor narrowly won over Cass
Free-Soil Party: nominated Martin Van Buren & opposed expansion
Compromises to Preserve the Union
Gold Rush (1849)
100k+ settlers into California → need for law & order in the West
California Constitution
In 1849, California drafted a state constitution — one that banned slavery
President Taylor supported admitted California + N. Mexico as free states
Henry Clay’s Proposed Compromise
Southern extremists discussed secession, until Clay proposed this plan:
Admit California as a free state
Divide the rest of the Mexican Cession into Utah & N. Mexico & allow their settlers to decide the slavery issue by popular sovereignty
Give the land in dispute b/t TX & the New Mexico territory to the new territories, for the nat’l gov’t to assume TX’s debt of $10 million
Ban the slave trade in DC, but not slavery
New Fugitive Slave Law & heavily enforce it
Daniel Webster supported it to save the Union
John C. Calhoun opposed & insisted the South be given equal rights
N. opposition mostly came from younger antislavery lawmakers like William H. Seward
Passage of the Compromise of 1850
Passed by President Fillmore after Z. Taylor died in 1850
North had more political power since California was admitted as free
Deepended the commitment of many Northerners to save the Union from secession
Fugitive Slave Law + popular sovereignty = controversial
5.5 Sectional Conflict: Regional Differences
Sectionalism: regional interests that vary across a country/territory
Immigration Controversy
More immigrants = opposition about their ethnicity, religious faiths, or fear that they’d take low-wage jobs
Irish
Discriminated for Roman Catholic faith + competed w/A. Americans for domestic work & low-wage jobs
Most stayed where they landed → N. cities developed Irish community like Boston & NY
Many Irish immigrants entered politics & joined the Democratic Party (anti-British & pro-worker)
Secured job’s in NYC’s Democratic organization – Tammany Hall – by 1850s & controlled it by the 1880s
German
Moved West for cheap & fertile farmland → established homesteads throughout the Old NW
Strongly supported public education & strongly opposed slavery
Formed communities where German was spoken & some established Roman Catholic or Lutheran churches
Nativist Opposition to Immigration
Native-born Americans = alarmed that immigrants would take jobs & dilute their culture
Opponents to immigration were often Protestant, Irish + Germans were typically Roman Catholics
Nativism: hostility to immigrants → rioting in big cities
Dissolved after division over slavery increase
American/Know-Nothing Party: antiforeign society formed by nativists
Wanted to increase the time immigrants need for citizens from 5 years to 21 years & only allow native-born citizens to hold public office
Gained strength in N. England & Mid-atlantic states after the Whig Party dissolved
The Expanding Economy
Territorial expansion → economic growth b/t 1840s-1857
Industrial Technology
Before 1840: factory production was mainly in textile mills in N. England
After 1840: industrialization spread to other Northeast states
Clothing, sewing machines, firearms, and iron products (for railroads)
Elias Howe invented the sewing machine → clothing production into factories
Samuel F. B. Morse’s electric telegraph helped speed up communication & transportation along with railroads
Impact on sectionalism: the economic interests of various regions were transformed, which contributed to greater devotion to one’s region & increased tensions about slavery
Railroads
Emerged as America’s largest industry → expanded across Northeast + Midwest
Required lots of capital & labor → complex business organizations
Local + state gov’t helped by granting special loans + tax breaks
U.S. gov’t gave 2.6 million acres of federal land for Illinois Central Railroad
This transportation promoted Western agriculture + united commercial interests of Northeast + Midwest, which gave the N. advantages during the Civil War
Impact on sectionalism: increased connectivity nationwide, helped Northern economy, but hindered the South’s ability to diversify its economy
Panic of 1857
Decreased prices for Midwestern agricultural products + unemployment in N. cities
Cotton prices = high; South was less affected
Southern farmers believed plantation economy was superior & continued union with N. economy wasn’t needed
Impact on sectionalism: further illustrated the economic disparities b/t the North & South
Agitation Over Slavery
Period b/t Compromise of 1850 + Kansas Nebraska Act (1854) → political tensions had slightly relaxed
Fugitive Slave Law
Persuaded Southerners to accept California as a free state; resented by Northerners
Aimed to help owners track down runaway slaves that had escaped to the N. & return them to their Southern owners
Enforcement
Removed fugitive slave cases from state courts → exclusive to federal gov’t
U.S. commissioners could issue warrants to arrest fugitives
A captured person who claimed to be free was denied a trial by jury
State + local law officers were required to enforce this law
Opposition
Anyone who attempted to hide a runaway or failed to enforce the law was subject to heavy penalties
Black + White activists in the N. bitterly resisted
Tried to protect A. Americans from slavery through court cases, protests, and sometimes force
Underground Railroad
A network of activists who helped enslaved people escape to freedom in the N./Canada
Most “conductors” = free A. Americans who had escaped slavery + White abolitionists
e.g) Harriet Tubman (helped ~300 ppl escape)
Free Black citizens in the N. + abolitionists organized vigilance committees to protect fugitive slaves from catchers
Books on Slavery
Uncle Tom’s Cabin: portrayed slaveowners as cruel and inhuman – moved Northerners
Aunt Phillis’s Cabin in response → pro-slavery
Impending Crisis of the South: anti-Slavery & attacked it by using statistics to demonstrate how it weakened the Southern economy
Pros: increased awareness, further motivation to end slavery
Cons: graphic content, bias, and increased tensions about slavery
Southern Reaction
Argued that slavery benefited both the master & enslaved
Supported by: the Constitution & Bible
Contrasted N. wage “slaves” with bonds developed b/t slaves & their masters on plantations
George Fitzhugh: best-known proslavery author – attacked the wage system
Effect of Law & Literature
Northerners who opposed slavery for economic reason were worried about the moral issues of slavery
Wealthy Southerners were worried Northerners would abolish slavery
5.6 Failure of Compromise
The North and South were divided on: (1) the morality of slavery, (2) constitutional rights of states (esp. the right to protect slavery), and (3) differences over economic policies
National Parties in Crisis
As slavery led to political instability, Democrats & Whigs grew weak & divided over how to resolve sectional differences on slavery
The Election of 1852
Whigs focused on improving roads & harbors, but the sectional issue of slavery couldn’t be ignored → the party was on the verge of splitting
Democrats nominated Franklin Pierce because he was overall acceptable (e.g. he supported the Fugitive Slave Law — appealed to Southerners) → won the election
The Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)
Stephen A. Douglas proposed a transcontinental railroad to promote Western settlement
Douglass introduced a bill that allowed settlers in Kansas & Nebraska territories to vote on whether to allow slavery — appealed to Southerners to expand slavery, so they would support the railroad
Repealed the Missouri Compromise & greatly increased tensions over slavery
Extremists and Violence
“Bleeding Kansas”
Fighting broke out b/t proslavery and antislavery groups as a result of:
Antislavery farmers in Kansas, proslavery settlers from Missouri, & the New England Emigrant Aid Company (N. abolitionists + Free Soilers paid for transportation of antislavery settlers to Kansas) who voted on the act
Proslavery Missourians/”border ruffians” created a proslavery legislature in Kansas, & antislavery settlers created their own legislature in turn
John Brown & his sons attacked a proslavery settlement - Pottawatomie Creek
The Pierce administration failed to keep order in Kansas → Democratic Party become more divided
Caning of Senator Sumner
Sumner-Brooks incident: Charles Sumner’s “The Crime Against Kansas” attacked Democratic administration & South Carolina’s senator Andrew Butler
Butler’s nephew - Preston Brooks - beat Sumner over the head with a cane
Demonstrated growing passion on both sides
Birth of the Republican Party
As tension increased, those were frightened joined the Know-Nothing Party - didn’t last long
Ex-whigs who supported expanding slavery normally joined the Democratic Party
Ex-whigs who opposed slavery formed the Republican Party in 1854, as a result of the Kansas-Nebraska Act
It was composed of Free-soilers + antislavery Whigs & Democrats; strictly Northern
It aimed to prevent slavery from spreading into the territories
James Buchanan (Democrat) won the 1856 election against Republican John C. Fremont
Constitutional Issues
Lecompton Constitution
A proslavery state constitution for Kansas → many Democrats joined Republicans in Congress to reject it
Kansas settlers opposed it as many were antislavery Republicans
Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
The Supreme Court ruled against Dred Scott who sued for his freedom because:
He wasn’t constitutionally considered a citizen
Congress couldn’t exclude slavery from any federal territory or deprive any person of property without due process of law
Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional
In turn, Supreme Court declared all Western territories open to slavery
Northerners suspected Democrats had planned the Dred Scott decision → thousands of Democrats voted Republican
Lincoln-Douglas Debates
Lincoln’s “house-divided” speech won him fame & Southerners viewed him as radical
Made him a leading contender for Republican nomination in 1860 election
Freeport Doctrine upset S. Democrats since Douglas didn’t strongly support the Dred Scott decision
5.7 Election of 1860 & Secession
The Road to Secession
John Brown’s Raid at Harpers Ferry
Oct. 1859: John Brown led a raid attempting to arm slaves in Virginia to start a slave revolt
Southern whites saw the raid as proof of North’s intentions to use slave revolts to destroy the South
The Election of 1860
Breakup of the Democratic Party
N. + S. democratic held different nominating conventions
S. Democrats nominated John C. Breckinridge & called for the unrestricted extension of slavery in the territories + the annexation of Cuba
Republican Nomination of Lincoln
The Republican platform called for: exclusion of slavery from territories, protective tariff, free land for homesteaders, and internal improvements to encourage western settlement
4th Political Party
Constitutional Union Party: enforce laws + the Constitution & preserve the Union
Consisted of ex-Whigs, Know-Nothings, & moderate Democrats
Election Results
Lincoln won with 59% of the electoral votes, but less than 50% of the popular vote
Showed that populous free states had enough electoral votes to select a president without the need for a single electoral vote from the South
Secession of the Deep South
Lincoln’s election led to the secession of South Carolina from the Union → other states from the Deep South followed
Formed the Confederate States of America + placed limits on the gov’t ability to impose tariffs & restrict slavery
Crittenden Compromise
John Crittenden proposed a constitutional amendment that allowed the right to hold slaves in all territories S. of the old Missouri Compromise line, 36°30´ — Lincoln didn’t accept it since it violated the Republican position against the extension of slavery
A Nation Divided
Fort Sumter
Confederate forces opened fire after Lincoln announced he was sending provisions of food to the small federal garrison
United Northerners behind a patriotic fight to save the union
Marked the start of the Civil War in April 1861
Secession of the Upper South
4 additional states seceded & joined the Confederacy — 11 total
Keeping the Border States in the Union
Military & political goal: keeping the border states in the Union
South’s population increase by 50% if they gained the border states
Lincoln initially rejected calls for emancipation of slaves
5.8 Military Conflict in the Civil War
Civil War caused 750k+ deaths → “costliest American war”
4 million slaves were freed + the N. was greatly industrialized & modernized
War | Differences
Military
Confederacy: fought a defensive war → moved troops + supplies shorter distances
Indented coastline= difficult to blockade, experienced troop leaders & high troop morale
Union: population = 22 million; South population = 5.5 million
Union population enhanced during the war by 800,000 immigrants
Emancipation brought 180,000 African Americans to the Union army (in critical years of war)
U.S. Navy was loyal - gave command of territorial waters
Economic
Union controlled the majority of factories, railroads, and even farmland
Confederacy counted on outside help for success
Political
Union had a strong central gov’t w/strong public support
Confederates hoped Union would turn against Lincoln + Republicans would quit due to war’s costliness
Confederate States of America
Confederate Constitution: modeled after U.S. Constitution, but denied…
Congress the power to levy a protective tariff & appropriate funds for internal improvements
Prohibited foreign slave trade
Jefferson Davis: president who tried to increase his executive powers; S. governors resisted
Economy: short of money
Issued $1 billion+ → inflation
Had to make resources last until the Union stopped fighting
First Years of War: 1861-62
Union Strategy
Winfield Scott had a 3 part plan to win the war:
U.S. Navy to blockade S. ports - Anaconda Plan
Take control of Mississippi River → split South in half
Train army of 500k+
1st Battle of Bull Run
30k+ Union troops attacked Confederate forces at Bull Run Creek
Confederate reinforcements counterattacked → Union troops lost
Peninsula Campaign
General George McClellan’s troops had extended training
Invaded Virginia → stopped by Confederate Robert E. Lee’s troops + tactics
2nd Battle of Bull Run
Union forces were quickly defeated by Lee + the confederacy → withdrew to defend D.C.
Antietam
U. troops intercepted Confederates → bloodiest day of Civil War (22k+ killed/wounded)
Confederacy aimed to gain recognition + support from Britain & France
Failed + retreated to Virginia
Union didn’t lose → Lincoln used this to issue the Emancipation Proclamation
Fredericksburg
U. General Burnside attacked Confederate troops in Virginia → immense losses
Showed no prospect of victory for either side
Monitor v. Merrimac
Confederate Merrimac vs. Union Monitor
Turning point in naval warfare: ironclad ships (covered in metal plates) replaced wooden ones
Grant in the West
Ulysses S. Grant led the campaign for control of the Mississippi River
Captured Forts Henry + Donelson & 14k+ Confederate troops
Later, Confederate forces surprised Grant in Shiloh, TN → retreated
David Farragut captured New Orleans, which helped Grant
Foreign Affairs & Diplomacy
Confederates hoped cotton would induce Britain + France to aid their war effort
Union needed to prevent this; many British ppl wanted to end the American democratic experiment
Trent Affair
Confederate diplomats were traveling to England → Union warship stopped the ship & imprisoned them
Britain threatened war → Lincoln released them & Confederacy wasn’t recognized by foreign nations
Confederate Raiders
British allowed confederacy to purchase warships → harmed U.S. merchant ships
Failure of Cotton Diplomacy
“King Cotton” didn’t have enough power for foreign intervention
Britain didn’t intervene after:
Confederates didn’t have a decisive victory at Antietam
Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation → appealed to British working class
Union Triumphs: 1863-65
Early 1863: Confederacy was in bad shape → economy suffered & starving soldiers deserted
Turning Point
Vicksburg
General Grant captured this city
Federal warships controlled entire Mississippi River → cut off states like TX from confederacy
Gettysburg
Lee led this attack & aimed for Union to call for peace OR to gain foreign intervention
50k+ casualties overall → confederacy retreated & never regained the offensive
Grant in Command
Grant’s Plan
Wear down Confederate armies by destroying their supply lines
He reduced Lee’s army gradually → forced it into a defensive line around Richmond
Sherman’s March
William Sherman led 100k+ men through Georgia/the South & destroyed infrastructure
Helped break the spirit of the Confederacy
The End of the War
What led to surrender?
Union blockade, Sherman’s March, hunger throughout the South
Fall of Richmond: April 1865
Surrender at Appomattox
Confederacy tried to negotiate → Lincoln demanded restoration of the Union
Lee tried to escape to the mountains after the Fall of Richmond → surrendered to Grant
5.9 Government Policies During the Civil War
Lincoln acted in unprecedented ways like:
After Fort Sumter he called for 75k volunteers to put down the Confederate ‘insurrection’
Authorized spending for a war
Suspending the writ of habeas corpus (ppl could be arrested w/o knowing the charges against them)
The End of Slavery
Military & political goal: keeping the border states in the Union
South’s population increase by 50% if they gained the border states
Lincoln initially rejected calls for emancipation of slavery
Confiscation Acts
Union army could seize enemy property (e.g. enslaved people), used to wage war against the United States.
Freed ppl enslaved by one who rebelled against the U.S.
Emancipation Proclamation
Lincoln issued a warning after the Battle of Antietam (Sep. 1862) that slaves in states still in rebellion by 1863 would be free
Gave Union a shift in motivation & goal of war to end slavery + unification
African Americans in the War
~200k A. Americans served in the Union army
All-black units like the Massachusetts 54th Regiment
Susie King Taylor gained freedom & was a nurse for the Union military
Effects of the War on Civilian Life
Political Change
Radical Republicans: immediate abolition of slavery
Free-soil Republicans: economic opportunities for Whites
Most Democrats: supported war; criticized Lincoln
Peace Democrats/Copperheads: opposed war; wanted to negotiate peace
Civil Liberties
Lincoln focused on prosecuting the war than protecting constitutional rights
Only congress could suspend habeas corpus → Supreme Court ruled Ex Parte Milligan that the gov’t had improperly subjected citizens to military trials
The Draft
Union’s Conscription Act: all men aged 20-45 were liable for military service
Irish & German immigrants feared that freed A. Americans would take their jobs
100+ killed before temporary suspension of draft
The Election of 1864
Lincoln ran as a “Unionist” with War Democrat Andrew Johnson → won
Political Dominance of the North
Military triumph of the Union → supremacy of the federal gov’t
Gettysburg Address signified the importance of reunifying the nation + abolishing slavery
Economic Change
Financing the War
Union financed war by borrowing money through gov’t bonds
N. prices rose ~80%
Greenbacks: paper currency ordered by U.S. treasury; caused inflation
Modernizing N. Society
War accelerated a modern industrial economy
Republican politics stimulated economic growth in the N. & West
Morrill Tariff Act: raised tariffs rates → protect American manufacturers
Homestead Act: promoted settlement of Great Plains; offered free land to people who farmed it for 5+ years
Morrill Land Grant Act: encouraged federal land grants → find + maintain agricultural & technological colleges
Pacific Railway Act: transcontinental railroad; link W. + E. economies
Assassination of Lincoln
Lincoln was killed by John Wilkes Booth in 1865
Sec. of State Seward was also killed that day
5.10 Reconstruction
Postwar Conditions
Conflicts that existed prior to & during the Civil War continued after
N. Republicans = continue economic progress they began during the war
S. aristocrats = low-cost labor for their plantations
Physical rebuilding of S. left up to states + individuals; federal gov’t focused on political issues
Lincoln’s Reconstruction Plans
Lincoln’s believed Southern states could not constitutionally leave the Union
He viewed confederates as a disloyal minority
Proclamation of Amnesty
Political reconstruction of Southern state gov’ts; Unionists would be in charge
Presidential pardons for Confederates who took a loyalty oath to the Union + U.S. Constitution & accepted the emancipation of slaves
State gov’t re-established after at least 10% of voters in the state took loyalty oath
Required rewriting of state constitutions
Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
Congress passed - 50% of voters in a state needed to take loyalty oath + only non-Confederates could vote for a new state constitution
Lincoln vetoed → tensions rose b/t president & Congress
Freedmen’s Bureau
Welfare agency for Americans left destitute by Civil War
Initially could resettle freed blacks on confiscated land in the South
Given back after Johnson pardoned Confederate owners
Biggest success was education; ~3000 schools for freedpeople
Johnson’s Reconstruction Plans
Johnson’s Reconstruction Policy
Disenfranchised all former leaders of the Confederacy & Confederates with $20k+ in taxable property
President could grant pardons → former Confederate leaders were back in office
Gave southern state governments ability to restrict rights of black people with their constitutions (didn’t expand voting rights and were able to more easily gain seats in Congress)
Johnson’s Vetoes
Vetoed a civil rights bill that nullified Black Codes + granted A. Americans full citizenship
Black Codes restricted rights and movement of former slaves
Congressional Reconstruction
Republican Divisions
Moderates: concerned with economic gains for White middle class
Radicals: civil rights for Black citizens
13th Amendment
Prior to this, only laws had banned slavery → this amendment abolished slavery
Civil Rights Act of 1866
All African Americans were U.S. citizens + aimed to provide a legal shield against Black Codes
Frederick Douglass’s “The Composite Nation” speech argued for Chinese Americans to be citizens
14th Amendment
All those born or naturalized in US were citizens
Obligated states to respect rights of US citizens
Report of the Joint Committee
Reorganized Confederate states weren’t entitled to representation in Congress
Congress has the power to determine conditions for allowing states to rejoin the Union
The Election of 1866
Republicans had an overwhelming victory; more than 2/3 majority is the HOR + Senate
Reconstruction Acts of 1867
Divided South into military districts each under the control of the Union army
Increased requirements to rejoin the Union
Impeachment of Andrew Johnson
Congress passed the Tenure of Office Act - prohibited president from removing a federal official w/o Senate approval
Johnson dismissed his Sec. of War, Stanton → Congress impeached him
Reforms After Grant’s Election
Election of 1868
Ulysses S. Grant won - due to 500k votes from Black men
15th Amendment
Universal male suffrage
States still passed other restrictions on voting rights
Civil Rights Act of 1875
Equal accommodations in public places + A. Americans were able to be on juries → poorly enforced
Reconstruction in the South
Composition of the Reconstruction Governments
Military Troops
Each Republican controlled gov’t was under military protection until Congress felt a state had met its Reconstruction requirements
Scalawags & Carpetbaggers
Derogatory terms from Democratic opponents:
Scalawag: Southern Republican
Carpetbagger: Northern newcomers
African American Legislators
South sent 2 A. Americans to the Senate + over a dozen to the HOR
African Americans Adjusting to Freedom
Building Black Communities
Reuniting families, learning to read and write, or migrating new cities
Drive for autonomy → hundreds of independent African American churches
Established independent schools + colleges like Howard & Shaw
Emigrate South to frontier states
North During Reconstruction
Rise of Spoilsmen
Republican leadership passed to political manipulators → gave jobs + favors to supporters
Corruption in Business & Government
Credit Mobilier affair: insiders gave stock to influential Congress members to avoid investigation into their profits
Election of 1872
Grant administration scandals → reform-minded Republicans broke from their party
Liberal Republicans: civil service reform, reduced tariffs, and freer trade
Grant won reelection
Panic of 1873
Overspeculation + overbuilding by industry & railroads → business failures + depression
Diverted the North’s attention away from the South → hurt Black Southerners
Women’s Changing Roles
Civil War → women had more responsibilities
Held jobs, operated farms, & were military nurses
Women’s Suffrage
Increased responsibilities boosted demands for equal voting rights
Advocates like Susan B. Anthony & Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Wyoming Territory was the first territory to grant women’s full suffrage rights
5.11 Failure of Reconstruction
Lincoln’s last speech suggested he likely would’ve moved to have more progressive views
Addressed whether freedmen should be given the right to vote & encouraged Northerners to accept Louisiana as reconstructed
Evaluating the Republican Record
Accomplishments: universal male suffrage, property rights for women, promoted internal improvements, & provided state-supported public school systems
Failures: wasteful spending & corruption from politicians
The End of Reconstruction
Redeemers
Southern conservatives who took control of state governments
States’ rights, reduced taxes + spending on social programs, & White supremacy
Ku Klux Klan
A secret society that aimed to intimidate A. Americans & White reformers
Burned Black-owned buildings & murdered thousands of freedmen to stop them from voting
Force Acts
Passed by Congress; allowed federal authorities to stop KKK violence & protect civil rights
Southern Governments
11 ex-Confederate states qualified to become part of the Union
e.g) drew state constitutions that repudiated secession & ratified the 13th amendment
Didn’t extend voting rights to Blacks & former Confederate leaders had Congressional seats
Black Codes
Restricted rights of A. Americans
e.g) Couldn’t rent land/borrow money to buy it & couldn’t testify against Whites in court
13th amendment allowed one convicted of a minor crime to be rented from the gov’t to a landowners - essentially slave labor
Sharecropping
Landlord provided seed & needed farm supplies in return for a share of the harvest (often ½)
It offered little economic opportunity & became a new form of servitude
Amnesty Act of 1872
Removed restrictions on ex-Confederates, except for top leaders
Allowed Southerners to vote for Democrats & retake control of state gov’ts
Election of 1876
Democrat candidate - Tilden - had won the popular vote, but..
A special electoral commission determined who gained the disputed votes from SC, FL, and LA → Republican candidate - Hayes - won & Democrats were outraged
The Compromise of 1877
Democrats allowed Hayes to become president if he withdrew federal troops in the South & supported a S. transcontinental railroad
Brought Reconstruction to an end; most looked westward & focused on industrial growth