limits involving infinity
finite limits are x→±∞
- the symbol for infinity does not represent a real number; we use it to describe the behavior of a function when the values in its domain or range outgrow all finite bounds
- x→±∞: increasingly to the right or left
- a function may have multiple horizontal asymptotes (one to positive infinity and the other to negative infinity)
- in general, for a rational function of the form f(x)/g(x) where f(x) and g(x) are both polynomials, the end behavior model (EBM) is found by dividing the highest powered term of f by the highest powered term of g
- the key to end behavior is that while the EBM ≠ the original function, it has the same limit as the original function

for a function of the form f(x)/g(x), where f and g are polynomials,
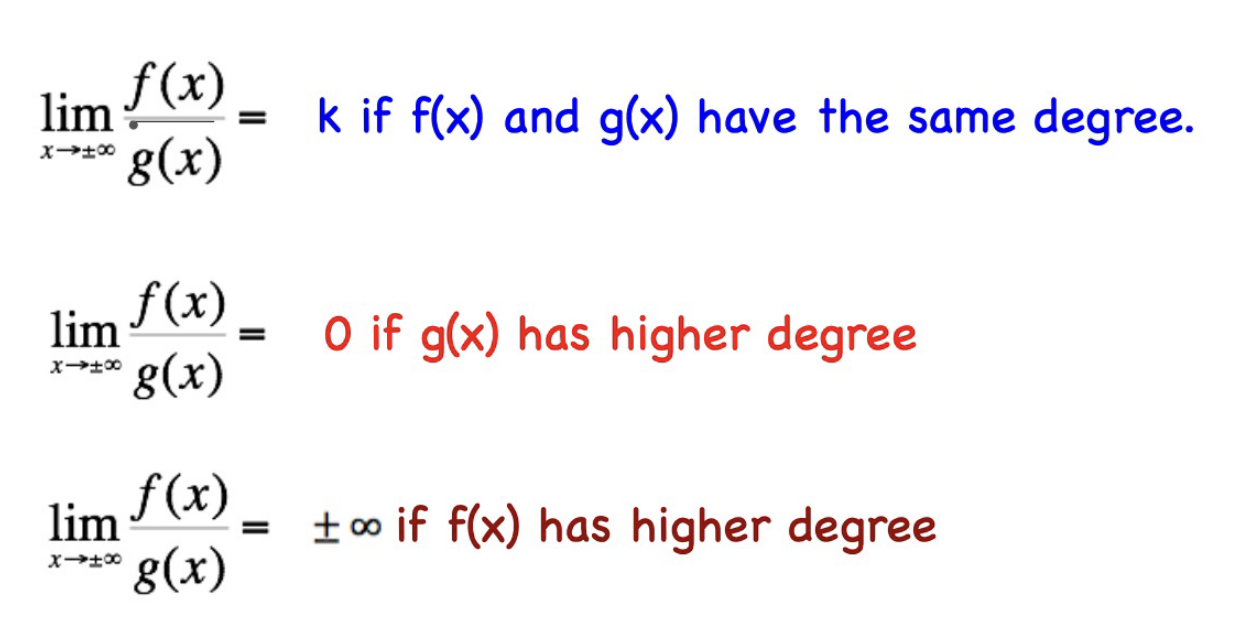
- the sandwich theorem and limit properties also hold for x→±∞