Psychology - Sensation and Perception
Why do psychologists study sensation and perception?
sensation and perception change our mental process
The Five Senses:
touch
taste
hearing
smell
sight
Sensation: the activation of the sense organs by a source of physical energy; EX: sensing a bright light, sound, or pinch
Perception: the sorting out, interpretation, analysis, and integration of stimulus involving the sense organs and brain (brain kicks in); EX: feeling the heat of a hot pepper
Stimulus: energy that produces a response; EX: bright light causes you to squint
Absolute threshold: the minimum stimulation level an organism needs to sense a stimulus
Sensory adaptation: a phenomenon in which the body adjusts to external stimuli over time, becoming less sensitive or responsive to that particular stimulus
Extra Sensory Perception (ESP): belief that some people have knowledge of information that is not gained through the senses
Telepathy - mental transfer of information from one person to another
Clairvoyance - medium (communicate with the dead) or finding lost people
Pre-Cognition - predicting future events
Intuition and Deja-vu - gut feeling/feeling that something has happened
The Visual Spectrum
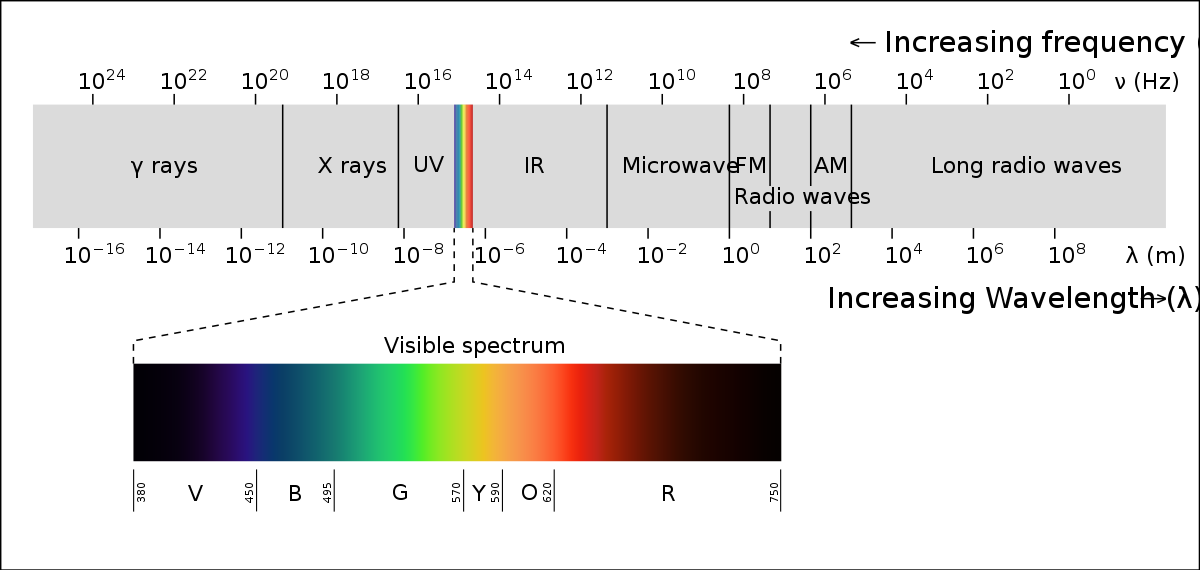
Vision
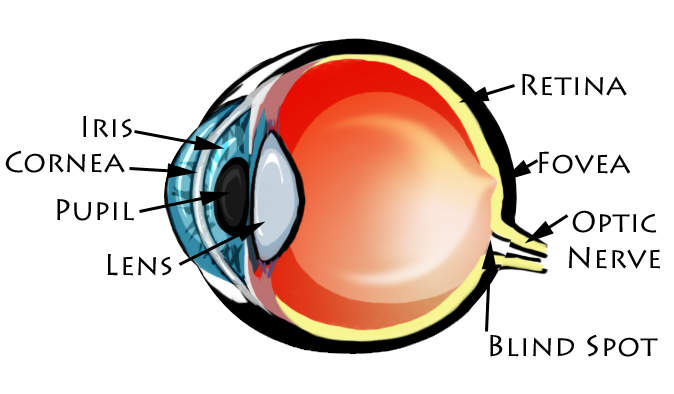
Parts of the Eye:
Iris: the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil, it regulates the amount of light that enters the eye
Cornea: the clear tissue in front of your eye, helps to protect your eye and filters out some UV light
Pupil: the opening at the center of the iris through which light passes, The size of the pupil adjusts to control the amount of light that enters the eye
Lens: a clear disk behind the iris, that bends light and focuses it for the retina to help see images clearly
Optic Nerve: connects the eye directly to the brain
Blind Spot: the spot in the retina where the optic nerve connects, there are no light-sensitive cells, so this part of the retina cannot see
 Peripheral Vision: how well can you see what you’re not staring at
Peripheral Vision: how well can you see what you’re not staring at
Important for:
Balance
Safety (driving)
Sports
fear causes the narrowing of blind spot
tunnel vision
Rods: microscopic structures in the eye that help you see in the dark
Cones: microscopic structures in the eye that help you see color
lack of cones = varying degrees of colorblindness
Light Adaptation: eyes adapting to bright light
Dark Adaptation: eyes adapting to a dark environment
eyes adapt quicker to bright light than to dark
Color Blindness: when you have fewer or no cones
the average person can see 7 million colors
1/50 men are colorblind
1/5000 women are colorblind
women can see more colors than men even if not colorblind
Afterimage: an image that you seem to see when you are no longer looking at an image
Hearing
women prefer deeper voices
men prefer higher-pitched voices
women can match voice to face with 60% accuracy
can predict age, height, weight, and social class
men can match voice to face with 20% accuracy
Smell
Pheromone: Naturally occurring chemicals in the body that are secreted into the environment. These secretions produce a reaction in other members of the same species
Flashbulb Memory: a memory is triggered when one of the senses is stimulated. That memory is so memorable because it was surprising, unexpected, and/or unusual (songs, scent)
How it impacts behavior:
choosing where you go to eat
choosing whether or not to stay in a room
Women have a better sense of smell:
mothers can identify babies by their scent
women who live together sync menstrual cycles
It impacts attraction
women prefer the smell of men with different immune systems
Children would receive genetic coding of both parents and would therefore have a stronger immune system
 Knowt
Knowt
