Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System
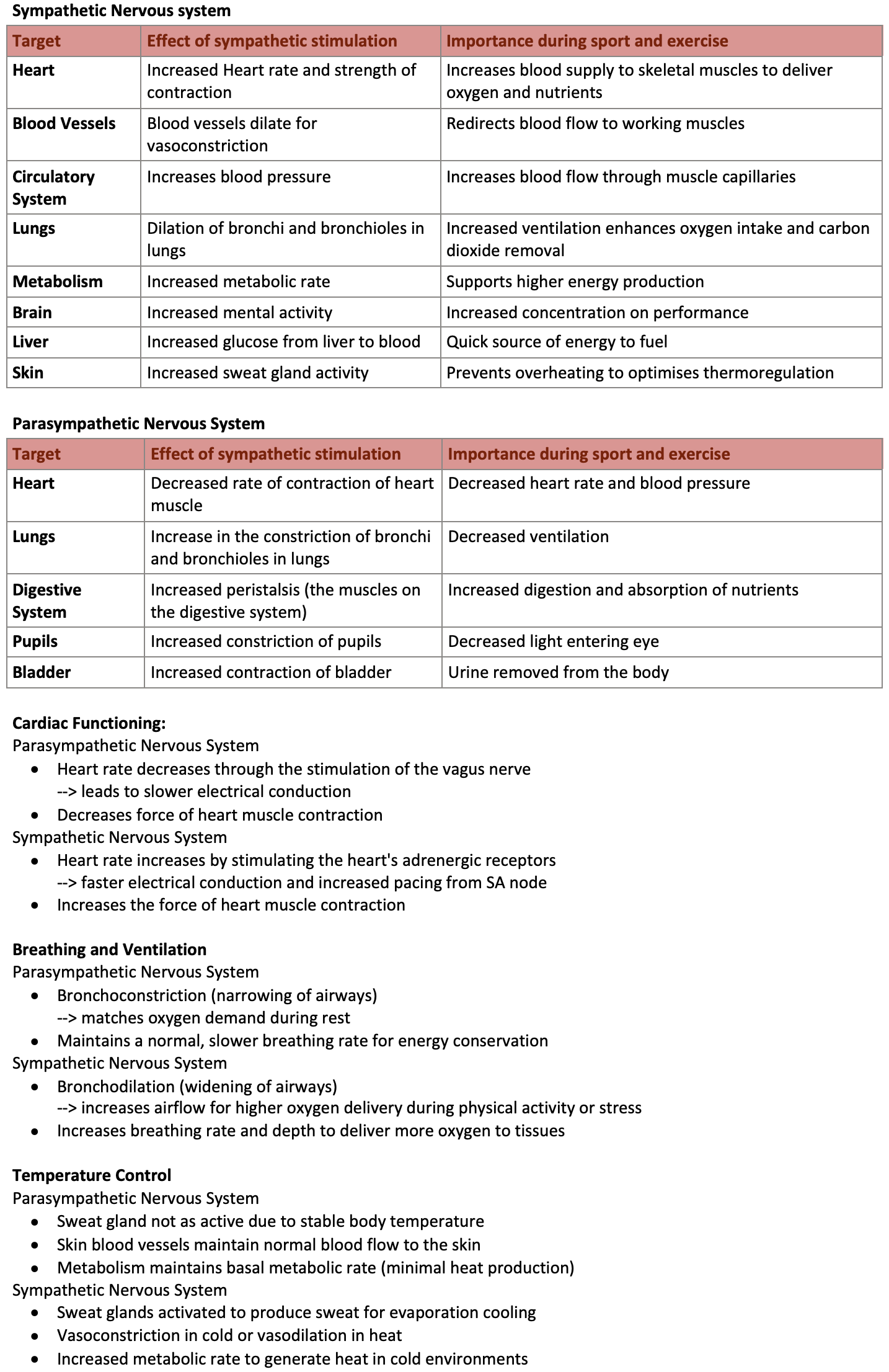
Sympathetic Nervous system
Target | Effect of sympathetic stimulation | Importance during sport and exercise |
Heart | Increased Heart rate and strength of contraction | Increases blood supply to skeletal muscles to deliver oxygen and nutrients |
Blood Vessels | Blood vessels dilate for vasoconstriction | Redirects blood flow to working muscles |
Circulatory System | Increases blood pressure | Increases blood flow through muscle capillaries |
Lungs | Dilation of bronchi and bronchioles in lungs | Increased ventilation enhances oxygen intake and carbon dioxide removal |
Metabolism | Increased metabolic rate | Supports higher energy production |
Brain | Increased mental activity | Increased concentration on performance |
Liver | Increased glucose from liver to blood | Quick source of energy to fuel |
Skin | Increased sweat gland activity | Prevents overheating to optimises thermoregulation |
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Target | Effect of sympathetic stimulation | Importance during sport and exercise |
Heart | Decreased rate of contraction of heart muscle | Decreased heart rate and blood pressure |
Lungs | Increase in the constriction of bronchi and bronchioles in lungs | Decreased ventilation |
Digestive System | Increased peristalsis (the muscles on the digestive system) | Increased digestion and absorption of nutrients |
Pupils | Increased constriction of pupils | Decreased light entering eye |
Bladder | Increased contraction of bladder | Urine removed from the body |
Cardiac Functioning:
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Heart rate decreases through the stimulation of the vagus nerve
--> leads to slower electrical conduction
Decreases force of heart muscle contraction
Sympathetic Nervous System
Heart rate increases by stimulating the heart's adrenergic receptors
--> faster electrical conduction and increased pacing from SA node
Increases the force of heart muscle contraction
Breathing and Ventilation
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Bronchoconstriction (narrowing of airways)
--> matches oxygen demand during rest
Maintains a normal, slower breathing rate for energy conservation
Sympathetic Nervous System
Bronchodilation (widening of airways)
--> increases airflow for higher oxygen delivery during physical activity or stress
Increases breathing rate and depth to deliver more oxygen to tissues
Temperature Control
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Sweat gland not as active due to stable body temperature
Skin blood vessels maintain normal blood flow to the skin
Metabolism maintains basal metabolic rate (minimal heat production)
Sympathetic Nervous System
Sweat glands activated to produce sweat for evaporation cooling
Vasoconstriction in cold or vasodilation in heat
Increased metabolic rate to generate heat in cold environments