Chapter 7: Atmospheric Pollution
7.1: Introduction to Air Pollution
- Air pollution: It occurs when harmful or excessive quantities of substances are introduced into Earth’s atmosphere.
- Parts per million (ppm): The most common form of expressing air pollutants.
- Primary Pollutants: Emitted directly into the air.
- Secondary Pollutants: Result from primary air pollutants’ reacting together and forming new pollutants.
- Point source air pollution: It occurs when the contaminant comes from an obvious source.
- Non-point source air pollution: It occurs when the contaminant comes from a source that is not easily identifiable or from a number of sources spread over a large, widespread area.
- Criteria air pollutants: These are a set of eight air pollutants that cause smog, acid rain, and other health hazards and are typically emitted from many sources in the industry, mining, transportation, power generation, and agriculture.
7.2: Atmospheric CO2 and Particulates
- Industrial smog: Trends to be sulfur-based and is also called gray smog.
- Formation of Industrial Smog
- Carbon in coal or oil is burned in oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide gas.
- Unburned carbon ends up as soot or particulate matter (PM).
- Sulfur in oil and coal reacts with oxygen gas to produce sulfur dioxide.
- Sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen gas to produce sulfur trioxide.
- Sulfur trioxide reacts with water vapor in the air to form sulfuric acid.
- Sulfuric acid reacts with atmospheric ammonia to form brown, solid ammonium sulfate.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Carbon monoxide: It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly less dense than air and is produced from the partial oxidation of carbon-containing compounds.
- %%It forms when there is not enough oxygen to produce carbon dioxide.%%
- Carbon monoxide is present in small amounts in the atmosphere, primarily as a product of the following:
- Natural and man-made fires.
- Photochemical reactions in the troposphere.
- The burning of fossil fuels
- Volcanic activity
- Methods to reduce carbon monoxide pollution include the following:
- Building more public transportation infrastructure
- Requiring catalytic converters on all cars worldwide; however, this only converts carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide—a greenhouse gas
- Switching to renewable energy sources
Lead (Pb)
- Lead: It is used in building construction, lead-acid batteries for vehicles, bullets and shot fishing weights, solder, and shields for radiation.
- Exposure to lead can occur from inhalation of polluted air and dust and from the ingestion of lead in food and/or water.
- Symptoms of lead poisoning include failure of the blood to make hemoglobin, which results in anemia disruptors, mental retardation and disabilities, hypertension, miscarriages and/or premature births, and even death at relatively low concentrations.
Nitrogen Oxides
- Nitrogen Oxide: A generic term for nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide, which are produced from the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen gases in the air.
- These gases are %%formed whenever nitrogen occurs in the presence of high-temperature combustion.%%
- Nitrous oxide: It is a major air pollutant, with levels of N2O having increased by more than 15% since 1750.
- It causes ozone depletion.
- It is formed by denitrification and nitrification.
Ozone
- Ozone: It is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula O3, and tropospheric (ground-level) ozone is a secondary air pollutant.
- Tropospheric ozone: It does not have strong global effects, but instead is more influential in its effects on smaller, more localized areas.
- Tropospheric ozone can have the following effects:
- Cause asthma and bronchitis
- Harm lung function and irritate the respiratory system
- Result in heart attacks and other cardiopulmonary problems
- Suppress the immune system.
Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PANs)
- Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PANs): These are secondary pollutants. Because they break apart quite slowly in the atmosphere into radicals nd NO2, PANs are able to move far away from their urban and industrial origin.
- It causes:
- Eye irritation
- Impaired immune systems
- Inhibited photosynthesis
- Reduced crop yields by damaging plant tissues
- Respiratory problems
- Methods to reduce PANs include the following:
- Limiting wood-burning fireplaces and stoves in new home construction
- Reducing smokestack emissions through baghouse filters, cyclone precipitators, scrubbers, and/or electrostatic precipitators
- Reducing the incineration of municipal and industrial wastes
- Reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, especially oil and coal
Sulfur Dioxides
- Sulfuric Dioxide: A colorless gas with a penetrating, choking odor that readily dissolves in water to form an acidic solution.
- Sulfur dioxide emissions come from power stations, oil refineries, and large industrial plants burning fossil fuels.
- It is toxic to a variety of plants and reduces crop yields.
- Sulfur dioxide, emitted in sufficient quantities at low or ground level, can %%combine with air moisture to form an acid solution that dissolves stonework%%.
- It irritates the throat and lungs, and, if there are fine dust particles in the air, can damage the respiratory system.
- Steps that can be taken to reduce the amount of SO2 in the atmosphere include the following:
- Fluidized gas combustion
- Using only low-sulfur coal
- Using scrubbers in the smokestacks
- Washing the coal
Suspended Particulate Matter
- Suspended particulate matter (PMx): It is microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in Earth’s atmosphere.
- The “x” refers to the size of the particle.
- The smaller and lighter a particle is, the longer it will stay in the air.
- Larger particles tend to %%settle to the ground by gravity in a matter of hours%%, whereas the smallest particles can %%stay in the atmosphere for weeks%% and are mostly removed by precipitation.
- Particulate Matter
- affects the diversity of ecosystems;
- changes the nutrient balance in coastal waters and large river basins;
- depletes the nutrients in the soil;
- damages sensitive forests and farm crops;
- increases health issues with humans and animals
- makes lakes and streams more acidic.
- Airborne particulate matter can be reduced by:
- conserving energy to reduce demands on power plants;
- increasing air-quality standards for emissions of particulate matter from smokestacks;
- increasing automobile emission standards;
- limiting the use of household and personal products that cause fumes;
- not burning leaves and other yard waste;
- not using wood in fireplaces
| Naturally Occurring PMx | Anthropogenic Occurring PMx |
|---|---|
| Dust storms | Burning of fossil fuels—power plants |
| Forest and grassland fires | Incineration of wastes |
| Sea spray | Soil erosion—desertification, deforestation |
| Volcanoes | Vehicle exhaust |
Volcanic Organic Compounds
- Volcanic Organic Compounds (VOCs): These are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure (easily evaporate) at ordinary room temperature.
- Their high vapor pressure results from a low boiling point, which causes large numbers of molecules to evaporate and enter the surrounding air.
- Health effects of “sick building” syndrome include
- cancer;
- damage to the liver, kidney, and central nervous system;
- eye, nose, and throat irritation; and
- headaches, loss of coordination, and nausea.
7.3: Photochemical Smog
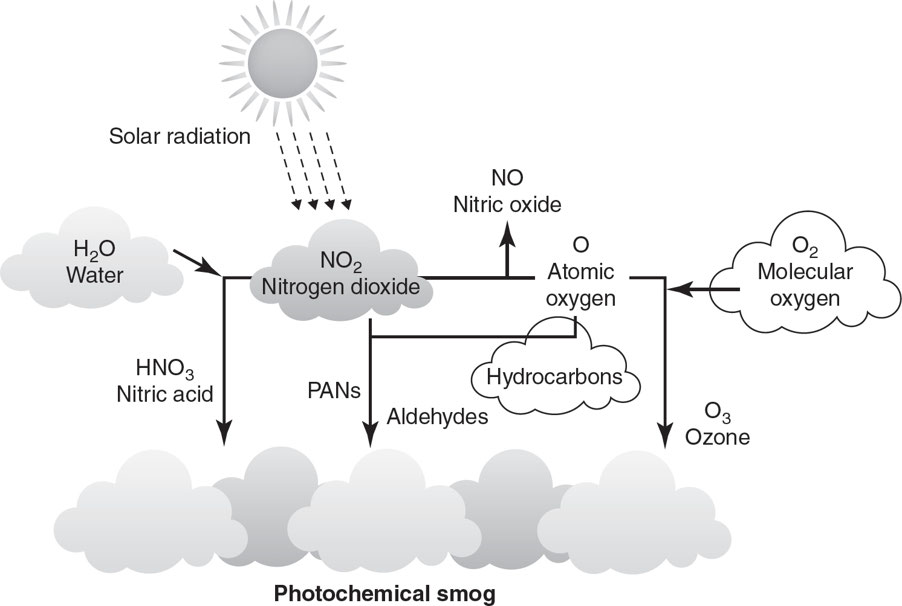
Photochemical smog: It is catalyzed by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, tends to be nitrogen-based, and is referred to as brown smog.
Forming Photochemical Smog
- 6 A.M.–9 A.M.: As people drive to work, concentrations of nitrogen oxides and VOCs increase.
- 9 A.M.–11 A.M.: As traffic begins to decrease, nitrogen oxides and VOCs begin to react, forming nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
- 11 P.M.–4 P.M.: As the sunlight becomes more intense, nitrogen dioxide is broken down and the concentration of ozone (O3) increases.
- Nitrogen dioxide also reacts with water vapor to produce nitric acid (HNO3) and nitric oxide (NO).
- Nitrogen dioxide can also react with VOCs released by vehicles, refineries, and gas stations to produce toxic PANs (peroxyacyl nitrates).
- 4 P.M.–Sunset: As the sun goes down, the production of ozone is halted.
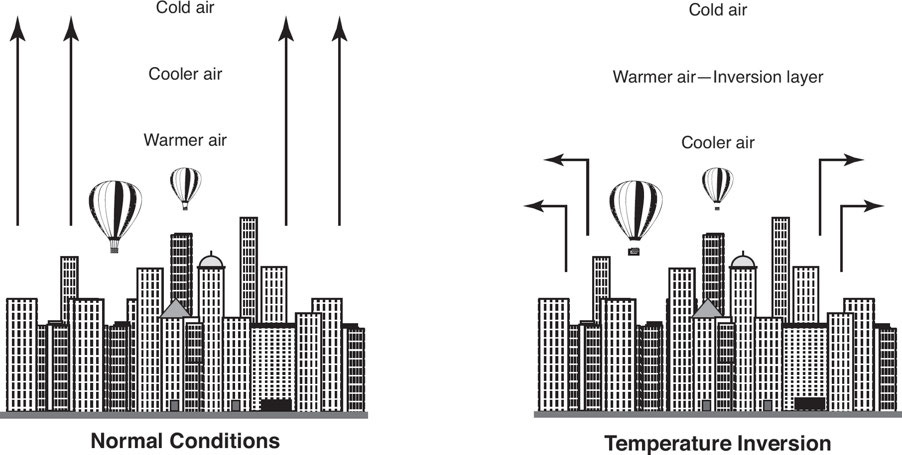
7.4: Thermal Inversion
Thermal inversions: These occur when air temperature rises with height instead of falling.
This effect traps pollution like smog close to the ground, which may harm human health.
This usually happens at %%night when solar heating stops and the surface cools, cooling the atmosphere above it%%.
A warm air mass moving over a colder one traps the cooler air below and stills the air, trapping dust and pollutants and increasing their concentrations.
Antarctica has a nearly constant temperature inversion.
7.5: Outdoor and Indoor Air Pollutants
- “Sick building” syndrome (SBS): It is a term used to describe a combination of ailments associated with an individual’s place of work or residence.
- Asbestos: It is inexpensive, durable, and flexible and naturally acts as an insulating and fireproofing agent.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning: It is the most common type of fatal indoor air poisoning in many countries because it easily combines with hemoglobin to block the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Formaldehyde: It is an organic chemical that is prevalent in the indoor environment and is a carcinogen that is linked to lung cancer.
- Radon: It is an invisible radioactive gas that results from the radioactive decay of radium, which can be found in rock formations beneath buildings.
- Cigarette smoke: It contains almost 5,000 chemical compounds, including 60 known carcinogens (cancer-causing chemicals), one of which is dioxin.
Remediation Steps to Reduce Indoor Air Pollutants
- Add plants that absorb toxins.
- Do not allow smoking indoors.
- Install air purification systems and ensure adequate fresh air ventilation when temperatures permit.
- Maintain all filters and vents.
- Monitor humidity levels to reduce mold and mildew.
- Test for radon gas and other dangerous indoor pollutants.
- Use “green” cleaning products.
- Use natural pest-control techniques.
7.6: Reduction of Air Pollutants
Controlling Air Pollution/Pollution-Control Devices
Catalytic converter: It is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic chemicals in the exhaust of an internal-combustion engine into less harmful substances.
Catalyst: It stimulates a chemical reaction in which by-products of combustion are converted to less toxic substances by way of catalyzed chemical reactions.
Most present-day vehicles that run on gasoline are fitted with a “three way” converter, since it converts the three main pollutants:
Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide:
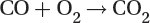
Oxidation of unburned hydrocarbons to carbon dioxide and water:
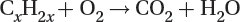
Reduction of nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen:
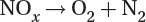
Catalytic converters remove hydrocarbons and other harmful emissions, but they do not reduce fossil fuel-produced carbon dioxide.
Remediation Steps to Reduce Air Pollution
- Ban open burning of waste.
- Buy smaller cars and energy-efficient appliances.
- Decrease unnecessary travel.
- Distribute solar cook stoves to developing countries to replace wood and coal.
- Drive within the speed limit and keep tires inflated.
- Institute flexible work shifts.
- Maintain vehicle properly with regular tune-ups and oil changes.
- Reduce idling and turn off engines while waiting.
- Use mass transit systems or carpool when possible.
- Toughen Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards.
- Toughen legislation to reduce sulfur content in fuel.
- Use fans instead of air conditioners.
- Use fluorescent or LED lighting.
- When buying a car, consider its fuel efficiency.
7.7: Acid Rain (Deposition)
- Acid deposition: It occurs when atmospheric chemical processes transform sulfur and nitrogen compounds and other substances into wet or dry deposits on Earth.
- Dry Deposition: In dry areas, acidic chemicals in the air may become dust or smoke and stick to the ground, buildings, homes, cars, and trees, which rainstorms wash away, increasing acidic runoff.
- Wet Deposition: Acid rain, fog, and snow. As this acidic water flows over and through the ground, it affects a variety of plants and animals.
- Acid rain: It causes acidification of lakes and streams.
- It damages trees at high elevations and many sensitive forest soils by nitrogen saturation and acidification that harms decomposers and mycorrhizal fungi.
- Acid shock: Caused by rapid melting of snow pack with dry acidic particles, raises lake and stream acid concentrations five to ten times higher than acidic rainfall.
- Acid deposition due to sulfur dioxide begins with sulfur dioxide being introduced into the atmosphere by burning coal and oil, smelting metals, organic decay, and ocean spray.
- It then combines with water vapor to form sulfurous acid which then reacts with oxygen to form sulfuric acid.
- Acid deposition due to nitrogen oxides begins with nitrogen oxides formed by burning oil, coal, or natural gas.
- They are also found in volcanic vent gases and are formed by forest fires, bacterial action in the soil, and lightning-induced atmospheric reactions.
Effects of Acid Deposition
- Acid shock
- An increase in fish kills.
- Changes in animal life due to changes in vegetation
- Vegetation changes due to soil pH and ecosystem changes affect food webs.
- Increased leaching of soil nutrients
- Increased solubility of toxic metals, including methyl mercury, lead, and cadmium
- Reduced buffering capacity of the soil
Heat Islands and Air Pollution
- Urban heat islands: These occur in metropolitan areas that are significantly warmer than their surroundings.
- Since warmer air can hold more water vapor, rainfall can be as much as 30% greater downwind of cities when compared with areas upwind.
- Reasons for higher urban temperatures are as follows:
- Air conditioning, transportation, lighting, and other fuels generate heat.
- Urban impervious materials reduce the cooling effect of soil and leaf evaporation and tree shading.
- Buildings block Earth's thermal radiation.
- There is a lack of vegetation and standing water.
- More black asphalt and building surfaces absorb heat and reduce sunlight reflectivity.
- Street Canyon: A place where the street is flanked by buildings on both sides, creating a canyon-like environment.
- High levels of pollution in urban areas can also create a localized greenhouse effect.
- Urban heat islands can directly influence the health and welfare of urban residents who cannot afford air conditioning
7.8: Noise Pollution
- Noise pollution: It is an unwanted human-created sound that disrupts the environment.
- The dominant form of noise pollution is from transportation sources.
Effects of Noise Pollution
- Sensory hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear and is the most common form associated with noise pollution.
- Excessive noise can cause:
- a decrease in alertness and the ability to memorize;
- anxiety and nervousness;
- cardiovascular problems, which manifest as an accelerated heartbeat and high blood pressure; and
- gastrointestinal problems.
Techniques to Reduce Roadway Noise
- Create computer-controlled traffic flow devices that reduce braking and acceleration, and implement changes in tire designs.
- Create noise barriers.
- Introduce newer roadway surface technologies.
- Limit times for heavy-duty vehicles.
- Place limitations on vehicle speeds.
Techniques to Reduce Aircraft Noise
- Develop quieter jet engines.
- Reschedule takeoff and landing times.
Techniques to Reduce Industrial Noise
- Create new technologies in industrial equipment.
- Install noise barriers in the workplace.
- Control residential noise, such as power tools, garden equipment, and loud entertainment equipment, through local laws and enforcement.