Atoms, Molecules and Ions
Atoms are the smallest particle of any element
| Sub-atomic particle | Proton(p) | Neutron(n) | Electron(e) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Mass | 1 | 1 | 1/1840 |
| Relative Charge | +1 | 0 | 1 |
- Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus which is positively charged and contains most of the mass
- Mass of electrons too small to be counted as part of the mass
- atom is electrically neutral as the number of positively charged protons is equal to the number of negatively charged electrons
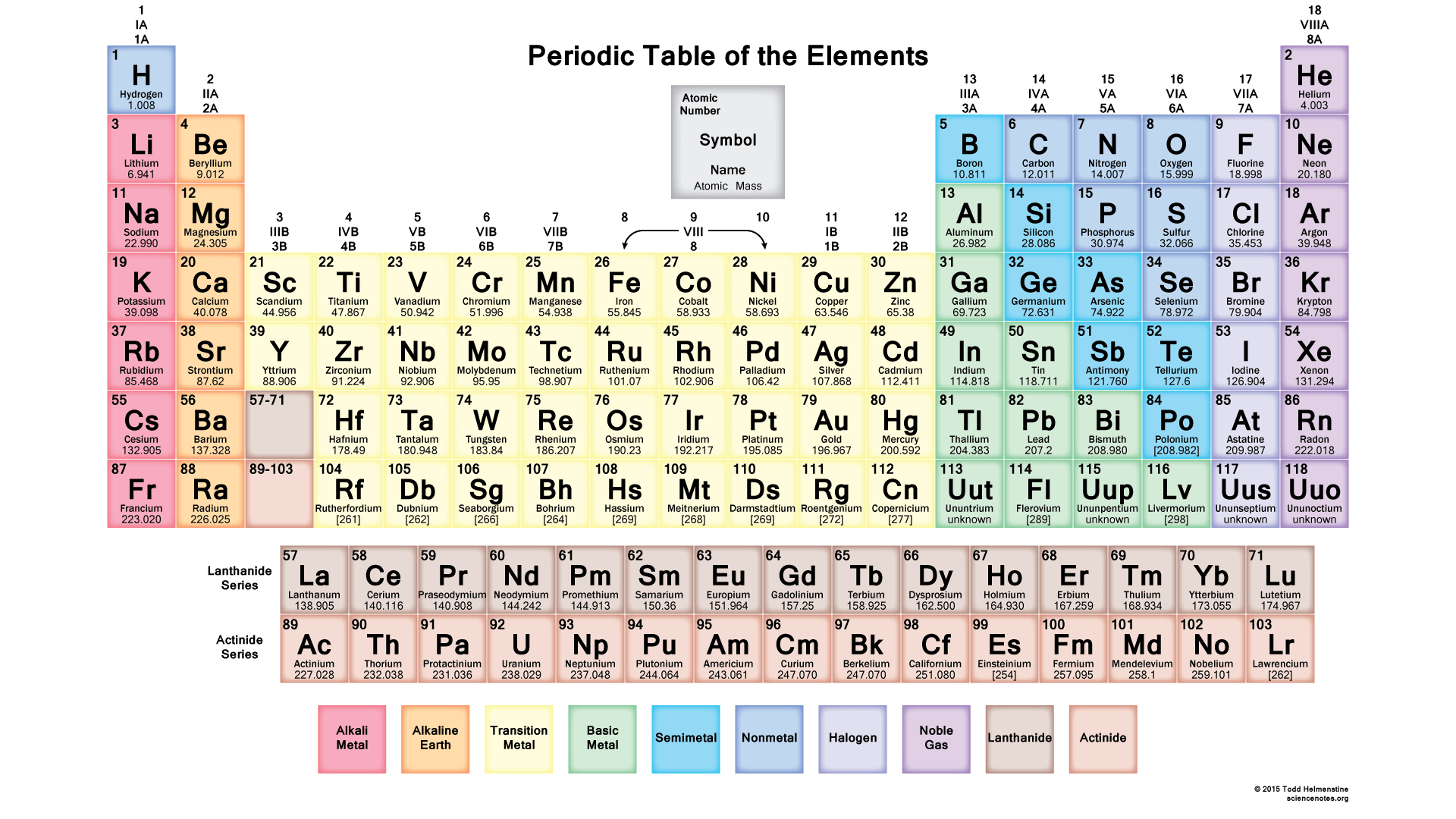
Periodic Table
Contains metals, non-metals and metalloids-have properties of both metals and non-metals
Atoms(Noble gases) in group 18 are stable due to having a Completely Filled Outermost Electron Shell (CFOES) and are inert and exist as single atoms
Have a duplet(2) or octet(8) electronic configuration
Will share, lose or gain valence electrons for atoms to attain a stable noble gas electronic configuration
Therefore, atoms may need to lose or gain electrons to become stable in which they become charged particles called ions
- Gains valence electrons>negative ions (anions)
- Loses valence electrons>positive ions (cations)
Chemical Compound of Ions
- Positive ions attracts negative ions in which an ionic compound is formed and an ionic bond exists between them>electrostatic forces of attraction
- Ions formed through transfer of valence electrons from metals to non-metals
Example:
| Name of Ion | Name of atom before the ion is formed | Charge of Ion | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | Hydrogen | +1 | H+ |
| Oxide | Oxygen | -2 | O2- |
| Chloride | Chlorine | -1 | Cl- |
Transition Metals
| Name of Ion | Name of atom before the ion is formed | Charge of ion | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper(I) | Copper | +1 | Cu+ |
| Iron(II) | Iron | +2 | Fe2+ |
| Iron (III) | Iron | +3 | Fe3+ |
Finding the Chemical Formula
Sodium Chloride
| Formula of ions | Na+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|
| Charge | +1 | -1 |
| Simplest Ratio | 1 | 1 |
Chemical Formula: NaCl
Magnesium Chloride
| Formula of Ions | Mg2+ | Cl- |
|---|---|---|
| Charge | +2 | -1 |
| Simplest ratio | 2 | 2 |
Chemical Formula: MgCl 2
*To find the chemical formula, you criss-cross the formula of the ions and the simplest ratio of the combining ions
Polyatomic Ions
Two or more atoms chemically combined to form an ion
Example:
| Name | Number of each type of atom | Charge | Formula of Ion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxide ion | 1 oxygen atom and 1 hydrogen atom | -1 | OH- |
| Sulfate ion | 1 sulfur atom and 4 oxygen atoms | -2 | SO4 2- |
| Ammonium ion | 1 nitrogen atom and 4 hydrogen atoms | +1 | NH4+ |
Molecules
- Two or more elements chemically combined together
- Molecule of an element is made up of the same type of atoms
- Molecules of a compound is made up of two or more different types of atoms
Examples:
Molecule of an Element
| Element | Chemical Formula | Number of atoms in molecule |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | H2 | 2 |
| Oxygen (O) | O2 | 2 |
| Nitrogen (N) | N2 | 2 |
| Sulfur (S) | S8 or S | 2 |
| Fluorine (F) | F2 | 8 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Cl2 | 2 |
| Bromine (Br) | Br2 | 2 |
Molecule of Compounds
| Chemical Name | Number of each type of atom | Chemical Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom | H2O |
| Carbon dioxide | 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms | CO2 |
| Nitrogen dioxide | 1 nitrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms | NO2 |
| Sulfur dioxide | 1 sulfur atom and 2 oxygen atoms | SO2 |
Chemical Equations
Must be balanced
Number of atoms of each element before and after the reaction must be equal
Mass is conserved during a chemical reaction
Tips from a wise woman
Use numbers like 2 and 3
Always try to make odd numbers even
Balance ‘H’ and ‘O’ last
Go for LCM (lowest common multiple)
Always check answer
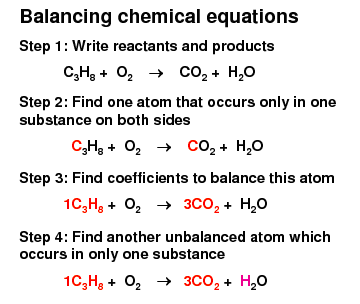
Image by By Ansaroo