Sedimentation
Forces and processes during sedimentation
In a rectangular basin at the left end we have the ==influent zone==, in the middle we have a large space called the ==settling zone==, at the right end we have the ==eluent zone== and at the bottom we have the ==sludge zone==.Particles settling are collected at the sludge zone.
Water comes in from the influent pipe into the center stimming well(influent zone) then it leaves and spreads into the settling zone and the particles collect.
Fupthrust = 𝜌V𝑔
Fg = mg. Ffrict = 6𝜋𝜂𝑟𝑣 = fv
Fg = Fupthrust + Ffrict
Forces during sedimentation
Centrifugal force: inertial force in a rotating system, it is radial from the center and equal to centripetal force.
Fcentrifug = mr(angular velocity)^2
Buoyancy: depends on volume immersed in liquid, density of the liquid and acceleration.
Fb = 𝜌fluid• m/𝜌body •r(angular velocity)^2
Drag force: resistance force caused by movement of a body (transferring energy to molecules) through a fluid
Fd = fv
Methods of sedimentation
- Sedimentation velocity
- Sedimentation equilibrium
- Density gradient
Centrifuge types
a. Preparative: separation of molecules based on size and mass of molecules.
- Angle rotor. - Swing out rotor
b. Analytical: determination of size and mass of particles.
Sedimentation constant
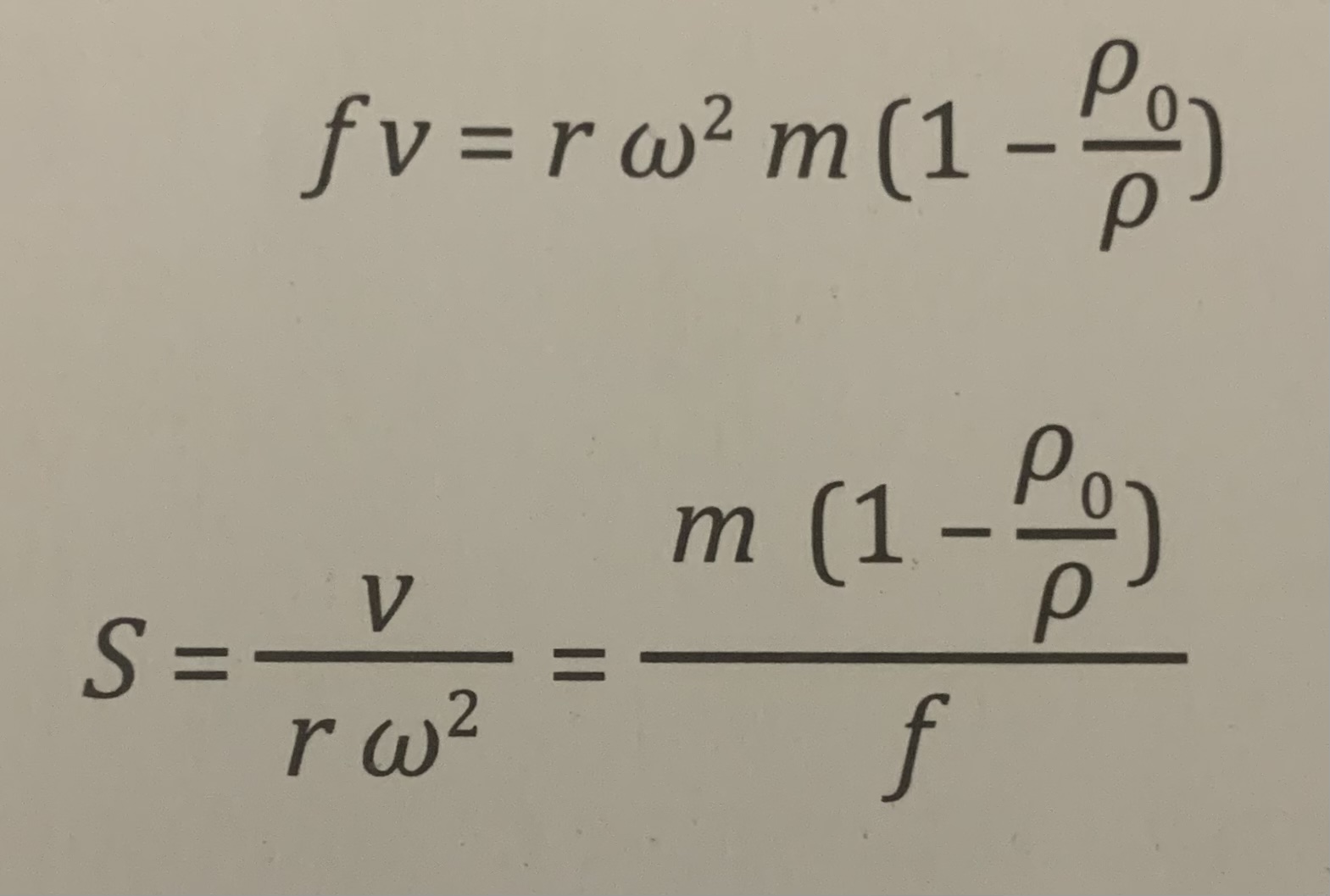
This equation is transformed to give Svedberg constant(S). The sedimentation constant gives the moving velocity of a particle at certain centrifugal acceleration.
t = K/S
Electrophoretic mobility(uel)
Fc = QE = ZeE
Fc is Coulombs force, Q is charge number, E is Field strength.
A particle is accelerating till the coulombs force is equal to the frictional force.
uel = v/E = Ze/f
Ze is charge number f is shape factor
Principle of Electrophoretic method
Agarose gel:separating nucleic acid based on charge. Use horizontal electrophoretic tanks and the molecules move from the negative to positive end, fluorescent dye is used to visualize.
SDS PAGE: separation of protein based on its size using a vertical tank. Blue staining solution to visualize.
a) Isoelectric focusing: separation of proteins based on isoelectric points(pH value where they have no net charge), it is the first step in 2D electrophoresis.
b) 2D electrophoresis: the proteins are then separated based on their molecular weight by SDS-PAGE.