APHG REVIEW Fall Final 2024
2024 Fall APHG Final Exam Learning Target (Units 1-5)
Topic 1.1 Geographic Categories
Economic - that which pertains to financial value
Social - that which relates to the organization of human society, ideas, customs, and social behaviors of people
Political - that which relates to the government, public affairs, laws, boarders or territories of a country
Environmental - that which describes that natural world and the impact of human activity on its condition
Topic 1.3: Spatial Analysis “The Why of Where”
Spatial Analysis (Spatial Thinking) - why things are where they are
Distance Decay - as distance increase the intensity of a connection between locations decreases: AKA the less they should in common
Friction of Distance - distance is caused by the friction of a distance. The further away the more friction that caused connections to be lost
Time-Space Compression -
Topic 1.4: Human-Environment Interaction
What is Human Environment Interaction/HEI? How people interact and relate to the physical world through adaptations and modifications
How are environmental determinism and possibilism different? Environmental determinism is where landforms and climate shape human behavior and societal development, as to where possibles is how cultures respond to their environment
Topic 1.5: Scale of Analysis
Geographic Scale (of Analysis) - the amount of land a map shows. Global scale means map of the world; other scales: regional, local, etc
Common Scales of Analysis:
Global: all the world's landmass
Regional: the landmass for a country
National: the landmass for a small region of countries like a continent or a collection of sub-states within a country like the “Midwest”
Local: the landmass of a state, country city, school district, census tract
How does Scale Impacts Perspective? To show how show the way data is chunked and visualized on a map
Local Global Continuum - interdependencies among scales events at one scale can affect events at another scale
Topic 1.6: Regional Analysis
Formal/Uniform Region - areas with a high level of consistency (internal uniformity) with common attributes such as economic, social, political, or environmental characteristics that unify a space
Functional/Nodal Region - areas that are connected by a node, hub, or centerpoint based upon movement of economic foods, communication or transportation
Perceptual/Vernacular Region - areas grouped with no crisp of perfect boundaries, based upon people’s belief, feelings and attitudes about a region that may or may not be true about the region: the idea of where they begin and end changes easily
Topic 1.8: Geographic Data
Positive Correlation (When two variables work in the same direction; when one increases and the other increases or when one decreases the other decreases) vs Negative Correlation (when two variables work in the opposite direction; when one increases the other decreases)
Quantitative (defines: numbers, hard data, statistics) vs. Qualitative (Describes: characteristics, approximates, descriptions, collected through interviews and interpretations, could be subjective)
Topic 1.11: Types of Maps
Types of Thematic Maps (Visually Recognize and Distinguish Between)
Choropleth: uses shading to show different levels of data, tend to be the most common type of thematic map
Pindot - maps that use dot symbols to show the presence or quantity of a phenomenon; the closer the dots are together, the higher the occurrence
Isoline - maps that use lines to connect equal points of value on a map
Cartogram - this map shows electoral votes; larger states on the map have more electoral votes as they have a larger population n
Topic 1.12: Map Projections
Map Projection - is a way to make a 2D flat representation of the 3D Earth
Big Concept: Distortion - every map must have distortions that result from making a 2D representation of a 3D sphere
Cylindrical /Mercator Projection
Purpose: spatial distributions in relation to areas
Strengths: size of land masses are correct
Distortions: shapes are inaccurate; especially near the poles
Conic Projections
Purpose: general use in mid latitudes
Strengths: lines of longitude coverage curves shape and area are close to reality
Distortions: directions are not constant
Plane/Polar/ Azimuthal Projection
Purpose: general use in mid latitudes
Strengths: lines of longitude coverage, lines of latitude curve, shape and area are close to reality
Unit 2: Population and Migration
Topic: 2.1 Population Distribution and Density
Demography/Demographics - the study of population; demographics
Ecumene - portion of the earth’s surface occupied by permanent human settlements
Population Density - refers to the number of people in relation to the space they occupy
Arithmetic Density - the number of people per unit of land
Physiological Density - the number of people per unit of area arable land (agriculturally productive land)
Agricultural Density - the number of farmers per unit of arable land
Population distribution/Regional Clusters: Eastern USA /Eastern South America/East Australia/Sub-Saharan Africa/Europe/South Asia/East Asia
Topic 2.2: Analyzing and drawing inferences from Population Pyramids
Rapid Growth Pyramid Medium Growth Pyramid |
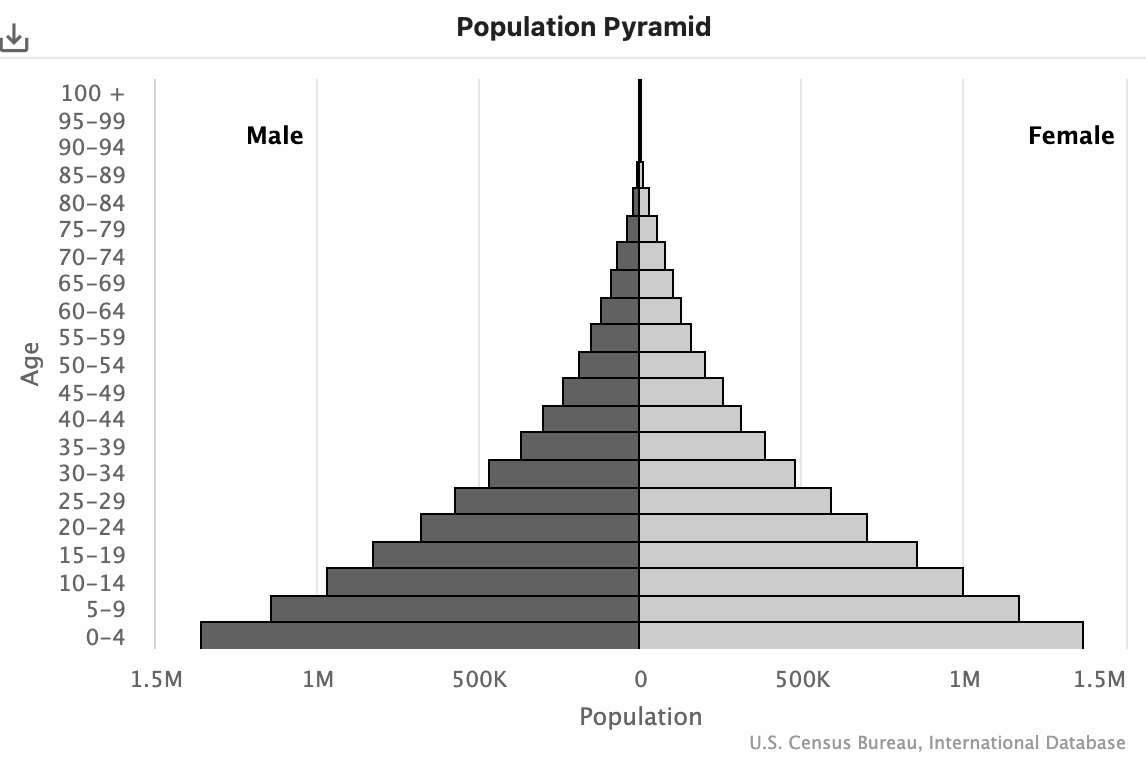 Level of development: periphery/less developed Notes:
Examples: Malawi 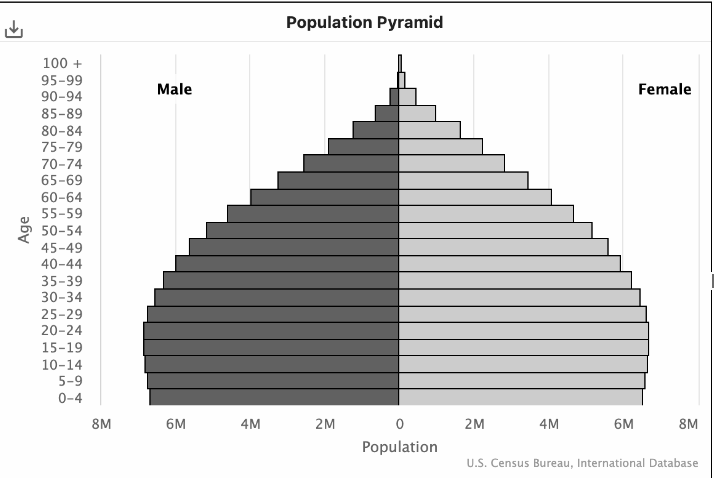 Level of development: newly industrialized, (NIC), semi-periphery Notes
Examples: brics/mint countries |
Slow Growth Pyramid Negative Growth Pyramid |
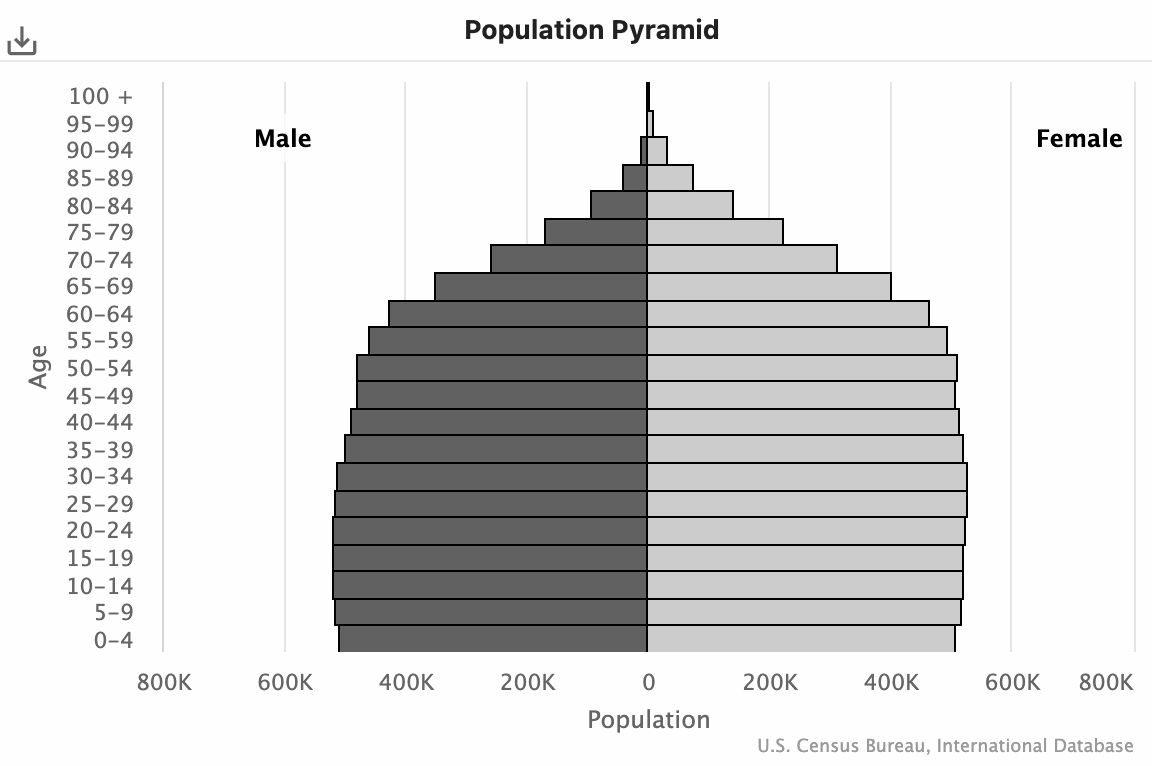 Level of development: Developed/core Notes:
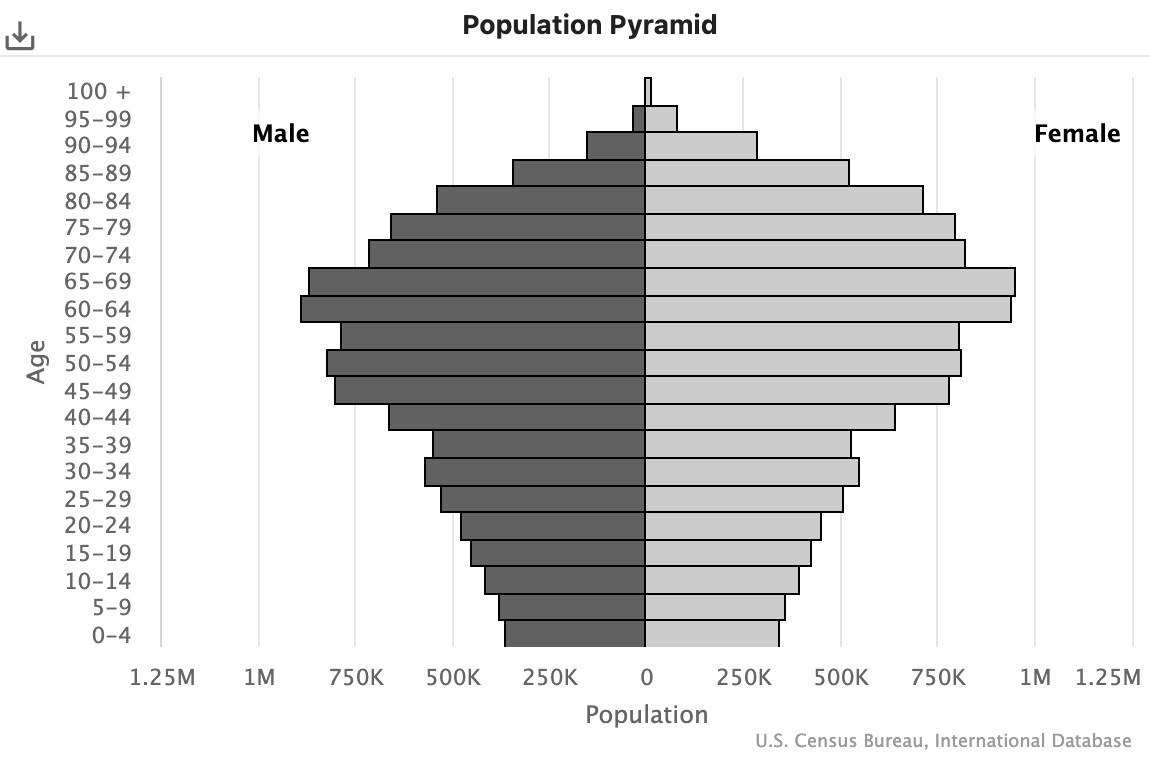 Level of development: developed/core Notes - dr higher than br Examples: Japan, Italy, South Korea |
Topic 2.3: Consequences of Population Distribution
Demographic Momentum - once a country has a rapidly growing population, it is difficult to effectively slow population growth
Consequences of overpopulation
Education: more schools & teachers, higher operating expenses
Health Care: more sick people to care for; babies require extra medical care
Employment: job shortages
Housing: housing shortages
Consequences of Underpopulation
Labor shortage, not enough workers
Loss of heritage, tradition dies off
Topic 2.4: The Demographic Transition Model
Demographic Transition Model (DTM) Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Exceptions to the DTM: Russia’s Population Decline All of the terms/concepts to the left will be covered in the graphic organizers in this section. |
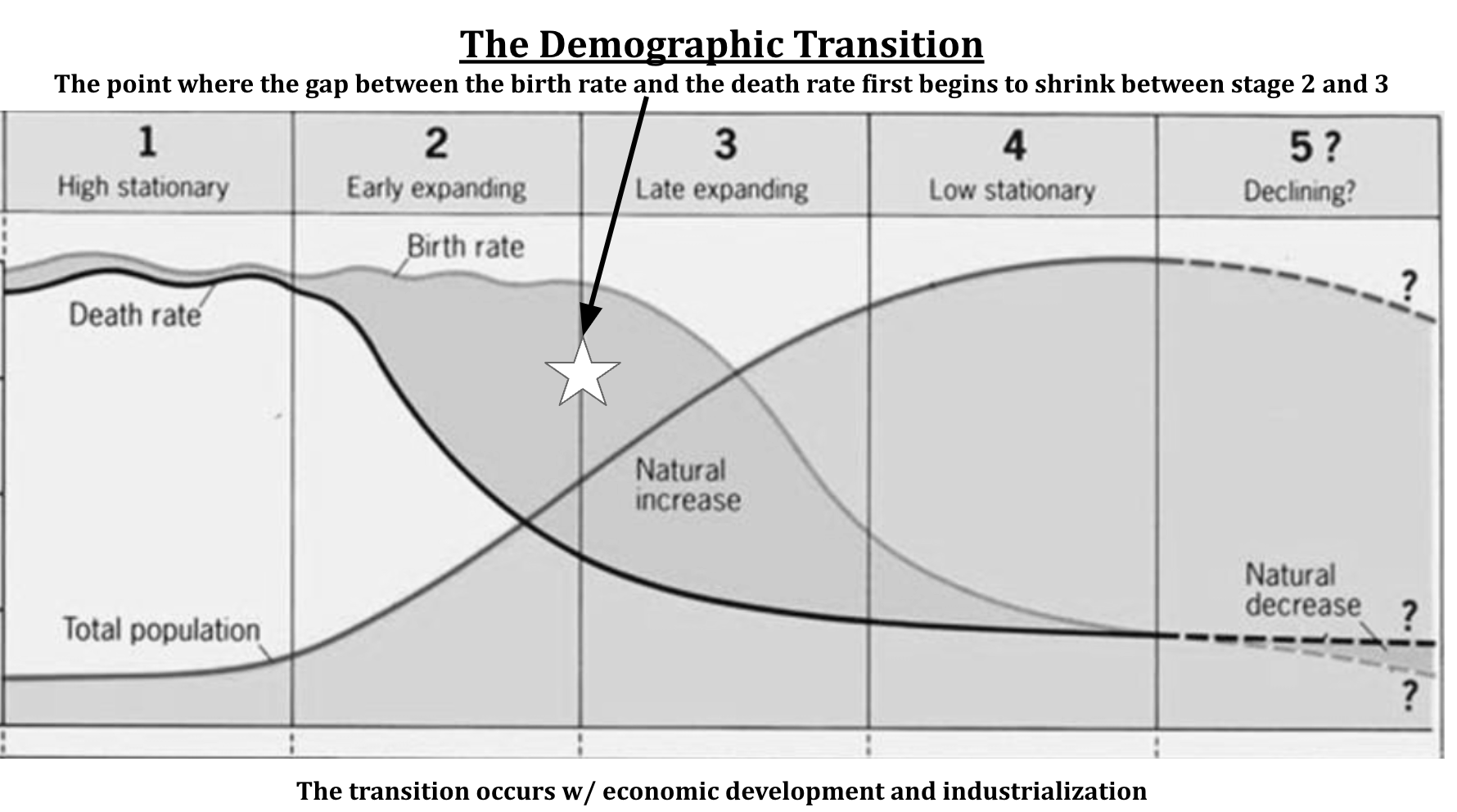
Characteristics of the Stages of the Model
Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 |
Pyramid Shape N/A Wide Base/ Rapid Growth Moderate Growth Slow Growth Negative Growth |
Examples Pre-Industrial revolution *no present day example Periphery Brics & Mint Core Countries Japan, Italy, Germany |
Birth Rate Very High Very High Slowly Falling Low Belower DR |
Death Rate Very High Rapid decrease Leveling Off Low Higher than BR |
RNI Rate Natural Increase Slow Rapid Increase Slower Increase Very slow Negative RNI |
Level of Development N?A Developing / Periphery Newly Industrialized & Periphery Developed/Core Developed/core |
Why is the birth rate high, low, or declining? Agrarian Society, high IM rate, little family planning Role of women changing, shifting away from farming, low IMR, some family planning Family planning, improved women’s status, late marriage |
Why is the death rate high, low, or declining? Disease, irregular food supply, poor medical practices Improved medical care, safe water, sanitation, lower IMR, more consistent food supply Excellent healthcare and food supply |
Topic 2.5 : Population Dynamics (Influences on population growth and decline)
Fertility Indicators:
Total fertility rate - the average number of children a woman will have in her reproductive years
Replacement fertility rate - the number of children/female it takes to keep the population stable
Crude birth rate: the total number of live births per 1000 in a population in a year
Rate of Natural Increase: the crude birth rate minus the death rate, otherwise known as the growth rate
Mortality Indicators:
Infant mortality rate - number of deaths per 1000 live births of children under one year of age
Child mortality rate - number of deaths per thousand children within the first five years of life
Crude death rate - is the number of deaths occurring among the population of an area during a given year, per 1000
Life expectancy - the average number of years a person may expect to live
Factors of Fertility. How do the following increase or decrease fertility rates?
Social - if women are valued by the number of kids the have, the birth rate will be high
Political
Economic - the higher the level of economic development, the lower the BR
Topic 2.6: Malthusian Theory
Malthusian Theory (Thomas Malthus) - believed and theorized that the population would grow exponentially (1,2,4,6,8,16) while food supply would grow arithmetically (1,2,3,4,5). Resulting in a lack of food and water.
Neo-Malthusians - they fear that we will face a lack of resources.
The growth of less developed countries are outstriping resources
World population is not just stripping food but other resources aswell
Demand anti-natal policies such as birth control and family planning
Cornucopians - the opposite of Neo-Malthusians
They will believe that society will find a way to solve resource problems
Topic 2.8: Population Policies
Pro Natal Policies - encourages people to have babies; used to increase population growth
Anti Natal Policies - discourages people from having babies; used to control/slow growth
One Child Policy - reduce population growth by limiting family size
Kerala, India Policy - education for women, women in workforce, access to birth control
Topic 2.9 : Consequences of Old/Young Populations
Dependency Ratio
Consequences of Aging Population(too many old people)
Consequences of Young Population (too many kids)
Topic 2.10 : Catalysts of Migration
Emigrant - to move from a country
Immigrant - to move to a country
Catalysts of Migration
Push Factors: are events or conditions that impel an individual from a location
Cultural - changes or lack there of societal norms regarding gender roles, religious practices, or attitudes on societal roles of groups of people
Demographic
Economic - lack of economic opportunity (#1 factor)
Environmental - natural disasters
Political
Pull Factors: Cultural/Demographic/Economic/Environmental/Political
Topic 2.11: Forced and Voluntary Migration
Internal Migration - is the moves people make within a particular country or region
The Gravity Model - larger (by population) and closer cities have more gravitational pull or influence on migrants than smaller or more distant cities
Step Migration - is an an eventual long-distance migration that is undertaken is stages: farm, village, small town, city
Intervening Opportunities - helps continue your migration process or something that could help you make a transition to a new country easier: job opportunities/facilitation options, assistance programs, positive present ions of immigrants
Intervening Obstacles - hinders your migration process or something that could make a transition to a new country difficult: challenges physical geography, restrictive immigration policies, negative perceptions of immigrants, cultural/language barrier, securing employment
Cyclical Movement - this movement has a closed route an generally happens on a regular basis
Types of Cyclical movement include:
Activity Space - focuses on a interrelationship between activities in this space and the constraints imposed by these interrelationships
Commuting - is the travel between one’s home and place of work on a regular basis
Pastoral nomadism - they move their animals to water sources and pastures on a regular basis
Voluntary Migration - has an element of choosiest based on some perceived opportunity such as family/kinship
Periodic Movement - does not necessarily involve returning to the same place, it takes place over a longer period of time away from the home base
Types of Periodic movement include:
Transhumance - moving animals up to mountains for summer pasturing and down into valleys during the winter
Seasonal Movement - typically movement to areas seasonally to perform certain jobs
College students - to and from college towns when school is in and out of session
Chain Migration/Kinship Links - migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationally previously migrated there
Rural to Urban
Forced Migration - is when the element of choice is removed
Impelled Migration - is when the individuals are not “forced” out of their country, but leave due to unfavorable situations such as warfare, political problems, natural disasters, or religious persecution
Internally Displaced Persons - are people displaced within their own countries
Asylum Seekers - someone who is usually a refugee and is seeking permanent protection/residency/assistance by another country to escape persecution
Refugee - people who flee war, violence, conflicts, or persecution
Unit 3: Culture and Identity
Topic 3.1 Introduction to Culture
Cultural Traits - individual culture practice
Culture Complex - a interrelated web of cultural traits that are characteristic of a group
Cultural Relativism - all cultures are different; what is accepted in one culture might be taboo in another
Ethnocentrism - evaluating another culture based on the culture norms or one’s own culture
Topic 3.2 Cultural Landscapes
Cultural Landscape (Built Environment) - modifications to the environment caused by human imprints and activities that reflects aspects of their culture
Ethnic Neighborhoods/Enclaves - areas of a city associated with a single ethnic group
Ethnic Islands - rural areas settle by a single distinctive ethnic group that places its imprint on the landscape
Symbolic Landscapes - implies that there is more to the cultural landscape than meets the eye
Sacred Space - natural or human-made sites that posses religious meanings for some religious groups or origin myth of a cultural group
Sequent Occupance - over time, different groups of inhabitants leave their distinctive imprint on the cultural landscape
Topic 3.3 Types of Diffusion
Cultural Diffusion - culture spreading or the process of how an idea or innovation is transmitted
Culture Hearths To Know: (Mesoamerica, Andes Mountains, West Africa, Nile River Valley, Mesopotamia, Indus River Valley, Ganges River Valley, The Huang He River Valley)
Independent invention - similar cultural traits with different culture hearths that developed independent of each other
Relocation diffusion - individuals migrate/move and carry their ideas to a new location
Expansion diffusion - the idea remains in the hearth (where they began) and diffuses to other locations
Types of Expansion Diffusion:
Contagious - outward from hearth to adjacent groups
Hierarchical - spreads from hearth in hierarchical “ranked” manner
Stimulus - the same concept but tweaked
Topic 3.4 Contemporary Causes of Diffusion
Globalization - the expansion and intensification of linkages and flows of capital, people, goods, ideas, and cultures across national boarders
Topic 3.5 Effects of Diffusion
Acculturation - is the process by which a culture is substantially changed through interaction with another more powerful culture
Assimilation - immigrants become fully integrated into a new culture
Ethnic/Folk Culture - is the combination of various beliefs, customs, practices, etc
Pop/Popular Culture - a culture found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics
Placelessness - the feeling resulting in the standardization of the built environment; occurs where local distinctiveness is erased and many places end up with similar cultural landscapes
Postmodern Landscape - are devoted to consumers (targeting buyers to purchase things) and are looking more alike globally
Commodification - cultural trait is used for commercialization or profit
Unit 4: Language and Religion
Topic 4.1 Introduction to Languages
Standard Language - a way a language is spoken and written according to the formal rules of the language
Official languages - the language used by the government when making laws, reports, govt. documents, money and stamps
Dialect - regional variations of the same language using different vocabulary and grammar
Isogloss - geographic boundary line spreading where different linguistic patterns can be heard
Pidgin - is a simplified combination of two languages that is used informally in the marketplace of for work administration
Creole languages w/examples - when pidgin becomes the first language of a group of speakers, it is now considered a creole language
Lingua Franca w/examples - is a third language used by people who could not otherwise understand each other
Topic 4.4 Introduction to Religion
Ethnic Religion - are religions people are born into
Universalizing Religion - seek converts
Traditional/Indigenous Religion - tiny ethnic religions closely associated with localized culture groups
Animistic - religions that believe that non-human entities contains spiritual powers
Syncretic Religions - blending of two or more religious belief systems into a new unique system
Topic 4.6 Culture and Centripetal Forces
Centripetal Force - an action that unites or pulls people together
Centrifugal Force - an action that divides of forces people away from each other
Monolingual states - states where only dominant language is spoken which generally correlates to one dominant ethnicity
Multilingual states - states where multiple languages are spoken
Interfaith Conflict - conflicts between two different religions
Intrafaith Conflict - conflicts involving the same religion
Unit 5: Political Organization of Space
Topic 5.1 Political Power and Territoriality
Territoriality- a groups control of, desire to control, or attachment to a piece of land
Sovereignty - the ability of a state (country) to control its economy and govern itself without interference from other states
Autonomy - is a wide ranging term meaning the ability for a county, group or individual to make its own decisions w/o coercation from the outside
Peace/Treaty of Westphalia
Topic 5.3 Nations, States, and Political Entities
Nation - a group of people that has a common ancestry, regardless of it controlling a territory
State - an organized political unit with an established government
Enclave - political areas of one country separated from the main body by another country
Exclave - a cluster of a minority ethnic group different from the major ethnic group in an areas
Nation-State - political entity where the group of people within/controlling a country are ethnically homogenous
Stateless Nation - a culture group that has no state they control
Multinational State - a culture group that has no state they control
Multi-State Nation - contains 2 or more ethnic groups that has no state they control
Topic 5.5 The Political Function of Boundaries
Defined Boundary - a boundary that is defined within a legal document
Delimited Boundary - cartographers create or “draw” or “delimit” the actual boundary agreed upon by all sides on a map
Demarcated Boundary - a boundary is demarcated or visually on the ground by some visible means such as walls, posts, signs, fences
Natural/Physical - boundaries that follow a natural feature in the landscape
Geometric Artificial Boundaries - delimited boundaries that are usually drawn according to latitude and longitude
Antecedent Boundary - a boundary that is established after an area has been settled
Subsequent Boundaries - are settles after an area has settles
Types of Subsequent Boundaries:
Consequent - boundaries drawn along cultural lines such as language, religion, ethnicities
Superimposed - boundaries forcible drawn by a conquering or colonizing power without reference to pre-existing cultural patterns
Types of Boundary Disputes:
Definitional - the legal language of the boundary is disputed
Operational - disagreement on how a border should function or be administered
Allocational - conflicts related to the location of boundaries with regard of the natural resources
Topic 5.6 UNCLOS
What is the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)? - a zone that extends 200 miles off a country’s coast in which they alone have mineral and fishing rights
What is the 12 Mile Territorial Sea? - the first miles off a country’s coast in which a country has economic control
What is the Median Line Principle? - if countries have an overlapping 12 mile or 200 mile zones, a boundary will be set that splits it 50/50
How does UNCLOS relate to current conflicts in the South China Sea? - All the countries have ownership of their respective parts but China is taking over
Topic 5.7 Supranational Organizations
Types of Supranational Organizations:
Economic - make more money via increased trade
Military - military protection
Environmental - protect environment
Military Supranational Organizations:
NATO -
Economic Supranational Organizations:
EU
ASEAN
USMCA
WTO
Topic 5.9 Factors of Devolution
Devolution Definition
Factors that can lead to the devolution: Physical Geography/Ethnonationalism/Ethnic Separatism/Regional Economic Differences/Irredentism
Topic 5.10 Challenges to Sovereignty: Devolution in Action
What is an Autonomous Region?
3 Main Types of Autonomous Regions: Economic/Distance/Sub-Political National Territory
Examples of Sub-Political National Territory
Balkanization
Breakup of Czechoslovakia: The Velvet Divorce
Topic 5.12 The Collapse of the USSR (Soviet Union)
Cold War
Domino Theory
Containment Policy
Satellite State
Shatterbelt
Buffer state
Russia’s “Near Abroad”
Proxy War
Topic 5.13 Geopolitical Theories
Define Geopolitics
What is a Geopolitical Theory?
Specific Geopolitical Theories (know theory and real world application) Ratzel Organic/Mackinder Heartland/Spykman Rimland/Wallerstein World Systems Theory
Topic 5.14 Forms of Governance
How are confederations, federal systems and Unitary systems different?
What are the characteristics of Primate Cities
What is a forward capital, why are they created and what are some examples?
Topic 5.15 Electoral Geography
What is the US census, how often is it and what is the data used for?
Describe reapportionment.
Describe redistricting.
What is Gerrymandering and how is it connected to redistricting?
 Knowt
Knowt