Physiology
tissue:: a collection of cells, usually held together by cell junctions, that work together to perform a specific function
organ:: two or more tissues that function together
organ system:: a group of functionally integrated organs
evolution is:: an undercurrent of all biological concepts
diffusion versus bulk transport is a:: scaling issue
bulk transport example:: breathing air using a pump system, moving nutrients using the cardiovascular system
Ohm’s law:: the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance wrt membrane potential
homeostasis:: dynamic steady state of the constituents in and properties of the internal fluid environment that surrounds and exchanges materials with cells
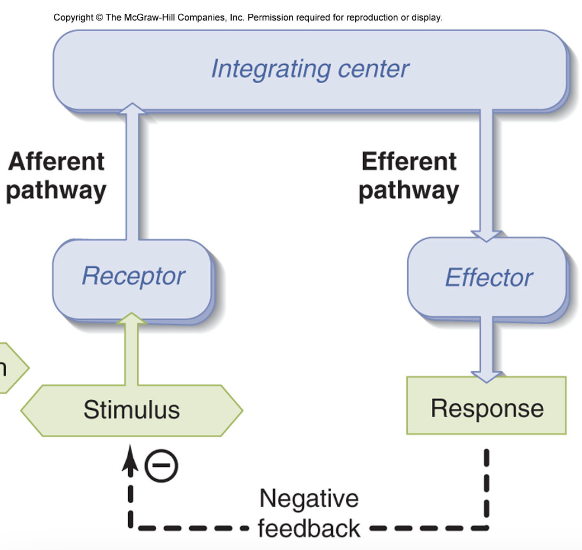
negative feedback:: stimulus>sensor>integrator>effector>stop stimulus
homeostasis/osmolarity values are:: always a ballpark/average value that fluctuates within and between individuals
main fluid compartments:: plasma, interstitial fluid, intracellular fluid
extracellular fluid:: plasma and interstitial fluid
regulated internal fluid properties:: pH, ion concentration, temperature, volume and pressure, water
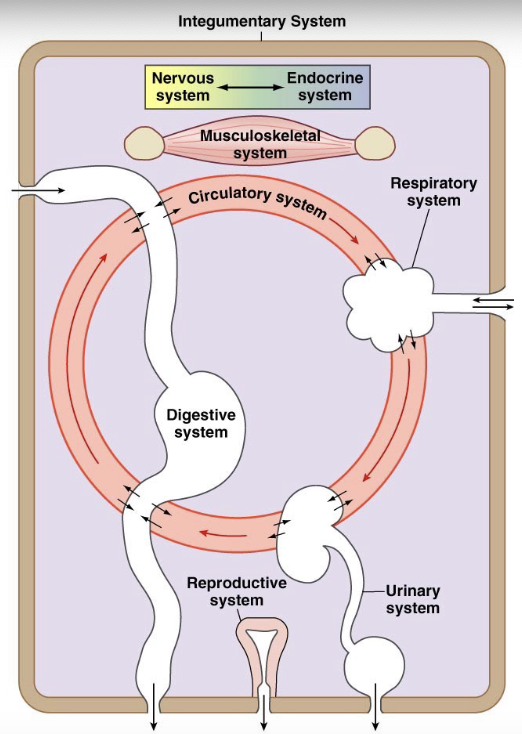 diffusion happens between:: circulatory system and all others
diffusion happens between:: circulatory system and all others
nutrients/products are transferred between:: all body systems
negative feedback def:: the output of a process inhibits the process that created it
positive feedback def:: the output of a process stimulates the process that created it
feed-forward def:: a process is up or down regulated in anticipation of an event
neg feedback example:: thermostat, insulin
pos feedback example:: birth (until end with negative feedback)
feed-forward example:: smell food, stomach rumbles and prepares
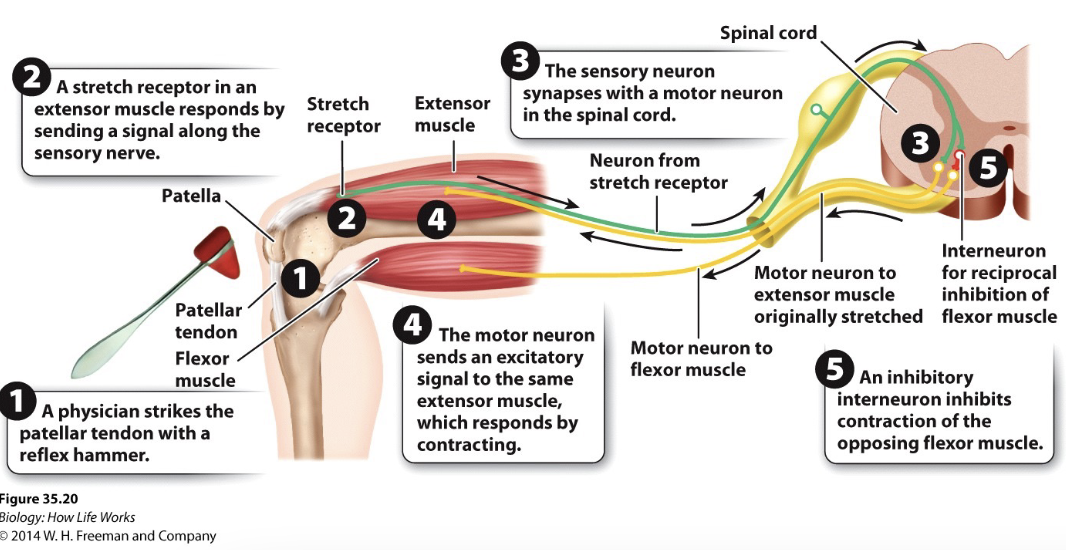
reflex arc functions as:: an involuntary negative feedback control system
reflex definition:: simple, involuntary response to a stimulus
afferent pathway:: carries signal away (sensory receptor to integrating center)
efferent pathway:: carries a signal around (integrating center to effector), generates a response

chemically/ligand gated channels:: specific molecule binds to a channel to open or close it
voltage gated channels:: change in membrane potential opens and closes the channel
mechanically gated channel:: deformation of the membrane opens and closes the channel
leak channel:: always open
channels:: select what gets through a pore in the membrane based on size and charge
carriers:: select what gets through based on binding specificity
carrier protein:: transported substances bind to specialized sites and cause a change in conformation
pumps are:: primary active transport
primary active transport:: direct input of energy via ATP
pumps:: transport proteins use direct input energy to move substances against energetically favorable direction
secondary active transport:: harnesses potential energy of an ion gradient to drive another substance in energetically unfavorable direction
secondary active transport example:: electron transport chain
pump example:: sodium-potassium pump
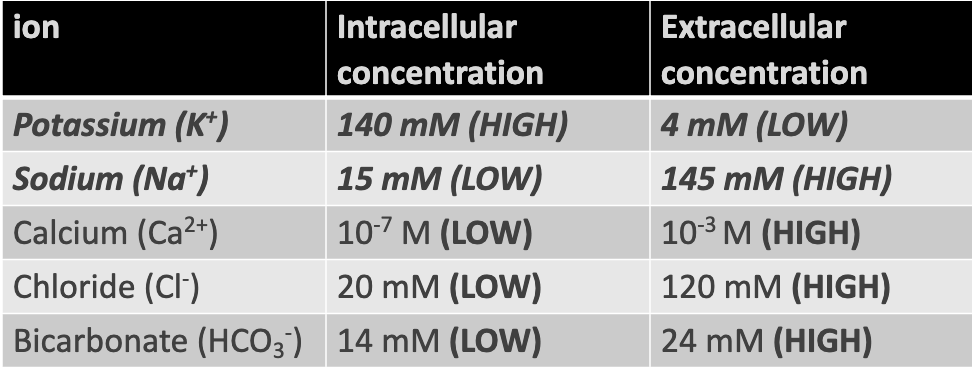 opening and closing channels changes:: membrane permeability of the membrane to specific ions
opening and closing channels changes:: membrane permeability of the membrane to specific ions
cells expend energy on ion gradients because:: they use the stored potential energy to do work
ICF and ECF generally:: osmotic equilibrium/total amount of solute or volume of fluid is the same
extra negative ions in ICF and positive ions in ECF creates:: membrane potential
Day 2
osmosis:: the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane up a solute concentration gradient
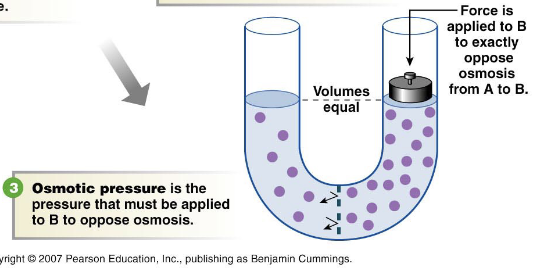 osmosis depends on:: the number of particles in a given volume of solution
osmosis depends on:: the number of particles in a given volume of solution
osmolarity:: = molarity * particles/molecule
hyperosmotic:: higher osmolarity in relation to another solution
hypoosmotic:: lower osmolarity in relation to another solution
isosmotic:: the same osmolarity in relation to another solution
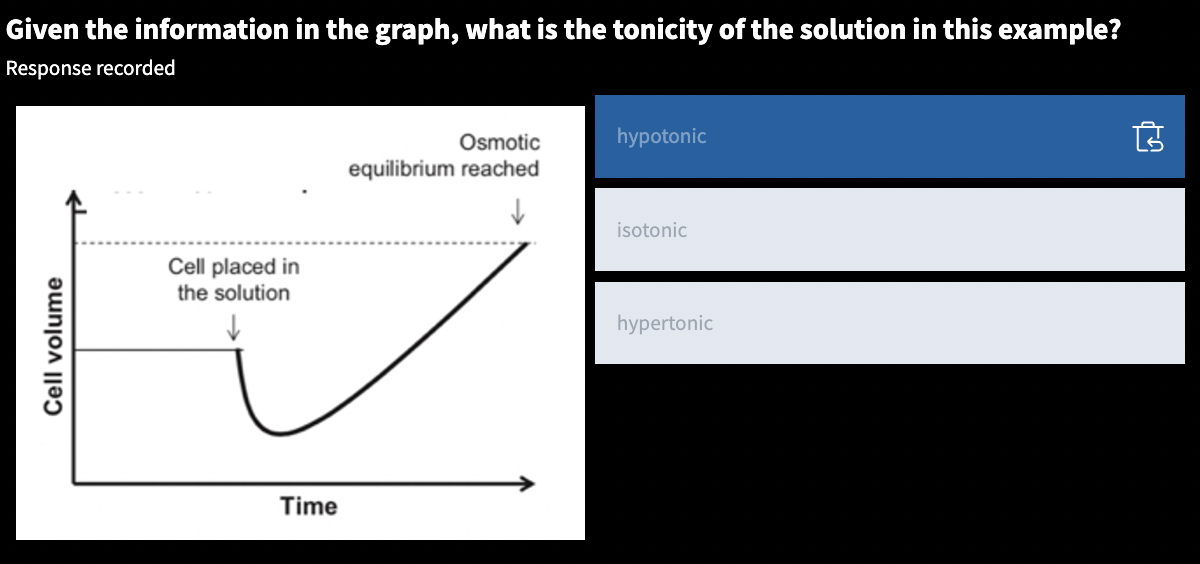
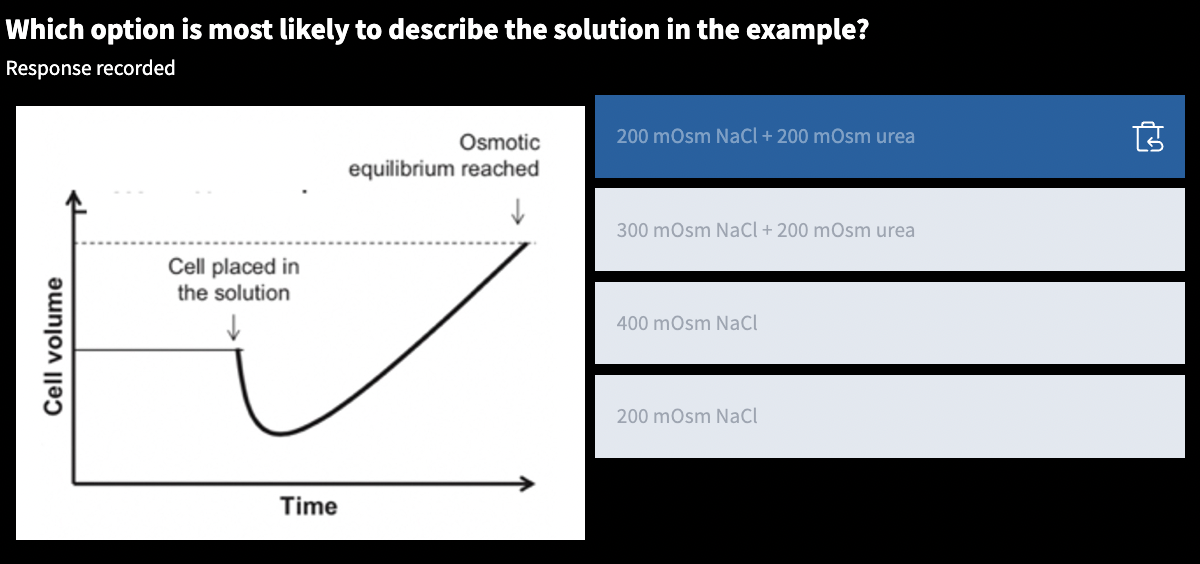
tonicity:: describes a solution based on its effects on the volume of a cell placed in the solution
hypertonic:: water diffuses out, shrinking
hypotonic:: water diffuses in, swelling
lysis:: a very hypotonic solution causes _____
isotonic:: water diffuses normally, no effect to the cell
nonpenetrating solutes:: only solutes that effect osmolarity and tonicity


body fluid osmolarity:: 300 mOsm
 nonpenetrating:: assume that all intracellular solutes are _____
nonpenetrating:: assume that all intracellular solutes are _____
 Knowt
Knowt
