Theories of Personality: Sigmund Freud
Biography
- Lived 1856 - 1939
- Used to be a physician
- THEORY: based on clinical population
- THEORY: influenced by “Victorian times”
- Died in UK – oral cancer – suicide (heavy smoker)
- Most of his patients were women (OBJECTS)
- Suicide (overdose morphine) age 83
The Psychoanalytic Perspective
- Freud’s theory proposed that childhood sexuality and unconscious motivations influence personality
- Free Association
- Reaction against hypnosis
- Ex. The patient is asked to relax and say whatever comes to mind, no matter how embarrassing/trivial – seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions
- First came up use of hypnosis – influenced by the work of Dr. Mesmer
- Hypnosis
- Altered state of consciousness
- Case of Anna O.
- With colleague and mentor J. Breur (hypnosis)
- Unexplainable symptoms (paralyzed but no cause)
- Root issues: father’s illness, dog’s bite
- As Anna started talking, symptoms lessened
- Free Association => chimney sweeping
- Started talking about her father
- Unconscious
- According to Freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories
- Contemporary viewpoint – information processing of which we are unaware
Personality Structure
Freud’s idea of the mind’s structure
- Iceberg metaphor
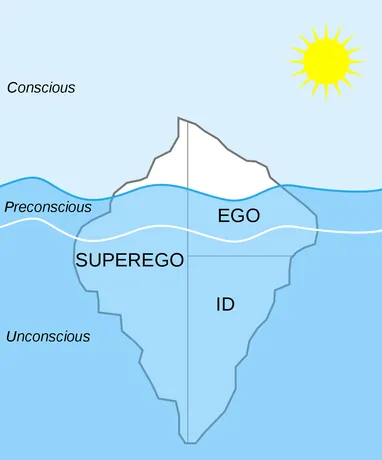
Id
- Contains a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy
- Strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives
- Operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification
Superego
- The part of personality that presents internalized ideas
- Represents “rules” of society
- Operates on the morality principle, provides standards for judgment (the conscience) and for future aspirations
Id and Superego
- In constant conflict
- Causes guilt and anxiety
- People need to learn how to cope with this conflict
- Some do it successfully and others don’t
- Conflicts must be resolved by ego
Ego
- The largely conscious, “executive part” of the personality
- Mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality
- Operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id’s desire in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain
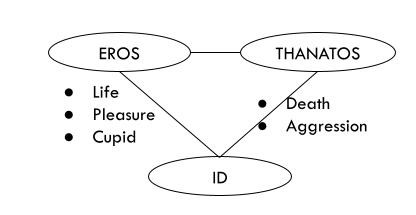
*Eros takes precedence over Thanatos
Defense Mechanisms
- The ego’s protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality (can be a normal process, but can also lead to disordered behavior)
- Motivators are unconscious
- Tactics that reduce/redirect anxiety in various ways, but always by distorting reality
- Repression
- A defense mechanism that pushes threatening thoughts into the unconscious
- Forgetting
- Often connected with trauma (abuse, PTSD, MPD)
- Denial
- A defense mechanism in which one refuses to acknowledge anxiety provoking stimuli
- When you deny something exists
- Rejecting it exists
- Projection
- A defense mechanism in which anxiety arousing impulse are externalized by placing onto others
- Putting own anxiety to others
- Displacement
- A defense mechanism in which the target of one’s unconscious fear/desire is shifted away from the true cause
- Sublimation
- A defense mechanism where dangerous urges are transformed into positive, socially acceptable forms
- Dangerous urges -> positive forms
- Ex. Surgeon who becomes excited at the sight of blood
- Regression
- A defense mechanism where one returns to an earlier, safer stage of one’s life to escape present threats
- Emotionally unstable -> fetal position
- Rationalization
- A defense mechanism where after the fact (post hoc) logical explanations for behaviors that were actually driven by internal unconscious motives
- Forced self-justification
- Ex. “I did it because of you.”
- Reaction Formation
- A defense mechanism that pushes away threatening impulses by overemphasizing the opposite of their anxiety-arousing unconscious feelings
- Opposite of what you really mean
- Engaging in the opposite feelings
- Ex. express a disdain for pornography but really enjoy it
Personality Development
- Psychosexual Stages
- The childhood stages of development during which the id’s pleasure-seeking energies focus on distinct erogenous zones
- Majority of personality is formed before age 6
Stages of Psychosexual Development
- Oral Stage: Birth to 2 years
- Need for oral stimulation
- Achieved through sucking and later chewing
- If the oral stimulation was inadequate the individual would continue to seek it throughout life
- Oral Dependent Personality: gullible, passive, and need lots of attention
- Oral Aggressive Personality: like to argue and exploit others
- Oral activity and means of aggression
- Anal Stage: 2-3 years
- Gratification now comes from emptying the bowel
- Attention turns to the process of elimination. Child can gain approval/express aggression by letting go/holding on
- Anal Retentive: stubborn, stingy, orderly, and compulsively clean (hold on)
- Anal Expulsive*:* disorderly, messy, destructive, or cruel (letting go)
- Phallic Stage: 3-6 years
- Interest in genitals develop
- Child now notices and is physically attracted to opposite sex parent
- Child derives pleasure from playing with genitals
- Latency Stage: 6 years to Puberty
- Less interest in own and others’ bodies
- Little cross sex interaction
- Freud thought sexual energies were submerged/repressed during this stage
- Genital Stage: Puberty to Adulthood
- Sexual nature now develops fully with adult needs and desires
- Recurrence of masturbation and interest in sexual matters
- Freud thought there was a progression to interest in the opposite sex if latency stage was fully resolved. If not, result was homosexuality.
Identification
- The process by which children incorporate the parents’ values into the developing superegos
- The reason our culture placed so much emphasis on traditional families
Fixation
- A lingering focus on pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, where conflicts were unresolved