Human Anatomy & Physiology
Respiratory System -
Nasal cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli
Bronchi are further divided up by:
Primary Bronchi → secondary bronchi → Tertiary Bronchi → Bronchioles
Bronchioles are further divided like:
Tertiary bronchi → Terminal bronchioles → Respiratory bronchioles → Alveoli
Nasal cavity - where the air is warmed, humidified, and filtered by mucus and hair
Pharynx - Junction for both air and food
Larynx - voice box
Trachea - Cylinder tube with rings of cartilage that provide support
The pharynx acts as the crossroads for food and air where the food is supposed to go to the esophagus and the air is supposed to go to the pharynx
Epiglottis - stops food from going into our trachea
There are two main bronchi: Right and Left
Bronchioles - smaller branches of bronchial airways
Alveoli - tiny air sacs in the lungs at the end of the bronchioles that allow for rapid gaseous exchange
Alveoli are surrounded by clusters of alveolar sacs. In these sacs are the actual sites of where gas exchange occurs
There are two lungs: Right and left.
Lungs are divided into sections called lobes.
The right has 3 lobes
The left has 2 lobes
The left lung has an indention at the bottom called the cardiac notch where it makes space for the heart. This contributes to the smaller size of the left lung. You can remember which lung has the smaller amount of lobes because less lobes = smaller. The left is smaller because of the heart and your heart is on the left side
Conducting zone - The areas in which air is transported between from the outside to the site of the gas exchange. It’s commonly referred as the “dead space” as no gas is actually exchanged in this area.
The conducting zone includes the nose all the way to the bronchus. (Nose/mouth → pharynx → larynx → trachea → Bronchus)
Respiratory zone - Structures in the lungs where gas exchange occurs
Includes Respiratory Bronchioles, Alveoli, and Alveoli ducts
The Respiratory System works with:
The cardiovascular system
Red blood cells carry the oxygen throughout the body and picks up the CO2
Skeletal system
protects lungs through our ribcage
Nervous system
Voluntary and involuntary control of respiratory by using pH
Muscular system
Work together to expand and contract the thoracic cavity, aiding in breath
intercostal muscles (muscles in between ribs)
Diaphragm (beneath our lungs)
Abdominal wall
Inspiration - Air drawn into lungs or inhalation
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
Expiration - air pushed out of the lungs
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax
Diaphragm pushes down and thoracic cavity volume increases during inhalation
Causes negative pressure relative to the atmosphere, causing air to flow in
Diaphragm rises and thoracic cavity volume decreases during inhalation
Increases pressure compared to the atmosphere, causing air to flow out
pH scale - A measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is
Acid - Substances that increase concentration of hydrogen ions
Base - substances that decrease concentration of hydrogen ions
Increase in acidity of blood signal the brain to increase respiration
Higher levels of CO2 will lead to higher levels of hydrogen ion concentration causing blood acidity to rise
Lower levels of CO2 will cause lower levels of hydrogen ion concentration causing blood to become alkaline
More CO2 = more hydrogen ions
pH scale is from 1-14
<6 is acidic (1-6)
>8 is alkaline (8-14)
7 is neutral
Perfusion - delivering blood to the body’s tissues, organs, and cells
Ventilation - movement of air in and out of the lungs (breathing)
Hyperventilation - Fast breathing
Blood pH is acidic → not getting enough O2
increased O2 = hyperoxia
decreased CO2 + hypocapnia
When there’s too much O2, blood becomes basic
Hypoventilation - slow breathing
pH is basic → too much O2
lower O2 = hypoxia
higher CO2 = hypercapnia
Hyperventilation and hypoventilation disrupt the normal process of breathing as well as the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body
Cardiovascular System -
Blood - red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals
Primary function: maintain homeostasis
pH
Temperature
Osmotic pressure
Transports:
Hormones
Nutrients
Gases
The cardiovascular system carries oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the tissue of the body
Blood is always red in color
the brighter the blood, the more oxygen it has
Blood is composed of:
Plasma
Platelets
Erythrocytes
Plasma - liquid portion consisting of lipids, salt, protein, and water
Erythrocytes and cells:
Red blood cells
Transports
White blood cells
fight infection
Platelets - help w/ clotting
Hemoglobin - what gives blood its red hue
Arteries carry blood AWAY from the heart, typically oxygen rich
A in Away stands for Arteries
Veins - carry blood back to the heart, typically oxygen poor
VERB - Veins Efficiently Return Blood
Pulmonary arteries carry oxygen-poor blood
Pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood
Capillaries - tiny blood vessels where gas exchange for oxygen and carbon dioxide happen
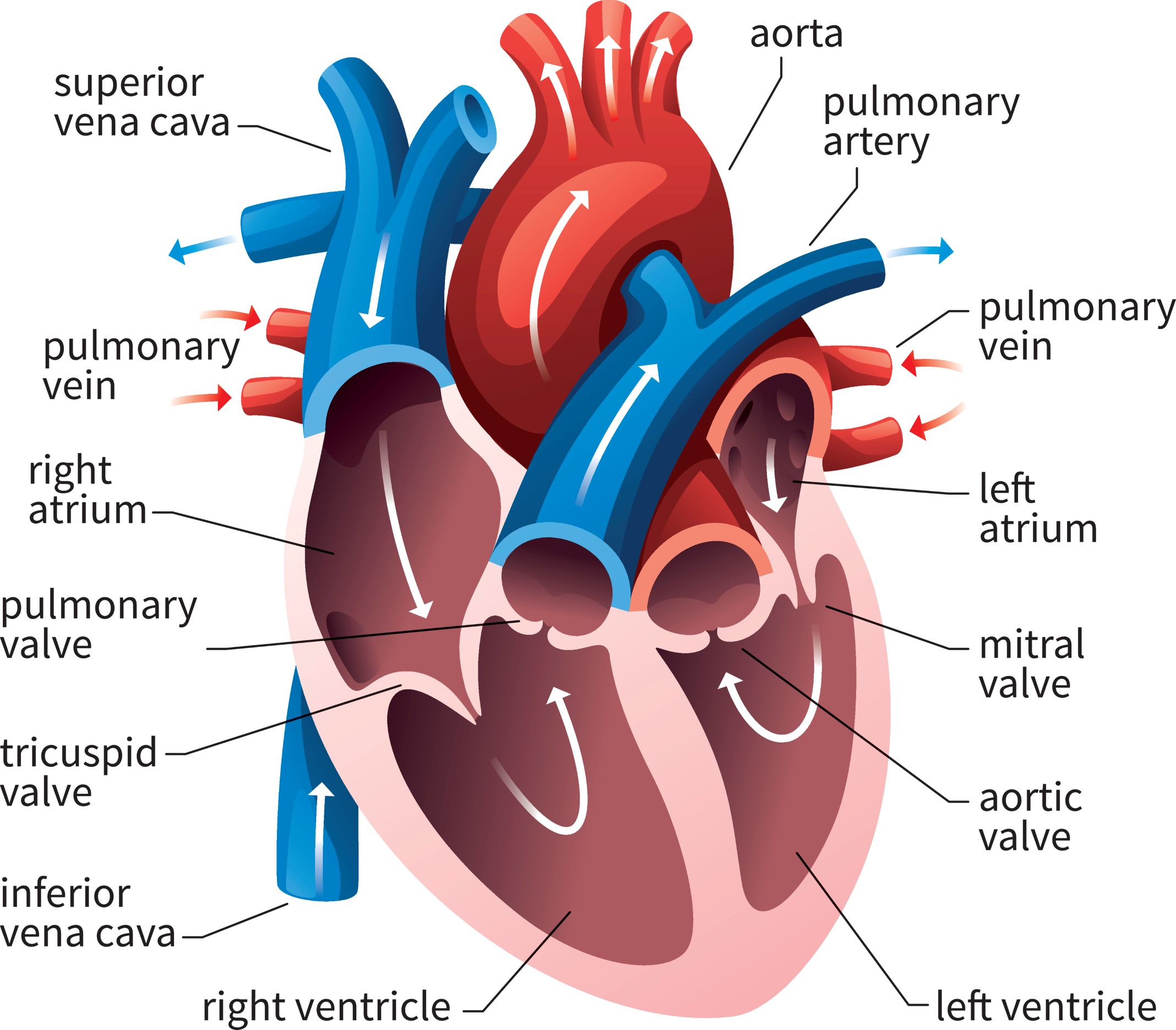
Heart
Atrium at the top, Ventricle at the bottom
A comes before V in the alphabet
Heart valves prevent backflow
Atria have thin walls while ventricles have thick walls
Right of the heart usually carries deoxygenated blood
Left of the heart usually carries oxygenated blood
Blood flow: deoxygenated blood goes to the lungs to get reoxygenated
Blood comes from tissues and re-enters heart through the superior or inferior vena cava
Inferior vena cava is blood from the lower parts of the body while Superior vena cava comes from the higher parts of the body
Superior/Inferior Vena Cava → Right Atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonic valve → pulmonary artery → Lungs
Oxygenated blood moves from the lungs to the heart and back to the tissues
Lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left Atrium → Bicuspid/mitral valve → Left ventricle → aortic valve → Aorta
Coronary Arteries
Right coronary artery
Left coronary artery
Circumflex artery
Right Marginal Artery
Left Anterior descending artery
Posterior interventricular Artery or posterior descending artery
Coronary arteries originates from the aorta and delivers nutrients and oxygen to the heart
Coronary veins
Great cardiac vein
Small cardiac vein
Coronary sinus
Middle Cardiac vein
Coronary veins carry deoxygenated blood return to right atrium from coronary sinus
Interatrial Septum - thin, muscular membrane structure that consists of two parts: fossa ovalis and the limbus of the fossa ovalis
Separates the right and left atrium
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) - a congenital heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the interatrial septum, allowing blood to flow between the two atria
Interventricular septum - Thick, muscular wall that consists of two parts: a membranous and muscular portion
Separates the right and left ventricles
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) - A congenital defect characterized by one or more holes. in the interventricular septum, allowing to mix between ventricles
The Interatrial Septum and the Interventricular septum separate the oxygen-rich blood from the oxygen-poor blood between the chamber
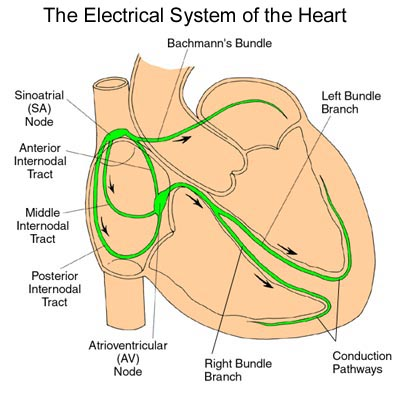
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart
Sinoatrial node (SA)
Main Pacemaker
Starts electrical impulse
Triggers atrial contraction
60-100 BPM
Situated in the right atrium where it meets the Superior vena cava
Bachmann Bundle - brings signal from SA to the left atrium
Internodal Pathways
Three routes: Anterior, middle, posterior
Signal from SA node goes to AV node
Atrioventricular node (AV)
Secondary Pacemaker
In the right atrium but near the tricuspid valve and coronary sinus
Relay signals from SA node
Allow atria to contract → allows ventricles to fill
40-60 BPM
The AV has a delay on the relay of signals which allows the atria to fully contract and that blood reaches the ventricles
Bundle of His
Only route between atria and ventricles
Two branches:
Right bundle branch - signal to right ventricle
Left bundle branch - signal to left ventricle
Purjinke Fibers
Last ditch pacemaker
Connect w/ myocytes
Initialize depolarization → leads to contraction
20-40 BPM
Depolarization - contraction
Repolarization - Relaxation
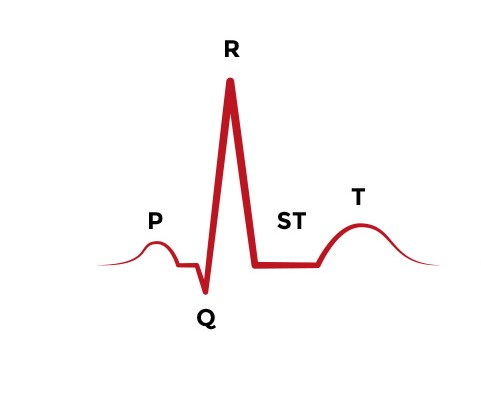
ECG Basics
P Wave: Atrial depolarization
Signifies Atrial contraction
QRS Complex: Ventricular Depolarization
Signifies ventricular contraction
Normal range: .06-.12 seconds
T Wave: Ventricular Repolarization
Signifies Ventricular relaxation
Atrial Repolarization happens concurrently with the QRS complex
Systolic Pressure - Contraction of the heart
“Lub” sound
Top # on the reading lowest pressure in arteries
Lower than 120
Diastolic Pressure - relaxation of the heart
“Dub” sound
Bottom # on reading lowest pressure in arteries
Lower than 80
Nervous System -
Body’s command center – made up of your brain, spinal cord, and nerves that sends highly complex sensory info to different parts of the body
Two Types:
Central Nervous System - made up of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System - Everything else outside the brain and spinal cord
Primary Function:
Central Nervous System:
Process info
Command center
Motor response or regulate body mechanism
Peripheral nervous system
Sensory info for the CNS
Central Nervous System
The brain will be categorized into 3 regions:
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
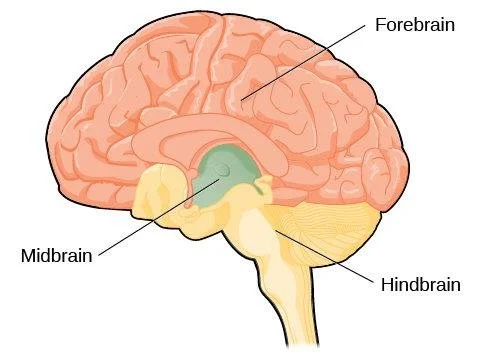
Hindbrain is made up of:
Cerebellum
Pons
Medulla
Medulla - regulates breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate
Pons - transmits signals between forebrain and cerebellum
Cerebellum - Balance & movement coordination
“Medulla manages, pons passes, and cerebellum coordinates”
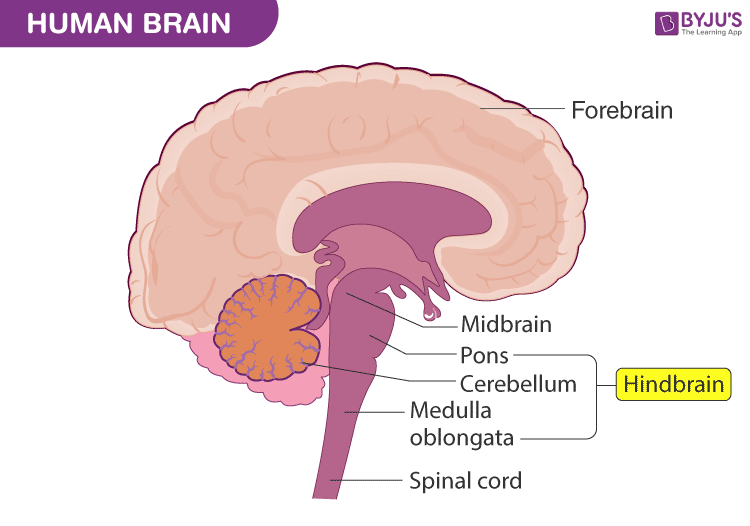
Midbrain
Primary function:
Alertness
Sleep/wake cycle
Motor activities
“MID Controls”
M - movement
I - Involvement in the sleep/wake cycle
D - Detection of auditory and visual reflexes
Forebrain
Contains the cerebrum, the largest and most developed part of our brain
Divided into two hemispheres: Left and Right
Primary function:
Contains primary motor and sensory cortices
Association areas allow for complex analysis of internal/external environment
Limbic system: Memory and emotional aspect of behavior
Highest aspects of cognitive function
Substrate for conscious experience
Cortex - the cerebrum’s outer layer
Composed of gray matter
Gray matter - site of integration
The cell body and axon terminal of a neurotransmitter
White matter - signal highways
Axon covered with myelin
Frontal Lobe - Think “forehead” for deep thought and decision making
Parietal Lobe - Think “parachute” covering top of head; in charge of sensory information
Occipital Lobe - In charge of vision.
Temporal Lobe - Think “tempo” for hearing and rhythm in speech and memories

Peripheral Nervous System
Anything outside of the brain and spinal cord
Two Categories:
Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System - responsible for internal temperature, regulating GI function, excretory & endocrine systems, and cardiac muscle activityes
Sympathetic - Fight or flight response
Increase heart rate
Increases respiration
slows digestion
Parasympathetic - Rest and Digest
Decrease heart rate
Digestion occurs
Sympathetic friends will take you out after a break up and hype you up, sympathetic parents (“PARA”) will comfort and calm you
Somatic Nervous System - responsible for motor function of skeletal muscles (voluntary and somatic)
Two main types of tissues in the nervous system
Neurons
Glial
Glial cells - help maintain chemical balance that allows signals to be sent and help maintain the blood-brain barrier
Myelin sheath production
Generate cerebrospinal fluid
Immune function
Afferent neurons - sensory neuron input
Signal goes to our CNS
“Afferent arrive to CNS”
Efferent Neurons - motor neuron output
Signals away from CNS to motor neurons
“Efferent Exits”
Gastrointestinal System +
The organs that take food and liquids and brakes them down into substances that the body can use for energy, growth, and tissue repair
Ingestion - Taking in food (eating)
Digestion - Biomolecule polymers break down into building blocks
Absorption - Absorbs nutrients
Elimination - Waste is removed
Ingestion
Begins when food is brought into our mouths
Digestion
Begins after food is brought is brought into our mouths
Mechanical digestion - physically breaking down food into smaller particles
Mouth as you chew
Churning of the stomach
Chemical digestion - enzymes break down nutrients into smaller molecules
Saliva
Hydrochloric acid and pepsin in stomach
Epiglottis - flap that covers the trachea during swallowing so food does not enter the lungs
Peristalsis - Involuntary constriction and relaxation, creating wave-like movements to push contents down the canal of the esophagus
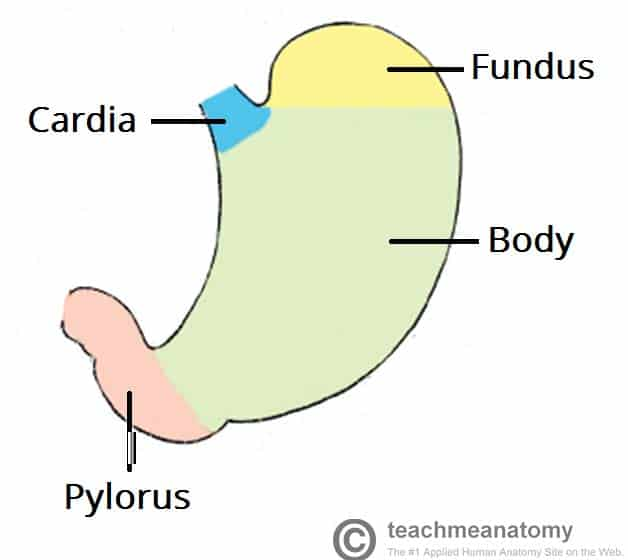
Chyme - Pulpy acidic fluid which passes from the stomach into the small intestine
Hydrochloric Acid - Strong acidic solution of the gas hydrogen chloride in water
Pepsin - Chief digestive enzyme in the stomach that breaks down proteins into polypeptides
Lower Esophageal sphincter - separates the stomach from the esophagus
Prevents gastric acid from splashin or coming back up the esophagus
Pyloric sphincter - separates the stomach from the small intestine
Controls the entrance of partially digested food into the small intestine
Prevents backflow of intestinal contents into the stomach
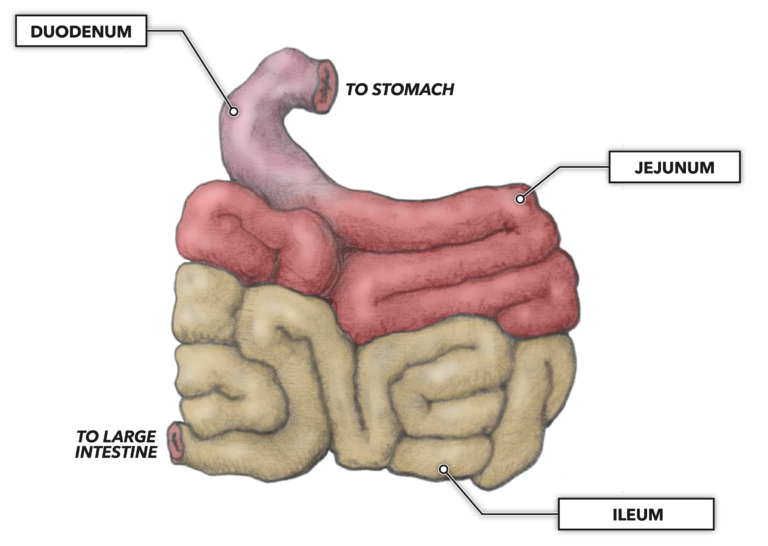
Absorption
Begins at the small intestine
Small intestine is made up of three sections:
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Duodenum - shortest segment of the small intestine and beginning of it
Chemical digestion of chyme
Breaks down fats, proteins, and carbs
Absorbs iron and other minerals
Duodenum does it all → breaks down all the macronutrients
Jejunum - middle segments of small intestine
absorbs nutrients
Carbs and protein are absorbed into the bloodstream
Jejunum will judge you if you’re fat → does not absorb lipids/fats
Ileum - final segment of small intestine
Absorb nutrients
Vitamin B12, bile salts, and products of digestion are absorbed
Order of the parts can be remembered with: “ Digestive Juices Intake”
Villi - tiny hair-like projections that line the intestines and help w/ absorption into the bloodstream
Large Intestine - Water absorption
3 Parts:
Ascending colon - first segment of large intestine
Absorbs water and salts
Solidify waste into formed stool
Transverse colon - longest, most mobile part of the large intestine
Storage site for digested food
More absorption of water and minerals
Descending colon - descending segment of the large intestine
Carries solid waste towards rectum
more absorption of water and minerals
store feces until defecation
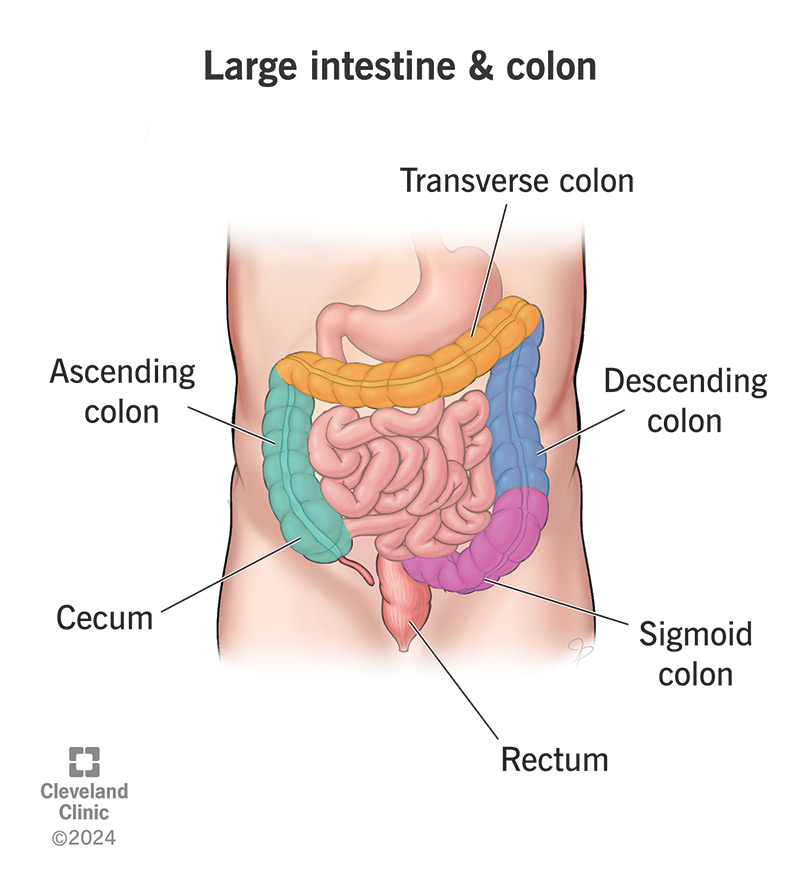
Elimination
Waste is removed
In the rectum
Rectum - final segment of large intestine
Stores feces until they are expelled through the anus
Accessory organs of GI system:
Liver
Carb and protein metabolism
Creates bile to help w/ the breakdown of lipids in small intestine
Gallbladder
Store the bile produced by the liver
Pancreas
Produces pancreatic juices to help neutralize chyme
GI System Enzymes & Hormones
Gastrin - Stimulate gastric glands to secrete pepsinogen and HCL
Found in G cells of the stomach
Cholecystokinin - digests fats & proteins and stimulates the gallbladder to release bile
Found in the I cells of the duodenum and jejunum
Secretin - regulates pH by inhibiting gastric acid secretion and stimulating bicarb production
Found in the S cells of the duodenum
Insulin - responsible for glucose metabolism and stores glucose as glycogen
Found in beta cells of pancreas
Glucagon - raises blood glucose levels
Found in the alpha cells of pancreas
Bile - emulsifies fats
Produced by liver, stored in gallbladder
Muscular System -
Composed of muscle cells & tissues that brings about movement of an organ or body parts
Cardiac muscle - specialized, organized type of tissue that only exists in the heart
Involuntary control
Controlled by autonomic nervous system
Smooth muscle - narrow, spindle shaped cells w/ a single centrally located nucleus
Involuntary control
Found in digestive system, arteries, veins, bladder, and eyes
Skeletal muscle - highly organized tissue that attach to bores or skin to produce movement
voluntary control
Controlled by somatic nervous system
Found in tongue, diaphragm, upper esophagus
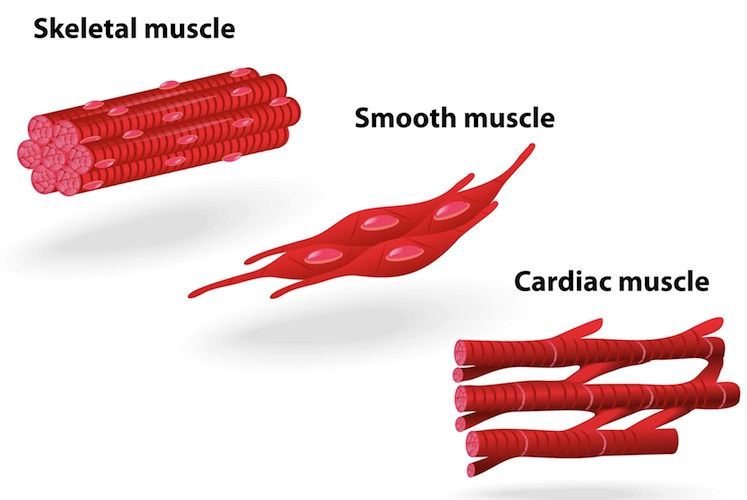
Characteristics of Muscle Tissue:
Extensibility - ability to stretch or extended
Elasticity - Ability to return to its original length when relaxed
Excitability - ability to respond to a stimuli from a motor neuron or hormone
Contractibility - ability of muscle to shrink or contract
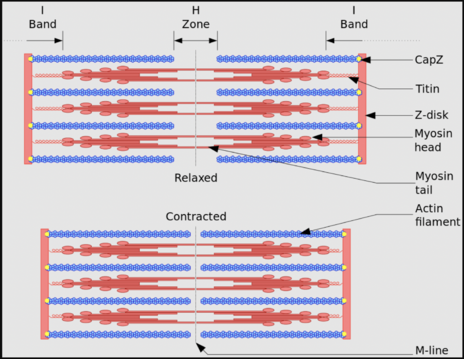
Each muscle is composed of muscle fiber, there are multiple myofibrils
Myofibrils are composed of sarcomeres. Sarcomeres are composed of actin and myosin
Actin (thin filaments) - protein that forms the contractile filaments of muscle cells
Myosin (Thick filaments) - fibrous globulin of muscles that can split ATP and react to actin in muscle contraction
Reproductive System -
Collection of organs and glands that work together to produce offspring. Includes a network of hormone production that allows for conception and pregnancy
Accessory organs:
Glands
Ducts
External genitalia
Gonads:
Male reproductive systems: Testes
Female reproductive system: Ovaries
Includes sex hormones and sperm and egg gametes
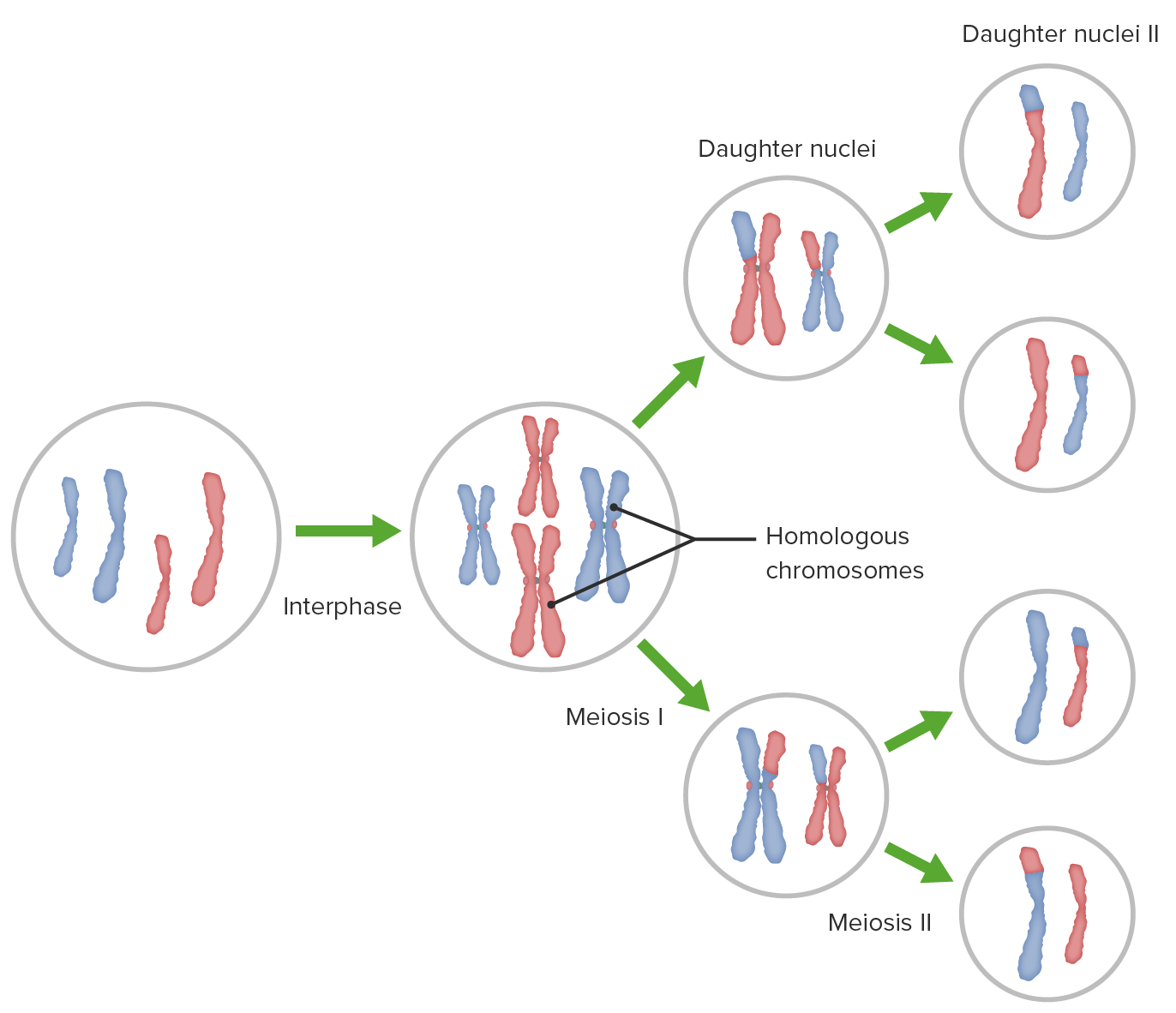
Gametes are haploid cells that are produced through meiosis
Meiosis:
Primary spermatocytes (males) - Primary oocytes (females)
46 unduplicated chromosomes (2n) → DNA replication → 46 duplicated chromosome (2n) → 46 chromosomes are split up into two groups of 23 → Meiosis II → 23 unduplicated chromosome (n) for each gamete
Sperm + Egg → fertilization → zygote
Male reproductive System
Epididymis - storage of sperm
Testes produce testosterone and produce sperm
Separated by lobules which house seminiferous tubules → sperm production through spermatogenesis

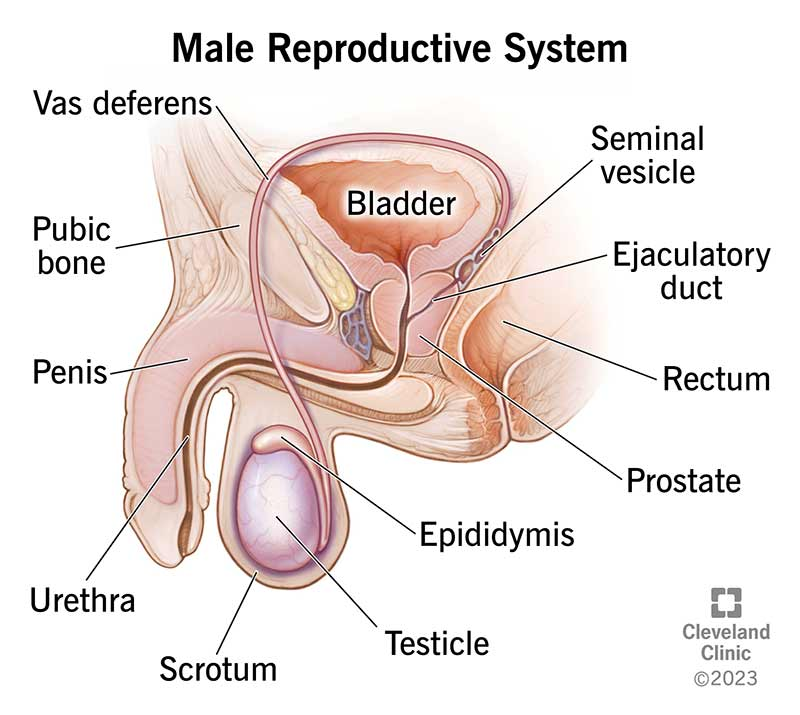
Seminal glands - produces fluids that will turn into semen
Produces the semen
Prostate - produces fluid for semen and surrounds the urethra
Activates the semen
Bulbourethral gland - discharges a component of seminal fluid into urethra that lubricates the glans penis
Also known as the Cowper’s gland
Sperm and semen are two different things. Semen does not contain sperm cells but instead mix w/ it in the ejaculating duct
Female Reproductive System
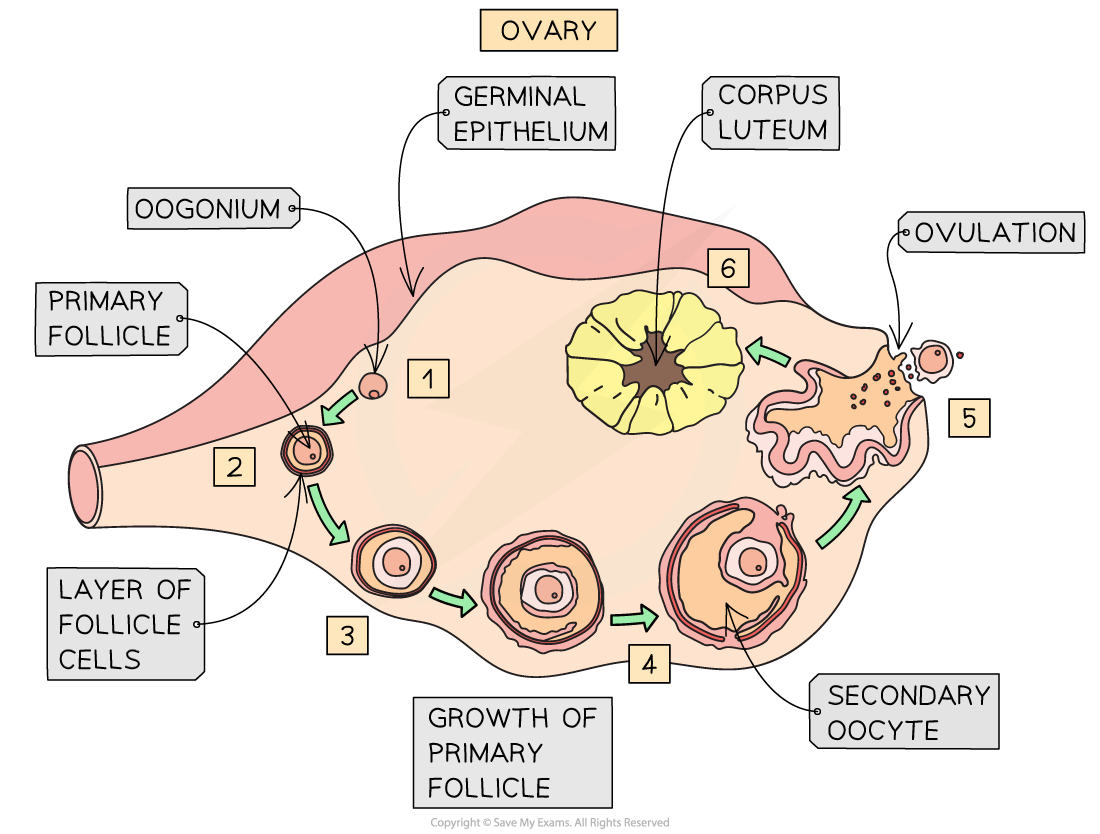
Ovary:
Oogenesis - The process of female gamete formation
Ovary produces sex hormone estrogen and progesterone
Primordial follicle → vesicular follicle
Ovaries - oval-shaped glands where eggs form and hormones estrogen and progesterone are made
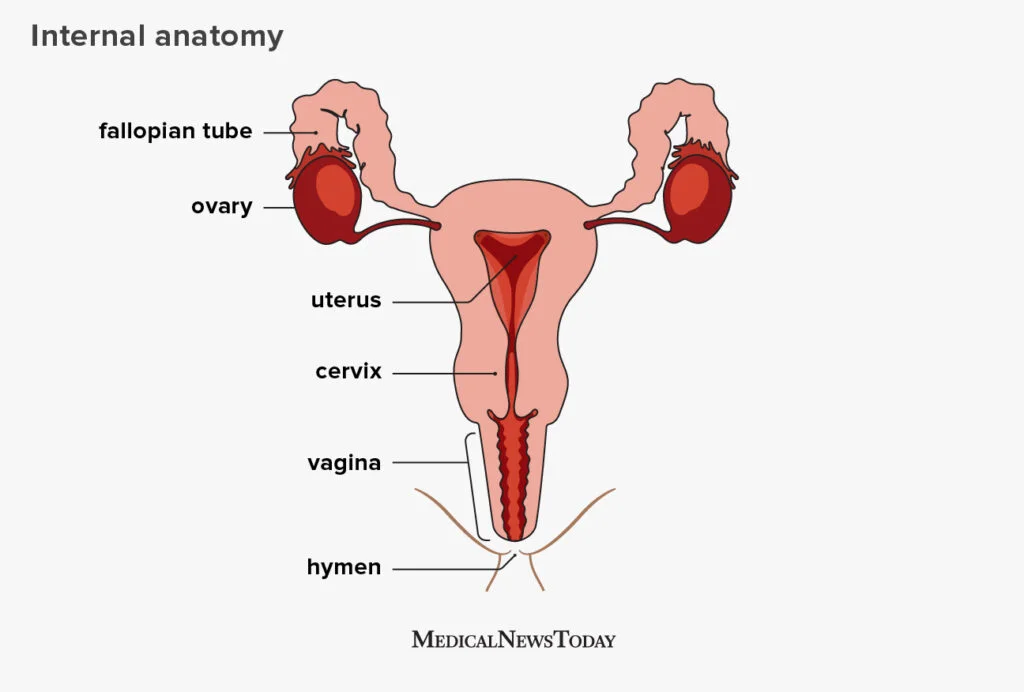
Fallopian tubes - Bilateral conduits between ovaries and the uterus
Uterus - hormone-responsive sex organ that is responsible for gestation, menstruation, and labor
Cervix - lower, narrow end of uterus that connects the uterus and vagina
Vagina - muscular, copulatory canal that goes from the uterus to the outside of the body
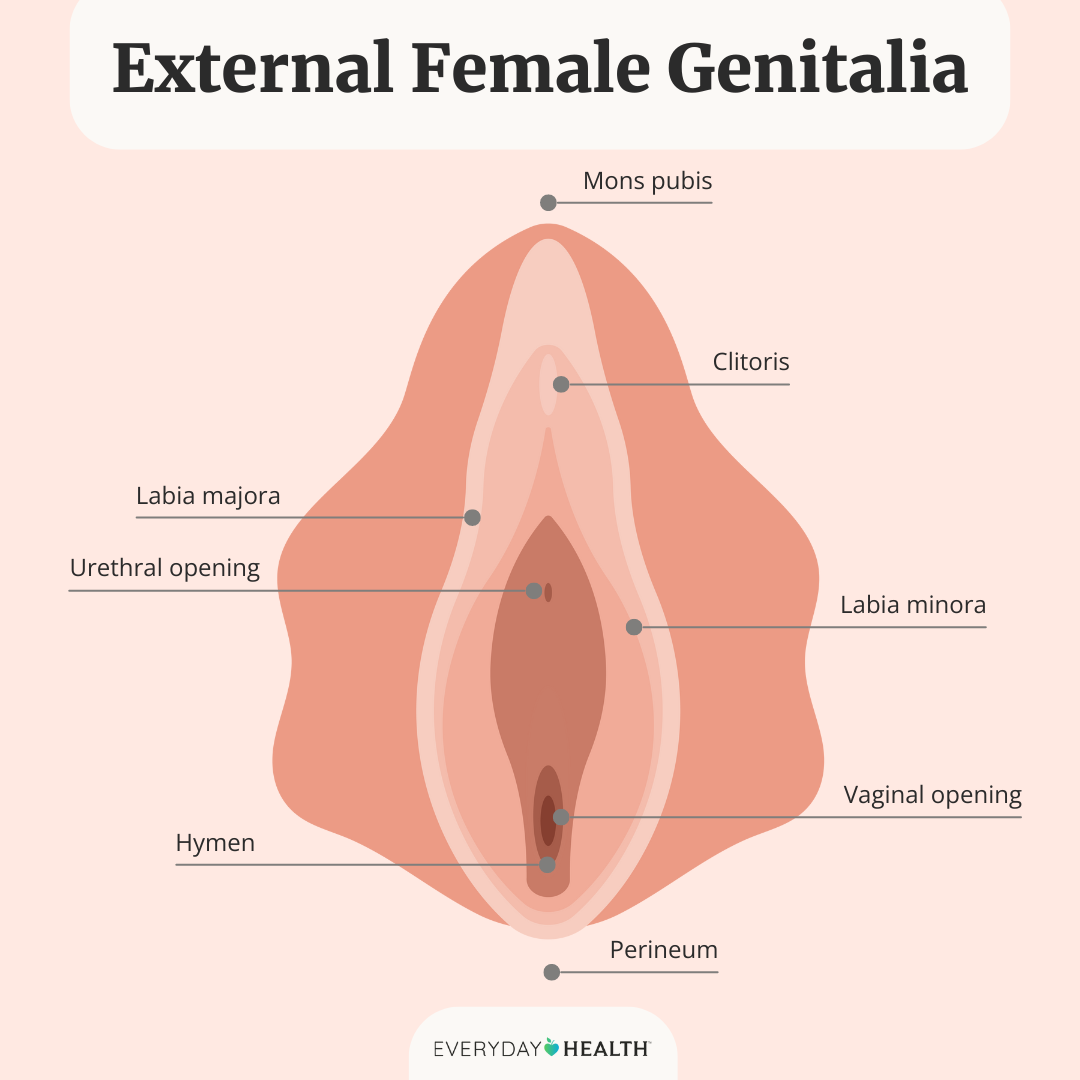
Mons pubis - area of fatty tissue that covers the pubic bone
Labia Majora (Outer/larger lips) - fleshy folds of tissue that extend down from the mons pubis to merge with the skin of the perineum
Labia Minora (Inner/smaller lips) - Two inner folds of skin that surround the opening of the vaginal vestibule
Vestibule - space between the labia minora that houses the urethral orifice and vaginal orifice
Urethral opening - opening in which urine is discharged from the body
Vaginal orifice - slit below and behind the the opening of the urethra for menstrual menstrual flow and childbirth
Anus - opening of the rectum to the outside of the body which solid waste matter leaves
Endocrine/Reproductive Hormones
Hypothalamus
Pineal glands
Pituitary glands (posterior and anterior)
Hypothalamus:
Acts as the control system/command center
makes their own hormones such as oxytocin
Posterior pituitary gland:
Stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus such as oxytocin
Anterior pituitary gland:
Makes their own hormones such as:
Prolactin
follicle stimulating
Luteinizing hormone
Regulated by hypothalamus
Oxytocin - causes increased contractions of the uterus during labor
Stimulates ejection of milk into the ducts of the breasts
Prolactin - stimulates milk production in mammary glands
Follicle - stimulating - formation of ova or sperm
Luteinizing hormone - stimulates ovulation in females and androgen in men
Produced by gonads:
Estrogen - steroid hormone develops female sex characteristics
Progesterone - creates healthy uterine lining for menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Androgen - develops male sexual characteristics and reproduction
Integumentary System -
Largest organ in the body that forms a physical barrier between our external and internal environments
3 layers of skin:
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis subcutaneous tissue
Primary functions:
Homeostasis
Physical barrier
Protecting from pathogens
Vitamin D production
Sensory functions
Keratinocytes - produces keratin, a protein that enhances water resistance and toughness in our cells
Found throughout the epidermis
Order of the Epidermis:
“Come Let’s Get Sun Burnt”
Come: Stratum Corneum - Outermost layer and is made up of lipids and keratinocytes.
Let’s: Stratum Lucidum - Thin, clear layer of dead skin cells found in thick skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Only found in those areas
Get: Stratum Granulosum - Thin layer of cells that contain granules of lipids to form a waterproof layer
Sun: Stratum Spinosum - Keratinocytes held together by desmosomes to make skin flexible and strong
Burnt: Stratum Basale - Single columnar or cuboidal row of cells that divide to replace the epidermis as it wears away
Langerhans Cells - tissue macrophages of the skin
Melanocytes - cells in the skin produce and contain the pigment called melanin
Dermis
Contains blood vessels, sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and connective tissue
Connective tissue - non-epidermal tissue that serves to bind structures together
Dermis is made up of two types of protein: Collagen and Elastin
Elastin and Collagen are made by specialized cells called fibroblasts
The Dermis is made up of two layers:
Papillary layers - looser connective tissue
Reticular layers - more dense and packed connective tissue
Scars - fibrous connective tissue develops and leaves a mark on the skin
Scars are created if the wound happens in the dermis layers
Scars cause skin to lose elasticity, causing hindrance to movement for larger scarring/wounds
Keloids - irregular fibrous tissue formed at the site of a scar due to increase of collagen production
Hypodermis
Connects the skin to bone and muscle tissue
Primarily composed of adipose tissue which store body fat
Adipose tissue aid the body with insulation
Sweat glands
Aids in thermoregulation
As sweat evaporates, the surface of the skin cools
Sebaceous glands - produce oil
waterproofs and lubricates hair and skin
Hair follicle
Hair bulb undergoes mitosis to drive hair root growth
Nails
Nail root undergoes mitosis to drive nail growth
Skin Cancer
Most common cancer in the US
Basal cell carcinoma - abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells
Melanoma - A tumor of melanin forming cells
Squamous cell carcinoma - Cancer growth that make up the middle and outer layers of the skin
Burns
First degree burns - involves the outer layer of the skin (epidermis)
Minor inflammation and redness
Second degree burns - Extends through the epidermis into the upper layers of the dermis
Swelling, blistering, and significant pain
Third degree burns - penetrates the full depth of the dermis and epidermis
White/charred skin and numbness due to nerve damage
Endocrine System -
Messenger system comprising of feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands and target distant organs. The hypothalamus is the neural control center of all endocrine systems
Brain:
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Pituitary gland
Neck/Chest:
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thymus
Abdomen/Pelvis
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Gonads - ovaries & testes
Endocrine - releases hormones into their surroundings. No special ducts
Exocrine - A gland that makes substances and releases them through a duct or opening to the body
Exo → Excrete
Hormones
A regulatory substance in an organism and transported in tissue fluid to stimulate specific cells or tissue into action
Function:
Bind specific target cells and will cause some kind of action to occur
Hormones can be derived from various biomolecules such as:
Amino acids (polypeptides)
Lipids (steroids)
Posterior pituitary hormones
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic hormone - constricts blood vessels and control salt in water in body
Anterior pituitary hormones:
Growth hormones - promotes growth in hormones
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) - Activates release of thyroid hormones
Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) - triggers release of cortisol from adrenal glands
Pineal gland hormones:
Melatonin - involved in sleep/wake cycle
Thyroid hormones:
Thyroxine (T4) - increases rate of chemical reactions in cells and helps control growth and development
Triiodothyronine (T3) - Stimulates nervous system in wakefulness, alertness, and responsiveness to external stimuli
T stands for thyroid. Both T4 and T3 turn up metabolic rate
Calcitonin - lowers blood calcium
“Calci-tone-it-down” → lowers calcium in blood
Parathyroid hormones:
Parathyroid hormone - raises blood calcium
Thymus hormone:
Thymosin - help make T cells
Adrenal glands are comprised of two distinct parts:
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla hormones:
Epinephrine - works on heart
Norepinephrine - works on blood vessels
Adrenal cortex hormones:
glucocorticoids - steroid hormones that play a role in glucose, proteins, and fat metabolism
EX: cortisol
Mineralocorticoids - steroid hormone that plays a role in salt and water balance
EX: aldosterone
Pancreas hormones:
Insulin - controls blood sugar levels and metabolism - turn food into energy
Puts glucose into cells to lower blood sugar
Glucagon - helps regulate blood sugar levels when too low
Raises blood sugar levels by raising glucose
Gonads hormones:
Estrogen
Progesterone
Androgen
Urinary System
The organs that make up urine and remove it from the body
Survival function:
Maintain osmotic balance
Remove metabolic waste

Nephrons - the fundamental units of the kidney
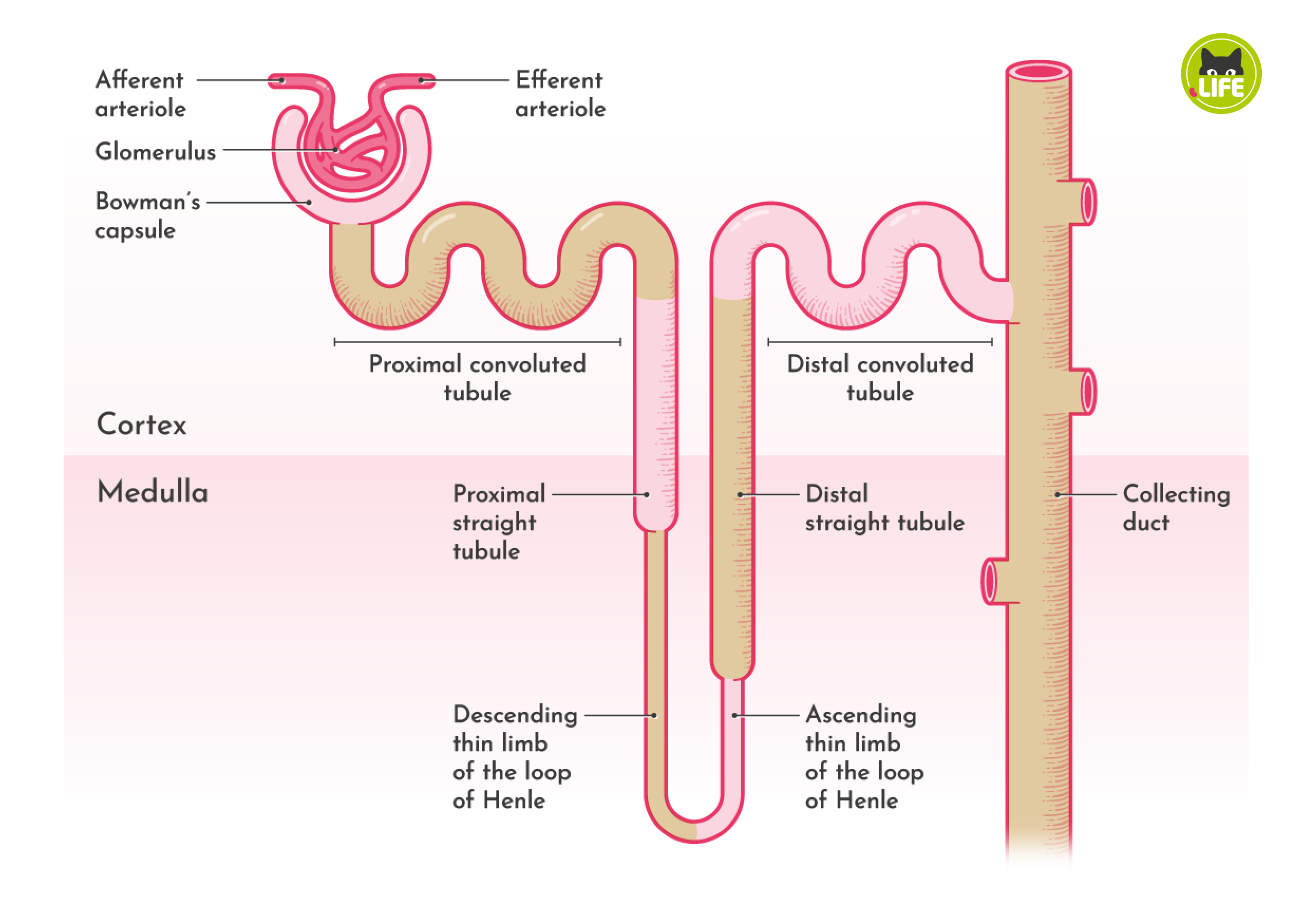
Fluid found in Bowman’s capsule:
Water
Glucose
Amino Acids
Salts
Hydrogen ions
Bicarbonate ions
Medication & vitamins
Urea
Fluid pushed into the Bowman’s capsule is called filtrate
Filtrate is either re-absorbed or secreted
Reabsorption - Tubular reabsorption is the process by which most solvent and solutes are recovered back into the belly
Secretion - Tubular secretion is the transfer of materials from the capillaries into the renal tubular lumen
Two ways of transport:
Passive transport
Active transport
Passive transport:
Diffusion - movement of small particles
Facilitated diffusion - movement of large particles
Osmosis - movement of water
Active transport - Molecules move from a lower concentration gradient where solutes/fluid move from higher concentration
Journey through the kidney:
1) Bowman’s capsule
2) Proximal convoluted tubule
Reabsorbed:
Salts
Water
Bicarbs
Glucose
amino acids
potassium
Secrets:
Hydrogen
Water
3) Descending loop of Henle
Reabsorbs: water
4)Ascending loop of Henle
Reabsorbs: salt
5) Distal Convoluted Tubule
Reabsorbs:
salts
water
bicarbs
secrets:
Hydrogen
Ammonium
Potassium
6) Collecting duct: hormone controlled
Reabsorbs:
Salts
Urea
Water
Immune System -
A complex of cells, tissue, organs, and proteins that protect the body from infection, disease, and other threats
Pathogens - A bacterium, virus, protists, worms, or other microorganism that can cause disease
White blood cells:
Macrophages - engulfs pathogens
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
B cells
T cells
& more
External protection:
First line of defense:
Skin
Mucous membranes
Non-specific defense
Second line of defense:
Non-specific defense
Macrophages (phagocytic white blood cells)
Second & first line of defense are innate immunity
Mast cells - assist with allergic & inflammatory responses
Contains histamine which makes blood vessels dilate and more permeable to allow white blood cells to reach the affected area
Complement System
Engages in both specific & non-specific defense
Works to enhance or complement the actions of the immune system
Draws more white blood cells to site of injury/infection
3rd line of defense:
Specific defense
Adaptive immunity
B & T cells (lymphocytes)
Adaptive Immunity - A type of immunity that develops when a person’s immune response to a foreign substance or microorganisms, such as after an infection or vaccination
Two types:
Cell mediated
Humoral
Cell mediated:
Cytotoxic T cells - destroys infected cells by causing apoptosis
Two processes:
An infected cell presents antigen from pathogen that has infected it. Cytotoxic T cell binds and causes apoptosis
Macrophages release chemical signals. Helper T cells bind and then release signals. Stimulates the cytotoxic T cells
Helper T cells - helps activate other white blood cells
Also involved in humoral
Antibodies - A blood protein produced in response to and counteract a specific antigen
IgG - Most abundant type of antibodies. Enhances phagocytosis, neutralizes, toxins, trigger complement system
IgA - Mucosal Immunity
IgM - 1st antibody produced in response to infection. Forming complexes w/ antigens and activating complement
IgE - Allergic reactions and parasitic infections
IgD - less understood antibody role in initiating early immune response
Produced by B cells
Skeletal System -
The body’s support system. It’s part include bones, muscles, cartilage, and connective tissue like ligaments and tendons
Primary functions:
Supporting body
Protecting internal organs
Reservoir for minerals
Produces RBC & WBC
Enables movement
2 types:
Axial skeleton
Appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton:
Skull
Ossicles
Hyoid
Vertebral column
Rib cage
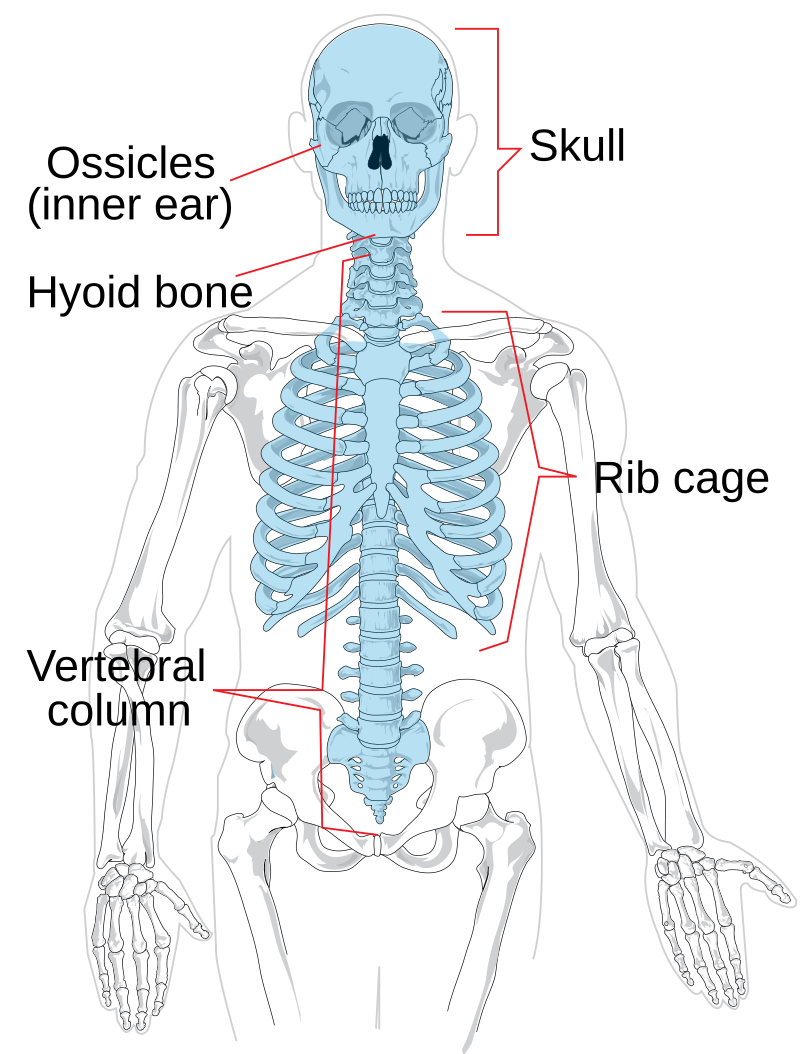
Appendicular skeleton:
Shoulder girdle
legs & feet
Arms & hands
Pelvic girdle

Long bones - longer than they are wide
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Phalanges
Metacarpals
Metatarsals
Short bones - Length & width are close to equal, like a cube
Carpals
Tarsals
Sesamoid bones - round bones
Patella
Flat bones - curved and thin
Cranial bone
Scapula
Irregular bones - no specific shape description
Vertebrae
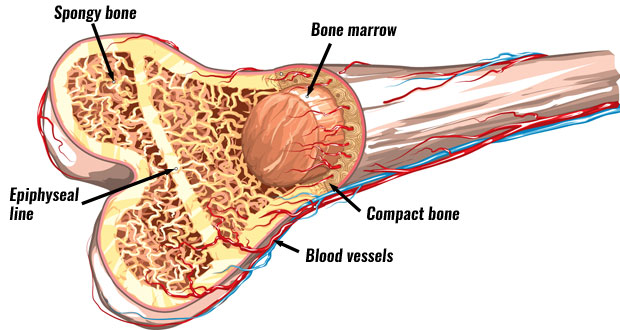
Compact bone - hard, dense outer layer of bones
Protects & strengthens bones
Spongy bone - porous, honeycomb like structure
Also known as cancellous or trabecular bone
Red bone marrow - contains hematopoietic stem cells that produce:
RBCs
WBCs
Platelets
Yellow bone marrow - contain mesenchymal stem cells that produce:
Fat
Cartilage
Bone
Osteoblasts - cells required for bone synthesis & mineralization
Osteocytes - mature osteoblasts
Osteoclasts - cells that breaks down bone tissue
Bone remodeling - old bone is systematically removed and new bone is formed in its place
Resting state - inactive state where no remodeling is happening
Resorption - Osteoclasts create acidic environment to dissolve mineral component of bone
calcium is released during resorption process
Reversal - mononuclear cells appear on surface and is a transition between resorption and formation
Formation - osteoblasts begin to create new osteoid at resorption site to replenish bone
Mineralization - osteoid mineralizes; to restore mechanical strength & support
Chondroblasts - cells that form cartilage
Chondrocytes - mature chondroblasts
Cartilage:
Supports bones
Joint connection
Template for bone placement
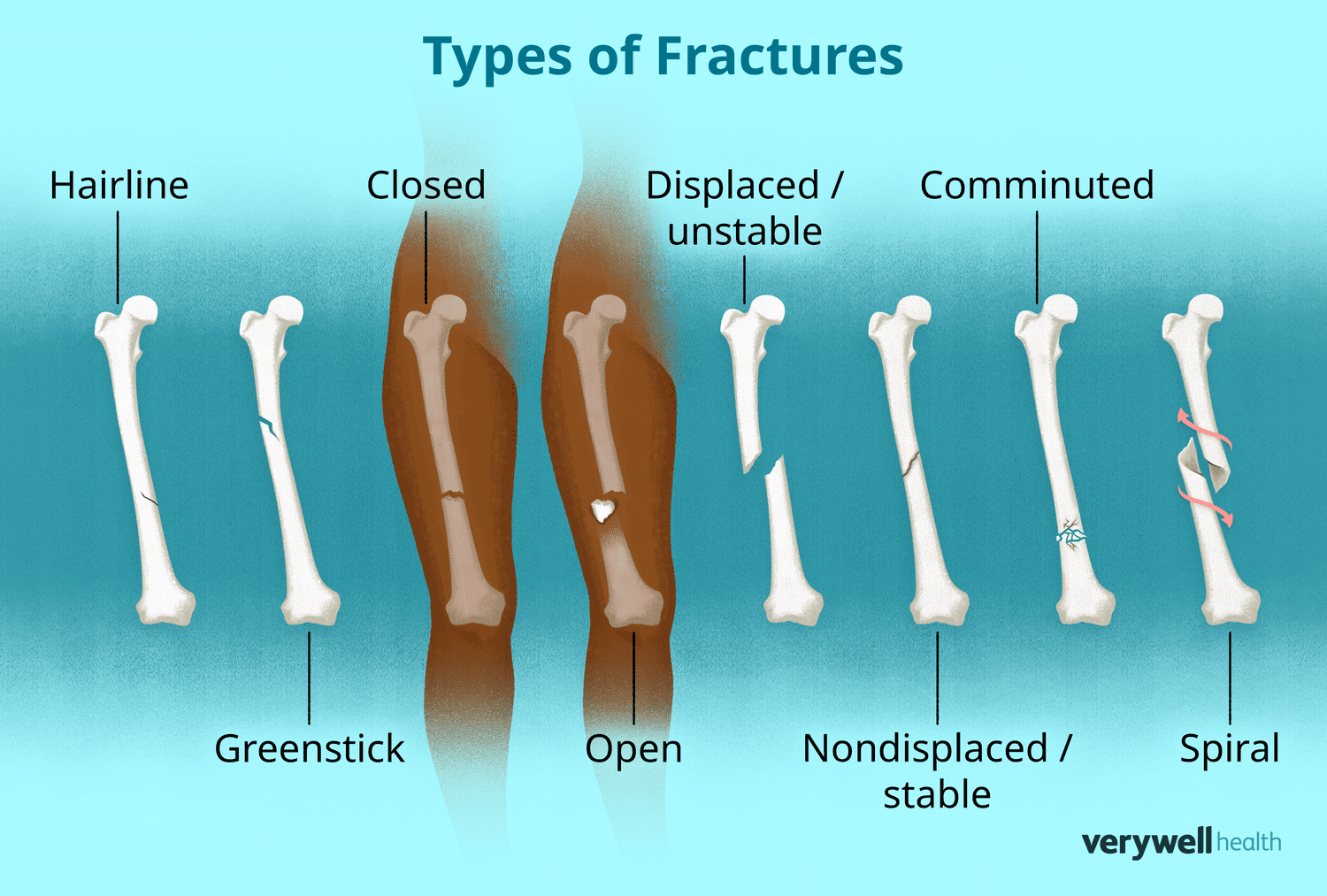
Closed fracture - simple fracture, doesn’t penetrate skin
Open fracture - open/compound fracture, does penetrate skin
Comminuted - Bone shatters into 3 or more pieces
Impacted - Buckle fracture end of bones driven together
Greenstick - Bone bends and cracks; doesn’t break all the way