Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Direction
Basic Definitions
- ==Kinematics==: study of motion without reference to forces
- ==Dynamics==: study on the effects forces have on motion
- ==Mechanics==: branch of physics that studies motion based on both kinematics and dynamics
2.1: Displacement
- To describe motion, you must be able to specify the location of an object.
- In 1D motion, the initial position is referred to as x₀ and the final position is referred to as x.
- ==Displacement== is a vector that accounts for both distance (between initial and final positions) and direction measured in meters (m).
- Δx = x - x₀
- ==Distance== is the total movement of an object without regards to direction.
- Displacement ≠ distance.
- For example, car can drive around in a large circle and stop at its start point.
- Displacement would be 0 m
- Distance would be the circumference of the circle
2.2 Speed and Velocity
Average Speed
- ==Speed== only indicates how fast an object is moving
- Average speed = distance (m) / elapsed time (s)
Average Velocity
- ==Velocity== is a vector that indicates how fast an object is moving and in which direction, measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Doesn’t tell you anything about how fast or in what direction something was moving at a certain instant.
- Average velocity = displacement (m) / time (s)
- vₐᵥ = Δx / Δt
Instantaneous Velocity
==Instantaneous velocity== indicates how fast and which direction an object moves at each instant of time.
==Instantaneous speed== is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity (quantity only)
As time approaches 0, so does displacement. Therefore, the ratio Δx / Δt approaches the instantaneous velocity.
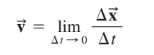
Acceleration
==Acceleration== is a vector of the rate of change of velocity over time measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
- Acceleration points in the same direction as the change in velocity.
Average acceleration is the average rate of change of velocity over time.
- aₐᵥ = Δv / Δt
As time approaches 0, the average acceleration and instantaneous acceleration become equal.
- In many situations, acceleration is actually constant.
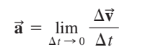
An object ==decelerates== whenever the acceleration and velocity vectors point in opposite directions, causing the object to slow down.
2.4: Equations of Kinematics for Constant Acceleration
Assume x₀ = 0 m when t₀ = 0 s.
| Missing Variable(s) | Equation |
|---|---|
| x | v = v₀ + at |
| a | x =vt = 0.5(v₀ + v)t |
| v | x = v₀t + 0.5at² |
| t | v² + v₀² + 2ax |
2.5: Applications of the Equations of Kinematics (Solving Problems)
Make a drawing.
Decide which directions to be positive and negative relative to a convenient location for the origin.
Neatly list values of the five kinematic variables (x, a, v, v₀, and t) given or implied in the question. At the same time, identify the variable(s) you are being asked to find.
Check to see if you have information about at least three different kinematic variables.
If so, select the appropriate relation from the table above.
If not, solve for a missing variable with other data given in the question.
- Ex: given x, x₀, and t, → find vₐᵥ
If the motion of an object is divided into segments, remember the final velocity of one segment is the initial velocity of the next.
It is possible to have two answers for kinematics problems. Try to visualize the different situations to which the answers correspond.
2.6: Freely Falling Bodies
- ==Free-fall==: idealized motion in which an object falls without encountering air resistance and acceleration is constant.
- Since acceleration is constant, kinematics equations can be used to solve free fall problems.
- Since objects fall vertically, position is referred to as y instead of x.
- This acceleration of of a freely falling body is called the ==acceleration due to gravity== and always points downwards.
- This is why when an object is thrown up, it will eventually stop momentarily and come back down.
- When an object is thrown up, it is still free falling because it is under the influence of gravity alone.
- Near Earth’s surface, g = 9.8 m/s²
- Symmetry of freely falling objects:
- ==Time symmetry==: it takes the same time to go up as down.
- ==Speed symmetry==: an object falling down will be traveling at the same speed as when it went up at a certain height.
2.7: Graphical Analysis of Velocity and Acceleration
- ==Position vs. time==
- Linear graph: slope = velocity
- Parabolic: slope of tangent line = instantaneous velocity
- ==Velocity vs. time==
- Slope = acceleration
- Area under the curve = displacement