Chapter 11: Basic Economics Concepts, Economic Indicators, and the Business Cycle
11.1 The Circular Flow and GDP
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): total value of all final goods and services produced in a year in a country
- Calculated using expenditure approach or income approach
- GDP = aggregate income = aggregate expenditure
- National income (NI): sum of income earned by factors of production of the country’s citizens
- Personal income (PI): income received by a household before personal income taxes
- Disposable income (DI): personal income - personal income taxes
- Depreciation: decline in value of capital over time
- Due to wear or obsolescence
11.2 Unemployment
- Labor force: includes employed and unemployed adults
- Unemployed must be able to willing to work, and made an effort to find work in past 4 weeks
- Labor force participation rate: number of people in labor force divided by working-age population
- Discouraged workers: people who are able and willing to work but stop trying to find work due to frustrations
- Full employment: level of unemployment that corresponds with natural rate of unemployment
- Okun’s Law: for every 1% increase in unemployment rate above natural rate, output falls 2-3%
11.3 Price Indices and Inflation
- Inflation: sustained increase in overall price level
- Deflation: sustained decrease in overall price level
- Nominal salary: actual number of dollars a person earns
- Real salary: purchasing power of dollars
11.4 Real vs Nominal GDP
Consumer Price Index (CPI): government’s gauge of inflation
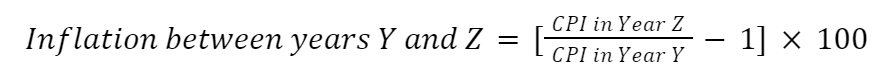
Producer Price Index (PPI): measures changes in prices of wholesale goods
- Ex) Lumber, steel
Gross Domestic Product Deflator: alternative general price index that reflects importance of products in current market baskets
11.5 Business Cycles
- Business cycle: repeating fluctuation of financial and economic activity
- Occurs nonperiodically during certain period of time
- Say’s Law: supply creates its own demand