Chemistry
define an element
a substance that consists of only one type of atom
5 elements and their uses
carbon - used in pencils
oxygen - in breathing equipment
tin - coating in a food can
chlorine - in swimming pool water
mercury - used in some thermometers
properties of metals
- most are solids (except mercury)
- hard and dense
- shiny when freshly cut (lustrous)
- can be hammered into sheets (malleable)
- can be drawn into wires (ductile)
- makes a ‘bell’-like sound when struck (sonorous)
- are good conductors of heat and electricity
properties of non-metals
- some are solids, some are gases, one is liquid (bromine)
- most are softer than metals (exception is diamonds as they are a form of carbon)
- most are dull
- solids are easily broken when you attempt to change their shape
- not sonorous
- poor conductors of electricity and heat
where are metals on the periodic table?
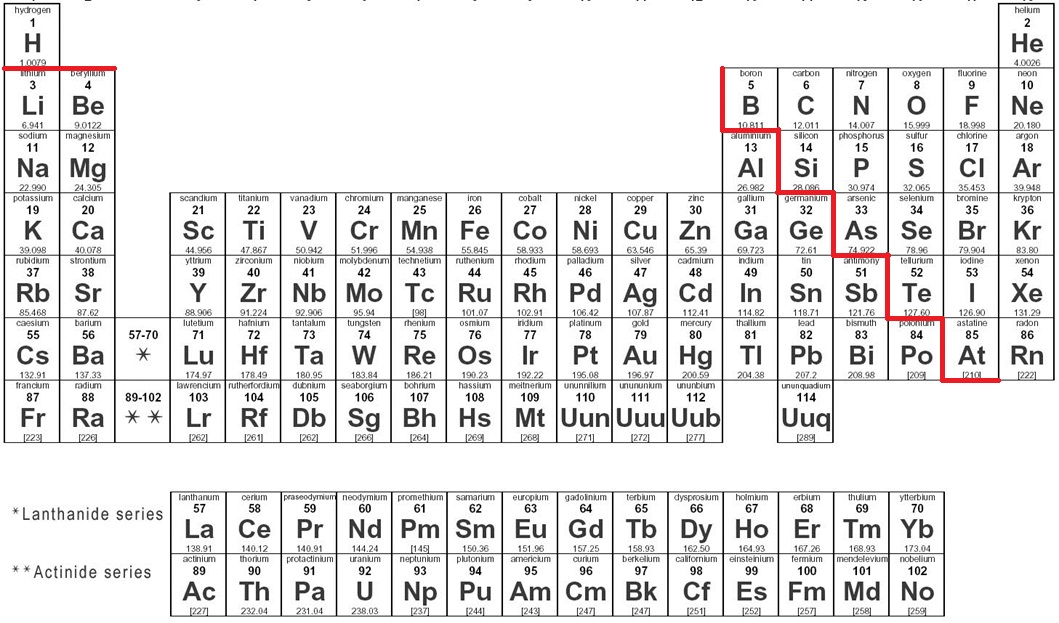
all metals are to the left of the staircase
all non-metals are the right of the staircase
apparatus and chemicals to prepare hydrogen
chemicals
- dilute sulfuric acid
- zinc
apparatus
- boiling tube
- test tube rack
- lit splint
test for hydrogen
if you put a lit splint into the gas and it makes a squeaky pop then the gas is hydrogen
bar charts
- equally spaced out and equal bars#
- title and axis labels (also goo y axis spread)
- title starts with “A bar chart to show…”
compound
compound - a substance that contains two or more element chemically joined
molecule
molecule - particle which consists of two or more atoms chemically joined
reaction of iron and sulfur
a red glow spreads through the mixture and a grey/black solid forms (chemical reaction)
chemical change
- permanent colour change
- fizzing or sign of new gas
- heat or light produced
- solid form in a mixture of two solutions
physical change
- change in state (solid, liquid, gas)
- can be separated again
- easily reversed
properties of compounds ≠ properties of elements within
sodium chlorine (common salt) → sodium (very reactive silver metal) + chlorine (poisonous green gas)
water → hydrogen (colourless gas that pops when burned) + oxygen (colourless gas that supports burning)
carbon dioxide → carbon (black solid) + oxygen (colourless gas that supporting burning)
word equations
non-metal changes ending to ‘ide’
mixtures
behaves the same way as substances present behave
no chemical reaction
can be made in any proportion
compounds
has new properties
chemical change
made in fixed proportions
when do you use a sieve?
when separating mixtures such as sand and gravel since the sand will pass through but the gravel will not
how to separate sand and salt
- grind mixture
- pour in boiling water
- put the solution through a filter funnel with filter paper
- leave filtrate to evaporate
chromatography
chromatography - technique for separation of mixture into its components
why do we need to recycle?
to save finite resources and finite elements
when do you use filtration?
when trying to remove a solid from a solution