Chapter 7 - Quantum, Atomic, and Nuclear Physics
Basics
- Einstein’s postulates of special relativity
- All laws of physics remain the same in a uniformly moving frame of reference
- The speed of light in a vacuum is always 3 x 10^8 no matter the motion of the source of light or the observer
- Summary: time and distance are relative according to your frame of reference
- ==E = mc^2==
- Mass is a solid form of energy and can be converted into energy and vice versa
- Big 4 subatomic particles
- Proton (p)
- Mass = 1.67 x 10^-27 kg = 1 amu
- Charge: positive
- Electron (e)
- Mass = 9.11 x 10^-31 kg
- Charge: negative
- Neutron (n)
- Mass = 1.67 x 10^-27 kg = 1 amu
- Charge: 0
- Photon (ɣ)
- Mass = 0
- Charge: 0
- Electron-Volts (eV)
- Electron-Volt: a unit of energy - the amount of energy needed to change the potential of an electron by 1 volt
- ==1 eV = 1.6 x 10^-17 J==
- Photons
- Light is made of photons
- ==E = hf = hc/λ==
- E: energy of a photon
- h: Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10^-34 Js = 4.14 x 10^-15 eVs
- f: frequency (Hz)
- c: speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s)
- λ: wavelength (m)
Photoelectric Effect
- Applications: solar panels, photosynthesis, tanning, photographic film
- Photoelectric effect: when incident light is shined on a metal, electrons detach
- ==K(max) = hf - ɸ==
- K(max): max kinetic energy of the emitted electron
- h: Planck’s constant
- f: frequency
- hf: energy of the incident photon
- ɸ: work function - the energy required to remove an electron from a specific element/material
- When the frequency of incident light increases, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron increases linearly
- Threshold frequency: minimum frequency for electron emission
- Photon Momentum
- When a photon collides with an atom and the atom emits an electron, momentum and energy are conserved
- ==p = h/λ = E/c==
DeBroglie Wavelength
- If a particle has a shorter wavelength, it behaves more like a particle
- If a particle has a longer wavelength, it behaves more like a wave
- To find the wavelength for a particle (de Broglie’s wavelength), use ==λ = h/p = h/mv==
- λ: de Broglie’s wavelength
- p: momentum of particle
- Particles have a wave function representing the probability of finding the particle at a specific location
- Ѱ: wave function
- Ѱ = 0: no probability of finding the graph
Energy Levels in an atom
- For an electron to move from one energy level to another, it will either have to absorb or emit energy in the form of a photon
- The nucleus of an atom is positive and electrons are negative so it takes energy to pull the electron away from the nucleus by overcoming their attractive force
- Electrons take less energy if they’re in a higher energy level
- Key points
- n1 is called the ground state - the lowest possible energy level for the electron
- Moving from lower to higher energy levels tells you the atom absorbed a photon
- Moving from higher to lower energy levels tells you the atom emitted a photon
- There are no intermediate levels between energy levels
- ==E (photon) = E (final) - E (initial)==
- If there is extra energy after jumping from one energy level to another, that energy is converted to kinetic energy of the emitted electron
Nuclear Decay
Particles involved with nuclear decay:
- Alpha particle (𝞪): two protons and two neutrons together (helium nucleus)
- Beta particle (β): either an electron or positron
- Gamma particle (Ɣ): a gamma ray photon - massless and chargeless
Isotopes - same atomic number of an element but different mass numbers
- Notation for Isotopes: element symbol with two small numbers to the left (one on top of the other)
- Top number on the left side of the symbol: mass number = neutron # + proton #
- Bottom number on the left side of the symbol: # of protons in the nucleus = atomic number
Alpha (𝞪) decay: a Helium nucleus is emitted from the original isotope
Beta (β) decay: either a positron or electron is emitted
- β+ (also symbolized as e+): positron - +1 charge with negligible mass
- β- (also symbolized as e-): electron - -1 charge with negligible mass
Gamma (Ɣ) decay: massless and chargeless photon
- The photon carries away some energy and momentum so the nucleus recoils
Neutron decay: a neutron is emitted
Mass defect: the slight difference in mass between the total mass present before the decay and after the decay
- This difference in mass is destroyed and converted into kinetic energy
- ==E = Δmc^2==
- Δm: mass defect
- c: speed of light
- E: energy produced
- ==1 u = 931 MeV/c^2==
- The mass defect may become the nuclear binding energy and will be equal to the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleus together
Half-life: the time it takes for a radioactive isotope to decay half its original amount
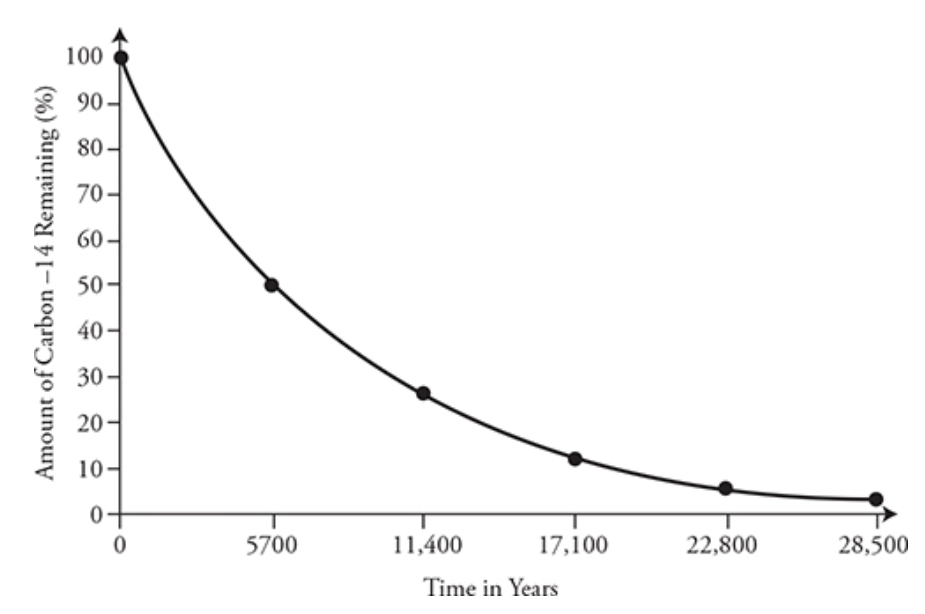
- Longer half life → slow decay rate
Fission reactions: when a heavy nucleus is split into two chunks
- Begun by shooting a neutron into the nucleus
- Nuclear power plants and weapons
Fusion reactions: when two light nuclei combine to make a heavier and stable nucleus
Induced Reaction: scientists bombard a nucleus with high-speed particles to induce the emittance of a proton
Antimatter: every normal particle has an antimatter to match it (electron and positron)
- When matter and antimatter meet, they annihilate each other
- Ex: electron and positron can turn into photon energy
- ==E (electron) + E(positron) = (2m)c^2 = hf==
- m: mass of electron
- c: speed of light
- h: Planck’s constant
- f: frequency