Chapter 2 (Campbell's Biology in Focus)
Concept 2.1
Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass
An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
A compound is a substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio
Essential elements are natural elements that an organism needs to live a healthy life and reproduce
Trace elements are required by an organism in only minute quantities
Subatomic Particles
The three main parts of an atom are
neutrons
protons
electrons
The unit of measurement for atoms and subatomic particles is a dalton
Different atomic forms of the same element are called isotopes
A radioactive isotope is one in which the nucleus decays spontaneously giving particles and energy
Potential energy is the energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure
Electrons Distribution and Chemical Properties
electrons are found in different electron shells
The chemical behaviour of an atom depends mostly on the number of electrons in its outermost shell
These electrons are called valence electrons and are found in the valence shell
The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms
Attractions between atoms are called chemical bonds
A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms
Two or more atoms held together by covalent bond constitute a molecule
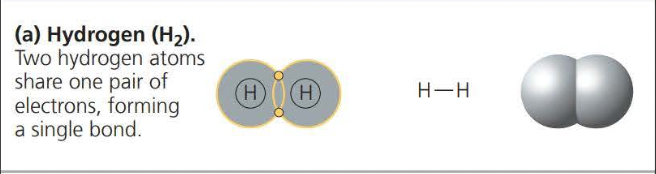
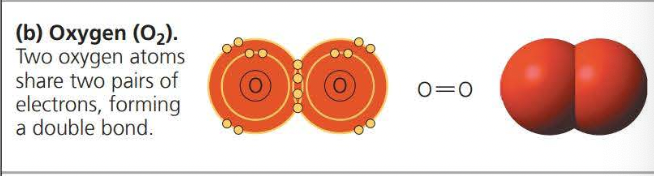
The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond is called its electronegativity
A nonpolar covalent bond is when electrons are shared equally because two atoms have the same electronegativity
A polar covalent bond is when an atom is bonded to a more electronegative atom, the electrons will therefore not share equally
Ionic Bonds
Two resulting oppositely charged are called ions
Positively charged results in a cation
Negatively charged results in an anion
A hydrogen bond is formed when there is a noncovalent attraction between hydrogen and an electronegative atom
Van Der Waals interactions occur when atoms get just close enough that a few electrons in their valence shell (electron cloud) touch
Chemical reactions make and break chemical bonds
The making and breaking of chemical bonds leading to changes in the composition of matter are called chemical reactions
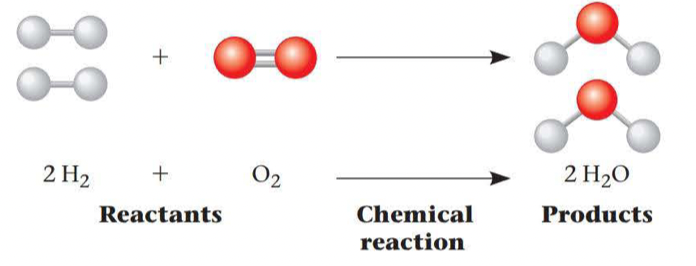
The point at which the reactions offset one another exactly is called chemical equilibrium
The unequal sharing of electrons and water’s V-like shape make it a polar molecule.
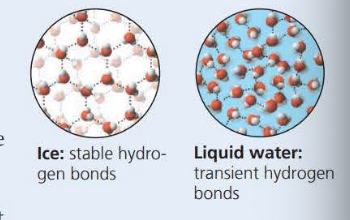
The phenomenon of the cohesion of water molecules is due to hydrogen bonds
Adhesion is the clinging of one substance to another
Surface tension is a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
Anything that moves has kinetic energy
The specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1C
The heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state
Evaporative cooling occurs because the hottest molecules, (those with the greatest kinetic energy) are the ones most likely to leave as a gas
Water: The Solvent of Life
A solution is a liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
A solvent is the dissolving agent of a solution
The solute is the dissolving agent of a solution
An aqueous solution is one in which the solute is dissolved in water, water is the solvent
A hydration shell is formed when there’s a sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion
Any substance that has an affinity for water is said to be hydrophilic
Substances that are nonionic and nonpolar are hydrophobic
Molarity is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
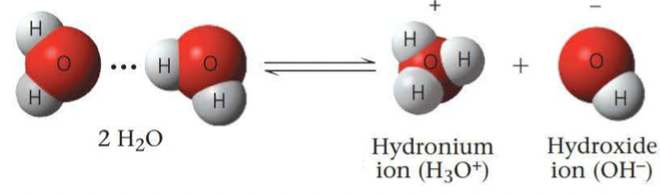
An acid is a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called a base
Properties of water:
Anomalous expansion of water
High specific heat capacity (evaporative cooling and heat of vaporization)
Hydrogen bonds (pattern when it freezes)
Its versatility of it as a solvent because of the polar molecules
Cohesion (surface tension)
 Knowt
Knowt
