Review Sheet: Barron's AP Environmental Science 2023
Chapter 1: Ecosystems
- Ecosystem: Community of living organisms interacting with non-living components.
- Organisms: A living thing that can function on its own.
- Species: Organisms that resemble each other
- Population: Same species occupying a specific area.
- Community: Population of different species.
- Symbiosis: Any type of close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms of the same or different species.
- Amensalism: One species suffers, other is not affeced.
- Commensalism: One species benefits, and the other isn’t.
- Competition: Rivalry of species over same resources.
- Mutualism: Both species benefit.
- Parasitism: One species benefits and the other is harmed.
- Predation: Predator kills and eat their prey.
- Saprottrophism: Organism that feeds on nonliving organic matter.
- Resource Partitioning
- Morphological partitioning: Two species shares same resources; evolved slightly different structures.
- Spatial partitioning: Species use same resource occupying different areas.
- Temporal partitioning: Two species eliminate direct competition; utilizing same resource at diffrent times.
- Terrestrial Biomes
- Deserts: An area that receives no more than 25 centimeters of rainfall a year.
- Forests: Area with large number of trees.
- Tropical Rainforests: Occurs in tropical areas of heavy rainfalls.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests: Occurs in association of seasonally wet and dry or monsoon climates.
- Temperate Coniferous Forests: Occurs in low levels of precipitation.
- Taiga: A forest of the cold, subarctic region.
- Southern Taiga: Also known as boreal forest.
- Northern Taiga: Approaches tree line and tundra biome.
- Grasslands: Lands dominated by grasses.
- Savannas: A grassy plain with scattered individual trees.
- Temperate Grasslands: Grasses are dominant vegetation, trees and shrubs are absent.
- Tundra: A flat, treeless, Arctic region.
- Arctic tundra: Circles North Pole extending South to the Taiga; cold, dry, desert-like.
- Alpine tundra: Located in mountains where trees cannot grow.
- Aquatic Biomes
- Antarctic: Cold, remote area in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Oceans (Marines)
- Ocean Zones
- Littoral Zone (Intertidal): Closest to the shore.
- Neretic Zone (Sublittoral): Extends to the edge of continental shelf.
- Photic Zone: Uppermost layer of water.
- Corals: Marine invertebrates that typically live in compact colonies.
- Fringing Reefs: Grow near the coastline.
- Barrier Reefs: Similar to the coastline but separated by deeper lagoons.
- Attols: Rings of coral that create protected lagoons; found in the middle of the sea.
- Lakes: Formed where precipitation or runoffs fills depressions in Earth’s surface.
- Lake Zones
- Benthic Zone: Bottom of the Lake.
- Limnetic Zone: Well lit, open surface water.
- Littoral Zone: Close to the shore that extends to depth penetrated by sunlight.
- Profundal Zone: No light regions.
- Types of Lakes
- Oligotrophic: Young Lake; deep cold; nutrient poor.
- Mesotrophic: Middle-Aged Lake; moderate nutrient content.
- Eutrophic: Old lake; shallow, warm, large surface area.
- Rivers and Streams
- River Zones
- Source Zones: Headwater streams; often begins as springs or snowmelt
- Transition Zone: Slower, warmer, wider, and lower-elevation moving streams
- Floodplain Zone: Result of large amounts of sediment and nutrients
- Riparian Areas: Lands adjacent to creeks, lakes, rivers, and streams that support vegetation
\
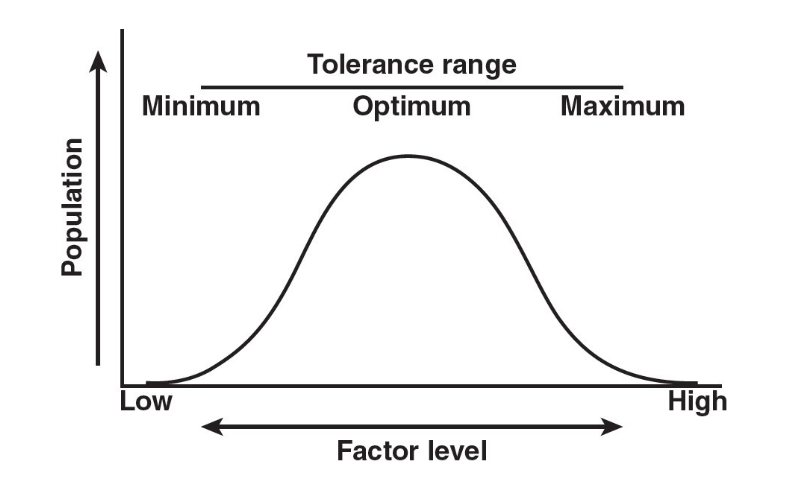
Law of Tolerance: It states that the existence, abundance, and distribution of species depend on the tolerance level of each species to both physical and chemical factors.
Limiting Factor: Any abiotic factor that limits or prevents the growth of a population.
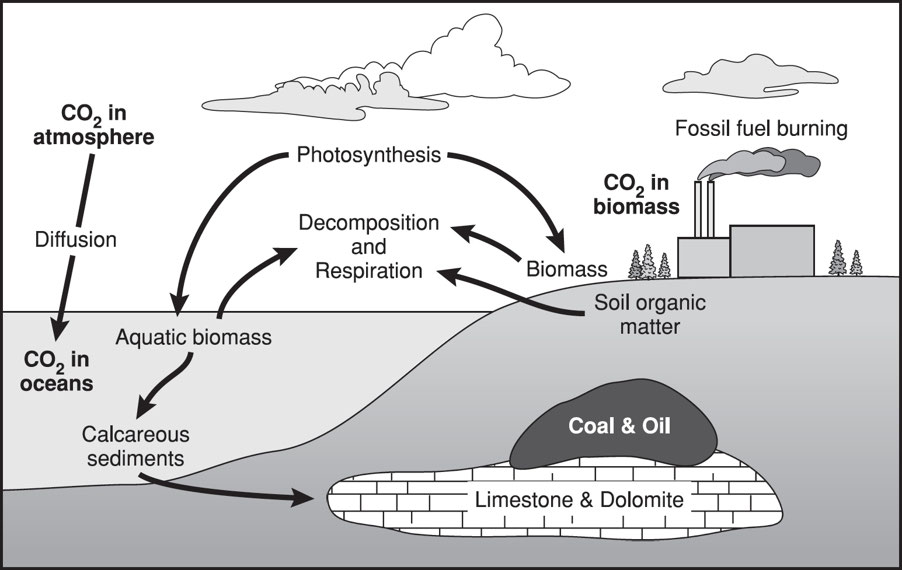
Carbon Cycle: The process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.
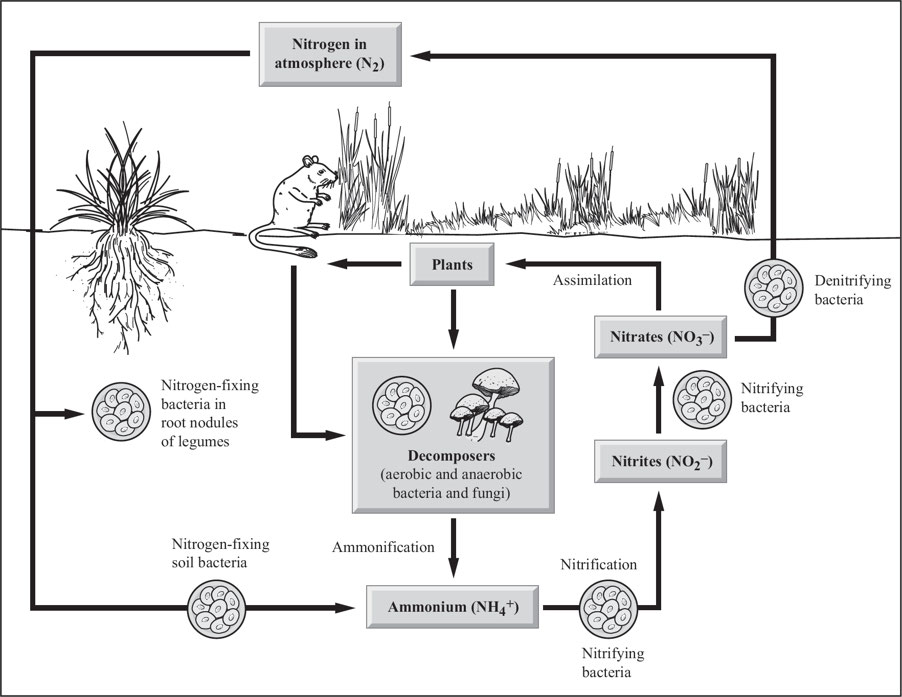
Nitrogen Cycle: A process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere.
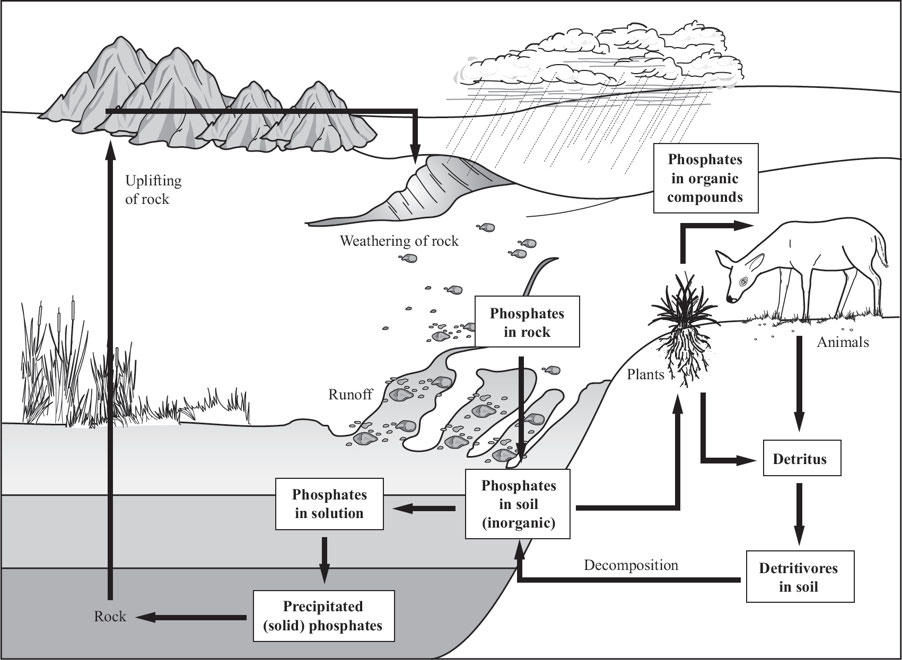
Phosphorous Cycle: A cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Hydrologic Cycle: It involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-Atmosphere.
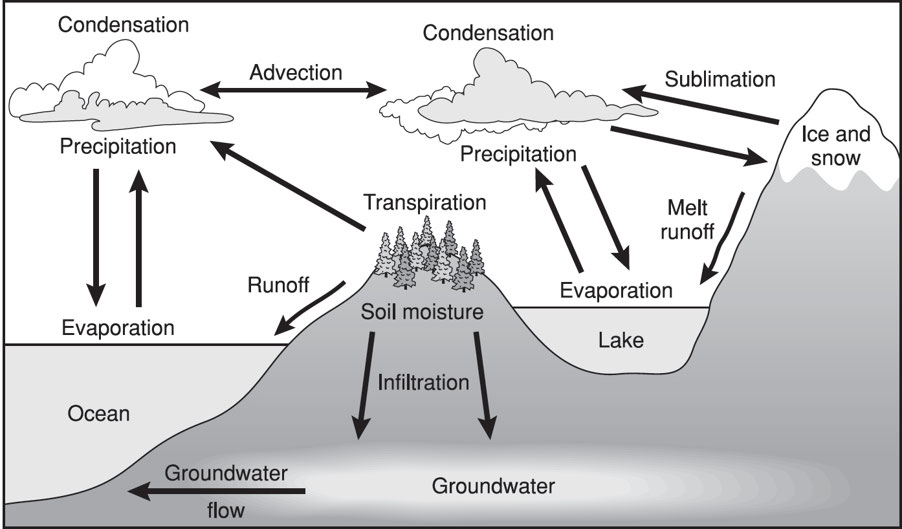
Aquifer: Contains water in quantities sufficient to support a well or spring.
- Recharge zone: The surface area above an aquifer that supplies water to the aquifer
- Unsaturated zone: The zone immediately below the land surface.
- Water table: The level below which the ground is saturated with water
Pyramids
- Biomass pyramid: It shows how much organic mass is within each trophic level.
- Energy Pyramids: These show the proportion of energy passed from one trophic level to the next-level consumers in an ecosystem
Photosynthesis
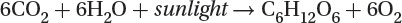
Cellular respiration
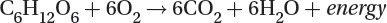
Gross primary production (GPP): The rate at which plants capture and fix a given amount of chemical energy as biomass in a given length of time.
Net primary production (NPP): The remaining fixed energy is the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy.
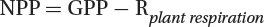
Chapter 2: Biodiversity
- Biodiversity: Variability among species, between species, and of ecosystems.
- Genetic diversity: Range of all genetic traits.
- Species diversity: Number of different species in a specific area.
- Ecosystem diversity: Range of habitats in specific area.
- Species
- Generalists: Live in different types of environments and have varied diets.
- Specialists: Require unique resources and have limited diets.
- Pioneer: Earlier successional plants; generalists.
- Keystone: Their presence contributes to the diversity of life; their extinction could lead to the extinction of other life forms.
- Indicator: Their presence, absence, or abundance reflects a specific environmental condition
- Ecosystem Services
- Cultural Benefits: Supports recreational services.
- Provisioning Benefits: Provides diversity of products.
- Regulating Benefits: Provided that help moderate natural phenomena
- Supporting Benefits: Provides more aid to the ecosystem.
- Island Biogeography: It examines the factors that affect the richness and diversity of species living in these isolated natural communities.
- Island: A suitable habitat for a specific ecosystem that is surrounded by a large area of unsuitable habitat.
- Theory of Island Biogeography: It proposes that the number of species found on an “island” is determined by immigration and extinction of isolated populations.
- Adaptations
- Behavioral Adaptation: Instincts, mating behavior, vocalizations.
- Physiological Adaptation: Methods of temperature control or how food are digested.
- Structural Adaptation: Physical features.
- Short Term Adaptations: Develops from environment’s temporary changes.
- Long-term Adaptations: Develops over long period’s of time in response to natural selection.
- Ecological Succession
- Facilitation: Species modifies the environment, meeting the needs of others.
- Inhibition: Species modifies the environment, not suitable for the environment.
- Tolerance: Species are not affected by the presence of others.
- Primary Succession: Species first colonize a lifeless habitat.
- Secondary Succession: Species recolonize a destroyed habitat.
- Earth system processes operate on a range of scales
- Episodic Process: Occurring occasionally and at irregular intervals.
- Periodic Process: Occurring at repeated intervals.
- Random Process: Lacking a regular pattern.
Chapter 3: Populations
Species
- Generalists: Able to use a variety of environmental resources
- Specialists: Use specific set of resources
- K-Selected: Not endangered
- R-Selected: Most endagered
Carrying capacity (K): It refers to the number of individuals that can be supported sustainably in a given area.
Survivorship Curve Table
- Type I: Late Loss
- Type II: Constant Loss
- Type III: Early Loss
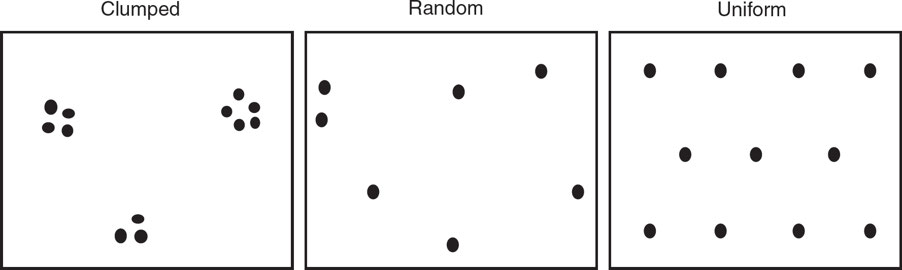
Population Dispersal Patterns
- Clumped: Some areas within a habitat are dense with organisms, while other areas contain few members.
- Random: Occurs in habitats where environmental conditions and resources are consistent.
- Uniform: Space is maximized between individuals to minimize competition.
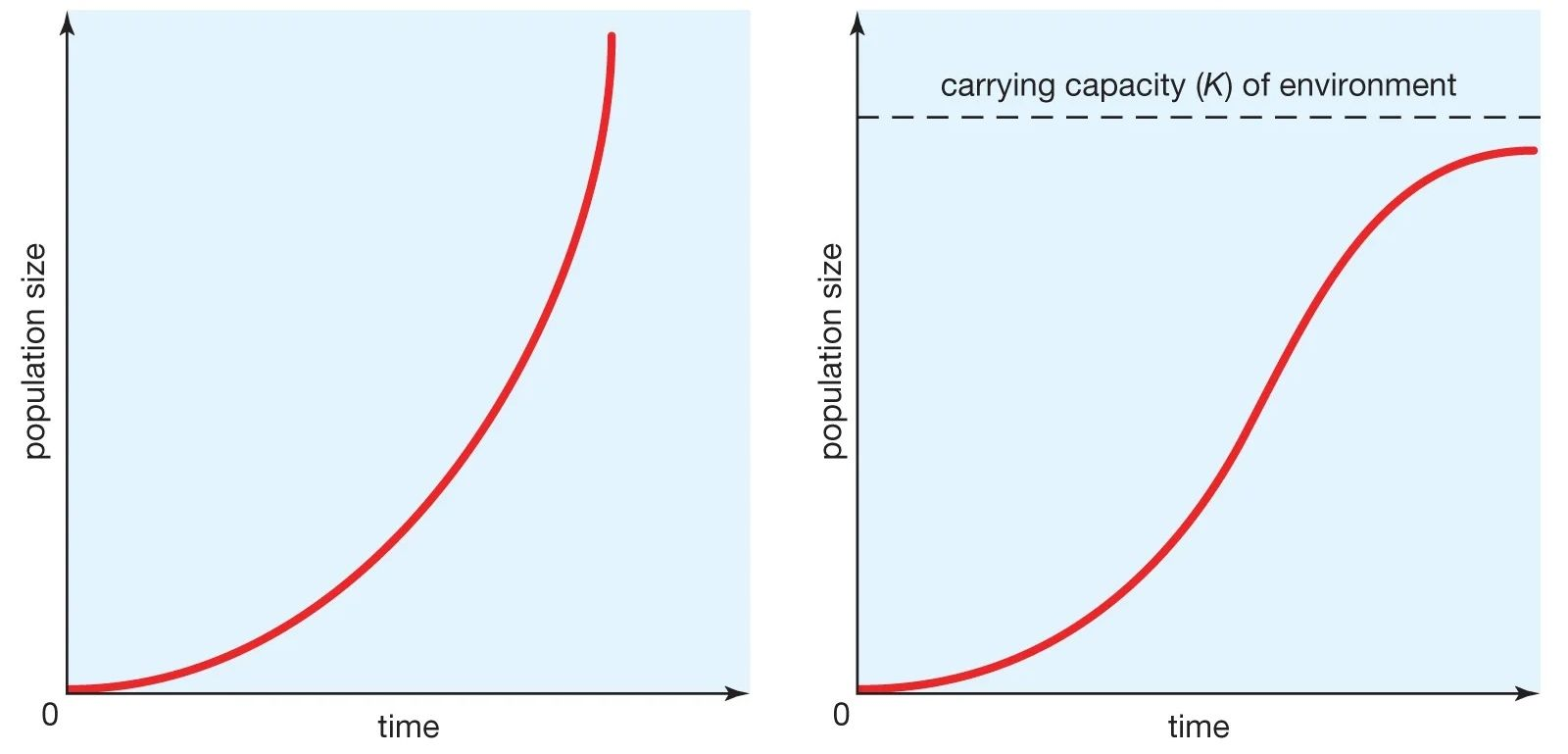
Curves
J-Curve: It occurs when an organism's population density grows exponentially or logarithmically in a new habitat, but then ceases abruptly due to environmental resistance or another issue.
S-Curve: It occurs when, in a new environment, the population density of an organism initially increases slowly but then stabilizes due to the finite amount of resources available.
Feedback Loops
- Positive Feedback: Change in a given direction causes additional change in the same direction.
- Negative Feedback: Change in a given direction causes change in the opposite direction.
Biotic potential: The maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimum environmental conditions.
- Environmental Resistance: Any factor that inhibits an increase in the number of organisms in the population.
Rule of 70: It helps to explain the time periods involved in exponential population growth occurring at a constant rate.
\
Important Population Formulas
Birth Rate (%) = [(total births/total population)] × 100
Crude Birth Rate (CBR) = [(b ÷ p) × 1,000]
Death Rate (%) = [(total deaths/total population)]× 100
Crude Death Rate (CDR) = [(d ÷ p) × 1,000]
Doubling Time = 70/% growth rate
Emigration = number leaving a population
Global Population Growth Rate (%) = [(CBR – CDR)]/10
Immigration = number entering a population
National Population Growth Rate (%) = [(CBR + immigration) – (CDR + emigration)]/10
Percent Rate of Change = [(new # - old #)/old #] × 100
Population Density = total population size/total area
Population Growth Rate (%) =
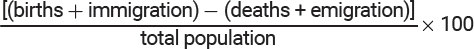
Age-Structure Diagrams
- Pyramid-shaped age-structure diagram: These are determined by birth rate, generation time, death rate, and sex ratios.
- Bell shape age-structure diagram: It indicates that the population has high birth rates and the majority of the population is in the reproductive age group
- Urn-Shaped age-structure diagram: It indicates that the post-reproductive group is largest and the pre-reproductive group is smallest, a result of the birth rate’s falling below the death rate, and is characteristic of declining populations
\
- Demographic Transition
- Stage 1: Pre-Industrial (High Stationary)
- Stage 2: Transitional (Early Expanding)
- Stage 3: Industrial (Late Expanding)
- Stage 4: Post-Industrial (Low Stationary)
- Stage 5: Sub-Replacement Fertility (Declining)
Chapter 4: Earth Systems and Resources
Plate Tectonics
- Plate Tectonic Theory: States that Earth’s lithosphere is divided into a small number of plates that float on and travel independently over the mantle.
- Continental Drift Theory: States that all present-day continents originally formed one landmass called Pangaea.
- Seafloor Spreading Theory: States that tectonic plates split apart from each other.
Types of Boundaries
- Convergent Boundaries: Two plates slides towards each other.
- Divergent Boundaries: Two plates slide apart from each other.
- Transform Boundaries: Two plates slide past each other in different directions.
Soil Profile
- Surface litter: Leaves and partially decomposed organic debris.
- Topsoil: Organic matter, living organisms, and inorganic materials
- Zone of leaching: Dissolved and suspended materials move downward.
- Subsoil: Tends to be yellowish in color
- Weathered parent material: Partially broken-down inorganic materials.
Soil Erosion: Movement of weathered rock and/or soil components from one place to another caused by flowing water, wind, and human activity.
- Landslides: These occur when masses of rock, earth, or debris move down a slope.
- Mudslides: It is also known as debris flows or mudflows, are a common type of fast-moving landslide that tends to flow in channels.
Rock types
- Igneous rocks: These are formed by cooling and classified by their silica content.
- Intrusive: Solidify deep underground, cool slowly, and have a large-grained texture.
- Extrusive: Solidify on or near the surface, cool quickly, and have a fine-grained smooth texture.
- Metamorphic rocks: These are formed by intense heat and pressure, high quartz content.
- Sedimentary rocks: These are formed by the piling and cementing of various materials over time in low-lying areas.
Soils: These are a thin layer on top of most of Earth’s land surface.
Soil Components
- Gravel: Coarse particles.
- Sand: Sedimentary material coarser than silt.
- Loam: Holds water but does not become waterlogged.
- Silt: Sedimentary material consisting of very fine particles between the sizes of sand and clay.
- Clay: Very fine particles.
Components of Soil Quality
- Aeration: Refers to how well a soil is able to absorb oxygen, water, and nutrients.
- Degree of Soil Compaction: It is measured by dry unit weight and depends on the water content and compaction effort.
- Nutrient-Holding Capacity: The ability of soil to absorb and retain nutrients so they will be available to the roots of plants.
- Permeability: The measure of the capacity of the soil to allow water and oxygen to pass through it.
- pH: It is the measure of how acidic or basic soil is.
- Pore Size: Describes the space between soil particles.
- Size of soil and particles: It determines the amount of moisture, nutrients, and oxygen that the soil can hold along with the capacity for water to infiltrate.
- Water holding capacity: It is controlled primarily by the soil texture and the soil organic matter content.
Atmosphere’s Current Composition
- Nitrogen: Fundamental nutrient for living organisms.
- Oxygen: Most abundant element by mass in Earth’s crust, making up almost half of the crust’s mass as silicates.
- Water Vapor: Largest amounts are found near the equator, over oceans, and in tropical regions.
- Carbon Dioxide: Produced during cellular respiration, the combustion of fossil fuels, and the decay of organic matter.
Atmosphere Structure
- Troposphere: The lowest portion of Earth’s atmosphere, 0–6 miles (0–10 km) above Earth’s surface.
- Ozone Layer: Absorbs high-energy ultraviolet radiation from the sun and is broken down into atomic oxygen (O) and diatomic oxygen.
- Stratosphere: It is located 6–30 miles (10–50 km) above Earth’s surface.
Weather: It is caused by the movement or transfer of heat energy, which results from the unequal heating of Earth’s surface by the sun.
Climate: The average weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period.
Breezes
Land Breeze: It occurs during relatively calm, clear nights when the land cools down faster than the sea, resulting in the air above the land becoming denser than the air over the sea.
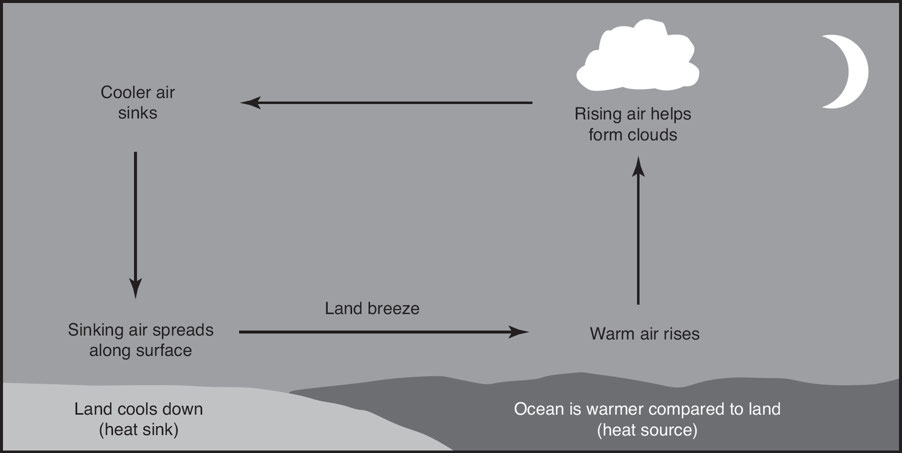
Sea Breeze: It occurs during relatively calm, sunny days, the land warms up faster than the sea, causing the air above it to become less dense.
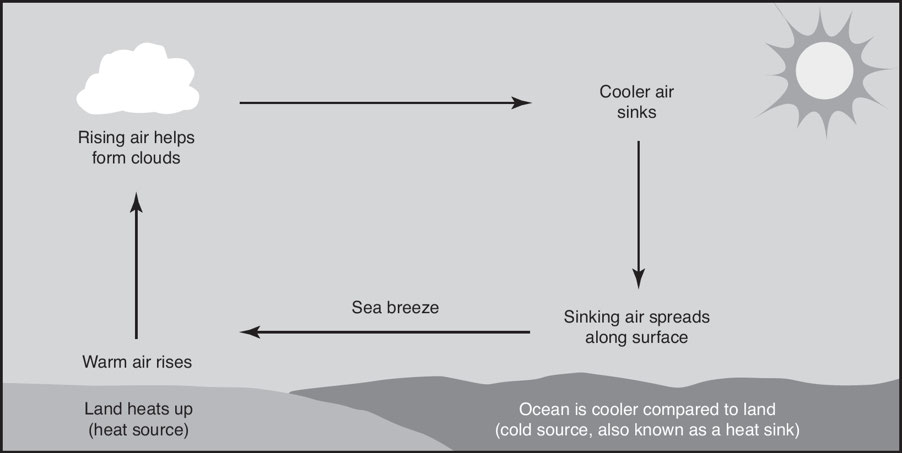
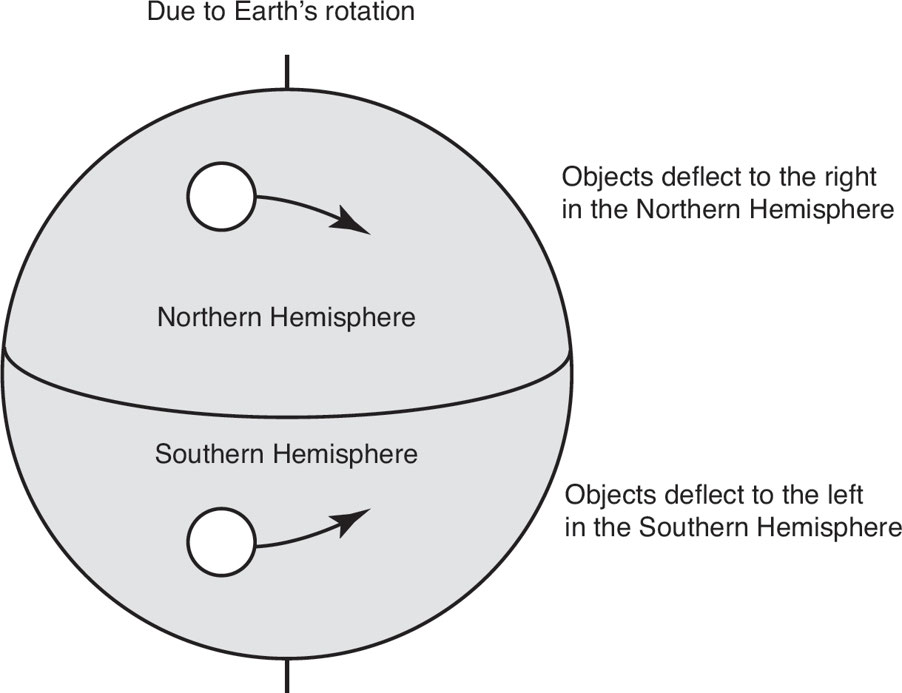
Coriolis Effect: A phenomenon wherein earth’s rotation on its axis causes winds to not travel straight, which causes prevailing winds in the Northern Hemisphere to spiral clockwise out from high-pressure areas and spiral counterclockwise toward low-pressure areas.
Circulation Cells
Hadley Air Circulation: Low latitude overturning circulations that have air rising at the equator and air sinking at roughly 30° latitude.
Ferrel Air Circulation Cells: Air flows poleward and eastward near the surface and equatorward and westward at higher levels.
Polar Air Circulation Cells: Smallest and weakest cells which extend from between 60 and 70 degrees north and south, to the poles.
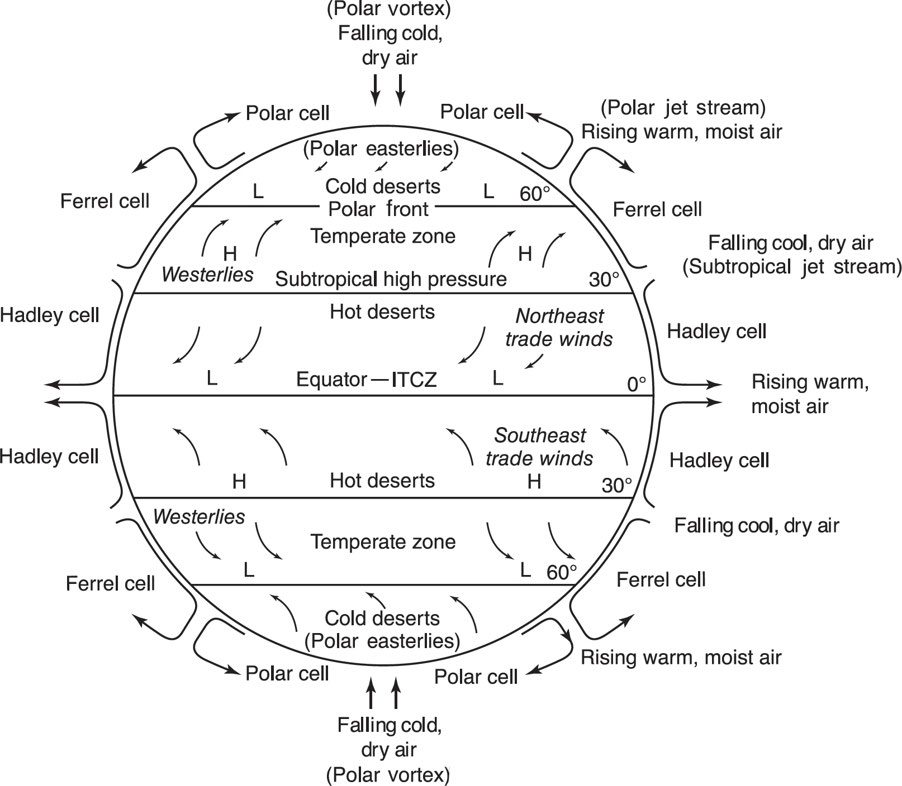
Polar Vortex: A low-pressure zone embedded in a large mass of very cold air that lies atop both poles.
Storms
- Hurricanes: Term used in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific.
- Cyclones: Term used in South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
- Typhoons: Term used in Northwest Pacific.
- Storm Surge: A rise in sea level that occurs during tropical cyclones, typhoons, or hurricanes.
Tornadoes: These are swirling masses of air with wind speeds close to 300 miles per hour (485 kph).
Monsoons: These are strong, often violent winds that change direction with the season.
Watershed: A land area that drains rainfall and snowmelt into a lake, ocean, or aquifer.
Mountain ranges: These are barriers to the smooth movement of air currents across continents.
- Rain Shadow Effect: The drier situation which is directly responsible for the plants that grow there, which in turn affects the animals that live there.
El Niño: Above-average sea-surface temperatures that periodically develop across the east-central equatorial Pacific.
La Niña: Periodic cooling of sea-surface temperatures across the east-central equatorial Pacific.
Chapter 5: Land and Water Use
- Clear-cutting: It occurs is when all of the trees in an area are cut at the same time.
- Edge Effect: It refers to how the local environment changes along some type of boundary or edge.
- Forest edges: Created when trees are harvested, particularly when they are clear-cut.
- Tree canopies: Provide the ground below with shade and maintain a cooler and moister environment below.
- Deforestation: It is the conversion of forested areas to non-forested areas
- Agricultural Practices
- Desertification: It is the conversion of marginal rangeland or cropland to a more desert-like land type.
- Overgrazing: Excessive grazing of grasslands.
- Fertilizers: It provide plants with the nutrients needed to grow healthy and strong.
- Inorganic Fertilizers: Mined from mineral deposits or manufactured from synthetic compounds.
- Organic Fertilizers: Originates from an organic source, such as bone meal, compost, fish extracts, manure, or seaweed.
- Slash-and-Burn Agriculture: Method of growing food or clearing land in which wild or forested land is clear-cut and any remaining vegetation is burned.
- Genetically modified foods: Foods produced from organisms that have had changes introduced into their DNA.
- Soil degradation: Decline in soil condition caused by its improper use or poor management.
- Tillage: Surface is plowed and broken up to expose the soil
- Irrigation Methods
- Ditch: Dug and seedlings are planted in rows.
- Drip: Water is delivered at the root zone of a plant through small tubes that drip water at a measured rate.
- Flood: Water is pumped or brought to the fields and is allowed to flow along the ground among the crops.
- Furrow: Small parallel channels are dug along the field length in the direction of the predominant slope.
- Spray: Uses overhead sprinklers, sprays or guns to spray water onto crops.
- Types of Pesticides
- Biological Pesticides: Living organisms used to control pests.
- Carbamates: Also known as urethanes
- Fumigants: Used to sterilize soil and prevent pest infestation of stored grain.
- Inorganic pesticides: broad-based pesticides; highly toxic.
- Organic pesticides: natural poisons derived from plants
- Organophosphates: extremely toxic but remain in the environment for only a brief time.
- POPs: Organic compounds can pass through and accumulate in living organisms' fatty tissues because they don't break down chemically or biologically.
- IPM: Ecological pest-control strategy that uses a combination of biological, chemical, and physical methods together; requires an understanding of the ecology and life cycle of pests.
- CAFO: Intensive animal feeding operation in which large numbers of animals are confined in feeding pens.
- Mining: Removing mineral resource from the ground.
- Surface Mining
- Contour mining: Removing overburden from the seam
- Dredging: Mining below the water table
- In situ: Small holes are drilled into the Earth
- Mountaintop removal: Removal of mountaintops to expose coal seams
- Open pit: Extracting rock or minerals from the Earth by their removal.
- Strip mining: Exposes coal by removing the soil above each coal seam.
- Underground Mining
- Blast: Uses explosives to break up the seam.
- Longwall: Uses a rotating drum with “teeth.”
- Room and pillar: Approximately half of the coal is left in place as pillars to support the roof of the active mining area.
- Urbanization: Movement of people from rural areas to cities and the changes that accompany it.
- Urban Sprawl: Expansion of human populations away from central urban areas into low-density and usually car-dependent communities.
- Urban development: Designing and shaping the physical features of cities and towns with the goal of making urban areas more attractive, functional, and sustainable.
- Urban runoff: It is surface runoff of rainwater created by urbanization.
- Ecological Footprint: A measure of human demand on Earth’s ecosystems and is a standardized measure of demand for natural capital that may be contrasted with the planet’s ecological capacity to regenerate.
- Sustainability: It refers to the capacity for the biosphere and human civilization to coexist through the balance of resources within their environment.
- Soil Conversion Techniques
- Contour plowing: Plowing along the contours of the land in order to minimize soil erosion
- No-till agriculture: Soil is left undisturbed by tillage and the residue is left on the soil surface
- Planting perennial crops: Perennials live for several years
- Strip cropping: Cultivation in which different crops are sown in alternate strips
- Terracing: Make or form into a number of level flat areas resembling a series of steps
- Windbreaks: Rows of trees that provide shelter or protection from the wind
Chapter 6: Energy Resources and Consumption
Energy: Fundamental entity of nature.
Forms of Energy
- Chemical energy: Stored in bonds between atoms in a molecule.
- Electrical energy: Results from the motion of electrons.
- Electromagnetic energy: Energy travels by waves.
- Mechanical energy: Potential and kinetic energies.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy in any object.
- Kinetic energy: Energy in motion.
- Nuclear energy: Stored in the nuclei of atoms, and it is released by either splitting or joining atoms.
- Thermal Energy: Energy an object has because of the movement of its molecules.
Units of Energy/Power
- British thermal unit (Btu): Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water by 1°F.
- Horsepower (HP): Unit used in automobile industries.
- Kilowatt hour (kWh): A unit of power; a measure of energy used at a given moment.
Law of Thermodynamics
- First Law of Thermodynamics: The law of conservation of energy; energy can't be created nor destroyed.
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: The total system work is always less than the heat supplied into the system.
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: If two bodies are each in thermal equilibrium with some third body, then they are also in equilibrium with each other.
Energy Resources
- Renewable Energy: Energy collected from resources that are naturally replenished on a human time scale.
- Nonrenewable Energy: ot sustainable because their formation takes billions of years
Fuel Types
- Fossil Fuels: Fuels formed from past geological remains of living organisms.
- Burning wood fuel: It creates the following by-products: carbon dioxide, heat, steam, water vapor, and wood ash.
- Peat: It is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter
- Coal: A sedimentary deposit composed predominantly of carbon that is readily combustible.
- Lignite: fuel for electric power generation
- Bituminous: fuel in steam-electric power generation
- Anthracite: residential and commercial space heating
- Natural Gas: Layers of buried plants and gases are exposed to intense heat and pressure
- Oil: Decomposition of deeply buried organic material (plants) under high temperatures and pressure
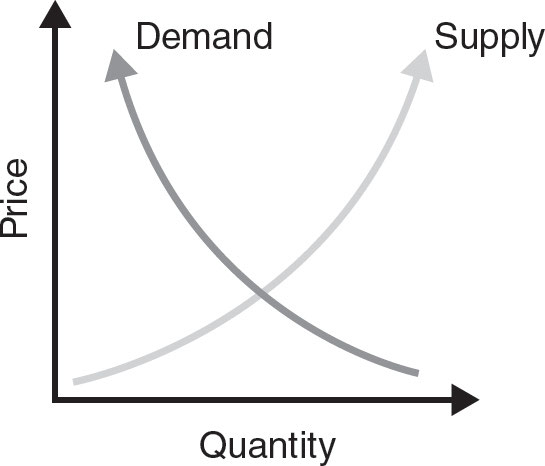
Law of Supply: All other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity of goods or services that suppliers offer will increase
Law of Demand: All other factors being equal, the quantity of the item purchased is inversely related to the price of the item.
Combustion
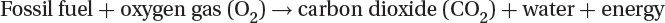
Nuclear Fuels
- U-235: Less than 1% of all-natural uranium on Earth.
- U-238: The most common isotope of uranium and has a half-life of 4.5 billion years.
- Pu-239: It has a half-life of 24,000 years and is produced in breeder reactors from U-238.
Nuclear Components
- Core: Contains up to 50,000 fuel rods.
- Fuel: Enriched (concentrated) U-235 is usually the fuel.
- Control Rods: Move in and out of the core to absorb neutrons and slow down the reaction.
- Moderator: It reduces the speed of fast neutrons, thereby allowing a sustainable chain reaction.
- Coolant: Removes heat and produces steam to generate electricity.
\
Biomass: Biological material derived from living organisms that can be burned in large incinerators to create steam that is used for generating electricity.
- Biofuel: A liquid fuel produced from living organisms.
Solar energy: It consists of collecting and harnessing radiant energy from the sun to provide heat and/or electricity.
Passive solar heating: absorb heat and then release it slowly to maintain the temperature throughout the building.
Active solar heating: absorb heat and then release it slowly to maintain the temperature throughout the building.
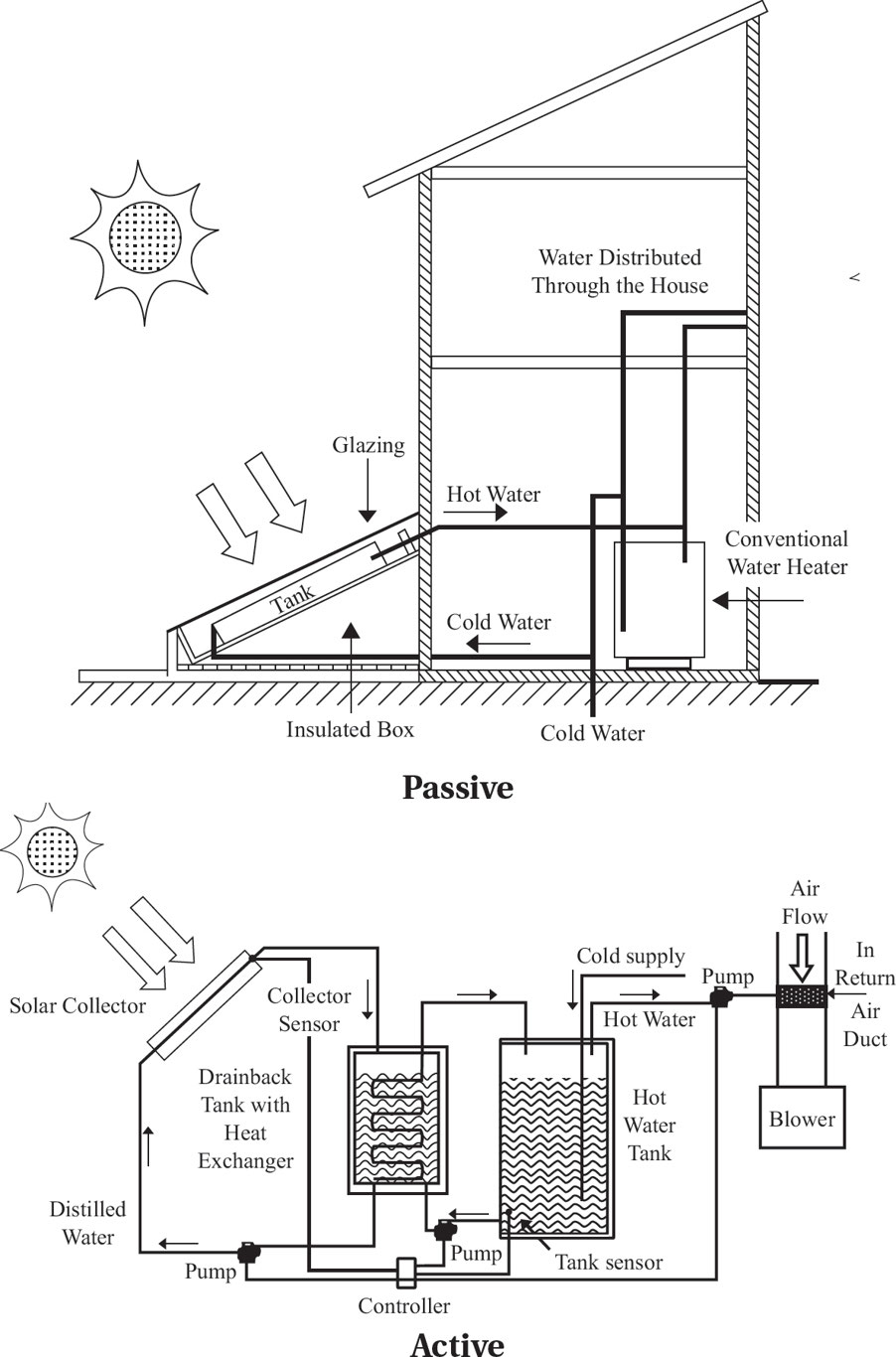
Geothermal Energy
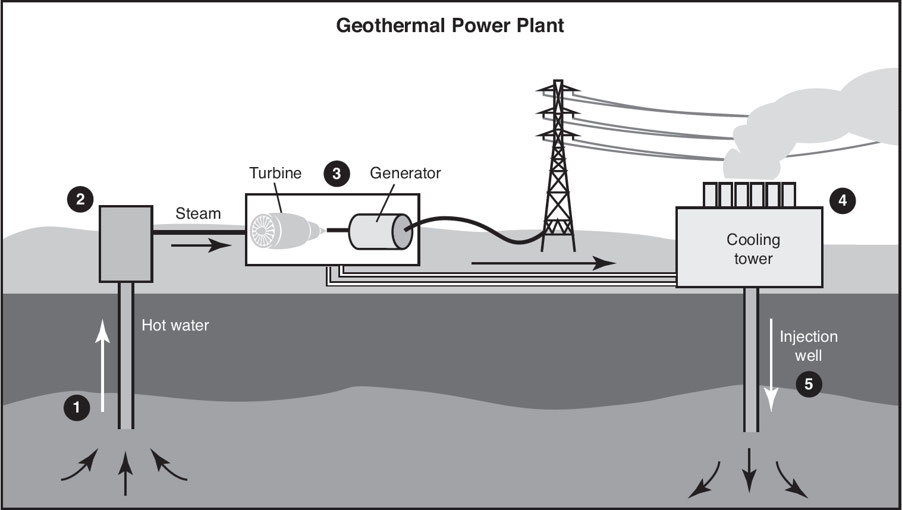
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Chapter 7: Atmospheric Pollution
Air Pollution: It occurs when harmful or excessive quantities of substances are introduced into Earth’s atmosphere.
- Primary Pollutants: Emitted directly into the air.
- Secondary pollutants: Result from primary air pollutants’ reacting together and forming new pollutants.
- Point sources: Contaminant comes from an obvious source.
- Non-point sources: Contaminant comes from a source that is not easily identifiable
Atmospheric CO2 and Particulates
- Carbon Monoxide: Produced from the partial oxidation of carbon-containing compounds.
- Lead: Used in building construction, lead-acid batteries for vehicles, bullets.
- Nitrogen Oxides: Generic term for nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
- Ozone: Inorganic molecule with the chemical formula O3.
- Peroxyacyl Nitrates: A component of photochemical smog, produced in the atmosphere when oxidized volatile organic compounds combine with nitrogen dioxide.
- Sulfur Dioxides: Colorless gas with a penetrating, choking odor that readily dissolves in water to form an acidic solution.
- Suspended Particulate Matter: Microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in Earth’s atmosphere.
- Volcanic Organic Compounds: Have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room temperature.
Photochemical smog: Catalyzed by UV radiation, tends to be nitrogen-based.
Thermal inversions: Occur when air temperature rises with height instead of falling.
Catalytic converter: Exhaust emission control device that converts toxic chemicals in the exhaust of an internal-combustion engine into less harmful substances.
- Catalyst: Stimulates a chemical reaction in which by-products of combustion are converted to less toxic substances by way of catalyzed chemical reactions.
Three Way Converters converting the three main Pollutants
Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide:
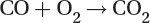
Oxidation of unburned hydrocarbons to carbon dioxide and water:
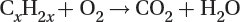
Reduction of nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen:
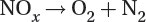
Acid Deposition: Occurs when atmospheric chemical processes transform sulfur and nitrogen compounds and other substances into wet or dry deposits on Earth.
Noise pollution: It is an unwanted human-created sound that disrupts the environment.
Chapter 8: Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution
- Water pollution: It is the contamination of water bodies.
- Point source pollution: Release pollutants from known locations
- Non-point source pollution: Combination of pollutants from a large area rather than from specific identifiable sources
- Thermal pollution: Degradation of water quality by any process that changes ambient water temperature.
- Great Pacific Garbage Patch: A large system of rotating ocean currents of marine litter in the central North Pacific Ocean
- Water quality: Measure of the condition of the water relative to the requirements of one or more biotic species and/or to any human need or purpose.
- Drinking Water Treatment Methods
- Absorption: When one substance enters completely into another.
- Adsorption: When one substance just hangs onto the outside of another.
- Disinfection: Using chemicals and/or cleansing techniques that destroy or prevent the growth of organisms that are capable of infection.
- Filtration: Removes clays, natural organic matter, precipitants, and silts from the treatment process.
- Flocculation sedimentation: Combines small particles into larger particles that then settle out of the water as sediment
- Ion exchange: Removes inorganic constituents.
- Endocrine System: A network of glands that make the hormones that help cells communicate with each other and is responsible for almost every cell, organ, and function in both humans and animals.
- Endocrine Disruptors
- Bisphenol A (BPA): Used in plastic manufacturing and epoxy.
- Dioxins: By-product of herbicide production and paper bleaching
- Phthalates: Used to make plastics more flexible.
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Used to make electrical equipment, heat transfer fluids and lubricants.
- Wetland: Place where the land is covered by water, which can be freshwater, saltwater, or brackish water.
- Mangrove: Shrub or small tree that grows in slightly salty water formed by seawater mixing with freshwater in estuaries.
- Bioaccumulation: It is the increase in the concentration of a pollutant within an organism.
- Biomagnification: It is the increasing concentration of a substance in the tissues of organisms at successively higher trophic levels within a food chain.
- Types of Wastes
- Municipal solid waste (MSW): Trash/garbage.
- Hazardous Wastes: Paints, chemicals, pesticides, etc.
- Organic Wastes: Kitchen wastes, vegetables, flowers, leaves, or fruits.
- Radioactive Wastes: Spent fuel rods and smoke detectors.
- Recyclable Wastes: Glass, metals, paper, and some plastics.
- Soiled Wastes: Hospital wastes.
- Incineration: Waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials and the conversion of the waste into ash, flue gas, and heat.
- Hazardous Wastes
- Radioactive wastes: Usually a by-product of nuclear power generation
- Low-level radioactive wastes: Contain low levels of radiation and remain dangerous for a relatively short time.
- High-level radioactive wastes: Contain high levels of radiation and remain dangerous for a very long time
- Reactive wastes: Wastes that are unstable under normal conditions.
- Source-specific wastes: Wastes from specific industries.
- Teratogens: Substances found in the environment that can cause birth defects.
- Toxic wastes: Wastes that are harmful or fatal when ingested or absorbed.
- Handling Hazardous Wastes
- Landfill capping: forms a barrier between the contaminated media and the surface
- Hazardous waste landfills: excavated or engineered sites for the final disposal of non-liquid hazardous waste are selected
- Permanent storage: isolates hazardous waste from the environment by condensing or concentrating it.
- Methods Used to Isolate and Store Hazardous Wastes
- Surface impoundments: used for temporary storage and/or for the treatment of liquid hazardous waste.
- Injection wells: stores fluid deep underground in geologically stable, porous rock formations
- Waste piles: non-containerized piles of solid, non-liquid hazardous waste that are used for temporary storage or treatment.
- Reduction and cleanup of hazardous wastes: occur by producing less waste, converting the hazardous material to less hazardous
- Brownfield: land that was previously used for industrial or commercial purposes
Chapter 9: Global Change
- Three Forms of UV Radiation
- UVA: It is closest to blue light in the visible spectrum and is the form of ultraviolet radiation that usually causes skin tanning.
- UVB: It causes blistering sunburns and is associated with skin cancer.
- UVC: It is found only in the stratosphere and is largely responsible for the formation of ozone.
- Chemicals that affect Ozone
- Chlorofluorocarbons: Nonflammable chemicals that contain atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine.
- Halocarbons: Organic chemical molecules that are composed of at least one carbon atom with one or more halogen atoms
- Ocean acidification: It occurs when atmospheric carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid,
- Biodiversity and Species
- Endangered Species: Species considered to be facing a very high risk of extinction in the wild.
- Invasive Species: Animals and plants that are transported to any area where they do not naturally live.
- Important Protocols for Global Climate Change
- Kyoto Protocol (2005): A plan created by the United Nations to reduce the effects of climate change, which results in a reduction in the pH of ocean water over an extended period of time.
- Montreal Protocol (1987): An international treaty designed to phase out the production of substances that are responsible for ozone depletion.
- Paris Agreement (2016): It deals with greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation.
\