International Trade and Finance
Module 41: Capital Flows and the Balance of Payments
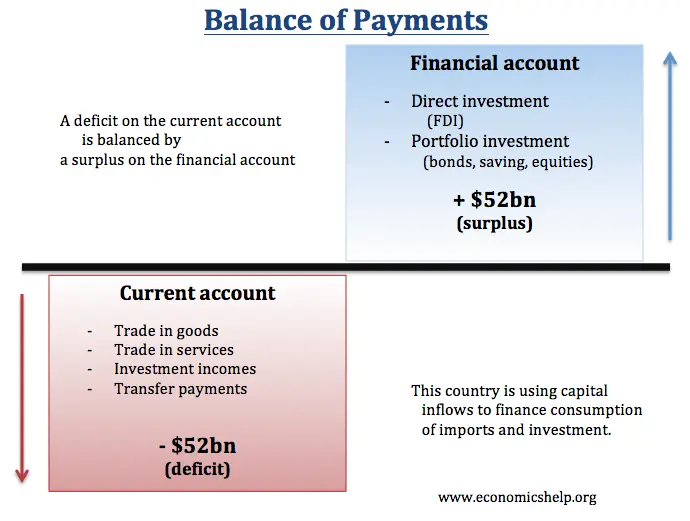
Balance of payments accounts is the summary of a country’s transactions with other countries
Amount of money gained + amount of money lost = 0
The current account is made up of goods and services, factor income, and transfers
The financial account is made up of assets/financial capital inflow and liabilities/outflow
Difference between a country’s sales to foreigners and foreign purchases
Real estate, stocks, and bonds
Capital flow
Payments to and from foreigners make up factor income
International transfers are funds sent from one country’s residents to another
Bonds lend money to the government to get it back later
The balance of payments on goods and services is the difference between the value and exports and imports during a given period
The trade balance is the difference between a country’s exports and imports
Only includes goods and not services
Capital is goods used to produce other goods
In foreign direct investment, companies build factories or acquire assets abroad
The equilibrium interest rate is the intersection of supply curve for loanable funds
Financial capital flows into countries with higher interest rates and out of those with lower interest rates
Two-way capital flows are common between economies
Module 42:
The foreign exchange market is the market where currencies are traded
Exchange rates are the prices at which currencies trade
When a currency’s value increases in terms of others, it appreciates
Exports fall and imports rise
When a currency’s value decreases in terms of others, it depreciates
Exports rise and imports fall
The equilibrium exchange rate is where currency quantity demanded is equal to currency quantity supplied
When demand for one currency changes, there is a corresponding change in the supply of the other currency
Real exchange rates are exchange rates adjusted for international differences in aggregate price levels
Other kind is nominal exchange rates
Accounts for differences in inflation rates
The aggregate price level is the general price of all goods and services over time
Purchasing power parity is the nominal exchange rate where something would cost the same price in each country
Ex: 1,000 pesos = $100
Increase in interest rates cause real exchange rates to decrease