🌱 AP Environmental Science Unit 7 Notes
7-10% of The AP Test
Topics
7.1 Introduction to Air Pollution
7.2 Photochemical Smog
7.3 Thermal Inversion
7.4 Atmospheric CO2 and Particulates
7.5 Indoor Air Pollutants
7.6 Reduction of Air Pollutants
7.7 Acid Rain
7.8 Noise Pollution
These notes are based on Mr Jordan Dischinger-Smedes’s YouTube videos and the fill in template notes for these videos created by Carolyn Kelleher Mendonca. Some changes were made. Videos available here.
Good luck on the AP Test! 🩷
7.1 Air Pollutant Basics
6 criteria pollutants:
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Primary
Cause: Coal combustion
Effects: Respiratory irritant, sulfuric smog, blocks sun, acid precipitation
Nitrogen Oxides (NOX)
Primary
Causes: Fossil fuel combustion
Effects: Ozone (O3), photochemical smog, acid precipitation
N2 + O2 = NO + O2 = NO2 + sunlight = NO
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Primary
Causes: incomplete/failed combustion
Effects: Ozone (O3), lethal to humans
Particulate Matter (PM)
Primary and Secondary
Causes: Fossil fuel or biomass combustion
Effects: Respiratory irritant, smog
Tropospheric Ozone (O3)
Secondary
Causes: Photochemical oxidation of NO2 and/or CO
Effects: Respiratory irritant, smog, damages plants
Lead (Pb)
Primary and Secondary
Causes: Metal plants, waste incineration, coal combustion
Effects: Nuerotoxicant

Air Pollutants vs. Greenhouse Gasses
CO2 is not one of 6 criteria pollutants in Clean Air Act (although 07’ SC ruling found EPA could greenhouse gasses and it began doing so in 09’)
CO2 does not directly* lower air quality from a human health standpoint
Not toxic to organisms to breathe
Not damaging to lungs/eyes
Does not lead to smog or decrease visibility
CO2 is a greenhouse gas; it does lead to earth warming, and thus env. and human health consequences (basis for SC ruling in 07’)
Bottom line: In APES, CO2 has not typically been included on FRQ scoring guides as an air pollutant (stick to surefire air pollutants on FRQs)
Other secondary pollutants: Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4), sulfate (SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), and Nitrate (NO3)
Lead → water pipes and paint chips
Ingestion / inhalation / skin
Mercury → seafood (tuna)
Ingestion / inhalation
CO → indoor biomass combustion
Inhalation
PM → dust, pollen,etc
Inhalation
Arsenic → rice, groundwater
Ingestion
Formaldehyde: carpet, paneling, treated wood, new furniture, Cigarettes
Radon: Radioactive Uranium in soil can leak into basement cracks or well water
Mercury: Fossil Fuel Combustion, Industry, (Mercury thermometers contain Hg but they are not used as much anymore-instead we use alcohol dyed red)
Lead: Old paint (which contained lead), old pipes (which contained lead), leaded gasoline, smelting
Carbon monoxide: incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, wood burning, tobacco smoke
VOC’s: paint, solvents. Cleaning products, preservation products (often in clothing, furniture, carpet)
Asbestos: Old insulation and fire retardants
Coal Combustion
Releases more air pollutants than other FFs; ~35% of global electricity
Releases CO, CO2, SO2, NOx toxic metals (mercury, arsenic, and lead) and PM (often carries the toxic metals)
Impacts of SO2
Sulfur aerosols (inflammation of bronchioles, lungs), worsens asthma & bronchitis
Sulfur aerosols (suspended sulfate particles) block incoming sun, reducing visibility & photosynthesis
Forms sulfurous (gray) smog
Combines with water & O2 in atmosphere to form sulfuric acid → acid precipitation
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Released by combustion of anything, especially fossil fuels
NOx refers to nitrogen oxides (both NO, and NO2)
NO forms when N2 combines with O2 (esp. during combustion)
NO can become NO2 by reacting with O3 or O2
Sunlight converts NO2 back into NO
EPA & Lead
Before CAA, lead was a common gasoline additive; EPA began phaseout of lead from gasoline in 1974
Vehicles made after 1974 are required to have a catalytic converters to reduce NOx, CO and hydrocarbon emissions (lead damages catalytic converters)
Also a known neurotoxin (damages nervous systems of humans)
Primary vs. Secondary Air Pollutants
Primary
Emitted directly from sources such as vehicles, power plants, factories, or natural sources (volcanoes, forest fires)
NOx, CO, CO2, VOCs, SO2, PM, hydrocarbons
Secondary
Primary pollutants that have transformed in presence of sunlight, water, O2
Occur more during the day (since sunlight often drives formation)
Tropospheric O3 (Ozone)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) & sulfate (SO42-)
Nitric acid (HNO3) & nitrate (NO3-)
7.2 - Photochemical Smog Precursors & Conditions
Precursors
NO2 | Broken by sunlight into NO + O (free O + O2 → O3)
VOCs | Volatile organic compounds (hydrocarbons) that bind & form photochemical oxidants
Carbon-based compounds that volatilize (evaporate) easily (this makes them “smelly”) and participate in photochemical reactions.
Sources: gasoline, formaldehyde, cleaning fluids, oil-based paints, even coniferous trees (pine smell)
O3 | Forms when NO2 is broken by sunlight & free O binds to O2.
Respiratory irritant in troposphere (@earth’s surface)
Damaging to plant stomata, limiting growth
Conditions
Sunlight | Drives O3 formation by breaking down NO2 to NO + O, then free O binds with O2.
Warmth | Hotter atmospheric temperature speeds O3 formation, evaporation of VOCs & thus smog formation
Normal O3 Formation
Sunlight breaks NO3 into NO + O
O bonds with O2 to form O3
At night, O3 reacts with NO to form NO2 and O2 once again; O3 levels drop overnight
O3 formation typically peaks in the afternoon when most direct and emissions from morning traffic traffic have peaked
Morning commute leads to high NO2 levels from exhaust
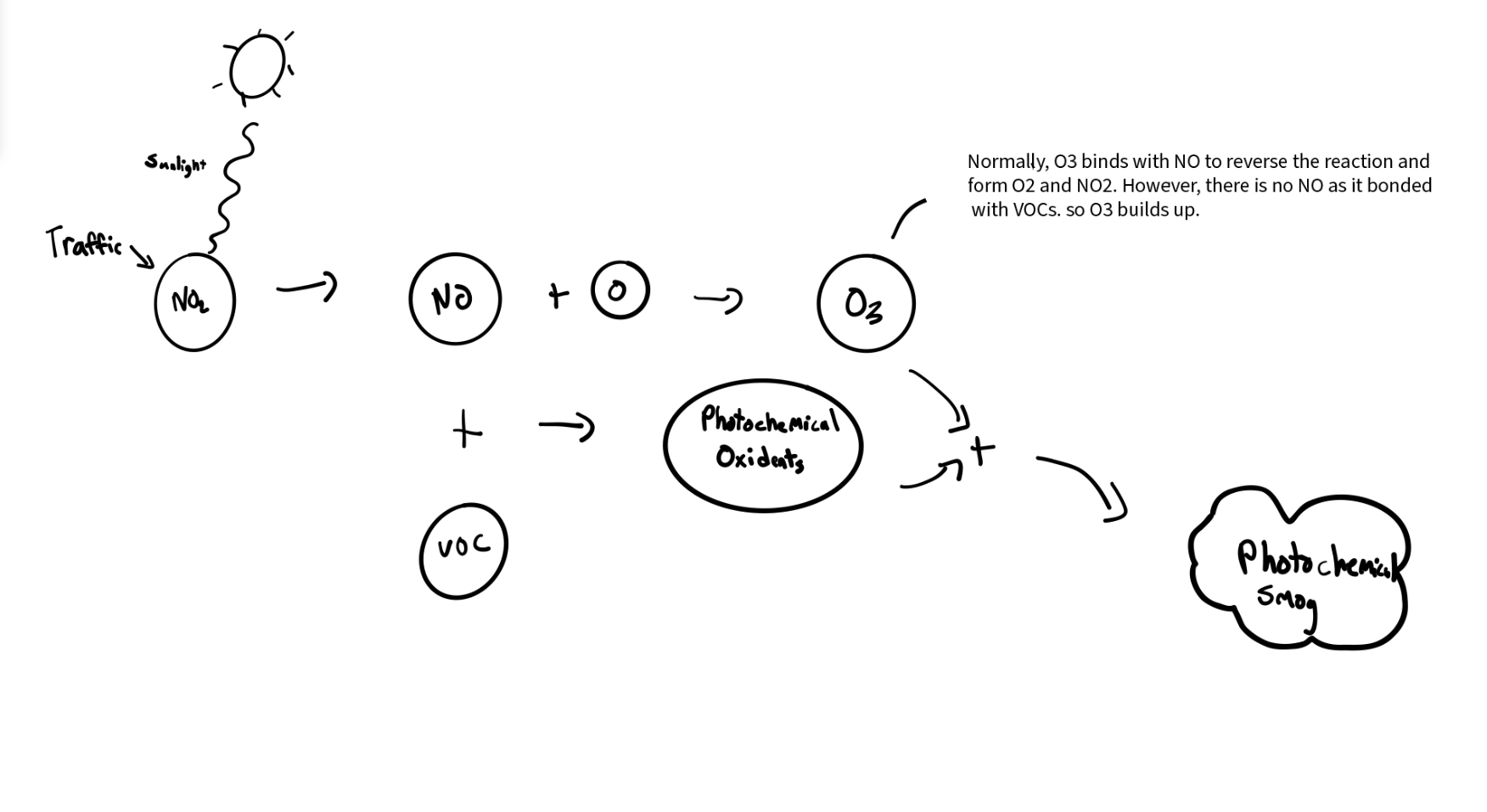
Photochemical Smog Formation
Sunlight breaks NO3 into NO + O
O bonds with O2 to form O3
Without NO to react with, O3 instead of returning to O2 and NO2 overnight
VOCs bond with NO to form photochemical oxidants
O3 combines with photochem. oxidants (NO + VOCs) to form photochemical smog
Factors That Increase Smog Formation
More sunlight (summer, afternoon) = more O3
Warmer temperature, speeds evaporation of VOCs and rxn that lead to O3
Higher VOC emissions (gas stations, laundromats, petrochem. & plastic factories)
Increased vehicle traffic; increases NO2 emissions & therefore O3 formation
Urban areas have more smog due to all of these factors
More traffic → more NO2
Higher temps due to low albedo of blacktops
More VOCs due to gas stations & factories
More electricity demand; more NOx emissions from nearby power plants
Impacts & Reduction of Smog
Impacts
Environmental
Reduces sunlight; limiting photosynthesis
O3 damages plant stomata and irritates animal respiratory tracts.
Humans
Respiratory irritant; worsens asthma, bronchitis, COPD; irritates eyes
Economic
Increased healthcare costs to treat asthma, bronchitis, COPD
Lost productivity due to sick workers missing work or dying
Decreased agriculture yields due to less sunlight reaching crops & damage to plant stomata
Reduction
Vehicles
Decreasing the number of vehicles on the road decreases NO2 emissions
Fewer vehicles = less gas = fewer VOC
Carpooling, public transport, biking, walking, working from home
Energy
Increased electricity production from renewable sources that don’t emit NOx (solar, wind, hydro)
Natural gas power plants release far less NOx than coal
7.3 Thermal Inversion
Urban Heat Island Effect
Urban areas tend to have higher surface and air temperature than surrounding suburban and rural areas due to:
Lower albedo; concrete & asphalt absorb more of sun’s energy than areas with more vegetation (absorbed sunlight is given off as IR radiation - heat)
Less evapotranspiration; water evaporating from surfaces and transpiration from plants carries heat from surface into the atmosphere
This cools off rural & suburban areas which have more vegetation
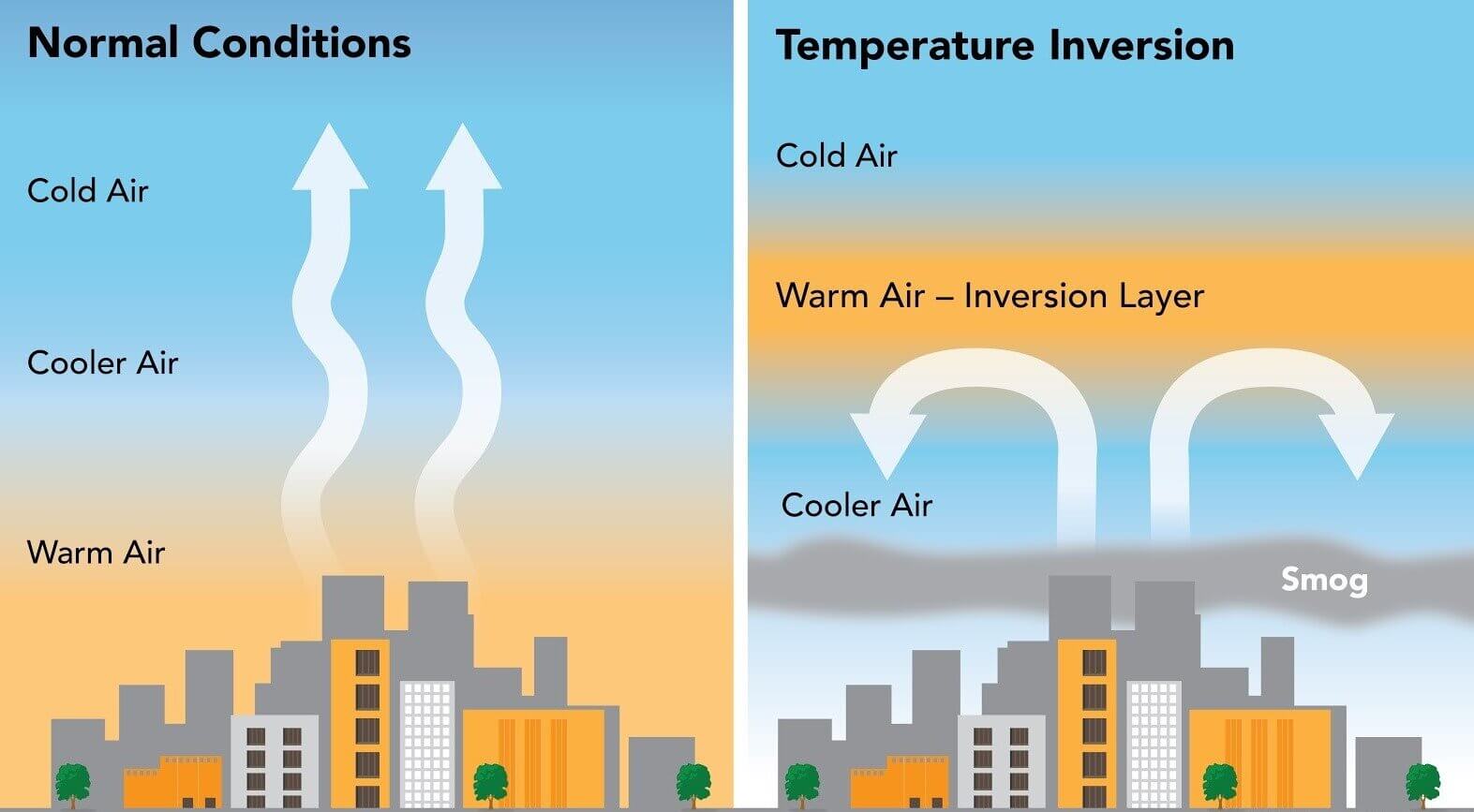
Thermal Inversion
Normally, the troposphere is warmest at earth’s surface, and cools as altitude rises
Because warm air rises, air convection carries air pollutants away from earth’s surface & distributes them higher into the atmosphere
During a thermal inversion, a cooler air mass becomes trapped near earth’s surface (Inverting normal gradient)
Due to a warm front moving in over the cool air
Or due to a hot urban surface cooling overnight while IR radiation absorbed during the day is still being released
Because cold air at the surface is trapped beneath the warmer mass above, convection doesn’t carry pollutants up and away.
Effects of Thermal Inversion
Air pollutants (smog, PM, ozone, SO2 , NOx) are trapped closer to earth
Respiratory irritant: asthma flare ups leading to hospitalization, worsened COPD, emphysema
Decreased tourism revenue
Decreased photosynthetic rate
7.4 Atmospheric CO2 and Particulate Matter (PM)
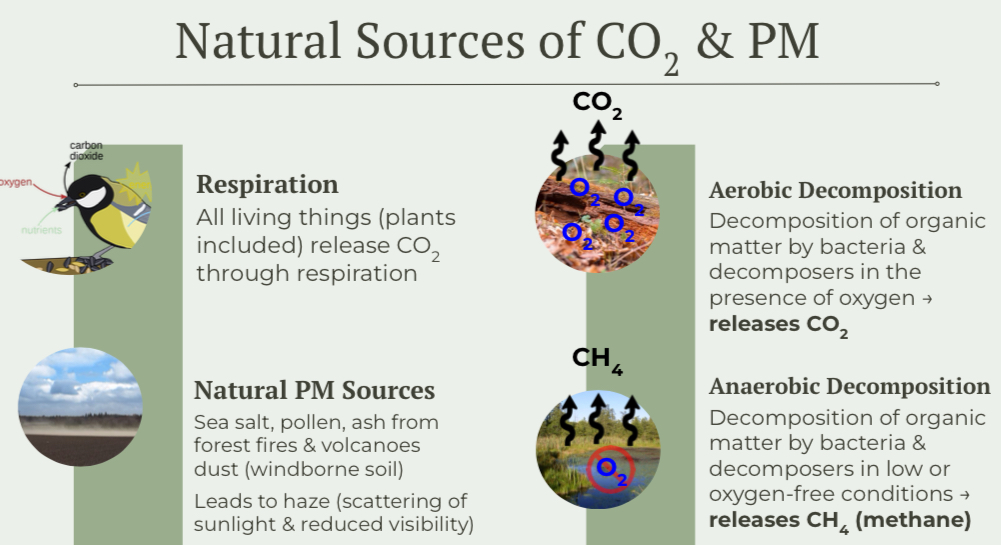
Natural Sources of Air Pollutants

PM10 vs. PM2.5
Particulate Matter: Solid or liquid particles suspended in air (also referred to as “particulates”)
PM10
(<10 micrometers)
Particles or droplets like dust, pollen, ash, or mold
Too small to be filtered out out by nose hairs and trachea cilia; can irritate the respiratory tract & cause inflammation
PM2.5
(<2.5 Micrometer)
Particles from combustion (especially vehicles) & smaller dust particles
More likely to travel deep into the lungs due to smaller size
Associated with chronic bronchitis and increased risk of lung cancer
7.5 Indoor Air Pollution
Developing vs. Developed Countries
Developing nations use more subsistence fuels such as wood, manure, charcoal (biomass)
Pollution from burning biomass
These biomass fuels release CO, PM, NOx, and VOCs ( can also cause deforestation)
Often combusted indoors with poor ventilation, leading to high concentrations
Est. 3 billion people globally cook with subsistence fuels, resulting in est. 3.5 - 4.3 million deaths annually
Developed nations use more commercial fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) supplied by utilities
Typically burned in closed, well ventilated furnaces, stoves, etc.
Major indoor air pollutants in developed nations come from chemicals in products: adhesive in furniture, cleaning supplies, insulation, and lead paint.
PM & Asbestos
Particulates (PM) are a common indoor air pollutant
Ex: Smoke (from indoor biomass combustion or cigarettes), dust, and asbestos
Asbestos is a long, silicate particle previously used in insulation (since been linked to lung cancer & asbestosis)
Phased of use, but still remains in older buildings
Not dangerous until insulation is disturbed and asbestos particles enter the respiratory tract.
Should be removed by trained professionals with proper respiratory equipments, ventilation in the area it’s being removed from, plastic to off area from rest of the building
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
CO is produced by incomplete combustion of basically any fuel
Not all the fuel is combusted due to low O2 or temperature.
CO is an asphyxiant: causes suffocation due to CO binding to hemoglobin in blood, displacing O2.
Lethal to humans in high concentrations, especially with poor ventilation (odorless and colorless - hard to detect)
Developed nations: CO released into home by malfunctioning natural gas furnace ventilation
Can be detected by carbon monoxide detectors (similar to smoke detectors)
Developing nations: CO emitted from indoor biomass combustion for heating/cooking
VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
Chemicals used in variety of home products that easily vaporize, enter air, and irritate lungs, eyes, and bronchioles
Adhesives/sealants: chemicals used to glue carpet down, hold furniture together, seal panels
Formaldehyde is a common adhesive in particle board and carpet glues (new carpet smell)
Cleaners: Common household cleaners and deodorizers such as febreeze
Plastics and Fabrics: both can release VOCs themselves, or from adhesives used in production
Radon Gas
Radioactive gas released by the decay of uranium naturally found in rocks underground (granite especially)
Usually enters homes through cracks in the foundation & then disperses up from basement/foundation through home
Can also seep into underground water sources & enter body through drinking water
2nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking
EPA recommends testing homes with airborne radon monitor
Sealing cracks in foundations can prevent it from entering and increases ventilation in the home can disperse it if it’s detected
Dust & Mold
Natural indoor air pollutants that can worsen asthma, bronchitis, COPD, emphysema
Dust settles in homes naturally, is disturbed by movement, entering air and then respiratory tract
Mold develops in areas that are dark and damp and aren’t well ventilated (under sinks/showers, behind panels in the walls and ceilings)
Black mold is a class of mold that releases spores into air
Especially harmful to respiratory tract
Can be removed by physically cleaning mold out and fixing the water leak or ventilation issue that lead to mold forming
Lead
Found in paint in old homes (EPA banned lead paint in 78’)
Paint chips off walls/windows and is eaten by small children (due to curiosity & sweet taste) or inhaled as dust
Lead water pipes can also release lead into drinking water sources sources (as in Flint) but it’s less common than lead paint
Damages the central nervous system of children due to their smaller size and still developing brain.
Can be removed from home by stripping lead paint and replacing with non-lead based paint
Lead water pipes can be replaced by cities with copper pipes
7.6 - Reducing Air Pollutants
Reducing emissions reduces air pollutants.
Drive Less
Conserve energy with smart applications
Eat more plants
Use renewable energy
Laws/Regulations
Clean Air Act
Allows EPA to set acceptable levels for critical air pollutants
Monitor emission levels from power plants and other facilities
Tax/sue/fine corporations that release emissions above levels
Pollution Credits
Similar to Individual Transfer Quotas for fish
Companies that reduce emissions well below EPA-set levels earn pollution credits
They can sell these to companies that release more than acceptable levels
CAFE Vehicle Standards
(Corporate Average Fuel Economy) standards require the entire US “fleet” of vehicles to meet certain average fuel
Requires vehicle manufacturers to work to make more efficient vehicles
More efficient vehicles burn less and release less NOx, PM, CO, and CO2
Reducing Vehicle Air Pollutants
Vapor Recovery Nozzle
Capture hydrocarbon VOCs released from gasoline fumes during refueling
Separate tube inside nozzle captures vapor & returns them to underground storage tanks beneath the gas station
Reduces VOCs, which contribute to smog & irritate resp. tracts
Also reduces benzene (carnivores) released from gasoline vapors
Catalytic Converter (CC)
Required on all vehicles after 1975
Contains metals (platinum & palladium) that bind to NOx and CO
CC converts NOx, CO, and other hydrocarbons into less dangerous chemicals (CO2, N2, O2, and H2O)
Reducing SOx & NOx
Crushed Limestone (SO2)
Used to reduce SO2 from coal power plants
Crushed coal mixed with limestone (calcium carbonate) before being burned in boiler
Calcium carbonate in limestone combines with SO2 to produce calcium sulfate, reducing the SO2 being emitted
Calcium sulfate can be used to make gypsum wallboard or Sheetrock for home foundations
Fluidized Bed Combustion (NOx)
Fluidizing jets of air pumped into combustion “bed”
Jets of air bring more O2 into rxn, making combustion more efficient and bringing SO2 into more contact with calcium carbonate in limestone
Also allows coal to be combusted at lower temperatures, which emits less NOx
Wet & Dry Scrubbers
Dry Scrubbers (NOx, SOx, VOCs)
Large column/tube/pipe filled with chemicals that neutralize (NOx, SOx, VOCs) from exhaust streams (emissions)
Calcium oxide is a common dry scrubber additive which reacts with SO2 to form calcium sulfite
Wet Scrubbers (NOx, SOx, VOCs + PM)
May involve chemical agents that absorb or neutralize NOx, SOx, VOCs, but also include mist nozzles that trap PM in water droplets as well
Mist droplets with pollutants and PM trapped in them fall to the bottom of scrubber or get trapped at the top by the mist eliminator
Sludge collection system traps polluted water for disposal
Reducing PM
Electrostatic Precipitator
Power plant/factory emissions passed through a device with a negative charged electrode, giving particles a negative charge
Negative charged particles (pollutants) stick to positive charged collection plates, trapping them
Plates are discharged occasionally so particles fall into collection hoppers for disposal.
Baghouse Filter (PM)
Large fabric bag filters that trap PM as air from combustion/industrial process passes through
Shaker device knocks/traps particles into collection hopper below
PM collected and taken to the landfill
7.7 - Acid Rain
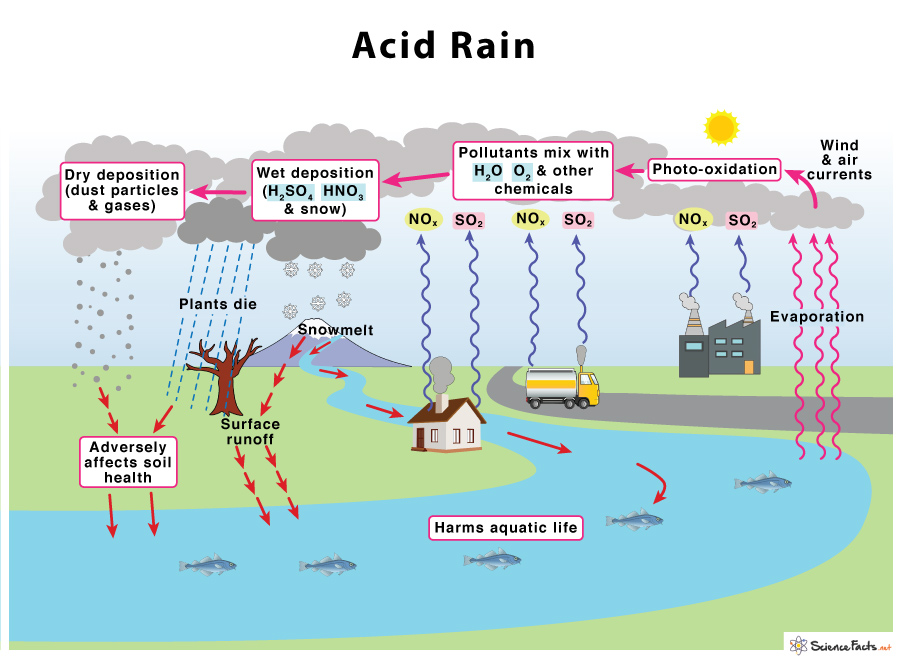
Sources of NOx & SO2
NOx and SO2 are the primary pollutants that cause most acid precipitation.
Major Sources
SO2 - Coal fired in power -pants, metal flavor tires, vehicles that burn diesel fuel
NOx - vehicle emissions, diesel generations, and coal power plants.
Limiting Acid Rain
Reducing NOx and SO2 reduces acid deposition
Higher CAFE standards
More public transit
renewable energy sources
More efficient energy use
Since passage of the clean air act acid deposition has reduced
Acid Rain Formation
NOx and SO2 react with O2 and H2O in the atmosphere, forming nitric acid and sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid and nitric acid dissociate in the presence of water into sulfate and nitrate ions, and hydrogen ions (H+)
Acidic rain water (higher H+ conc.) decreases soil and water pH; can limit tree growth in forests down wind from major SO2 & NOx sources
Environmental Effects of Acid Rain
Acidity = Higher H+ concentration
Soil/Water Acidification
H+ ions displace or leech other positively charged nutrients (Ca2+, K+) from soil
H+ ions also make toxic metals like aluminum and mercury more soluble in soil and water
This can slow growth or kill plants and animals living in the soil or water
Aquatic species have differing pH Tolerances
As pH decreases (more acidic) outside optimal range for a species, pop. declines
When pH leaves range of tolerance, they cannot survive at all, due to:
Aluminum toxicity
Disrupted blood osmolarity (Na /Cl-)
balance disrupted at low pH
Indicator species can be surveyed and used to determine conditions of an ecosystem (soil, water, etc.)
Ex: high whitemoss/filamentous algae pop. indicates pH < 6.0
High crustacean pop. indicates pH > 6.0
Mitigating Acid Rain
Limestone(calcium carbonate) is a natural base that can neutralize acidic soil/water Limestone
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) reacts with H+ ions, forming HCO3 and giving off Ca2+
This “neutralizes” acidic water/soil, moving it closer to a pH of 7
This happens because there is no lose H+ ion
Regions with limestone bedrock have some natural buffering of acid rain
Humans can also add crushed limestone to soils/waters to neutralize
Acid rain can corrode human structures, especially those made from limestone
Limiting SO2 & NOx
Decreasing these primary pollutants that drive acid rain can reduce it
Renewable energy sources, decreasing coal comb.
Fluidized bed combustion & lower burning temp. for existing coal power plants
Dry or wet scrubbers
7.8 - Noise Pollution
Urban Noise Pollution
Any noise at great enough volume to cause physiological stress (difficulty communicating, headaches, confusion) or hearing loss
Construction: jack hammers, trucks, concrete pouring
Transport: cars, busses, trains
Industrial activity: manufacturing plants
Domestic activity: neighbor’s music, lawn mowing, home projects
Wildlife Effects (land)
Noise pollution can disrupt animal communication
Physiological stress: caterpillar hearts beat faster when exposed to simulated noise pollution
Could drive pollinator species decline
Hearing: can prevent predators from hearing and vice versa; can prevent mates from locating each other (both of these decreasing the chance of survival)
Ex: lion cubs cannot hear mothers call to come for food due to human safari.
Wildlife Effects (Aquatic)
Aquatic noise pollution comes from the noise of ship engines, military sonar, and seismic air blasts from oil and gas surveying ships.
Physiological stress: hearing loss, disrupted communication, mating calls, predator and prey navigation
Whales are especially prone to having migration routes disrupted as their vocal communication is disrupted
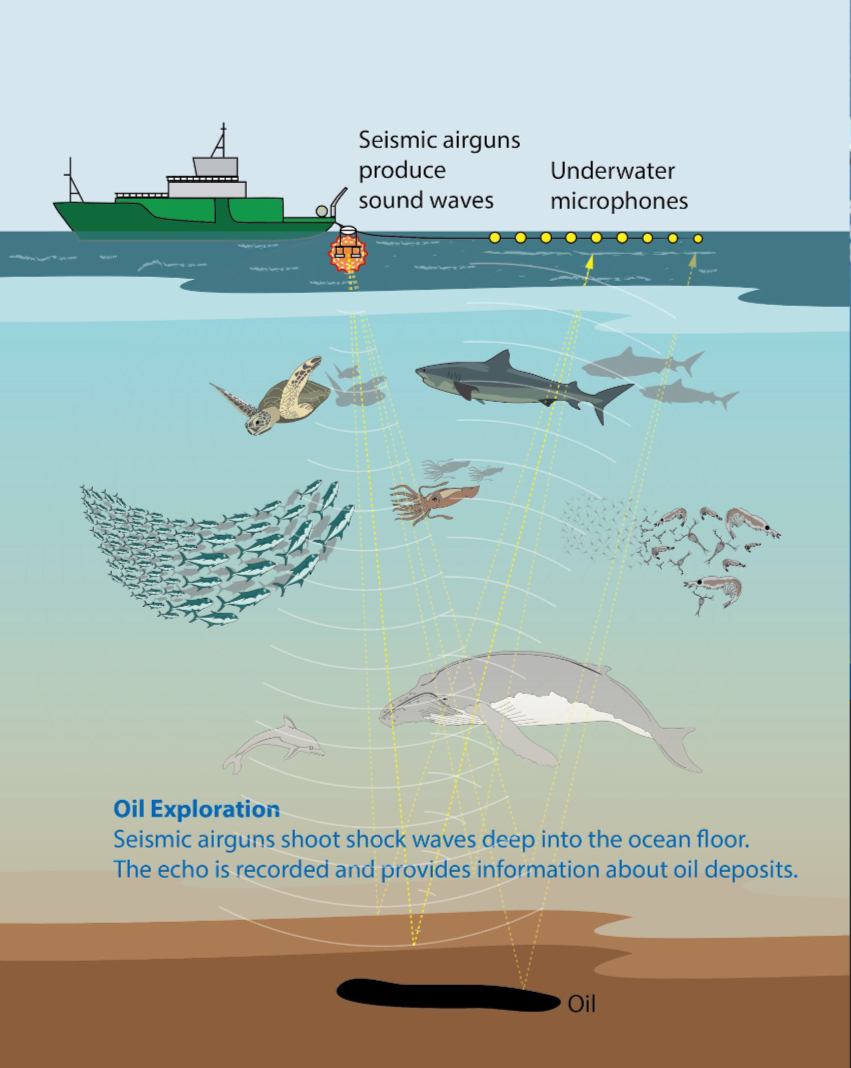
Seismic surveying ships send huge air blasts down into the water, searching for oil by recording how the echo is returned from ocean floor
So loud that researchers off the coast of Virginia can detect blasts from coast of Brazil