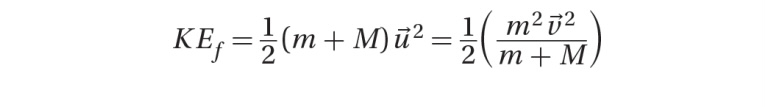Chapter 6: Impacts of Linear Momentum
Internal and External Forces in Physics:
- Internal forces are forces that act within a system, while external forces are forces that act on a system from outside.
- The net force acting on a system is the vector sum of all internal and external forces acting on the system.
- Internal forces always occur in equal and opposite pairs, according to Newton's third law of motion.
- External forces can cause a change in the motion of an object or a system, while internal forces cannot change the motion of the system as a whole.
- Examples of external forces include gravitational forces, electromagnetic forces, and contact forces such as friction and tension.
- Examples of internal forces include tension in a rope, compression or tension in a spring, and the forces between atoms in a solid.
Impact Forces and Momentum Changes:
An impact force is the force exerted on an object when it collides with another object.
The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and is a vector quantity.
During an impact, the total momentum of the system is conserved, according to the law of conservation of momentum.
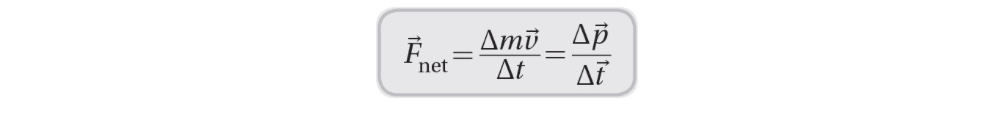
The impulse-momentum theorem relates the change in momentum of an object to the force exerted on it during an impact.
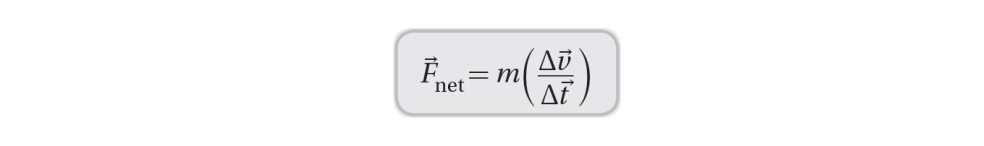
In a perfectly elastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved, while in an inelastic collision, some kinetic energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as heat or sound.
During an impact, the duration of the collision can affect the magnitude of the impact force, as a longer collision time will result in a smaller force.
TIP:
Momentum and impulse are both vector quantities.
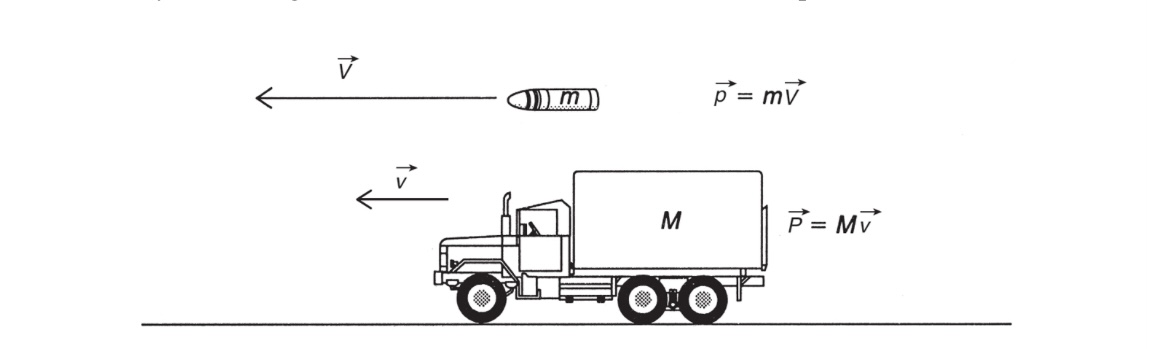
- To understand Newton's rationale, consider the action of trying to change the motion of a moving object. Do not confuse this with the inertia of the object; here, both the mass and the velocity are important.
- Consider, for example, that a truck moving at a slow 1 meter per second can still inflict a large amount of damage because of its mass. Also, a small bullet, having a mass of perhaps 1 gram or less, does incredible damage because of its high velocity. In each case (see Figure 6.1), the damage is the result of a force of impact when the object is intercepted by something else. Let's now consider the nature of impact forces.
Sample Problem
A 2,000-kg car is traveling at 20 m/s and stops moving over a 10-s period. What was the magnitude of the average braking force?
Solution

The Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum:
The law of conservation of linear momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system is conserved.
A closed system is a system that does not exchange mass or energy with its surroundings.
The law of conservation of momentum applies to both elastic and inelastic collisions.
The law of conservation of momentum can be used to analyze the motion of objects in a variety of physical systems, including collisions and explosions.
The law of conservation of momentum is a fundamental law of nature and is a consequence of the translational symmetry of physical laws.
The conservation of momentum can be used to predict the motion of objects after a collision or explosion.
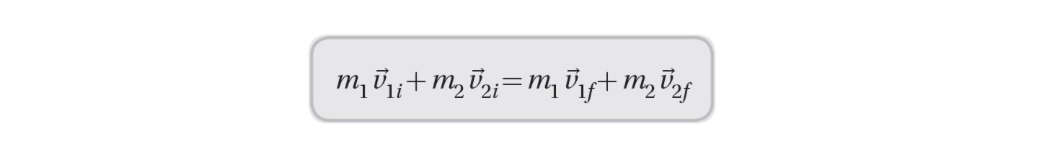
REMEMBER:
In an isolated system, the total momentum before an interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction.
Elastic Collisions:
- In an elastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved.
- During an elastic collision, the momentum of each object is conserved.
- Elastic collisions occur when there’s no loss of kinetic energy due to friction, deformation, or other factors.
- The collision between two billiard balls is an example of an elastic collision.
- Elastic collisions are rare in real-world situations, as some energy is usually lost as heat or sound.
- In an elastic collision, the relative velocities of the objects before and after the collision are the same.
TIP:
On the AP Physics 1 exam, you may be asked to set up, but not solve, a system of equations. Your understanding of physics is thus demonstrated without having to spend time doing the algebra!
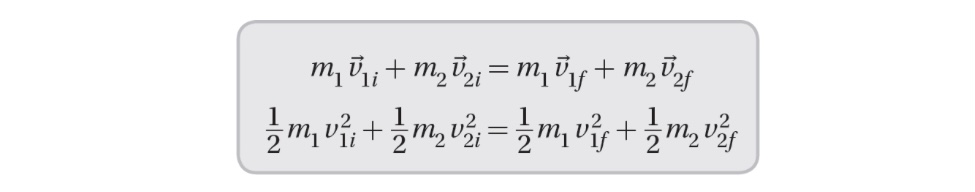
If we cancel out the factor (1/2) in the second equation, and collect the expressions for each mass on each side, we can rewrite the two equations as:
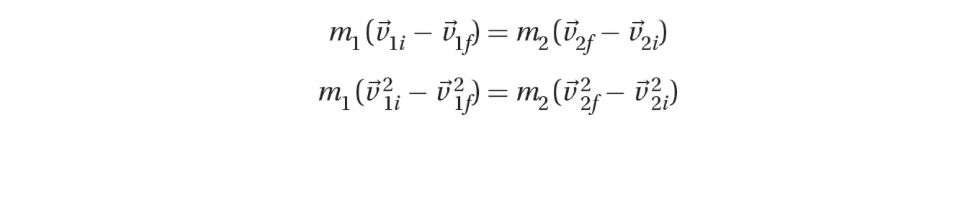 The second equation is factorable and so can be simplified. Again rewriting the expressions, we get
The second equation is factorable and so can be simplified. Again rewriting the expressions, we get
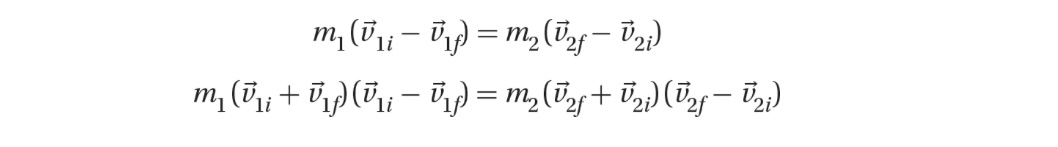
If we take the ratio of the two expressions, we arrive at an interesting result after collecting terms:
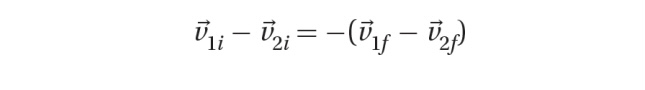
Sample Problem
A car traveling at 15 m/s rear-ends a car in front of it traveling at only 8 m/s. If this collision is approximated as elastic and the car that was hit from the rear is now traveling at 11 m/s, what is the final velocity of the other car?
Solution
Since the collision is elastic, the masses of the cars are not needed. The relative speeds of the two cars must be maintained:
Initially, relative speed = 15 - 8 = 7
They must be the same as negative relative velocities after the collision:
Sample Problem
A car traveling at 15 m/s rear-ends a car in front of it traveling at only 8 m/s. If this collision is approximated as elastic and the car that was hit from the rear is now traveling at 11 m/s, what is final velocity of the other car?
Solution
Since the collision is elastic, the masses of the cars are not needed. The relative speeds of the two cars must be maintained:
Initially, relative speed = 15 - 8 = 7
They must be the same as negative relative velocities after the collision:
-(x - 11)=7
x=4
The car that was traveling 15 m/s is now only traveling 4 m/s.
Inelastic Collisions:
- In an inelastic collision, some of the kinetic energy of the system is converted into other forms of energy, such as heat or sound.
- During an inelastic collision, the total momentum of the system is conserved, but the total kinetic energy is not.
- Inelastic collisions occur when there is some loss of kinetic energy due to friction, deformation, or other factors.
- The collision between a car and a wall is an example of an inelastic collision.
- In an inelastic collision, the relative velocities of the objects before and after the collision are not the same.
- Inelastic collisions are more common in real-world situations than elastic collisions.
TIP:
In an elastic collision, the kinetic energy of the system is conserved.
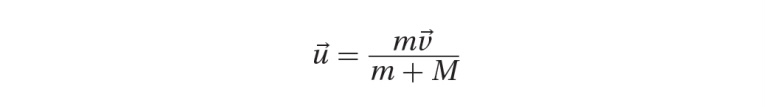
The initial kinetic energy is (1/2)mv7. The final kinetic energy is given by: