Unit 6: Open Economy—International Trade and Finance
6.1 Balance of Payment Accounts
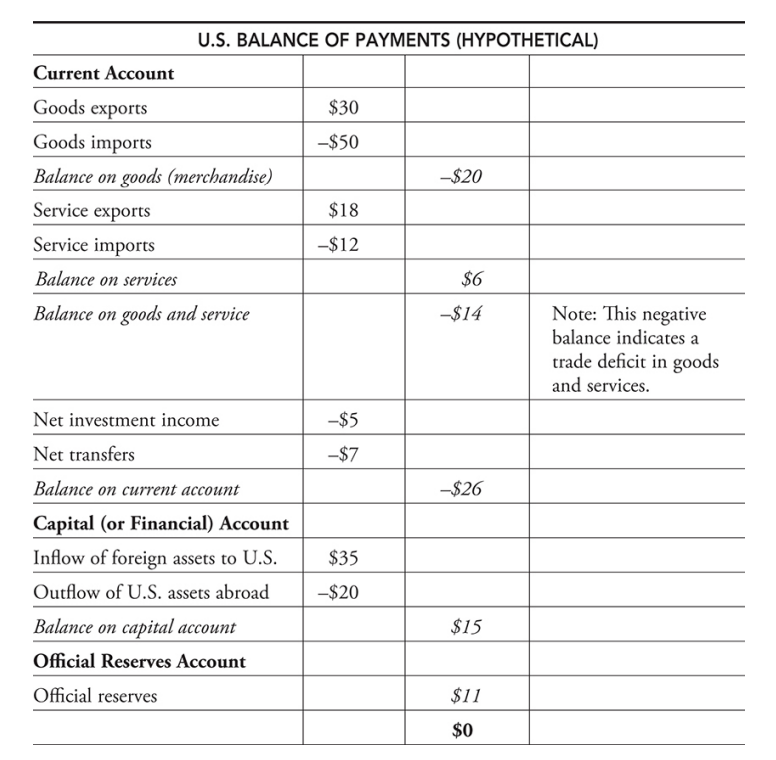
Balance of Payments Accounts
- Balance of payments statement - A summary of the payments received by the United States from foreign countries and the payments sent by the United States to foreign countries.
Current Account
Current account - This account shows current import and export payments of both goods and services and investment income sent to foreign investors of the United States and investment income received by U.S. citizens who invest abroad.
- Ex. → If a Canadian is receiving dividends from an American corporation or interest from a U.S. Treasury bill, these dollars would be sent out of the country.
- A deficit balance tells us that the United States sent more American dollars abroad than foreign currency received in current transactions.
Capital (or Financial) Account
- Capital (or financial) account - This account shows the flow of investment on real or financial assets between a nation and foreigners.
- Ex. → If a Swedish firm buys a manufacturing facility in Idaho, or if a Mexican citizen buys a U.S. Treasury bond, it is recorded as an inflow of foreign capital assets into the United States.
- A surplus balance tells us that there was more foreign capital investment in the United States than there was U.S. investment abroad.
Official Reserves Account
- Official reserves account - The Fed’s adjustment of a deficit or surplus in the current and capital account by the addition or subtraction of foreign currencies so that the balance of payments is zero.
- Balance of payments deficit - When the US has sent more dollars out than foreign currency has come in while adding the current and capital account. When this happens, the Fed credits the account to balance it.
- Balance of payment surplus - When more foreign currency was coming into the US than American dollars sent abroad. Here, the Fed transfers the surplus currency bank into official reserves.
A Circular Flow of Dollars
- The U.S. dollars that Americans send to foreigners are equal to the U.S. dollars that foreigners send to Americans.
- If Americans import more goods and services from abroad, the current account will move in the deficit direction but the capital/financial account will move in the surplus direction as those dollars return.
6.2 Exchange Rates
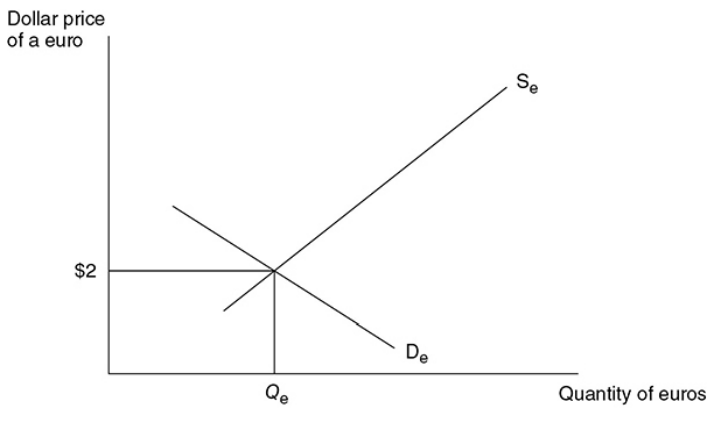
Currency Markets
Exchange rate - The price of one currency in terms of a second currency.
Ex. → If 2 dollars = 1 euro, 1 dollar = 0.5 euro.
Changes in Exchange Rate
- Determinants of exchange rates - External factors that increase the price of one currency relative to another.
- Consumer tastes - When domestic consumers build a stronger preference for foreign-produced goods and services, the demand for those currencies increases and the dollar depreciates. If foreign consumers increase their demand for U.S.-made goods, the dollar appreciates.
- Relative incomes - When a nation’s macroeconomy is strong and incomes are %%r%%ising, they increase their demand for all goods, including those produced abroad.
- Ex. → If Europeans are enjoying economic growth and the United States is in a recession, the relative buying power of European citizens is growing, meaning that the consumption of domestic and U.S.-made goods increases demand for the dollar appreciating its value.
- Speculation - Foreign currencies can be traded as assets causing investors to seek to profit from buying currency at a low rate and selling it at a higher rate.
- Ex. → If it appears that future interest rates will fall in the United States relative to interest rates in Japan, the yen seems like a good investment. Speculators would then increase their demand for Japanese assets, thus appreciating the yen and depreciating the dollar.
6.3 Foreign Exchange Market
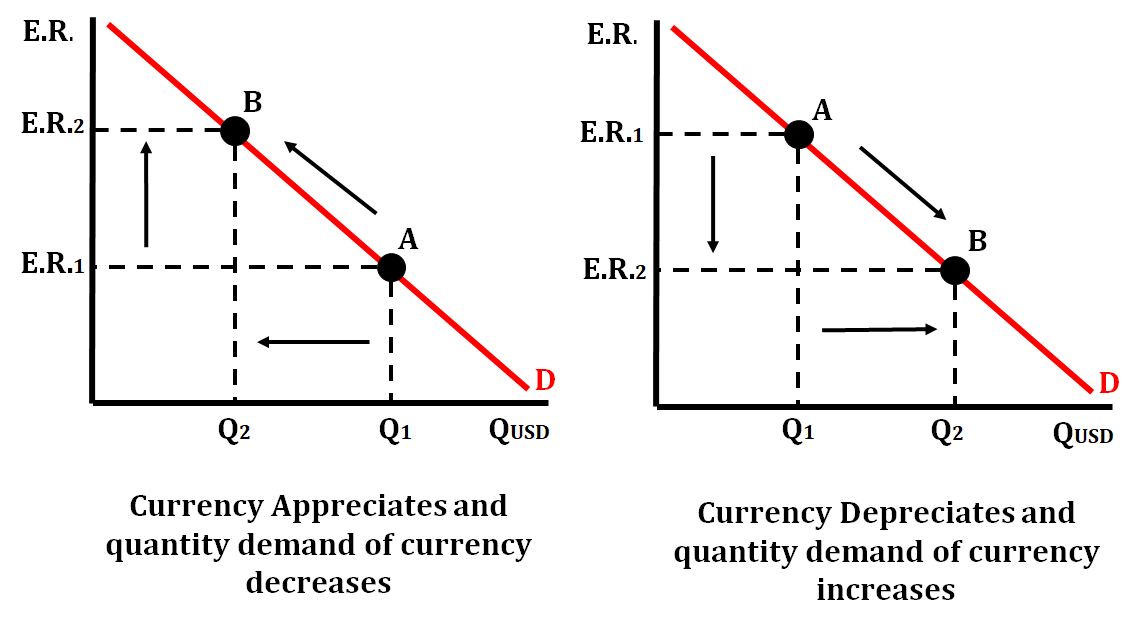
Foreign Exchange Demand
It is the quantity of an international currency that all domestic and foreign currencies are willing and able to purchase at various rates of exchange.
The relationship between exchange rates and the quantity of currency demanded is inverse:
- As the exchange rate rises, domestic and foreign consumers will purchase less quantity of the currency.
- As the exchange rate falls, domestic and foreign consumers will purchase more quantity of the currency.
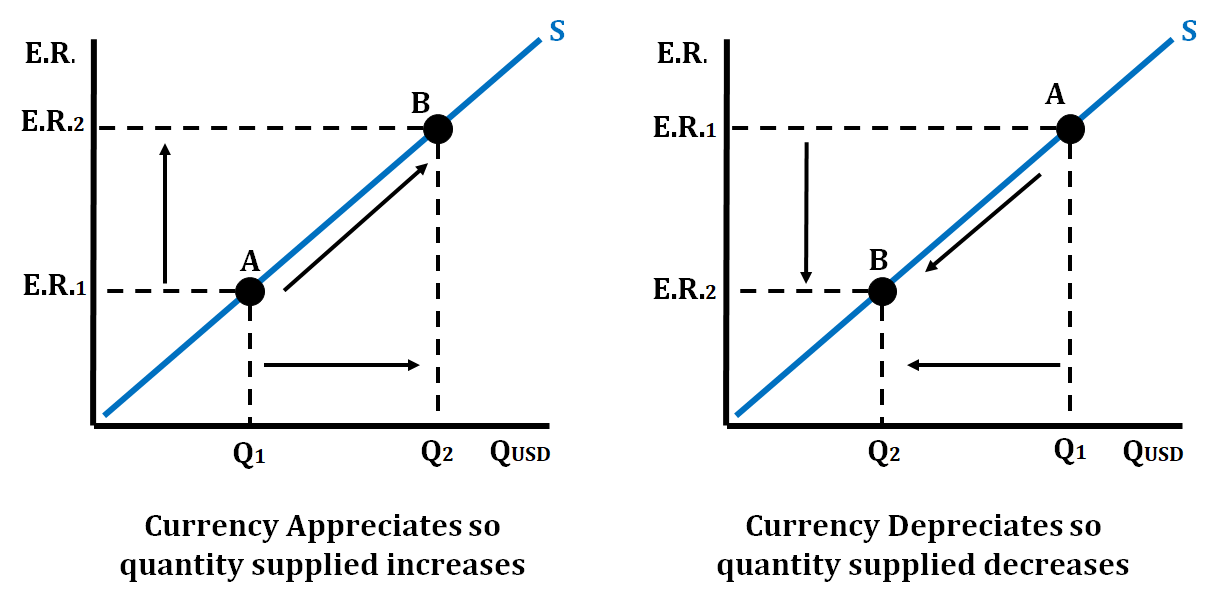
Foreign Exchange Supply
It is the quantity of an international currency that all domestic and foreign sellers are willing and able to sell at various rates of exchange.
The relationship between exchange rates and the quantity of currency supplied is positive or direct:
- As exchange rates rise, domestic and foreign consumers are willing to sell more.
- As exchange rates fall, domestic and foreign consumers are willing to sell less.
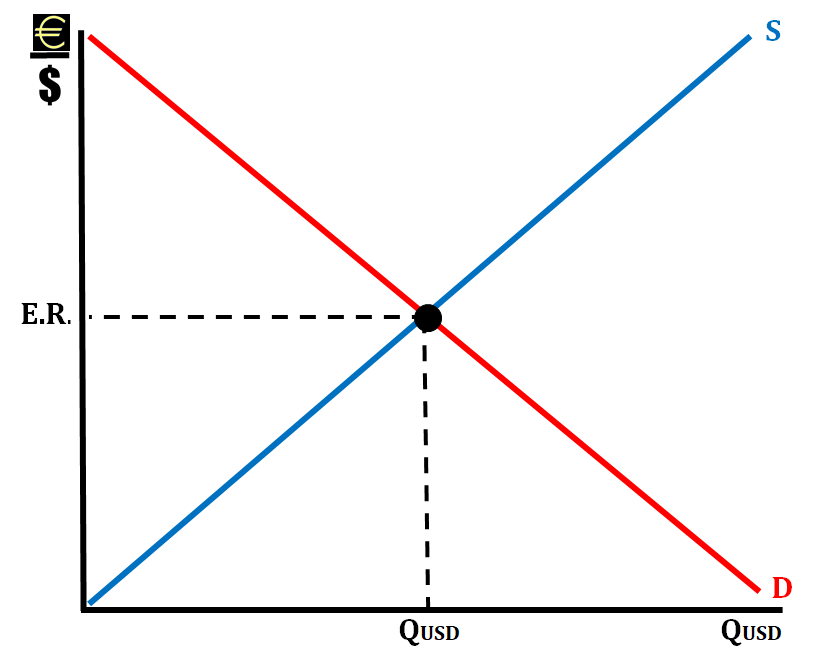
FOREX Market Equilibrium
It is achieved in the FOREX Market (the market in which foreign currency is bought and sold) when the quantity supplied of the currency equals the quantity demanded of the currency at a specific exchange rate.
The FOREX Market in equilibrium for EURO and U.S. Dollar
Connection to Monetary Policy
. When the Fed increases the money supply, the interest rates on American financial assets begin to fall, so the demand for the dollar falls and it depreciates relative to other foreign currencies.
- This makes goods in the US less expensive to foreign consumers, so American net exports increase shifting AD to the right.
If the Fed decreases the money supply, American interest rates begin to rise and the dollar appreciates relative to foreign currencies.
- This makes American goods more expensive decreasing the net exports which shift AD to the left.
When interest rates rise, capital investments decrease, and financial investments increase.

Demand for the U.S. dollar increases and the dollar appreciates relative to the euro if:
- European taste for American-made goods is stronger.
- European relative incomes are rising, increasing demand for U.S. goods.
- The U.S. relative price level is falling, making U.S. goods relatively less expensive.
- Speculators are betting on the dollar to rise in value.
- The U.S. relative interest rate is higher, making the United States a relatively more attractive place for financial investments.
6.4 Effect of Changes in Policies & Economic Conditions on the Foreign Exchange Market
Change in Demand or Supply in Currency
- There are four determinants that can change Four determinants canOREX Market.
- Foreign tastes
- Trade prices
- Income levels
- Real interest rates
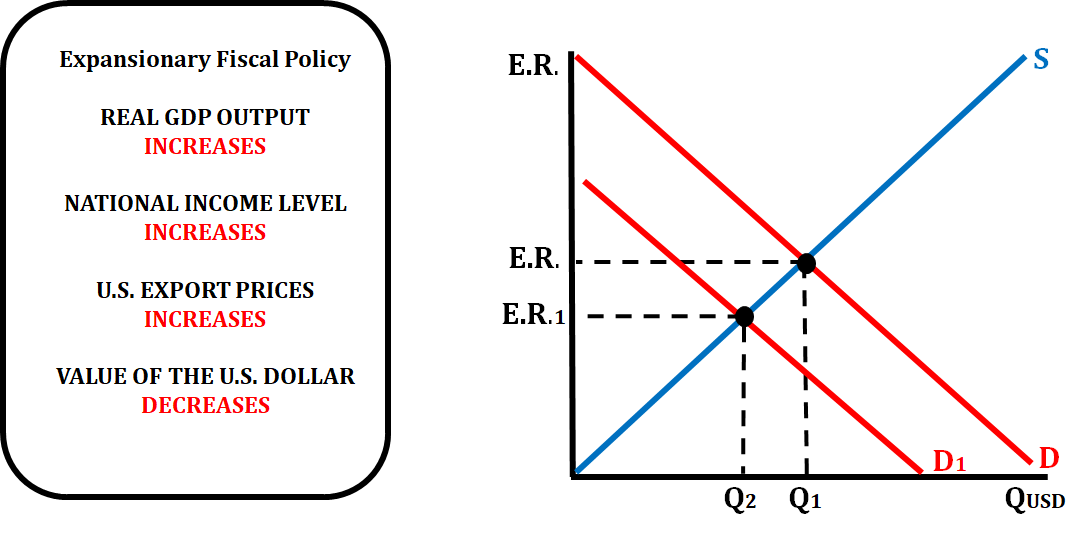
Fiscal Policy Impact on Exchange Rates
When the government practices an expansionary fiscal policy (increase in spending or decrease in taxes), there is an effect on the exchange rate for that country's currency.
- If the government increases spending or decreases taxes, aggregate demand will increase, GDP increase, and price increase.
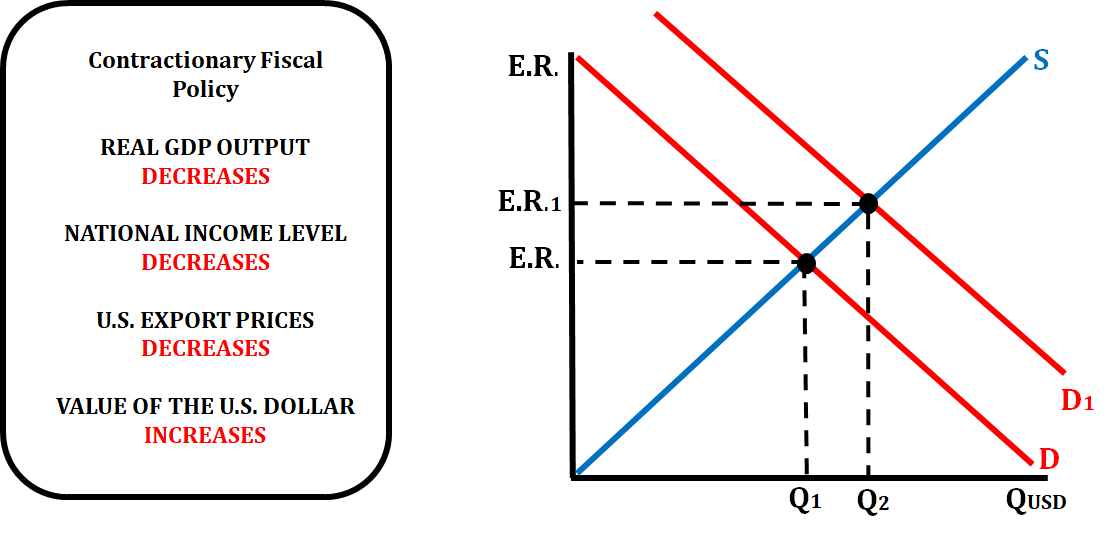
When the government practices a contractionary fiscal policy (decreases spending or increases taxes), there is an effect on the exchange rate of that country's currency
- If the government decreases spending or increases taxes, aggregate demand will decrease, GDP decrease, and price decrease.
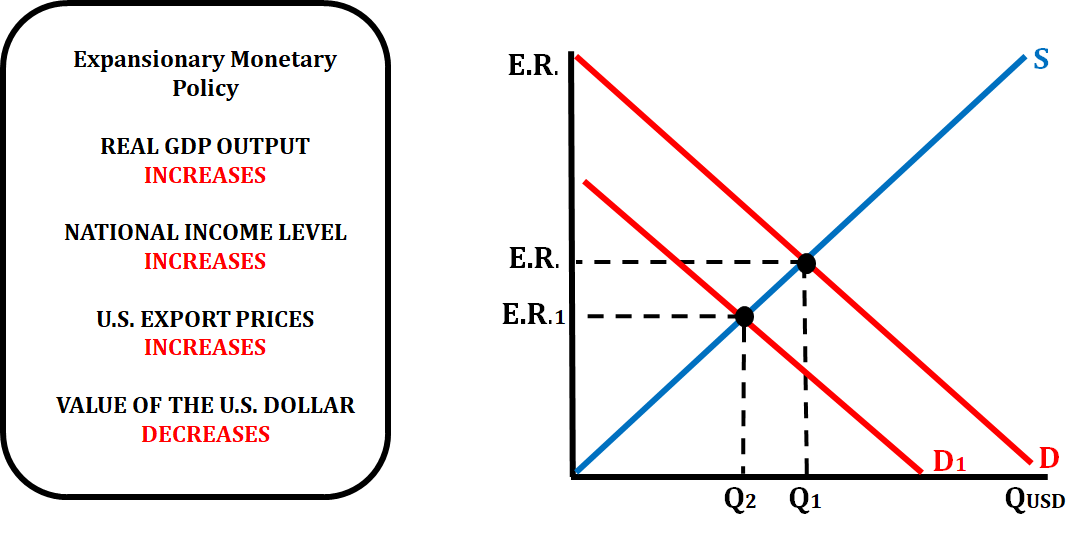
Monetary Policy Impact on Exchange Rates
If the central bank of a country is practicing an expansionary monetary policy (decreasing the reserve ratio, decreasing the discount rate, or buying bonds) it will affect the exchange rate as well.
- When the FED increases the money supply, that lowers the interest rate which will increase investment spending.
- When investment spending increases, aggregate demand increases which raises the price level.
- This means that both the national income levels and export prices will increase.
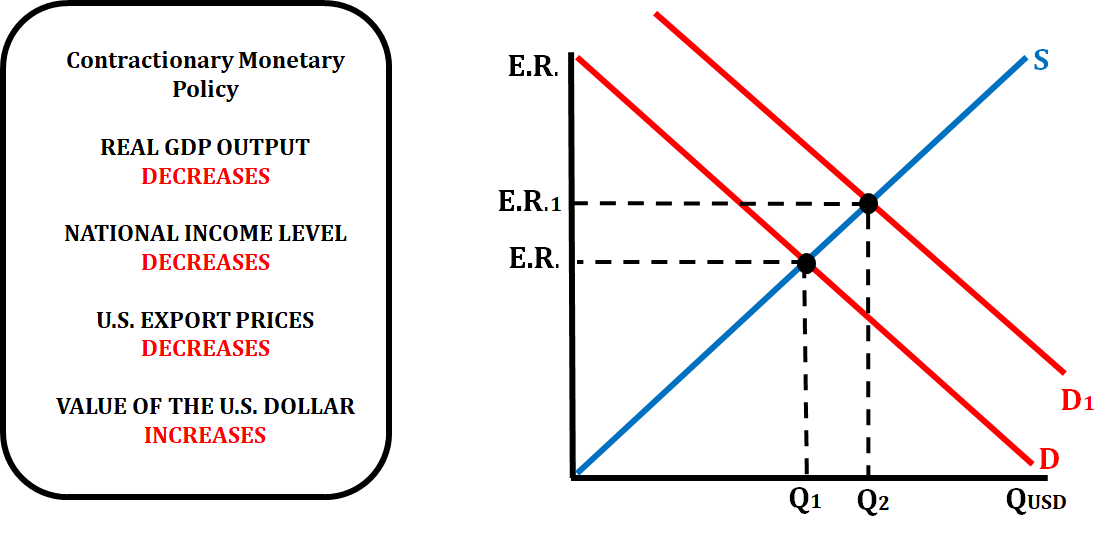
If the central bank of a country is practicing a contractionary monetary policy (increasing the reserve ratio, increasing the discount rate, or selling bonds), it will affect the value of the exchange rate.
- When the FED decreases the money supply, that raises the interest rate which will decrease investment spending.
- When investment spending decreases, aggregate demand decreases which lower the price level.
- This means that both the national income levels and export prices will decrease.
Tariffs
Revenue tariff - An excise tax levied on goods not produced in the domestic market.
- Ex. →The United States does not produce bananas. If a revenue tariff were levied on bananas, it would not be a serious impediment to trade, and it would raise a little revenue for the government.
Protective tariff - An excise tax levied on a good that is produced in the domestic market so that it may be protected from foreign competition.
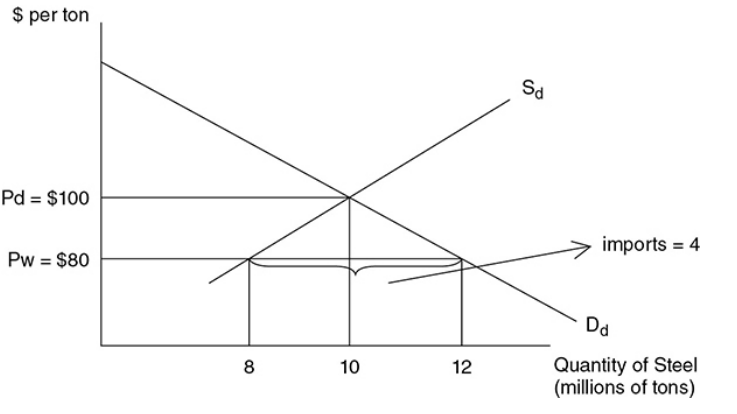
- Ex. → Assume the domestic steel price is $100 per ton and the equilibrium quantity of domestic steel is 10 million tons. Since other nations could produce it at a lower cost, in the competitive world market, the price is $80 per ton. At that price, the United States would demand 12 million tons but only produce eight million tons and so four million tons are imported. If the steel industry is successful in getting a protective tariff passed through Congress, the world price rises by $10, increasing the quantity of domestic steel supplied and reducing the amount of steel imported from four million to two million tons.
- A higher price and lower consumption reduce the area of consumer surplus and create deadweight loss.
Economic Effects of the Tariff
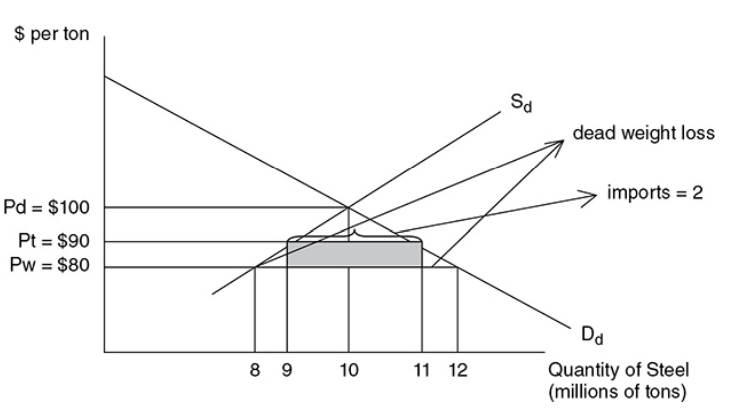
Consumers pay higher prices and consume less steel
Consumer surplus has been lost
Domestic producers increase output
- Domestic steel firms are not subject to the tariff, so they can sell more steel at the price of $90 than they could at $80.
Declining imports
- Fewer tons of imported steel arrive in the United States.
Tariff revenue
- The government collects $10 × 2 million = $20 million in tariff revenue. This is a transfer from consumers of steel to the government, not an increase in the total well-being of the nation.
Inefficiency
- The world price was lower than the domestic price because it was more efficient to produce steel abroad and export it to the United States. By taxing this efficiency, the United States promotes the less efficient domestic industry and stunts the efficient foreign sector. As a result, resources are diverted from the efficient to the inefficient sector.
The deadweight loss now exists
Quotas
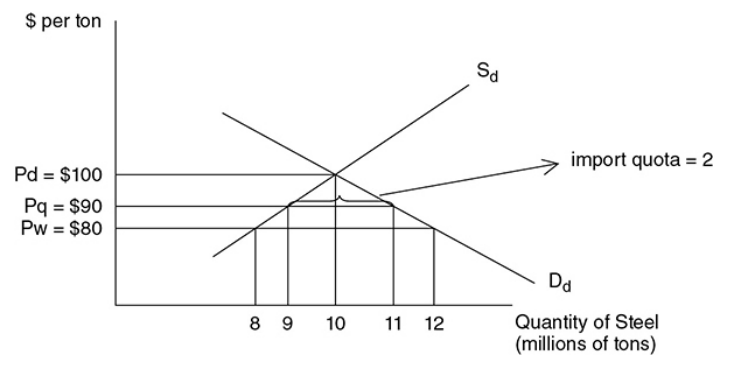
Import quota - A limitation on the amount of a good that can be imported into the domestic market.
- With a quota, the government only allows two million tons to be imported. So the impact of the quota, except the revenue, is the same: higher consumer price and inefficient resource allocation.
Tariffs and quotas share some of the same economic effects:
- Both hurt consumers with artificially high prices and lower consumer surplus.
- Both protect inefficient domestic producers at the expense of efficient foreign firms, creating a deadweight loss.
- Both reallocate economic resources toward inefficient producers.
Tariffs collect revenue for the government, while quotas do not.
6.5 Changes in the Foreign Exchange Market and Net Exports
Appreciating and Depreciating Currency
Appreciating or stronger currency - When the value of a currency is rising relative to another currency.
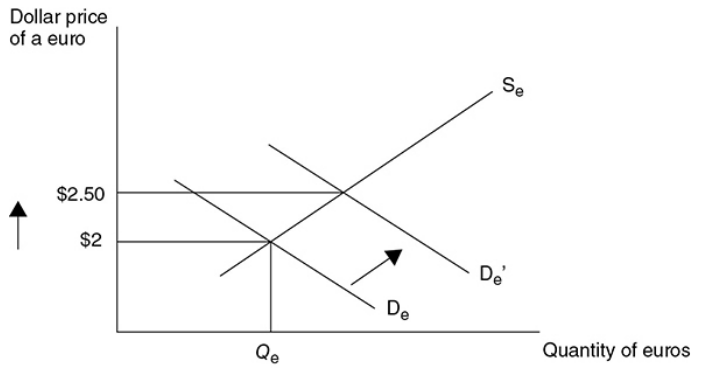
Depreciating or weaker currency - When the value of a currency is falling relative to another currency.
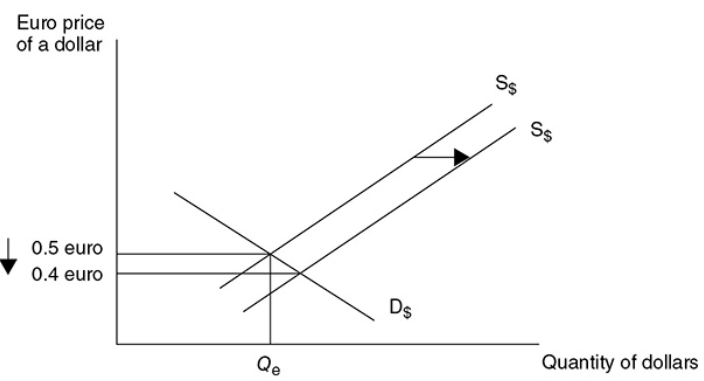
NOTE - It is very important to label the axes correctly. If the market is for the dollar, the x-axis should be labeled “Quantity of dollars.” The label on the y-axis depends on how the dollar is being priced. If we are pricing dollars in terms of the number of euros it takes to purchase 1 dollar, then the correct label is “Euros per dollar” or “Euro price of a dollar”.
Changes in Net Export: Consequences
- Changes in net export can bring significant impact.
- Decrease in net exports:
- decrease in aggregate demand.
- exports become more expensive.
- decrease in demand for domestic goods.
- decrease in production and employment.
- decrease in output.
- Increase in net exports:
- increase in aggregate demand.
- exports become cheaper.
- increase in demand for domestic goods.
- increase in production and employment.
- increase in output.
6.6 Real Interest Rates and International Capital Flows
Capital Flow
- Inbound capital flow
- It is the injection of funds into a domestic economy that occurs through the purchase of domestic assets by foreign investors.
- When real interest rates are high, it generates inbound capital flow.
- This is because foreign investors look to invest their money into assets that have high-interest rates because they can earn a higher profit.
- Outbound capital flow
- It is the extraction of funds from a domestic economy that occurs through the purchase of foreign assets by domestic investors.
- When real interest rates fall, it generates outbound capital flow.
- This is due to the foreign investors look to invest in other countries because the interest rate is higher there than in their own country.
Impact on net exports
- A higher real interest rate in one country compared to another will make the currency of the country with the higher interest rate more attractive to foreign investors, leading to an appreciation of that currency. This can make exports from the country with the higher interest rate more expensive for foreign buyers, and imports to that country cheaper, which can lead to a decrease in net exports.
- On the other hand, a lower real interest rate in one country compared to another will make the currency of the country with the lower interest rate less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a depreciation of that currency. This can make exports from the country with the lower interest rate cheaper for foreign buyers, and imports to that country more expensive, which can lead to an increase in net exports.
Central Banks and Domestic Interest Rates
- Central Banks
- It plays a major role in determining domestic interest rates.
- It uses monetary policy tools such as open market operations, discount rates and reserve requirements to influence interest rates.
- When the central bank raises the interest rate, it will encourage banks to raise their own interest rates as well.
- Domestic Interest Rates
- Affects net capital inflows:
- country’s assets become more or less attractive to foreign investors.
- domestic interest rate high → foreign investors may be likely to invest.
- domestic interest rate low → foreign investors may be less likely to invest.
- Banks affect domestic interest rates:
- When banks raise the interest rates they charge on loans, it can lead to higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, which can, in turn, lead to higher interest rates across the economy.
- When banks raise the interest rates they pay on deposits, it can lead to higher returns for savers, which can encourage them to save more and spend less, which can also lead to higher interest rates across the economy.