Week 1 Introduction to App Development with .NET & .NET Overview
The History & Basics
.NET Architecture & Component Stack
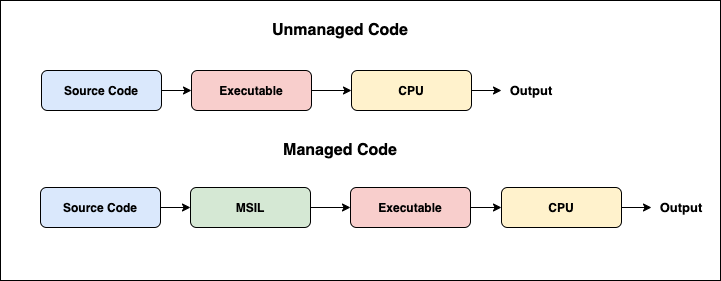
When code is compiled in C# it is transferred into byte code and then translate back into a native code. A CLR is in charge of translating the byte code back into the native code. The FCL provides a bunch of functions and packages which can be used appropriately.
WinForms, ASP.NET and ADO.NET are applications that are used to help build applications:
WinForms: included as a part of .NET and .NET Framework which provides a platform to write client applications
ASP.NET: Open-source framework for building websites and web applications.
ADO.NET: Made from a set of classes which provides access to a database.

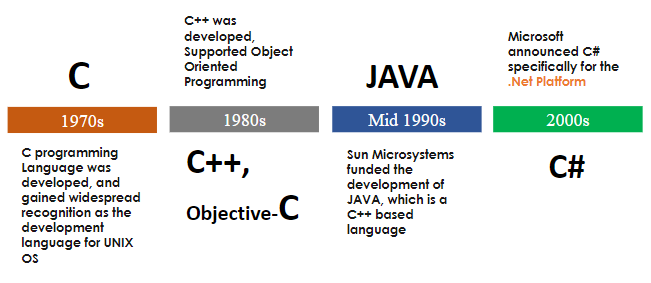
C# History
1970s : C widespread as a language for UNIX OS
1980s : C++ supports an object oriented programming style
1990s : Java is heavily based upon C++.
2000s : C# announced for the .Net platform.
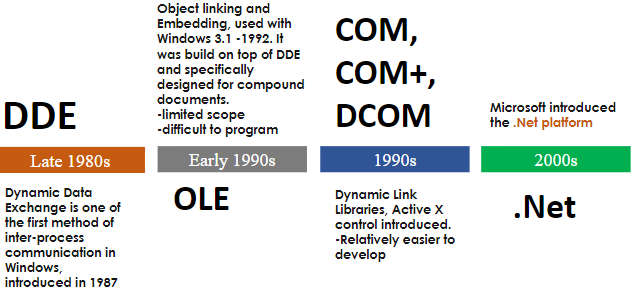
.NET History
1980s : DDE (Dynamic Data Exchange) is the first method of inter-process communication in Windows.
1990s : OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) is a mechanism which allows users to create/edit documents created by multiple applications.
1990s : COM, COM+, DCOM are dynamic link libraries.
2000s : .NET platform was introduced by Microsoft.
What is .NET, .NET Core, .NET Framework, Xamarin
What is .NET?
.NET is a free open source development platform for building various applications consisting of different languages such as C#, F# and Visual Basic.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple languages
- Editors/IDEs and libraries to build apps for web, mobile, desktops, gaming and IOT
- Consistent API
- Libraries
What is .NET Core?
.NET Core is a general purpose development platform maintained by Microsoft and the .NET community on GitHub. It is also cross-platform, open source and supports C#, F# and Visual Basic as languages.
Composition:
- .NET Runtime
- Framework Libraries
- SDK tools and language compilers
- “dotnet” app host used to launch .NET Core apps
What is .NET Framework?
The .NET Framework is a development platform for building apps for web, Windows, Windows phones, Windows Server and Microsoft Azure.
.NET Framework Components
It consists of the Common Language Runtime (CLR) and the .NET Framework class library. These have a broad range of functionality and support for many industry standards.
This comes with Windows allowing users to run .NET Framework Applications
.NET Core VS .NET Framework
The key differences between the .NET Core and Framework are that the framework applications are for Windows specifically and the Core is cross-platform and an open-sourced framework. Although they both share the same API (Application Programming Interface).
| .NET CORE | .NET Framework | |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Platform | Windows, Linux and MAC OS | Windows OS |
| Security | No in-built security features | In-built security features |
| Devices | Gaming, mobile IOT, AI | Windows OS |

When do we use .NET Core?
- Cross Platform Requirements (Can run on windows, mac and Linux)
- Microservices
- Docker Containers
- High performance and scalable systems required
- Multiple versions of .NET run in parallel
- CLI control required
When do we use .NET Framework?
- When using technologies which are unavailable in .NET Core.
- Using third-party libraries or packages unavailable in .NET Core.
- Platform which doesn’t support .NET Core
What is .NET Xamarin/Mono?
.NET Xamarin/Mono is an implementation for .NET for running apps on all major mobile OS including IOS, Android and Windows Phones.
This provides a cross-platform development solution for mobiles, tablets and desktop applications.
CLR, FCL, Managed code, JIT
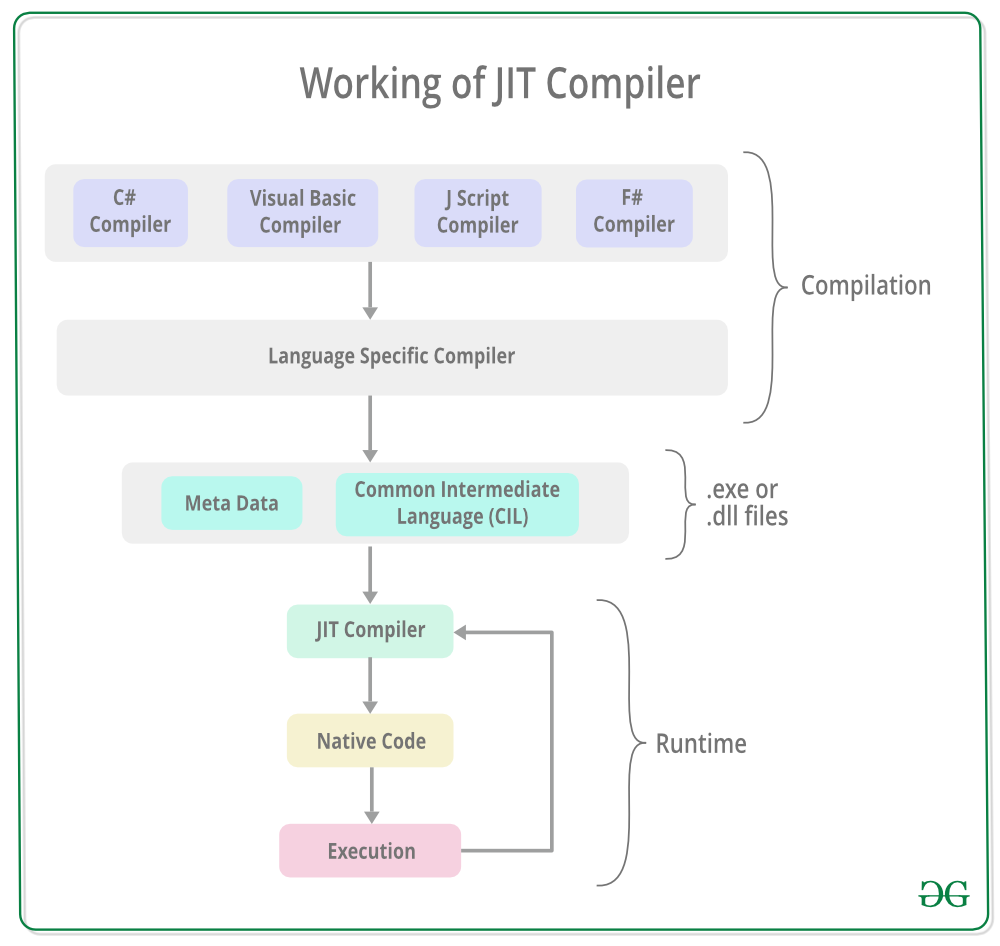
Common Language Runtime (CLR)
CLR is programming that manages code execution, core services and enforcing type safety of programs written in various supported languages.
- CLR acts as the foundation of the .NET Framework.
- Code Management is the fundamental principle of Runtime.
- Benefits are that it is both Language and Platform independent.
.NET Framework Class Library (FCL)
FCL is a large library of tested and reusable code which users can call from their own applications.
This includes reusable classes, interfaces and value types and provides the .core functionalities of the .NET Framework:
- Data types
- Data structure implementation
- Garbage collection
- Data access and database connectivity
- Network Communication
- Support for GUI development
What is Managed Code?
Managed code is code where their execution is managed by a Runtime (CLR). CLR takes the managed code and compiles it to machine code and executes it.
(MSIL is like a compiler)